The uterus is the main organ necessary for pregnancy. It consists of a bottom, body and neck. The latter looks like a tube connecting the uterus to the vagina. The successful course of pregnancy and natural childbirth directly depends on its condition. The cervix changes significantly before childbirth, although for the woman herself these changes are practically unnoticeable, since this process is not accompanied by any special symptoms. What happens in the prenatal period and why is special attention paid to the cervix?
Why is this necessary and when to start?
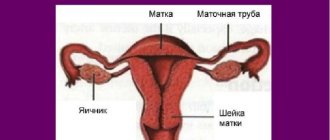
The cervix is a universal female organ, or rather, part of the uterus. While a woman is carrying a baby, the cervix ensures a tight closure so that the fetus does not leave its cavity prematurely. When it's time to give birth, the cervix begins to dilate, and when it becomes fully dilated, the fetal head can leave the womb and begin moving through the birth canal.
A normal full-term pregnancy ends with birth between 38 and 42 weeks. About a month and a half before this, numerous preparatory processes begin to take place in the cervix , because the opening of the cervix is a very responsible process, which is not subject to the will of the woman, it occurs reflexively. In many ways, the condition of the cervix depends on hormonal levels, muscle readiness, and the characteristics of a particular pregnancy.
But all women, starting from the 38th week, undergo a gynecological examination to determine the readiness of the cervix for the upcoming birth .
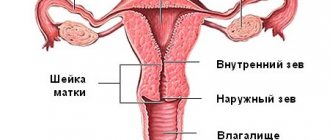
The cervix is a round muscle; inside it is the cervical canal, which connects the uterine cavity and the vagina. But nothing from the genital tract can enter the uterus during pregnancy, since the cervical canal is securely closed by a mucous plug.
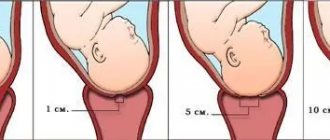
A month before giving birth, the cervix during a normal pregnancy begins to shorten. From 4 initial centimeters it decreases in length to one centimeter .
In these last weeks before giving birth, everything is very important - from hormonal levels to the psychological state, since the fears, worries and anxieties that the expectant mother may experience increase muscle tension, which not only interferes with the preparation of the cervix, but can also cause a lot of complications in the process childbirth
The process begins from the moment the stomach drops. The fetus begins to press its head on the inner ring of the neck. Under this pressure, a slow and systematic opening of the internal pharynx occurs. Hormones and enzymes are involved in the process.
As soon as the cervix becomes mature and shortens to 1-0.5 centimeters, it is believed that labor can start at any time.
In women who are waiting for the birth of their first child, the opening takes longer , the process starts in advance, the internal os gradually opens first, and the external one begins to open last. For those giving birth repeatedly, both the inner ring and the outer ring open almost simultaneously, with a slight difference in time, and therefore labor during the second or third pregnancy proceeds faster. Cervical preparation also begins very shortly before birth and proceeds much faster.
The preparation of the cervix for dilatation is carried out in a hospital, if after 38 weeks there are no signs of its ripening . This parameter is assessed in points on the Bishop scale. A cervix that scores, according to a gynecologist, from 5 to 8 points is considered mature . Anything less than these values is considered an insufficiently mature or immature cervix and requires medical intervention if the due date has already approached.
If there are still 1-2 weeks ahead, there is no reason to stimulate the cervix. It is quite possible to get by with methods that are passed down from generation to generation through the female line and are considered quite effective.
Condition of the cervix before childbirth
The cervix changes dramatically before childbirth (and almost imperceptibly for the expectant mother herself) - and this is what allows the child to be born unhindered. What exactly changes does the uterus undergo before childbirth, and in what cases is medical intervention necessary?
What should the cervix look like before natural childbirth?
What matters is its location in the pelvis, length and softness. The fact that a woman’s birth canal is prepared is indicated by the softening of the cervix before childbirth to such an extent that it begins to allow 1-2 fingers of the doctor inside. Due to such changes, the woman observes the release of the mucous plug. It turns out that the earlier the cervix begins to dilate before childbirth, the sooner the woman notices this clear sign of approaching contractions.
In addition, it is shortened. It is known (this is recorded using transvaginal ultrasound) that the length of the cervix before childbirth is no more than 1 cm. And it gradually smoothes out completely.
