Relatively recently, a pessary began to be used in gynecological practice, installing it in pregnant patients if necessary. According to reviews from patients and doctors, its effectiveness reaches 90%.
An obstetric pessary is a special device made of plastic or silicone that is inserted into the vagina to support the pelvic organs in the desired position. The main feature of the pessary is that it anatomically matches the structure of the female body, therefore it is conveniently located in the vagina and does not interfere. Pessaries come in different shapes and sizes.
The woman is trying to find out whether the pessary helps in opening the internal os, because the open cervical canal cannot protect the fetus properly. Bacteria from the vagina can easily enter the uterus. If inflammation begins, then there is a risk of infection of the fetus, and the likelihood of premature birth is also high. Pathology can be detected using ultrasound.
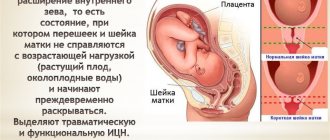
Most often, pessaries are installed in the presence of isthmic-cervical insufficiency (ICI), as well as for its prevention. ICI can occur for various reasons, the main ones being hormonal imbalance, scar tissue damage due to deep tears during previous births.
Previously, such cervical problems were solved only by surgery. The method is called cerclage and involves suturing the neck. Today they are gradually moving away from it, since surgical intervention is very traumatic for the body, and even during pregnancy it is generally undesirable.
In all cases, they try to start with conservative methods. First of all, the gynecologist may prescribe hormonal treatment. If there are no results, then obstetric rings are used.
What is ICN and why is it dangerous?
ICI during pregnancy is relatively rare, occurring in only 1-9% of women. What is hidden behind this phrase? To understand what it is and what processes lead to this pathology, you need to understand the structure of the uterus.
It consists of a body - a muscular hollow sac in which the child is born, and a cervix that closes the entrance to the uterus. Together with the isthmus, the cervix forms the first part of the birth canal. Both the neck and isthmus consist of two types of tissue: connective and muscle.
Moreover, muscle tissue is concentrated in the upper part of the cervix, near the internal os of the uterus. The muscles form a sphincter ring, which does not release the fertilized egg from the uterus prematurely.
However, in some cases, this very muscle ring is unable to withstand the increasing load: the weight of the fetus and amniotic fluid, the tone of the uterus. As a result, under the pressure of the fertilized egg, the cervix shortens and opens prematurely.
Why is ICN dangerous during pregnancy? Firstly, the dilated cervix provokes the descent of the fetus, the fetal membrane enters the uterine canal. During this period, it can open up from literally any sudden movement.
Secondly, a woman's vagina is never sterile. It always contains various bacteria, and often infections. As a result, infection of the fetal membrane occurs. At this point it becomes thinner and can rupture simply under the weight of amniotic fluid.
The opening of the membranes and the release of water cause the onset of labor. Thus, ICI becomes one of the most common causes of late miscarriages (up to 22 weeks), or premature births (from 22 to 37 weeks).
Typically, ICI develops between 16 and 27 weeks. In rare cases, pathology may develop earlier, even at 11 weeks.
Types and causes of isthmic-cervical insufficiency
What are the causes of ICN? They can be very different, and depending on the reasons, they distinguish between traumatic and functional failure.
With the first view, everything is clear from the name. Traumatic ICI develops if the muscles of the cervix have been injured in one way or another. What can cause injuries? Any procedure associated with dilation of the cervix is fraught with injury. These include abortions, curettage after miscarriage, and diagnostic curettage. In addition, the muscles of the cervix can be injured during childbirth, as well as after IVF (in vitro fertilization).
In this case, the mechanism of formation of ICI during pregnancy is extremely simple: at the site of any injury, a scar of connective tissue appears. Unlike muscle tissue, connective tissue is not able to stretch, and this causes insufficiency.
With a functional ICN everything is somewhat more complicated. Its causes may lie in various factors. However, most often this type of deficiency is associated with hormonal imbalances. As a rule, we are talking about a lack of progesterone, or an excess of male hormones - androgens. By the way, this is the second most common cause of ICI.
In this case, deficiency begins to develop in the early stages, from about 11 weeks of pregnancy. This is due to the fact that at this time the fetal pancreas begins to work. It produces male hormones, and if the mother has an increased amount of them or is sensitive to them, the consequences will immediately affect: the muscles in the cervix weaken and the cervix dilates.
ICI can also develop for more prosaic reasons. For example, if the pregnancy is multiple or there is polyhydramnios. In this case, the load on the cervix is greater than in a normal pregnancy, which can also lead to insufficiency. Do not forget about pathologies of uterine development.
Symptoms of ICN
Unfortunately, isthmic-cervical insufficiency is asymptomatic. Only in some cases, ICI in the early stages can manifest itself in much the same way as a threatened miscarriage: spotting, nagging pain in the abdomen, bursting sensations in the vagina. Typically, ICN has no symptoms during pregnancy.
Diagnostics of ICN
Due to the fact that ICI is practically asymptomatic, it is very difficult to diagnose. To do this, you need to regularly visit the gynecologist and conduct a vaginal examination at each visit. Unfortunately, many doctors believe that examining the birth canal is sufficient during registration and in the maternity hospital before birth.
As a result, the woman attends a consultation, but the doctor only measures her weight, abdominal size and blood pressure. In such conditions, a woman may find out about the diagnosis of ICI during pregnancy when it is already too late.
Often this is already known about a miscarriage or premature birth with the help of a special study: hysterosalpingography - an x-ray of the uterus and tubes using a radiopaque substance.
Of course, if a woman has previously had this pathology, her health will be monitored much more closely. However, you can insist that a vaginal examination be performed every time you visit a gynecologist.
During the examination, the doctor should pay attention to the softening of the cervix, a decrease in its length at the initial stage of ICI, and dilatation of the cervix at a later stage.
One question remains: what length of the cervix is considered normal? Much depends on the period, because closer to childbirth, a decrease in length is considered normal:
- at 24-28 weeks: 35-45 mm;
- after 28 weeks: 30-35 mm.
However, the doctor has only his own sensations and a gynecological speculum at his disposal. And if the external os of the uterus is not yet open, the gynecologist can only assume ICN, and more accurately make a diagnosis using ultrasound.
