Last update: 10/07/2019
Many women are faced with a diagnosis of cervical ectopia of the cervix, and almost everyone has the question “What is it?” This is a pseudo-erosion located on the outer part of the cervix.
- Signs, symptoms
- Causes
- Hormonal influence
- Ectopia with cervicitis
- Squamous metaplasia and ectopia
- What is the danger?
- Pregnancy period
- Treatment
- Video about erosion
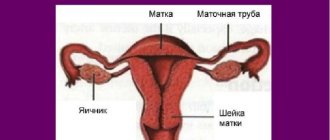
The cervical canal leads into the uterine cavity; it is covered with a layer of columnar epithelium. If this layer extends beyond the channel, it enters an unusual acidic environment, and cells grow that should not be on the outside. Types of ectopia
The disease should not be confused with ordinary erosion. It occurs as a result of infectious pathogens that lead to the destruction of the mucous structure and its inflammation. The inflammatory process is observed for no more than 1-3 weeks.
In cases of disorders not associated with erosion, the mucous membrane is more severely affected, and the stratified epithelium of the cervix is deformed and replaced by cervical cells. Normally, these two layers have a smooth transition. When a disorder appears, the boundaries of their junction are clearly visible, outwardly it is very similar to erosion.
This disease occurs:
- congenital,
- acquired.
Congenital ectopia of the cervix occurs in 11% of all women facing this problem. An acquired disease occurs due to different effects on the body and occurs in different ways:
- with complications
- without complications,
- progressing.
The uncomplicated form does not manifest itself in any way; most do not even suspect that they have this pathology. The complicated form occurs in parallel with other diseases, posing a threat to the entire body. The progression of the disease leads to various complications.
The following disorders are diagnosed based on the type of tissue proliferation:
- Papillary - growth of cylindrical tissue in the form of papillae, each of them has a vascular loop. Glandular – the presence of a large number of inflamed glandular structures.
- Epidermising - on the cylindrical epithelium there are foci of squamous epithelium. This type does not require medical intervention as healing occurs on its own.
Signs, symptoms
With congenital uncomplicated pathology, no symptoms or visible signs are observed. Only a gynecologist can determine it during an examination of the patient. The localization area of the ectopic focus is marked by a noticeable red spot, which comes in different sizes. Only a special study can determine exactly how badly the tissue structure is damaged. Colcoscopy and cytological examination are usually performed.
Constant monitoring by a doctor will help prevent the transition to a difficult stage. If ectopia of the cervix has developed into a complicated or regressive form, accompanying symptoms appear.
If you have the following signs, you should urgently contact a gynecologist:
- Itching, burning.
- Bleeding or bloody mucus after sexual intercourse.
- Copious discharge, clear or white.
- Mild nagging pain (pelvic area).
- Menstrual irregularities.
A complex type of pathology, with the presence of infectious inflammatory processes, leads to purulent vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor. Often a cycle disruption occurs when bleeding is observed on days other than critical ones. They can be dark brown to red in color.
Cervical ectopia of the cervix in an advanced state causes an exacerbation of other gynecological problems. Patients may experience severe pain in the lower abdomen, constant weakness, and increased body temperature. Sometimes discomfort and pain occur when urinating.
After childbirth, the disease sometimes disguises itself as the usual sore throats and leucorrhoea. These discharges are often confused with symptoms of the disease. But during a routine examination, the doctor should notice violations. Hormonal dysfunction is often present. With this course of the disease, problems with reproductive function are observed.
To confirm the diagnosis of cervical ectopia with the above symptoms, a number of examinations are performed.
In addition to cytological and colcoscopic examination, it is recommended to undergo the following tests:
- Diagnosis of vaginal microflora (smear, bacterial culture, PCR).
- Study of hormonal status.
- Biopsy.
These tests help to accurately determine the type of disease and the presence of concomitant infectious inflammatory processes.
Prevention
Uterine disease is easier to prevent than to treat. To do this you need:
- undergo an examination once a year;
- treat concomitant pathologies;
- use contraceptives;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- strengthen the immune system.
Women with cervical erosion are advised to undergo an annual examination. This measure helps prevent the development of cancer.
Causes
It is difficult to establish a specific cause in each individual case, since there are many of them. The congenital appearance is almost always hereditary in nature and is a physical feature.
In childhood or adolescence, when the female parts of the body are not yet fully formed, the presence of tissue of the cervical canal outside of it is due to a lack of estrogen, when the formation of the female reproductive system occurs. After the ovaries fully mature and the hormonal levels normalize, the boundary of this layer moves into place, and everything quickly returns to normal. Therefore, if the diagnosis is made to a child or teenager, there is no need to panic; the congenital type heals spontaneously.