As for the location, it becomes exactly in the center of the small pelvis, while the cervix during pregnancy, even 3-4 weeks before the onset of labor, is deviated posteriorly.
These 3 parameters are assessed on a two-point scale. With 5 points scored, the cervix is considered mature.
How to stimulate uterine dilatation using medical methods
If an examination of the cervix before childbirth shows that it is not yet mature, whereas, judging by the doctors’ calculations, you should be about to give birth, it is quite possible that you will be asked to speed up the process a little and carry out stimulation. Otherwise, there is a high probability that the child will suffer from oxygen starvation, since by 40-42 weeks the placenta can no longer properly perform its functions; it “grows old.” Stimulation by medical means is possible in a hospital setting. 4 methods are used, sometimes in combination with each other.
1. Intramuscular injections of Sinestrol.
This drug speeds up the preparation of the cervix for childbirth, but does not directly provoke contractions.
2. Introduction of kelp sticks - seaweed - into the cervix.
This procedure is performed by a doctor, while the patient is on a gynecological chair. The sticks, 5-6 cm each, are placed almost the entire length into the cervical canal. After approximately 3-4 hours, they begin to swell under the influence of moisture, thereby mechanically opening the cervical canal. Within a day, a dilatation of 1 cm is usually observed - a softened and short cervix before childbirth is the key to a quick and easy delivery.
3. Introduction into the cervical canal of a gel containing prostaglandins.
For example, Prepidil-gel. It usually acts very quickly, the neck opens in a few hours.
4. Intravenous administration of the drug Enzaprost containing prostaglandins.
With its introduction, the cervix becomes soft before childbirth, thereby shortening the period of contractions and expulsion of the fetus.
Self-induction of labor
More often, these techniques are used by women without indications and can be dangerous.
1. Cleansing enema.
It is noticed that after it the mucous plug quickly comes away and the cervix opens. This can only be done for those who have already reached their expected due date, that is, the baby is definitely full term.
2. Taking a warm bath.
This is not possible if the mucus plug and amniotic fluid have already drained. In addition, it is not recommended for women with high blood pressure.
3. Sex.
Sperm contains prostaglandins - the same substances that are part of the drugs used to induce labor in a hospital setting. Those who have already lost their mucous plug should not have sex, as there is a high probability of introducing an infection into the uterus. Well, having sex with a condom is useless in terms of stimulating the dilatation of the cervix.
4. Physical activity.
Walking up and down stairs, mopping floors while squatting, cleaning the house, etc. But don't overdo it. Especially if you have hypertension or gestosis, or placenta previa.
Now you know what the cervix should be like before giving birth. Just don’t try to independently diagnose how ready she is for childbirth. Leave this task to the doctors.
Preparation at home
It is believed that one of the most effective ways to help the cervix ripen and soften at the right time is sex without a condom . The ejaculate contains natural prostaglandins, which soften the teres muscle before labor.
But this method is not recommended for everyone: if there is placenta previa, if a woman is pregnant with twins, if she has an obstetric pessary installed, or has other complications of pregnancy, sex is contraindicated.
Also, do not have sex after even a small part of the mucus plug has separated from the cervical canal or when amniotic fluid is leaking - this will increase the likelihood of labor starting when the cervix is not ready, which is fraught with ruptures, and also increases the risk of infection entering the uterine cavity.
About a month before giving birth, you should add oil to your diet - olive, sunflower, flaxseed . They help increase the elasticity of muscle tissue. Products that help soften the cervix are fish and dairy products, chicken breast, fresh vegetables and fruits rich in plant fiber.
Raspberry leaves in the form of a decoction or as part of a cup of green tea are allowed to be taken from the 37th week of pregnancy . A drink in the amount of a glass per day if the pregnancy is 37 weeks, two glasses if the pregnancy is 38 weeks, at 39 weeks you can take three, and at 40 weeks up to a liter of raspberry leaf decoction per day will help to soften the neck.
How is it prepared in the hospital?
There are two types of medical preparation of the cervix, for which there are indications and contraindications:
mechanical methods - kelp sticks, Foley catheter;
medicinal methods - hormonal drugs - tablets, suppositories, gel for application directly to the cervix.
Stimulation of cervical ripening in the hospital is carried out at 40-41 weeks, if the degree of maturity of the cervix “does not reach” the norm. This can be alleviated by inserting a Foley catheter. To soften the cervix, this method is used less and less today, since more effective and less unpleasant methods have appeared.