The study is carried out using a vaginal sensor. The following factors are noted that help determine whether isthmic-cervical insufficiency occurs:
- cervical length;
- presence of opening of the internal pharynx.
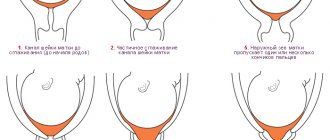
If the internal pharynx has already begun to open, and the external pharynx is still closed, the cervix takes on a V-shape, and this is clearly visible on an ultrasound. There are several additional tests that can clarify the diagnosis in complex cases. For example, a woman may be provoked to cough or put pressure on the fundus of the uterus (that is, in its upper part). This necessarily affects the cervix, and ICN makes itself felt.
Treatment of ICN
Only after the diagnosis has been accurately established, as well as the cause of the pathology, can treatment for ICI during pregnancy begin. Without knowing the cause, as in any other case, it will not be possible to select an adequate treatment.
First of all, functional ICI is identified, which occurs against the background of hormonal imbalances. In this case, hormonal therapy is prescribed to restore normal hormone levels. The medications are continued for 1-2 weeks, after which the patient is re-examined. If the situation has stabilized and the cervix no longer dilates, then the medications are continued, while maintaining constant monitoring of the pregnant woman’s condition. If the situation worsens, other methods of treatment are preferred.
What it is?
Placental tissue appears by the beginning of the second trimester of pregnancy. It functions actively throughout several months of pregnancy until birth. The normal location of the placenta is an important clinical sign. If the placental tissue is located abnormally, then this can be dangerous for the development of complications during pregnancy.
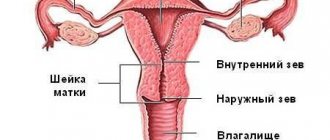
In order to understand how the placenta can be attached, we need to touch a little on the anatomy. The uterus is the main female reproductive organ in which the baby develops during pregnancy. Through its cervix it connects to the vagina. The outer boundary of such a connection is called the outer pharynx. The cervix is separated directly from the uterus itself by the internal os.
After pregnancy, quite a lot of changes occur in a woman’s reproductive organs. After fertilization, the color of the mucous membranes of the cervix changes - it becomes more bluish. The mucous membranes also change their density - they become denser and more elastic.
Normally, the internal os remains closed during pregnancy. This is necessary for the full intrauterine development of the baby. Closing the internal os also protects the amniotic sac from infection and keeps the fetus in the uterus.
If for some reason the tone of the internal pharynx changes, then dangerous complications of pregnancy may arise. In such cases, as a rule, the risk of spontaneous miscarriage increases many times.
Functions of the internal mouth
The internal os protects the uterus from foreign substances entering it. After the fertilized egg enters the cavity, it closes tightly and turns blue. A mucous plug appears between it and the vagina, which protects the fetus and placenta.
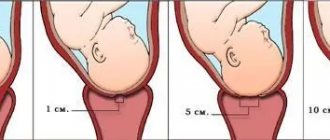
Childbirth occurs when the internal os begins to open. The possibility of the fetus leaving the uterus appears when the diameter of the opening of the pharynx reaches 10 cm. If deviations from the norm occur and for some reason it does not open completely, then the child is born prematurely and a rupture of the cervix (internal pharynx) occurs.
Location norm
The formation and location of placental tissue largely depends on the initial site of attachment of the fertilized egg. It is optimal if it occurs near the fundus of the uterus. In this case, the placenta will subsequently be formed physiologically. If for some reason the fertilized egg attaches low, closer to the cervix, then the location of the placenta will be changed.
Doctors evaluate the location of placental tissue at different stages of pregnancy. In this case, the norm of its location to the pharynx is determined by the weeks of pregnancy. So, in the 2nd trimester, the normal height of the placenta from the internal os is 5 cm.
If the lower edge of the placenta is only 3 cm or less above the internal os, then this condition is called low attachment. As a rule, doctors diagnose it only by the 12th week of pregnancy.
In the third trimester of pregnancy, the distance from the placenta to the internal os is normally 7 cm. If it is less than 5 cm, then this condition is defined as low placental attachment.
A pregnant woman can carry a baby even with low placental tissue attachment. In this situation, it is very important for her to monitor her well-being and carefully monitor all emerging symptoms. The appearance of sudden cramping pain in the lower abdomen and the appearance of bloody discharge should be a reason to immediately contact your obstetrician-gynecologist.
The low location of the placental tissue at 20 weeks requires more careful monitoring of the pregnant patient. At this time, the risk of developing intrauterine fetal hypoxia increases. This condition can be dangerous due to the development of bleeding, placental abruption, as well as arrest of intrauterine development of the fetus.
If the placental tissue is low, doctors recommend that patients carefully monitor their well-being. So, a pregnant woman with this arrangement should not lift weights. This may cause uterine bleeding.
With low placental tissue presentation, a pregnant woman should also monitor her emotional state. Stress and anxiety can provoke a dangerous condition - uterine hypertonicity. In this case, the risk of spontaneous miscarriage increases. To normalize the emotional background, the expectant mother is recommended to walk in the fresh air more often, as well as get a good night’s sleep.
If an expectant mother with low placental tissue presentation experiences uterine bleeding, she should be hospitalized. If bleeding develops at a fairly early stage, then doctors will formulate the correct tactics for further management of pregnancy.
If necessary, a woman can be left in the hospital for several weeks “for preservation.” After inpatient treatment, the expectant mother is prescribed medications as needed and recommendations are made for changing her daily routine.
Installation
An important advantage of a pessary is its safety for mother and child. The decision to install a ring can only be made by the doctor with your consent. Such a measure will not always be appropriate, it all depends on the duration of pregnancy and the condition of the cervix. The pessary is usually installed at 20 weeks, but with ICI it can be installed earlier. Please note that cerclage cannot be performed before 20 weeks.
The procedure for installing a pessary takes a few minutes and does not cause the woman any discomfort. No anesthesia is required. The bladder and bowels should be emptied and positioned comfortably on the gynecological chair.