An acquired disease occurs due to negative factors: Mechanical impact on the reproductive organ, its trauma (abortion, childbirth, contact with male genitalia).
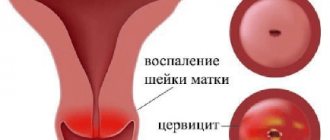
Ectopia with cervicitis
Cervicitis is a lesion of the cervical canal due to inflammation caused by an infection that has gotten inside. The patient’s health is deteriorating, but she can attribute everything to a cold and not seek medical help. As a result, a chronic type appears that can regress. The inflammatory process in the canal leads to hypertrophy of the mucosa, the inner layer grows and comes out. Cervical ectopia of the cervix with chronic cervicitis occurs.
The disease with cervicitis is accompanied by the same symptoms as with the usual degree. The discharge intensifies, and during menstruation, an exacerbation occurs, atypical pain in the abdomen appears, and the general condition deteriorates greatly. Intimate relationships also become painful. Sexual contact can provoke ruptures of the vessels of the cylindrical layer, and mucus and blood appear.
Appears for the following reasons:
- Infections caused by bacteria that are sexually transmitted.
- Viral infections, the most dangerous of which is papilloma.
- Inflammation of the vagina or external genital parts of the body.
- Urinary tract infections.
The combination of these two pathologies can lead to inflammation of the genital organs and subsequent infertility. Therefore, they require timely elimination.
What is a disease
Squamous metaplasia of the cervix occurs in patients of climatic age, usually after 50 years. If squamous cell metaplasia of the cervix is diagnosed, what is it and how can the pathology be explained to a woman in simple language? The disease is a precancerous condition. In the absence of proper treatment, an oncological malignant tumor develops. In general, metaplasia is a pathological process in which the glandular epithelium that normally covers the cervix is replaced by flat epithelium.
To make it clear what is happening inside, it must be said that the internal organs of a woman, more precisely, the uterus and its appendages, have a clear alternation of epithelium:
- closer to the vaginal canal there is flat stratified epithelium;
- the intermediate zone between the cervix and the vaginal canal is characterized by a complete absence of epithelium;
- columnar epithelium lines the uterine cavity and the cervical canal.
Normally, these types of epithelium do not shift at all; there is a clear boundary between them.
Metaplasia often develops in places where there is erosion, infectious lesions, inflammatory processes and other chronic diseases. Metaplasia, which is complicated by keratinization of cells, is especially dangerous for women if it develops in the cervical canal and the glandular epithelium is replaced by cylindrical epithelium.
In such cases, treatment should be carried out immediately to avoid dysplasia and tumor formation. In the initial stages, there is no need to treat metaplasia; the doctor simply monitors the course of the disease. If there are changes for the worse, drug therapy is started.
Squamous metaplasia and ectopia
Squamous metaplasia is a harmless process in which multilayered cells replace or cover cylindrical ones. Replacement occurs outside or in the canal itself.
Cervical ectopia with squamous metaplasia is a benign change in the tissue structure in the focal area. The course of this pathology depends on the environment in the vagina, hormonal levels, the presence of infections and other factors affecting the female genital organs. It occurs without symptoms and does not manifest itself until negative factors lead to concomitant inflammatory processes.
How is this pathology classified?
Based on the clinical form, this pathology is divided into:
- complicated;
- uncomplicated.
Complications include colpitis and cervicitis caused by infection. However, in many cases, uncomplicated pathology occurs, according to which, in the colposcopic nomenclature adopted today, this form of pathology is regarded as a normal physiological state.
Important! Over time, the ectopia heals with the replacement of the cylindrical epithelium on the cervix with multilayered squamous cells (with the help of germ cells). This phenomenon is called squamous metaplasia, and it is against this background that the development of malignant neoplasms in the organ significantly increases.
According to histological type, the following forms are distinguished:
- glandular (distinguished by the accumulation of glandular structures and inflammatory signs);
- papillary (characterized by the appearance of papillary growths, which are covered by cylindrical epithelium);
- pseudo-erosion, with the onset of squamous metaplasia.
What is the danger?
Congenital pathology itself or in an uncomplicated state does not pose a danger, but requires constant medical supervision. An acquired disease is almost always accompanied by other problems and requires intervention.
It has not been precisely proven that this disorder of the reproductive system leads to cancer. There is a risk that the presence of a cell transformation zone will lead to neoplasms that can develop into malignant ones. But this does not mean that the problem is related to a precancerous condition, since its initial benignity has been proven.
At the same time, it provokes a sluggish inflammatory process, which over time will lead to serious damage to the female reproductive system. Later, atypical growths will appear, which easily degenerate into malignant ones. Proper therapy effectively eliminates everything.