The catheter is a thin latex tube with a silicone coating. The lower end is equipped with a small balloon. The tube is inserted into the cervical canal and the balloon is filled with saline or water. The balloon puts pressure on the cervix, causing it to dilate. The result is assessed within 24 hours. But practice shows that in about half of women with post-term pregnancy, the Foley catheter did not bring anything other than pain.
Kelp sticks are dried seaweed about 6 centimeters in length. Their width varies, and the doctor decides which sticks to choose depending on how ready the cervix itself is for the birth process and how wide the cervical canal is. It is there that the sticks are introduced, which, under the influence of moisture, begin to swell and expand the canal mechanically.
Algae additionally produce a certain type of prostaglandin, which also helps soften and open the cervix. A day later, the signs are assessed and a decision is made - to go to give birth or to introduce more kelp. The effectiveness of wands is marginally higher than that of a Foley catheter .
Medicines (Mifepristone, Miropriston) show better results because they affect hormonal levels, sharply lowering progesterone levels. The drugs are also ambiguous. In world medical practice, they are used to terminate pregnancy in the early stages (medabortion). You have to take two tablets a day apart. Labor usually begins within 24-72 hours.
Sometimes women mistakenly call these drugs induction of labor. Mifepristone does not stimulate anything and does not affect contractions. It affects the cervix and changes hormonal levels.
If contractions do not begin within the designated period, it is possible to stimulate them by administering oxytocin, but only if the drug has worked and the cervix is ripe (the effectiveness of Mifepristone reaches 98%).
If the cervix is not ready for childbirth
A soft, shortened cervix, which is located in the center and slightly open, indicates the approach of labor. However, it also happens that the due date has already approached, but the maturity of the cervix has not yet occurred.
An immature cervix can lead to complications during labor, so if it is not ripe by the expected date of birth, the doctor may decide to induce stimulation.
Pregnancy after 40 weeks is post-term and dangerous for the baby. At this point, the placenta ceases to fully perform its functions. Therefore, if the cervix does not mature by this time, then its stimulation is mandatory.
In addition to postterm pregnancy, indications for stimulation are:
- The mother has a disease in which further pregnancy threatens her health.
- Development of hypoxia in the fetus.
- Large fetus or multiple pregnancy.
- The cessation or weakening of contractions during labor.
- Premature placental abruption.
In all other cases, the question of the need for stimulation is decided individually. There are various methods to prepare the cervix for childbirth.
Medical methods include the following:
- Kelp sticks. Kelp is seaweed. They are placed along the entire length of the cervical canal, where they swell with moisture and begin to mechanically expand it. Laminaria also secrete endogenous prostaglandins, which are involved in the process of cervical ripening.
- Synthetic prostaglandin. These can be suppositories or gels that are injected into the cervical canal, or intravenous injections. Synthetic preparations can soften the cervix faster than kelp, thereby bringing the moment of birth closer.
- Amniotomy. Piercing the amniotic sac provokes the release of anterior waters, as a result of which the fetus drops lower and puts more pressure on the cervix, thereby stimulating its opening.
There are other, non-medical methods to prepare the body for natural childbirth. Unlike the first ones, they can be used at home, but subject to full-term pregnancy, satisfactory health of the woman and baby, and only after consultation with a doctor. Otherwise, such stimulation can be dangerous. Non-medical stimulation methods include:
- Sex. Orgasm causes the uterus to contract, causing the cervix to open. In addition, semen contains a significant amount of prostaglandins, so unprotected sexual contact makes sense. This method is only suitable if the woman’s mucus plug has not come off, otherwise the risk of infection increases.
- Cleansing enema. This procedure causes the uterus to contract. After an enema, the mucus plug usually begins to come off, and the cervix gradually opens.
- Physical exercise. These include walking up stairs, washing floors, long walks, etc.
How to help?
Childbirth is considered normal when it occurs between 38 and 42 weeks. In this case, a full-term baby is born. Normally, about a month to a month and a half before the baby is born, the cervix begins to physiologically change and prepares to open. As a rule, a woman at the 38th week of pregnancy undergoes an examination by a gynecologist, where he determines how ready the cervix is to dilate.