On the eve of the installation of the pessary, the woman needs to have her vagina sanitized, which the doctor will do. If your candidiasis has worsened, which often occurs during pregnancy, you need to consult a gynecologist and undergo antifungal therapy in advance.
Immediately before installation, the ring is lubricated with a special product to moisten it.
Whether a pessary helps in opening the internal pharynx, you can see from your own experience. The doctor will carefully insert it into your vagina and place it on your cervix. With the correct size, the pessary is securely fixed and you will not feel it.
After the ring is installed, the pregnant woman is prescribed sexual rest - sex with penetration is prohibited until the birth. In addition, the doctor will prescribe regular smear tests to monitor the condition of the cervix, as well as periodic disinfection of the vaginal tract. When carrying out hygienic procedures, it is forbidden to try to do anything with the pessary yourself.
The gynecologist also removes the ring. This usually occurs after the 37th week, when the pregnancy is considered full-term. Like insertion, removing the pessary does not cause any pain.
Women, faced with a problematic cervix, are interested in who’s internal os closed after the installation of a pessary? For what other pathologies is it installed:
- If there is a threat of termination of pregnancy due to a history of miscarriages associated with the cervix, then the ring can help.
- For cervical ruptures and improperly fused tissue.
- If the patient is overloaded with physical labor during pregnancy. For example, there is another small child who requires care.
- Multiple pregnancy, due to particularly strong pressure on the cervix, also requires support in the form of a ring.
It is important to note that after installing an auxiliary unloading device, the woman feels better psychologically, because she knows that now her condition is not in danger and she will be able to carry the child to the desired term. Of course, sometimes the internal os remains open with a pessary, and with a shortened cervix, the risk of premature birth is quite high.
According to patient reviews, labor can begin quite soon after removing the pessary - within a couple of days, but it can take several weeks.
Contraindications
A pessary is not placed if:
- for some reason it is impossible to prolong pregnancy - there is a risk for the mother;
- constant bleeding is observed in the 2nd and 3rd trimester;
- emergency cases requiring urgent removal of the ring:
- amniotic fluid has broken;
- urgent need to induce labor;
- inflammation of the membranes of the fetus with penetration of infection into the amniotic fluid.
If the size is incorrectly chosen or for other reasons, the pessary moves, thereby causing colpitis of a mechanical nature. The doctor may choose another ring or try to replace it.
During installation, it happens that the uterus begins to actively contract. And this is a normal reaction of the reproductive organ to intervention. Therefore, before the procedure, it is recommended to take an antispasmodic; the gynecologist will tell you about this.
The pessary is never reused. If you had to remove it, then subsequent installation occurs using a new ring.
Clinical options
Placental tissue, as a rule, is located more often at the level of the anterior and posterior walls of the uterus. Also in some cases it reaches the side walls. Much less often, the placenta is attached directly to the fundus of the uterus or in the area of the tubal angles.
Doctors believe that not all clinical options for placental attachment are favorable for the course of pregnancy. Less physiological cases of the location of placental tissue can be dangerous for the development of complications.
The exact location of the placenta can be determined using ultrasound examinations. If the placental tissue covers the internal os, then this is a very dangerous pathology. In this case, the risk of spontaneous labor increases significantly. Also, with this option, there is a fairly high risk of infection from the external genital tract into the uterine cavity, where the fetus is located.
Types of pathologies
If placental tissue is detected directly at the site of the internal os, then this clinical condition is defined as presentation. It can be partial, complete and marginal. Each type of presentation is determined by the location of the placenta relative to the internal os.
It is necessary to determine the abnormal position of the placental tissue. This allows doctors to prevent quite a few dangerous pathologies that can develop during pregnancy.
Obstetricians-gynecologists identify several clinical variants of this pathological condition:
- Central. In this situation, the placental tissue is located in the lower part of the uterus and also covers the internal os.
- Lateral. In this situation, the placental tissue is also located in the lower part of the uterus, but the pharynx is not completely blocked.
- Regional. In this case, the placental tissue and pharynx practically touch their edges.
Placental tissue previa can be dangerous due to the development of very dangerous complications that arise during childbirth. They can manifest themselves as a weakening of labor, ingrowth of placental tissue, atonic uterine bleeding, various infections, as well as the possible development of septic pathologies.
With central placental presentation, obstetricians and gynecologists are forced to resort to cesarean section. Quite often, planned surgical obstetrics are carried out at 37 weeks of pregnancy.
In medical practice, there are cases when the chorion presentation along the posterior wall overlaps the internal os. Usually in this case, doctors conduct more careful monitoring of the development of pregnancy. It can be quite difficult for the chorion to “climb” along the back wall.
There are situations when he remains in this position and does not rise. In this case, it is very important to monitor the progress of pregnancy, as well as to choose the right delivery tactics in the future. It may also be that a caesarean section is required to give birth to the baby.
Uterine os during pregnancy
Before a toddler appears in the expectant mother's womb, she may not even know what the os of the uterus is and what it should be like. Let's look at the anatomy. A woman’s uterus is a hollow, pear-shaped organ within which the baby develops and grows. The uterus is separated from the vagina by the uterine cervix (cervix uteri) - a canal 3-4 cm long and 7-8 mm wide, one part of which opens into the uterine cavity, the other is directed into the vagina. The term "os" combines these two openings of the cervical canal - the upper and lower exit of the cervix. If a woman is pregnant for the first time, the uterine os has a transverse oval shape. Subsequently, the shape of the hole changes and takes on the appearance of a transverse slit, but the pharynx is still closed during pregnancy. With the appearance of a toddler in a woman’s uterus, a dense mucus plug forms in the cervical canal, which serves as an additional protective barrier against infections for the baby. With the onset of labor, the pharynx opens and the plug comes off.
What is an internal os during pregnancy?