Pregnancy period
During gestation, hormonal surges occur, leading to various changes in the body. If the epithelial lesions are significant, there is a risk of fetal infection. The doctor must first identify the causes. If this is a hormonal imbalance, then in most cases observation throughout pregnancy is sufficient.
In the presence of infectious inflammation, certain medications may be prescribed. But they are used only in exceptional cases, when bacteria are detected in the outbreak area. If the zone does not grow and is not accompanied by inflammation, regular examinations in each trimester are sufficient. However, it does not pose any danger to the fetus. After childbirth and lactation, it goes away.
Diagnosis of the disease
A doctor can diagnose ectopia during a gynecological examination. In the case of a congenital form of the disease, the diagnosis is made at the first visit to the gynecologist. With the acquired form of ectopia of the columnar epithelium, the doctor may note the formation of a small area of various shapes, bright red color, and when pressure is applied to it, blood appears. In this case, an additional examination is carried out using a colposcope.
Mandatory tests are:
- Schiller's test;
- taking a smear for bacteriological culture;
- PCR diagnostics of discharge and cervical smear, including the HPV spectrum;
- PAP test or cytological analysis of a smear from the vagina and cervix.
Without fail, the doctor takes a scraping for cytology to identify a possible atypical or inflammatory process, as well as to identify squamous and columnar epithelial cells.
If, after a series of studies, an abnormal development process or ectopia is diagnosed, then a biopsy is taken from the patient from the affected area on the neck for subsequent examination by specialists in the histological laboratory.
At the same time, the doctor may prescribe a blood test to check the level of sex hormones in the body; if their levels are elevated, a consultation with a gynecologist-endocrinologist is required.
Treatment
A competent approach quickly eliminates everything and does not lead to relapse. There are many methods for getting rid of pathology. But before eliminating it, it is important to get rid of inflammation and undergo antibacterial therapy. Only in the absence of inflammatory processes can treatment begin.
The most common methods:
- Laser removal.
- Radio wave therapy.
- Diathermocoagulation.
- Cryodestruction.
Laser therapy is a modern, safe method. It leaves no scars. The lesion is eliminated with a laser beam inserted into the vagina. This method allows you to very accurately remove only atypical cells without damaging healthy tissue. The effectiveness of laser therapy is high.
Manipulation of radio waves is more expensive than other methods and requires the presence of good specialists. With this method, a passive electrode is placed under the patient’s buttocks, and another, with a tip, is inserted into the vagina. Next, the tissue is treated with radio waves, which lead to the evaporation of the top layer. There are no scars after the procedure.
One of the most popular is the method of diathermocoagulation. This is the usual cauterization of the lesion with special electrodes. In place of the destroyed layer, a scab appears, which is later replaced by a normal structure. The method is effective, but is only suitable for those who have given birth. This is due to the fact that after treatment a scar remains, which will interfere with the desire to conceive a child. Another disadvantage is noticeable pain, which can be avoided by administering local anesthesia.
Cryodestruction - freezing using a special probe and nitrogen. Leaves smaller scars and does not require anesthesia. Applicable if the lesion area is no larger than the probe tip. It is performed in several stages, alternating between freezing and thawing. Efficiency is 10% less when compared with other methods.
After treatment, sexual intercourse, heavy physical activity, and the use of tampons and douching are prohibited for a month. In almost all cases, with competent and timely intervention, the disease disappears forever.
Clinical picture and diagnosis
It is known that symptoms are not characteristic of erosive defects in the absence of other diseases. If we talk about pseudo-erosion, in 80% of cases women observe symptoms that are a consequence of concomitant diseases:
- leucorrhoea;
- cycle disorders;
- bleeding;
- pain.
If the stain is uncomplicated, mucous discharge can be noted, since glands that produce secretions function on the surface. Contact discharge indicates extensive damage to the cervix. Sometimes a vaginal smear shows an increase in the level of white blood cells, which is not associated with infection.
The defect is detected during an examination of the cervix by a gynecologist. The doctor can judge the type of spot by the appearance of the spot. For example, displacement of the transformation zone occurs only with congenital ectopia. To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo an examination.
- In a simple colposcopy, the doctor examines the lining of the cervix under a microscope. During the extended procedure, the cervix is treated with special solutions. Based on the resulting colposcopic picture, pathology can be assumed. If there is a suspicion of precancer or malignant tumor, a biopsy is necessary.
- A biopsy involves taking a small piece of tissue for subsequent histological diagnosis in the laboratory. The procedure can be recommended for nulliparous women, but it is not recommended during pregnancy.
- Smears for flora, oncocytology, bacterial culture and genital infections using the PCR method allow you to identify atypical cells, inflammation and pathogenic microflora.
The scope of diagnostic and treatment methods, for example, for nulliparous girls, is determined by the doctor. First of all, he is guided by the clinical picture and anamnesis.