It is important that the uterus is elastic at the beginning of labor; this will ensure the correct birth of the baby without complications. By the time the baby is about to be born, the cervix should be mature. How correctly this process occurs in the body depends on the substances of prostaglandins. If a woman has a normal pregnancy, then these substances are produced in sufficient quantities on their own. But, often, today only a few pregnant women can boast of excellent health. Therefore, it is important in advance of labor to help your body prepare for childbirth, in particular to soften the cervix.
What can you do at home?
One of the most popular, simple and enjoyable ways to soften the cervix before childbirth is to regularly have sex without condoms. Sperm contains prostaglandins, which help ensure proper ripening of the cervix during pregnancy. Moreover, by experiencing an orgasm, a woman’s body “trains” for the upcoming birth. We would like to draw your attention to the fact that you can and should have sex only if there are no problems with bearing a fetus. Because frequent sex and orgasm can lead to labor starting prematurely. Therefore, it is better in this case to consult a doctor.
An important aspect in preparing the cervix for childbirth is proper nutrition. It is necessary to include various oils in your diet. For example, olive, flaxseed, sesame, sunflower. One excellent option is a freshly squeezed glass of carrot juice with the addition of one teaspoon of any of the oils. This combination perfectly helps improve the elasticity of the cervix. It is also important that your diet includes fish and fermented milk products, which help the intestines to function properly. But it is better to replace red meat with white.
How is the readiness of the cervix for the upcoming birth determined?
When pregnancy approaches 38–39 weeks, the gynecologist monitoring the pregnant woman is required to evaluate the cervix during a routine examination. The conclusion about her maturity is made on the basis of the scores given by the doctor for four parameters. The Bishop scale is used, giving 0–2 points. If the total result reaches 5, then the cervix is considered ready for childbirth.
The four parameters assessed by the gynecologist include:
- Consistency. The soft neck gets the maximum score. If it is softened, but has compactions, then it will be given a score of 1; a hard cervix is not ready for childbirth, it will be given a score of 0.
- Length. Up to 1 cm is considered the most optimal. For a length of 1–2 cm they give one, more - 0.
- Location. The middle position gets the maximum score. Deviation forward – 1, posterior – 0.
- Patency of the cervical canal. Closed external mouth – 0, closed internal mouth with open external one – 1, both open – 2.
What are the consequences of insufficient readiness of the organ?
A prepared, fully mature cervix before childbirth plays an important role in the favorable course of labor. If the organ is not mature by the time the baby is born, this can cause the following complications:
- internal and external breaks;
- fetal injury;
- premature discharge of amniotic fluid;
- protracted labor.
Long neck
One of the parameters by which one can judge whether the cervix is not ready for childbirth is its size. The normal length during pregnancy is 3–4 cm. As labor approaches, the cervix changes. Due to the pressure that the child puts on the base of the organ, it rises and shortens. An organ whose size during contractions exceeds 2 centimeters is considered long. An elongated cervix is unable to deliver the fetus, as it is dense and narrow, which will prevent the baby from passing through the birth canal on its own.
Complications of a long organ can include:
- weak labor activity;
- prolonged labor;
- injuries, ruptures;
- fetal hypoxia;
- untimely removal of the plug.
Tight, dense
Another indicator of cervical ripening is its consistency. When the cervix ripens, it softens. First, its edges become soft, then the upper segment softens. Before childbirth, it is considered ideal if the cervix has a soft consistency and allows up to 2 fingers to pass through. The fetus will pass through the birth canal without any problems.
A dense and tight cervix among gynecologists is called “oak cervix.” Sometimes the woman’s psychological state is “to blame” for the fact that she remains tight during labor. Some are so afraid of giving birth that they do not produce hormones responsible for softening tissue. Alas, this is fraught with a cesarean section or rupture or episiotomy.
Directed posteriorly
Throughout pregnancy, the cervix is positioned posteriorly, and this is normal. When the body prepares for the birth of a baby, and this process begins already at 32–34 weeks, the organ changes its position towards the center. This is necessary for the smooth exit of the newborn from the mother's womb.
Another position, forward or backward deviation is beyond the norm, which is fraught with the same complications of labor that are associated with the dense structure and too long size of the organ. For this reason, an important role is played by preparing the cervix for the upcoming labor, which is carried out both in the maternity hospital and at home.
What happens to the cervix before childbirth
The cervix begins to prepare for the birth of a child from 32 to 34 weeks of pregnancy. First, its edges soften, leaving a dense area of tissue along the cervical canal. Closer to childbirth, the uterus more often comes to tone, due to which its lower segment softens and becomes thinner. The upper myometrium, on the contrary, becomes denser.