The upper opening of the uterine cervix, directed towards the uterus itself, is called the internal os. That. the internal os is the end of the supravaginal part of the cervix, the edge of the cervical canal. It cannot be seen with the eyes or touched in any way. The physiological norm is the closed state of this hole, always. The only exception is the period of menstruation and childbirth. If artificial access to the uterine cavity is necessary, the internal os is opened mechanically. The main function of the internal pharynx is protective. With the onset of pregnancy, a tightly closed opening prevents various types of infections from entering the uterine cavity and does not allow the baby to come out before the due date. When the internal os is closed during pregnancy, this is the norm. The condition of the internal pharynx is monitored by assessing its location, density and diameter. If pregnancy proceeds without complications and pathologies, control is carried out at the 20th, 28th, 32nd and 36th weeks.
What is the external os during pregnancy?
The external os characterizes the area where the cervix enters the vagina, the beginning of its vaginal part, which leads from the vagina to the cervical canal. It is this hole that is accessible to observation during a gynecological examination. The shape of this hole also differs between women who have given birth and those who have not. If it is the first pregnancy, the hole is round; if not, it is slit-like. An increase in the diameter (opening) of the external pharynx also requires additional control and, if necessary, measures. The situation is fraught with the onset of labor earlier than expected.
Opening of the internal os during normal pregnancy
With a physiological course, the cervix begins to prepare for childbirth, starting at 32-34 weeks. During this period, it becomes softer at the edges and more often comes into tone, which leads to softening and thinning of its lower section. The part on top, on the contrary, becomes denser. These changes lead to the fact that the child begins to gradually descend and, with his weight, provoke its further opening. This process proceeds quite slowly and takes about a month, intensifying a few days before birth.
The following symptoms are signs of labor:
- the fundus of the uterus begins to descend. This takes about 3 weeks immediately before the contractions themselves. This process is a consequence of the fact that the fetus is pressed against the pelvis. A woman can notice this by the fact that it becomes easier for her to breathe;
- the baby's head puts pressure on the bladder and intestines, which leads to more frequent trips to the toilet and constipation;
- the uterus becomes more sensitive and reacts by becoming harder at the slightest irritation (sudden movements of the woman or fetus, when touching the abdomen);
- the woman feels preparatory contractions, which are felt less frequently and shorter than the real ones;
- the neck becomes plastic and soft.
Vaginal examination of the cervix is routinely performed at 20, 28, 32 and 36 weeks. If there are any problems, the inspection is carried out more often. The opening of the internal os at 36-38 weeks of pregnancy normally indicates the completion of preparation for childbirth. At the moment, there has already been a partial replacement of muscle tissue with connective tissue, which is able to stretch to a greater extent during childbirth. The doctor sees this by the fact that the cervix has become looser and its shortening leads to a gaping of the cervical canal. If a woman is preparing to become a mother for the first time, then the external pharynx allows only the tip of a finger to enter; in multiparous women - 1 finger. The cervix begins to open from the internal os. If the birth is the first, then the canal in its shape resembles a truncated cone with the base at the top. Further, the pressure of the fetus promotes stretching of the external pharynx. During repeated births, this process is simpler and takes less time, due to the fact that the external pharynx is already open by 1 finger. In this case, the outer and inner pharynx open almost simultaneously.
Cervical pharynx during pregnancy: reasons for opening and danger of pathology
To correct the situation and eliminate the disease, timely diagnosis of the pathology is important. The greatest danger of cervical dilatation lies in its almost asymptomatic occurrence.
Causes of throat opening during pregnancy
What factors can provoke opening of the pharynx?
- Hormonal imbalance.
An increased content of male hormones in a pregnant woman’s body provokes early ripening of the cervix. Women who have similar problems should be especially careful and control the diameter of the cervical pharynx.
- Multiple pregnancy.
Having several babies in the womb is a serious test for the whole body. The cervix also experiences increased pressure, which can lead to its early opening - an increase in the diameter of the pharynx.
- Injuries and pathologies of the cervical canal itself.
This factor is due to possible infectious diseases of the genital area (including a history), as well as mechanical manipulations on the cervix.
- ICI—isthmic-cervical insufficiency.
The weakening of the muscles of the cervix leads not only to its premature shortening, but also to the opening of the pharynx.
The danger of cervical dilatation lies in its practically asymptomatic course. In some cases, a pregnant woman may complain of soreness or a feeling of tension in the lower abdomen. But even such manifestations do not always happen.
Open throat during pregnancy - should you panic?
As was previously said, the pharynx can be external and internal. If the doctor has diagnosed a dilated throat, should you be nervous? Of course, the wording “opening the throat” does not put you in a good mood, but you shouldn’t fall into despair either. The greatest threat to the successful bearing of a baby is the opening of the internal pharynx - that part of the cervical canal that opens the entrance to the uterus and which is not visible when examined on a chair. Fixing this moment during an ultrasound is an alarming signal and should not be ignored under any circumstances. When it comes to opening the external pharynx - the vestibule of the vagina from the side of the cervix - the situation is not always critical. If during a gynecological examination the doctor has determined that the external os is dilated:
- First, ultrasound control is necessary to establish the condition of the internal pharynx.
- The second is evaluating the results. If the internal hole is closed, there is no reason to panic. Calm and observation of the situation is required. If the internal hole is also slightly open, radical measures are required. The latter include suturing the neck or installing a pessary.
Early cervical dilatation
Sometimes this process begins long before the desired time of delivery. For example, if the birth is still far away, and the doctor says that the cervix is dilated by 17 mm, and the internal pharynx is dilated by 6-7 mm, then we are talking about pathology. The greatest danger from early dilation is in the first trimester. The causes of this pathology are:
- isthmic-cervical insufficiency;
- previous pregnancy abortions and miscarriages;
- cervical injuries;
- erosion;
- lack of progesterone.
Normal pharynx during pregnancy
The parameters of the cervix - not only its length and condition, but also the size of the pharynx - an important diagnostic indicator that helps to identify cervical weaknesses in the early stages and promptly take the necessary measures for the safe bearing of the child. Normally, the throat of the cervix (both external and internal) should be closed, the diameter of the hole is most often within 2-3 mm, but should not exceed 6 mm. If pregnancy proceeds without the threat of premature termination, this picture persists from the 10th to the 36th week. Particular attention is required in situations where the expansion of the pharynx occurs at a period of less than 20 weeks.
The pharynx is dilated during pregnancy
Cervical dilatation can be diagnosed both during a gynecological examination in a chair and during an ultrasound.
It is worth clarifying that:
- On the chair, the doctor is able to establish the fact that only the external pharynx is dilated (a finger passes into the canal), the internal pharynx is not visible to him.
- A woman can find out about the condition of the internal pharynx based on the results of an ultrasound examination (ultrasound).
Bacterial culture from the throat of the cervix during pregnancy
The study of bacteriological culture from the cervical canal is an important criterion for assessing the health of the genital area of a pregnant woman and choosing treatment tactics. The reason for prescribing this study is the presence of an inflammatory process (increased white blood cells in a regular smear). If the inflammatory process affects the cervix, the disease is called cervicitis (or endocervicitis). If left untreated, the pathology often causes miscarriages and premature births.
- The biomaterial is collected with a sterile stick from the cervical canal - the secretion of the glands and desquamated cells (carriers of microflora).
- Before the procedure, you must refrain from any hygienic manipulations; you should not use intimate creams and vaginal suppositories.
- It is also worth excluding sexual relations (one day before the test) and taking antibacterial drugs (at least 1 week before the test).
As a result of bacterial culture analysis, it is possible not only to determine the type of pathogenic pathogen, but also to determine its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs that will be necessary for treatment.
Timely diagnosis of the condition of the cervix and its pharynx allows you to take the necessary measures in time and maintain the pregnancy.
Source
Pregnancy is one of the extremely important and exciting periods in a woman’s life. The period of waiting for the birth of a new life is filled not only with joyful emotions, but also with concern for the life of the unborn baby. Modern medicine has stepped far forward and today various pathologies can be identified at an early stage. However, expectant mothers still have questions related to this period. In particular, women are often concerned about the normal opening of the internal os during pregnancy. To answer this question, you need to understand how the female body works.
The internal os is open during pregnancy: pathology control
Diagnosing the opening of the internal pharynx requires taking action. Which ones exactly depends on both the degree of expansion of the canal and the duration of pregnancy.
- Drug therapy. In a hospital setting and on bed rest, the woman undergoes treatment using hormonal agents, vitamins and antispasmodics, and magnesia.
- Installation of a special ring on the neck - a pessary. A structure made of plastic or silicone is placed on the neck, thereby strengthening its walls. As a result, the process of opening the pharynx can be restrained. The ring is most often applied after the 20th week and removed at the 37th week. The procedure is performed without anesthesia. The doctor lubricates the pessary with silicone, inserts it through the vagina and places it on the cervix.
- Surgical intervention - suturing the neck. In this case, either a circular suture can be applied, leaving a drainage gap, or the external pharynx - the anterior and posterior lips of the cervix - can be completely sutured. The second method is less popular, because the created closed space is a favorable environment for the development of infection. The operation is performed before the 28th week of pregnancy.
Unfortunately, taking even radical measures is not always able to save a pregnancy.
Prevention of throat opening
To avoid this situation, women who are at risk of premature opening of the pharynx should follow the following recommendations:
- While carrying a child, exclude any sexual contact;
- Stop doing physical activity and lifting weights;
- Minimize the consumption of coffee and chocolate;
- Follow the diet prescribed by your doctor;
- Stay in the sun as little as possible;
- Avoid using hot baths, visiting saunas and steam rooms.
In addition to the above recommendations, it is worth completely curing gynecological diseases, normalizing hormonal levels and eliminating abortions.
Source
Prevention of throat opening during pregnancy
If a woman is at risk of premature opening of the internal os, the following recommendations should be followed:
- Exclusion of intimate relationships for the entire period of bearing the baby.
- Avoid physical activity, especially heavy lifting.
- Limit consumption of coffee and chocolate, follow the diet recommended by your doctor.
- Minimize exposure to stuffy and hot rooms.
- Limit sun exposure.
- Avoid visiting steam rooms and taking hot baths.
Treatment of internal os opening during pregnancy
First of all, a pregnant woman must provide herself with peace, eliminating physical and emotional stress. Maintain bed rest.
There are 2 ways to stop expansion:
- Surgical (cerclage when opening the internal pharynx). It involves placing sutures on the neck. The operation is performed under anesthesia. To carry it out, the following conditions are necessary:
- integrity of membranes;
- up to 28 weeks;
- absence of infectious processes.
When prolapse of the membranes is performed during pregnancy with twins, features and consequences.
The use of a pessary during multiple pregnancies, the prevention of premature birth.
The opening of the internal pharynx after sutures occurs normally after their removal at 37 weeks.
- Installation of a pessary. It is considered a less traumatic method than surgery. A fairly effective and safe method that can be used at any stage of pregnancy. If a woman is at risk, then installing an obstetric pessary at 15-16 weeks increases the result of the method to 97%. The principle of its operation is that it compresses the neck, preventing it from opening further. There is also a decrease in fetal pressure on the incompetent cervix. The redistribution of pressure leads to the closure of the neck by the central opening of the pessary, the formation and unloading of the neck. All this leads to the preservation of the child.
Our obstetric unloading pessaries are an effective measure for the prevention and treatment of ICI. The products have passed all the necessary clinical tests and have all the necessary certificates and permits.
A little anatomy
With conception, colossal physiological and hormonal changes occur in a woman’s body. The development of the fetus occurs inside the uterus - a hollow smooth muscle sac, the inner surface of which is covered with an epithelial layer. The lower part of the reproductive organ (cervix) is a muscular tube (cervical canal) that communicates with the vagina. It is this that prevents the premature exit of the underdeveloped fetus into the birth canal.
The cervical canal consists of two main parts:
- The external os is part of the smooth muscle tube that is located between the internal os and the vagina;
- The internal os is the inner part of the cervix, located between the uterine cavity and the external os.
Normally, in a non-pregnant woman, the total length of the cervix does not exceed 35-40 mm. During menstrual bleeding and ovulation it opens, and at the beginning of the menstrual cycle it closes.
Internal os during gestation
At the moment of fertilization of the egg and implantation of the embryo into the wall of the uterine cavity, hormonal fluctuations are observed in the female body, and therefore the shape and size of the cervical canal undergo changes. Due to an increase in the concentration of hCG, the internal pharynx becomes denser, which is associated with increased blood microcirculation in the pelvic organs.