Due to this, the fetus begins to gradually descend and put its weight on the neck, provoking its further opening.
Dilatation of the cervix before childbirth does not occur equally in women who give birth for the first time and in multiparous women. In the first, it begins with the opening of the internal pharynx.
In the latter, the process of opening the internal and external pharynx occurs simultaneously, since by the end of pregnancy their external pharynx usually already allows one finger through. As it opens, the neck thus becomes shorter. A couple of days before the onset of labor itself, the process of its maturation accelerates significantly. Gradually it completely smoothes out and easily lets through 2 fingers or more.
Based on the Bishop scale above, on the eve of childbirth the cervix should meet certain parameters.
A soft cervix is ideal for childbirth. Her softness is evidenced by the fact that she freely passes 2 or more fingers of the doctor. During this period, a woman may notice the release of the mucus plug. This is one of the harbingers of the upcoming birth, indicating the imminent onset of contractions. As for the length of the cervix, during pregnancy a length of 3 cm is considered normal for it. In this case, both ends of the cervical canal must be closed. Closer to childbirth, it shortens. The length of the cervix before childbirth should not exceed 1 cm, gradually smoothing out completely.
As for its location, it was tilted back throughout the entire pregnancy. This further helps keep the fetus inside. Gradually, due to the softening of the lower segment of the uterus, it begins to unfold forward. When the time comes for childbirth, it should be located exactly in the center of the small pelvis.
How is the cervix prepared for childbirth in a maternity hospital?
By the beginning of labor, the cervix should be ripe, but, according to statistics, in 16.5% of pregnant women who give birth for the first time, this is not the case. In such a case, the organ is prepared for childbirth. To speed up dilatation, soften or shorten the cervix, mechanical and medicinal methods are used.
The first includes the introduction of a Foley catheter into the cervix, laminaria or hygroscopic dilators and digital detachment of the fetal membranes (we recommend reading: Foley catheter before childbirth to dilate the cervix). These methods do not show high efficiency, and are also fraught with the possibility of infection.
Medicinal methods of stimulating cervical ripening include vaginal (in tablets or gel) or intracervical (in gel) administration of hormones:
- misoprostol;
- dinoprostol;
- mifepristone;
- oxytocin.
Beginning of labor: cervical examination
Upon admission to the maternity hospital, and then several more times during childbirth, the doctor will say: “Now we’ll do a vaginal examination” or: “Let’s see how the cervix is, how the baby is progressing.” We are talking about an internal obstetric examination, which allows us to determine the condition of the birth canal, observe the dynamics of cervical dilatation during childbirth, the mechanism of insertion and advancement of the presenting part of the fetus (head, buttocks). The initial examination upon admission of a woman in labor to the maternity hospital is carried out on a gynecological chair, and during childbirth - on the birth bed. The frequency of vaginal examinations depends on the characteristics of the course of labor. In the physiological (normal) course of labor, they are carried out no more often than after 4 hours, and if indications arise (rupture of amniotic fluid, changes in the nature of contractions, the appearance of bleeding, changes in the fetal heartbeat) - as necessary.
What can you do at home?
Every woman dreams of having a healthy baby and a quick, easy birth without complications. Alas, it is impossible to predict all the features of this process, but preparing the body by reducing the risk of unpleasant consequences is quite possible. For example, it is not difficult to take care of preparing the cervix at home, using different approaches - from gymnastics or taking herbal infusions to intimate intimacy.
Exercise and yoga
The first thing you can do at home to prepare the cervix is certain physical exercises or a special yoga routine for pregnant women (we recommend reading: how to dilate the cervix as quickly as possible before childbirth?). Both are aimed at stretching the muscles and ligaments of the perineum.
Any gymnastics should be performed with the permission of a doctor and preferably under the supervision of specialists, and not independently. You should start preparing the body for childbirth in this way in advance, somewhere from the 20th week, and not before the expected event. During this period, the method is useless.
The greatest effectiveness is shown by Kegel exercises, which involve contracting (squeezing) the muscles of the vagina and perineum and relaxing them. Those muscles with the help of which voluntarily stop urination are trained. First you need to strain them as hard and quickly as possible for 2 seconds, counting, then rest. Then you should tense the same muscles and keep them in this state for as long as possible, and then relax.