If the internal os of the uterus is closed during pregnancy, the risk of spontaneous abortion does not exceed 10%. Loosening of the walls of the smooth muscle organ and its opening increases the likelihood of miscarriage, and therefore the woman is hospitalized to prevent premature birth or termination of pregnancy.
Pathologies of the pharynx during pregnancy
There are two gynecological problems associated with the internal os during pregnancy:
- Opening of the pharynx in the early stages;
- The pharynx does not open even in late stages (more than 37 weeks).
Opening the throat at an early stage with an unformed fetus threatens premature birth. The pathology is scientifically called isthmic-cervical insufficiency. The disease occurs in women with weakened muscles, which does not allow the cervix to contract normally. The reasons for this condition are as follows:
- Congenital weakened muscles of the cervix;
- Acquired injuries of the uterus;
- Underdevelopment of the female genital organ;
- Hormonal imbalances in the body.
With premature dilatation, severe pain is felt in the vagina, however, the process can be asymptomatic. With such a diagnosis, the pregnant woman is hospitalized and further observation by specialists takes place in a hospital setting, right up to the birth.
If the pharynx does not open, then the possibility of natural childbirth is excluded. In this case, a caesarean section is prescribed.
Reasons for dilation of the uterine pharynx during pregnancy
The external and internal os of the reproductive organ prevent the fetus from exiting into the cervix and vagina. Normally, the smooth muscle organ is closed during gestation, thereby creating favorable conditions for the normal development of the embryo. The internal os performs several important functions:
- prevents infection from entering the uterine cavity;
- protects the fetal bladder from septic inflammation;
- holds the fetus inside the uterine cavity until natural delivery.
In the absence of pathologies of the reproductive organs, the cervical canal begins to shorten over time, and its walls begin to loosen. Due to this, the fetus gradually descends into the mouth of the birth canal during the prenatal period. Even partial opening of the smooth muscle ring during gestation can lead to premature birth, fetal infection or miscarriage.
The main reasons for the opening of the uterine pharynx ahead of schedule include:
- multiple births;
- uterine abnormalities;
- conization of the cervix;
- hormonal imbalance;
- high water;
- atony of smooth muscle fibers.
Attention!
Heaviness in the lower abdomen, heavy discharge and pain in the vagina during the gestational period may indicate partial opening of the internal uterine os. The above factors provoke the development of isthmic-cervical insufficiency, which is characterized by premature opening of the uterine pharynx. The pathology is fraught with the descent of the fetus into the lower part of the uterine cavity and, as a result, premature delivery.
Internal os during pregnancy: causes, discoveries – GYNECOLOGICAL HOSPITAL OF OMSK REGION
Which branch would you like to contact?
A little anatomy
With conception, colossal physiological and hormonal changes occur in a woman’s body.
The development of the fetus occurs inside the uterus - a hollow smooth muscle sac, the inner surface of which is covered with an epithelial layer.
The lower part of the reproductive organ (cervix) is a muscular tube (cervical canal) that communicates with the vagina. It is this that prevents the premature exit of the underdeveloped fetus into the birth canal.
- The external os is part of the smooth muscle tube that is located between the internal os and the vagina;
- The internal os is the inner part of the cervix, located between the uterine cavity and the external os.
Normally, in a non-pregnant woman, the total length of the cervix does not exceed 35-40 mm. During menstrual bleeding and ovulation it opens, and at the beginning of the menstrual cycle it closes.
Internal os during gestation
At the moment of fertilization of the egg and implantation of the embryo into the wall of the uterine cavity, hormonal fluctuations are observed in the female body, and therefore the shape and size of the cervical canal undergo changes. Due to an increase in the concentration of hCG, the internal pharynx becomes denser, which is associated with increased blood microcirculation in the pelvic organs.
If the internal os of the uterus is closed during pregnancy, the risk of spontaneous abortion does not exceed 10%. Loosening of the walls of the smooth muscle organ and its opening increases the likelihood of miscarriage, and therefore the woman is hospitalized to prevent premature birth or termination of pregnancy.
Reasons for dilation of the uterine pharynx during pregnancy
- prevents infection from entering the uterine cavity;
- protects the fetal bladder from septic inflammation;
- holds the fetus inside the uterine cavity until natural delivery.
In the absence of pathologies of the reproductive organs, the cervical canal begins to shorten over time, and its walls begin to loosen. Due to this, the fetus gradually descends into the mouth of the birth canal during the prenatal period.
Even partial opening of the smooth muscle ring during gestation can lead to premature birth, fetal infection or miscarriage.
The main reasons for the opening of the uterine pharynx ahead of schedule include:
- multiple births;
- uterine abnormalities;
- conization of the cervix;
- hormonal imbalance;
- high water;
- atony of smooth muscle fibers.
Attention! Heaviness in the lower abdomen, heavy discharge and pain in the vagina during the gestational period may indicate partial opening of the internal uterine os.
The above factors provoke the development of isthmic-cervical insufficiency, which is characterized by premature opening of the uterine pharynx. The pathology is fraught with the descent of the fetus into the lower part of the uterine cavity and, as a result, premature delivery.
Cervical length indicators by week
Normally, the internal and external os of the uterus are closed until 36-41 weeks of gestation. In this case, the length of the smooth muscle ring gradually shortens, and the opening diameter increases. This facilitates the passage of the fetus along the birth canal at the time of delivery.
Reference: in most cases, changes in the size of the cervical canal occur from the 20th week of gestation, however, a gynecological examination is recommended from the 14th week.
- up to the 10th week – 45 mm;
- 16-20 weeks – 40-45 mm;
- 25-27 weeks – 35-40 mm;
- 32-36 weeks – 30-35 mm.
Too short a uterine os between 14 and 24 weeks indicates a high risk of preterm birth:
- up to 10 mm – delivery at 32 weeks of gestation;
- no more than 15 mm – the gestational age of the child will not exceed 33 weeks;
- less than 20 mm – the child will be born at 34 weeks of gestation;
- no more than 25 weeks - the labor process will begin at 36-37 weeks of pregnancy.
Based on the condition of the internal os, you can determine the approximate date of birth of the child, as well as prevent premature birth in the early stages of gestation.
2 weeks before the birth process, the uterus matures almost completely, while the length of the cervix is shortened to 10 mm.
Under pressure from the fetus, the pharynx begins to gradually open, which can be easily determined using ultrasound and gynecological examination.
Methods for closing the uterine os
Premature dilation of the cervix is fraught with serious consequences, including spontaneous abortion. To prevent complications, specialists provide medical or surgical treatment.
Conservative therapy
You can prevent expansion of the uterine os with the help of a special ring (pessary) that is placed on the cervix. In this way, it is possible to reduce the load on the inside of the cervical canal and the likelihood of its premature opening.
Attention! An obstetric pessary can be used only in the early stages of isthmic-cervical insufficiency (ICI) with minimal opening of the uterine pharynx.
Surgery
In case of severe ICI, it is recommended to resort to surgical treatment, which involves suturing the cervix. The indication for surgical intervention is a real threat of interruption of gestation or premature birth. The operation is performed no later than 27-28 weeks of pregnancy, which is associated with a high risk of damage to the amniotic sac and infection of the placenta.
Important! Suture of the uterus is not used during the period of exacerbation of infection, as well as in case of pathological development of the fetus and placenta previa.
Conclusion
Normally, until 36-40 weeks of gestation, the internal os of the cervix is closed. This ensures normal development of the fetus and also prevents its premature exit into the cervical canal.
If it opens, they resort to treatment with hormonal drugs and a gynecological pessary. If conservative therapy is ineffective, surgery is prescribed, during which the cervix is sutured.
Source:
The internal os of the uterus closes during pregnancy - what does this mean, what to do?
During pregnancy, a woman becomes most vulnerable, as her body works for two. If there are several fruits, then the load increases. In this regard, ICI may develop - a dangerous pathology that leads to the loss of the baby. Find out how to determine the onset of the disease and avoid negative consequences from our article.
Placenta position
Doctors consider tracking the position and maturity of the placenta week by week to be very important in the process of monitoring the condition of a pregnant woman. After all, by the twelfth week it becomes possible to identify placental pathologies. Most often, women face the following two problems:
- premature ripening;
- low position relative to the throat.
If we talk about the first pathology, it should be noted that it is extremely rare. It can be briefly described as aging of the placenta, which does not correspond to the duration of pregnancy.
That is, the baby is not yet ready to be born, and the amount of nutrients it requires is gradually decreasing. At the same time, problems arise with oxygen supply.
All this puts the baby’s life in danger and forces doctors to take emergency measures.
Low placentation occurs quite often in women, but this diagnosis raises a lot of questions among pregnant women. So, what does low placenta and normal placenta position mean? Let's talk about this in more detail.
If after fertilization there is a normal attachment of the chorion (along the anterior wall of the uterus, the back or in the fundus), then the placenta will take the desired position within normal limits. But it is worth considering that over nine months, as the uterus stretches, it slightly changes its position.
This process is monitored by doctors during routine ultrasounds. For example, if in the second trimester the distance between the internal os and the placenta is about five centimeters, then these indicators are considered normal.
Approximately by the twentieth week, the distance changes, but it should not become less than seven centimeters.
In these cases, a woman may not worry about low placentation and calmly carry the baby to term. If no other problems are identified, doctors will recommend a natural birth with a high chance of giving birth to a healthy baby.
What should a normal pharynx be like during pregnancy?
After fertilization of the egg, hormones increase blood flow to the genitals and change the structure and density of the tissues of the cervical canal. The cervix becomes denser, and the tissues of the internal and external pharynx become immobile.
Mucus forms between the vagina and the uterus, which creates additional protection for the uterus from the penetration of pathogenic microflora.
Normally, both entrances to the cervical canal should be closed until the 36th week. The diameter of the external and internal pharynx can reach 2-4 mm (after numerous births, 6 mm is allowed).
The condition of the uterine lumen is checked during an ultrasound at 11-14, 20-22, 32-36 weeks.
The external gap is examined by a gynecologist at 20, 28, 32 and 36 weeks. After 36 weeks, the cervix softens. In nulliparous women, the passage into the cervical canal is open by approximately 0.5 cm; in women who have given birth, the opening opens by approximately 1 finger. Full opening is diagnosed after the outer hole reaches a diameter of 10 cm.
Methods for diagnosing the condition of the pharynx
The condition of the internal os of the uterus is determined in three ways:
- External examination by a gynecologist;
- Ultrasound examination;
- Analysis for bacterial culture from the throat of the cervix.
An examination by a specialist allows you to see deviations from the norm in the condition of the cervix. It is carried out on a special gynecological chair under conditions of absolute sterility using disposable instruments.
An ultrasound examination shows the condition of the internal organs, the development of the fetus and the woman’s readiness for childbirth and pregnancy. The expectant mother can see her baby on the monitor and ask a specialist to take a photo of his intrauterine development. This diagnostic method allows you to monitor the general condition of the woman, the course of pregnancy and the parameters of the cervix.
Bacterial culture from the throat of the cervix is taken to identify inflammatory processes. Diagnostics determines the type of infectious agent and its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs. The result obtained helps to prescribe the necessary medications.
Internal os during pregnancy
The cervix is a dynamic organ, it changes throughout the entire monthly cycle in a non-pregnant woman, the cervix opens during ovulation and menstruation, and at the beginning of a new cycle the cervix closes and rises.
If fertilization occurs, first of all, the appearance and location of the cervix changes: it lengthens and acquires a bluish tint due to increased blood circulation, becoming dense and tight.
During the examination, the doctor can accurately determine whether there is a threat of miscarriage; if the cervix is tightly closed, does not allow a finger to pass through, and is also slightly deviated, there is no threat. But if the cervix is partially dilated or loose, hospitalization is necessary to avoid premature birth.
Normally, the length of the cervix changes during the entire period of pregnancy in the following parameters:
- up to 14 weeks pregnancy length is 35-36 mm;
- 10-14 weeks – up to 39 mm;
- 20-24 weeks – 40 mm;
- 25-29 weeks – 42 mm;
- from 30 to 34 weeks it decreases to 37 mm;
- from 35 weeks the length is 29 mm.