The effect will be achieved subject to the following rules:
- each exercise is performed for 10 minutes at least 3 times a day;
- the time of muscle relaxation should always exceed the time of their tension;
- you need to ensure that other muscles are not included in the exercises;
- the period of tension should be gradually lengthened;
- You should start classes at least 6 weeks before the expected date of birth.
Some yoga asanas for pregnant women (pictured) are suitable for preparing the cervix. However, they should also begin to be performed long before childbirth. Then at the beginning of the first labor period they will help its opening. These asanas include:
- Baddha konasana. Sitting with a straight back and a tucked (if possible) stomach, pull your feet folded together towards you as close as possible, achieving a feeling of opening in the perineum. Stretch up, slowly lowering your knees to the floor using your leg muscles. Freeze, breathing deeply, for 15–20 seconds.
- Paschimottanasana. Sit on the floor with your legs extended straight forward, hip-width apart, placing your palms on the floor with your toes facing your feet. Toes point upward. Exhale and, leaning forward, clasp your toes with your hands. The spine must be kept straight and the shoulder blades must be connected. Stay in the pose for 20 seconds.
- Malasana. Place your feet with your toes in opposite directions at a distance of half a meter, transfer your body weight to your heels and slowly lower yourself, keeping your back straight. Place your palms together and slowly push your knees apart with your elbows. Stay in this position for about 30 seconds, breathing calmly and relaxing your pelvic muscles.
Sex without a condom
Another effective method to soften the cervix before labor begins is sex without a condom. This is due to the fact that sperm contains prostaglandin hormones, which help the cervix to ripen. It makes sense to use this method for several weeks before labor begins, unless it is contraindicated. If there is a threat of premature birth or placenta previa, this method is prohibited. You should also not use it if your partner has a sexually transmitted infection.
Infusions of medicinal herbs
If sex or any physical activity is prohibited, a pregnant woman faced with the problem of cervical immaturity can resort to other traditional medicine, namely infusions and decoctions of medicinal herbs. Well proven:
They promote faster dilatation of the cervix, speeding up the process and making it less painful. However, such products should be prepared and used very carefully, since many herbs are allergens and therefore can be dangerous.
Cervix of the uterus during early pregnancy: position, condition, dilation
Pregnancy is already marked from the very beginning with signs of the presence of a fertilized egg. Changes primarily affect the reproductive organs. Therefore, it is natural that the cervix in the early stages of pregnancy, photos of which are given in the article below, changes. And the changes happening to her are one of the symptoms of the event awaiting the woman.
Location of the cervix in early pregnancy
Few women will be able, if necessary, to explain what this segment of the reproductive system is and what its significance is. This is easy to explain - it is impossible to monitor the problems or health of the cervix on your own. Its assessment and examination is the responsibility of the gynecologist conducting the examination.
This is the part of the organ visible during examination, which is transitional to the vagina, and also connects them. At each stage of the menstrual cycle, it produces mucus.
At the same time, the role of the cervix in the early stages of pregnancy (see photo in this article) cannot be underestimated - it is it that largely ensures that the fertilized egg is kept in its proper place. Upon examination, only the vaginal part can be detected, although this is often enough to assess the state of health.
When examined, it looks like a rounded formation protruding forward, having a small hole in the middle and covered with a mucous membrane.
The usual size of the organ is 4 cm in length and 2.5 centimeters in circumference, the pharynx is closed, the consistency is solid, and on critical days it becomes a little wider for the free release of secretions.
Changes in the cervix during early pregnancy are clearly visible to the doctor, which makes it possible to detect this condition. It is considered one of the main signs along with the cessation of menstruation.
Main functions
A woman's internal genital organs work smoothly if she is completely healthy. In normal condition, this organ performs several functions that help maintain the balance of microflora inside. Let's describe the main functions:
- favorable microflora is maintained thanks to the canal located in the vagina;
- there is mucus inside the pharynx that prevents all kinds of bacteria and microbes from entering the uterus;
- signals any changes that can be seen during examination;
- protects the fertilized egg from falling out;
- stimulates the reproductive organs to function normally.
It is difficult to overestimate the importance of this organ for a woman’s health. However, only an experienced specialist can read all the information.
Signs of changes in the cervix
So, let's figure out what the cervix is like in the early stages of pregnancy. It begins to change noticeably from about the fourth week, when the fertilized egg causes a slight protrusion of the wall, as well as an increase in the size and asymmetry of the organ. This can also only be detected by a specialist.