A closed internal os of the cervix is important for the correct and safe development of the child, since it:
- promotes retention of the fetus in the uterus until timely birth;
- protects the fetal bladder from infection;
- prevents infection.
During normal functioning of the body, the cervix begins to shorten and expand, and also changes its structure to loose and soft. This allows the fetus to descend in preparation for birth.
If the pregnancy proceeds without complications, the internal os of the cervix should be closed, but there are cases when the os is partially opened, which can cause early miscarriage, infection or premature birth. There may be several reasons why the cervix does not close:
- hormonal changes in the body;
- abortions;
- carrying out conization in the treatment of diseases of the isthmus;
- large fruit, multiple births;
- congenital developmental anomalies.
All this develops isthmic-cervical insufficiency (ICI) - premature expansion of the internal pharynx, due to which the fetus descends into the lower cavity of the uterus, further dilatation and premature birth occur under pressure.
If a pregnant woman experiences symptoms such as heaviness in the lower abdomen; a feeling of fullness in the vagina, heavy discharge, the doctor conducts a gynecological examination using a speculum and prescribes a transvaginal ultrasound, which accurately examines the cervix and determines that the internal os is closed.
How to close the cervix
When the cervix is shortened and partial dilatation is observed, doctors carry out procedures to help close the pharynx. There are several methods to:
- therapeutic;
- conservative;
- surgical.
Medication method
Therapy consists of taking hormonal drugs based on progesterone, which help stabilize the condition and possible closure of the cervical canal.
Such drugs include Duphaston, Utrozhestan.
Two weeks after prescribing the drug, it is necessary to diagnose the cervical canal to determine the effectiveness of this method; if all is well, the drug is prescribed for long-term use.
Source: https://gb8-omsk.ru/prochee/vnutrennij-zev-pri-beremennosti-prichiny-otkrytiya.html
Cervical length indicators by week
Normally, the internal and external os of the uterus are closed until 36-41 weeks of gestation. In this case, the length of the smooth muscle ring gradually shortens, and the opening diameter increases. This facilitates the passage of the fetus along the birth canal at the time of delivery.
Reference: in most cases, changes in the size of the cervical canal occur from the 20th week of gestation, however, a gynecological examination is recommended from the 14th week.
The length of the external and internal pharynx during pregnancy is the norm by week:
- up to the 10th week – 45 mm;
- 16-20 weeks – 40-45 mm;
- 25-27 weeks – 35-40 mm;
- 32-36 weeks – 30-35 mm.
Too short a uterine os between 14 and 24 weeks indicates a high risk of preterm birth:
- up to 10 mm – delivery at 32 weeks of gestation;
- no more than 15 mm – the gestational age of the child will not exceed 33 weeks;
- less than 20 mm – the child will be born at 34 weeks of gestation;
- no more than 25 weeks - the labor process will begin at 36-37 weeks of pregnancy.
Based on the condition of the internal os, you can determine the approximate date of birth of the child, as well as prevent premature birth in the early stages of gestation. 2 weeks before the birth process, the uterus matures almost completely, while the length of the cervix is shortened to 10 mm. Under pressure from the fetus, the pharynx begins to gradually open, which can be easily determined using ultrasound and gynecological examination.
Methods for closing the uterine os
Premature dilation of the cervix is fraught with serious consequences, including spontaneous abortion. To prevent complications, specialists provide medical or surgical treatment.
Conservative therapy
To stabilize the condition of the reproductive organs and close the uterine pharynx, progesterone-based drugs can be used.
They stimulate contraction of smooth muscle fibers, due to which the internal diameter of the cervical canal decreases. You can prevent expansion of the uterine os with the help of a special ring (pessary) that is placed on the cervix. In this way, it is possible to reduce the load on the inside of the cervical canal and the likelihood of its premature opening.
Attention! An obstetric pessary can be used only in the early stages of isthmic-cervical insufficiency (ICI) with minimal opening of the uterine pharynx.
Surgery
In case of severe ICI, it is recommended to resort to surgical treatment, which involves suturing the cervix. The indication for surgical intervention is a real threat of interruption of gestation or premature birth. The operation is performed no later than 27-28 weeks of pregnancy, which is associated with a high risk of damage to the amniotic sac and infection of the placenta.
Important! Suture of the uterus is not used during the period of exacerbation of infection, as well as in case of pathological development of the fetus and placenta previa.
Sources
- https://mama66.ru/pregn/960
- https://www.o-krohe.ru/placenta/polozhenie-po-otnosheniyu-k-vnutrennemy-zevy/
- https://beremennuyu.ru/chto-takoe-zev-pri-beremennosti-normy-zeva-vo-vremya-beremennosti-chto-znachit-kogda-zev-matki-otkryt-i-zakryt
- https://klinika.k31.ru/napravleniya/ginekologija/vnutrenniy-zev-matki/
[collapse]
Throat closure methods
An open mouth can be closed in several ways:
- Therapeutic (medicinal);
- Conservative;
- Surgical.
Therapeutic method
involves taking hormonal drugs based on progesterone, for example, Duphaston, Utrozhestan. The effectiveness of the drugs is checked by diagnosing the cervical canal two weeks after the start of the course. Further use of medications is prescribed if the examination result is positive.
Important! Self-use of medications without consulting a specialist is strictly prohibited! The drug, duration of administration and dose are prescribed only by a doctor.
Conservative method
includes wearing a gynecological ring - a pessary. The item is able to relieve the load from the internal os, which allows you to close the cervix without surgical intervention. This method is allowed to be used at any stage of pregnancy. Most often, wearing a ring is prescribed to women in labor who have multiple pregnancies.
Surgical method
implies suturing the cervix. This method is used when there is a threat of losing a child and other methods are ineffective. The operation is prescribed only in the early stages (no later than 28 weeks). After the procedure, a weekly examination by a gynecologist is necessary to avoid increased uterine tone.
Important! Suturing the uterus is prohibited in case of exacerbation of sexually transmitted infections, pathological development of the fetus and placenta previa.