Moreover, what kind of cervix is in the early stages of pregnancy primarily depends on how much time has passed since its onset. In this case, the increase in progesterone observed after conception leads to a visual change in the organ. This is easy to notice during a gynecological examination.
An experienced doctor can accurately determine the period from the date of fertilization.
The cervix in the early stages of pregnancy acquires the following differences from its normal state:
- Its position changes significantly relative to the main part of the organ.
- The color of the mucous membrane acquires a bluish tint, which was pink before fertilization.
- When palpated, the texture of the tissue becomes different.
There is no need to be afraid of such changes; they are caused by the activation of metabolic processes and the proliferation of blood vessels. This is necessary to improve blood supply, since the formation of the membranes of the fetus, in addition, its nutrition requires an increased amount of oxygen.
Changing the location of the vaginal cervix
When an embryo appears, the reproductive organs adapt to it in such a way as to provide it with comfort, normal development, and also protect it from possible dangers. This is what explains the changed position of the cervix in early pregnancy.
It is not constant, changing at different stages of the cycle. But in general, this part of the organ is located quite high relative to the vagina. This is especially noticeable during ovulation - at this moment the body seeks to facilitate the penetration of sperm into the reproductive cell.
In the early stages of pregnancy, the cervix is low relative to its usual position. It is lowered by progesterone, thereby preventing the fertilized egg from falling out. The course of pregnancy depends on the level at which the cervix is located during early pregnancy - low or high.
If it is located high, this may indicate increased tone, which increases the risk of interruption. Due to this, some women have to spend almost the entire pregnancy lying down. But the doctor will take into account other signs. Probably, its high location is a feature of the body that does not threaten the fetus in any way.
Cervix consistency
The cervix in early pregnancy is soft to the touch compared to its previous state. This is explained by a significant dilation of blood vessels, more active work and swelling of the glands.
Progesterone also plays a role, making the uterus itself and its endometrium thicker and looser. Although the neck is denser than the walls of the organ. It is a certain lock that protects the fetus.
At the same time, she becomes more mobile.
Some people worry that if it is soft, it will not hold the fertilized egg.
The fears have no basis, since its channel is significantly narrowed, and the tissues will still be elastic normally and difficult to stretch for a certain time.
The glands begin to actively produce more viscous and thick mucus. A large clot called a plug appears in the cervical canal, which performs several functions:
- ensures the maintenance of microorganism balance;
- does not allow foreign bacteria to enter the uterine cavity;
- creates conditions for normal functioning of the reproductive organs.
If the cervix is too hard to the touch, this may indicate excessive tension in the organ (hypertonicity). This condition is dangerous due to the possibility of rejection of the fertilized egg. It is impossible to assess the consistency of the cervix on your own.
Therefore, there is no need to “wind up” yourself. Regular visits to the doctor are a guarantee that the pathology will be identified before it is too late to correct it.
Short neck
Not all women have a problem-free pregnancy. One of the most serious is the threat of interruption, caused by various reasons.
It is worth noting that the development of the fetus, in addition, its significant weight gain, increases pressure on the cervix. Sometimes it shrinks in size and can no longer be a full-fledged protection.
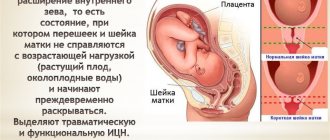
This condition is most often caused by hormonal reasons, although it occurs with injuries received in the past by the organ, polyhydramnios and multiple births. This phenomenon is called “isthmic-cervical insufficiency.”
It requires medical supervision and treatment. Let us highlight the symptoms of cervical shortening detected by the doctor:
- excessive mobility;
- too soft consistency of fabrics;
- dilated lumen (the cervix is slightly open in early pregnancy).
For some girls, these signs are mild, but in any case she herself will not notice the problem, especially in the first weeks. The anomaly must be seen by a doctor, which requires mandatory registration, as well as a huge number of examinations.
The danger of shortening the cervix
Shortening the cervix during early pregnancy is dangerous due to the high risk of miscarriage.
Isthmic-cervical insufficiency, instead of a very dense ring that protects the embryo from falling out, leads to the appearance of an element that provokes bleeding around it.
This part of the organ cannot contain the increasing pressure, which leads to tone. The uterus becomes tense, hard, its muscles can begin to actively contract at any moment, trying to reject the fertilized egg.
This is dangerous at an early stage because the symptoms of cervical contraction during pregnancy are not always visible to the woman herself. Shortening of a section of this organ is detected using transvaginal ultrasound, prescribed at different times. At the same time, some girls experience:
- the cervix bleeds in early pregnancy;
- the appearance of watery discharge;
- nagging pain in the lower back, lower abdomen, discomfort in the form of tingling in the vagina;
- frequent need to urinate.
From time to time, the short length of this part of the organ can be congenital, most often it is an acquisition. Although, in order not to provoke shortening of the cervix itself and not create a threat to the child, a woman should take care of this even before pregnancy, in other words:
- do not smoke, as this bad habit provokes the development of hormonal disorders;
- avoid abortion;
- do not overwork and do not be nervous during pregnancy itself.
Cervical examination
In addition to a gynecological examination using mirrors, as well as a two-handed examination, the gynecologist will refer the girl to undergo the necessary microflora analysis.
You should make sure that there is no fungus or sexually transmitted infections in her body that could harm the fetus.
We are talking about the microflora of the vagina, and it directly affects the general condition of the cervix.
The following cytology study allows us to study the normal structure of cells in a given area of the organ. At the same time, the cervix is not at all immune from their possible degeneration into malignant ones.
A changed cervix in the early stages is not just one symptom of an “interesting position.”
In addition to protective functions, it informs about possible problems that can lead to a sad end if the right measures are not taken.
Therefore, girls do not need to be afraid and avoid intravaginal ultrasound and gynecological examination, especially if there is a history of premature birth, miscarriage, or abortion.
Cervix is bleeding
If the discharge, which is a physiological norm, becomes brownish in color or includes inclusions of blood, there is a high probability that it is the cervix that is bleeding. This type of discharge is never associated with menstruation and is mostly spotty in nature.
Basically, the cervix bleeds due to existing erosion, which is small ulcers that secrete blood.
Damage to the mucous membrane is possible. They occur during sexual intercourse, in addition, during a medical examination, and this may also be accompanied by slight bruising of the cervix.
In addition, cervicitis (inflammatory processes), uterine polyps may also appear, sometimes the cause of the appearance of blood can be several of the above at the same time.
Early pregnancy: cervical discharge
In the first ninety days of pregnancy, the occurrence of spotting is not uncommon. They are observed in almost 20% of pregnant women. This process is not always associated with pathology.
For example, the cervix may bleed at the very beginning of pregnancy, after the egg attaches to the uterine wall, if it has been successfully fertilized. Such discharge continues for about 2 days.
In the 3rd trimester, the appearance of blood may already indicate placental abruption, and this requires prompt medical intervention.
Before starting treatment, you should find out exactly why the cervix is bleeding.
If erosion is the cause, the specialist will prescribe various healing medications, douching and herbal baths.
The main method of treating polyps, which cause bloody discharge from the uterus, is surgery.
Sometimes the appearance of blood occurs with cancer. In this case, a biopsy is mandatory.
Erosion
Already in the very first months, the expectant mother goes to the antenatal clinic for mandatory registration, where she undergoes all kinds of necessary medical examinations, and also prepares to meet her baby and the upcoming birth.
Consequently, it is possible to identify various pathologies or diseases in a timely manner, in addition to preventing their possible complications. Cervical erosion is one of the most common and most frequently diagnosed diseases.
It is detected very often at the very first gynecological examination. The doctor examines the girl using a special mirror and also makes a smear for cytology. The pathology looks like a small defect located on the cervix, namely on the mucous membrane, in the form of an ulcer or redness.
In medical practice, pseudo- and true cervical erosion are distinguished. The pregnant woman then makes a note in her personal card about the presence of the pathology. This is done so that other specialists who will be present at the birth pay close attention to this.
It should be noted that cervical erosion in early pregnancy can be the result of various reasons. The very first of them is a violation of the girl’s hormonal background, which begins to change at the very beginning, right in the first trimester.
In addition, the occurrence of cervical erosion is facilitated by all kinds of sexually transmitted infections (mycoplasma, chlamydia, gonorrhea) received by a woman before or during pregnancy, chemical and mechanical action, improper, rough douching, as well as many other factors.
In addition, the development of the disease is affected by frequent changes of sexual partners and decreased immunity.
Source: https://FB.ru/article/366816/sheyka-matki-pri-beremennosti-na-rannih-srokah-polojenie-sostoyanie-raskryitie