Ways to eliminate erosion
As a radical method of treatment, moderately painless, safe cauterization of cervical erosion is performed, which is divided into types:
- Exposure to liquid nitrogen promotes freezing of liquid in cells damaged by erosion. It does not form scars on the epithelium; rehabilitation after cauterization of the cervix with nitrogen occurs within 2 months.
- Laser removal is the most popular and painless solution to the problem. It consists of direct exposure to the affected areas with a laser. The procedure does not leave any tissue damage.
- Electric current is a highly effective method in the fight against disease. After cauterization, the healing process of the epithelium occurs after 60 days. This method is excluded for nulliparous women, as it may have a negative impact during childbirth due to scars on the tissues left from exposure to current.
- The chemical cauterization method helps to detach damaged cells. This method is considered safe at any age, healing begins after 2 procedures.
The entire process after cauterization is carefully monitored by the attending physician using a gynecological examination. How quickly the tissues of the mucous membrane heal directly depends on the area affected by erosion, and on the woman herself and her lifestyle.
Cervical erosion: should it be treated before pregnancy?
Various sources of information about cervical erosion provide conflicting information: some scare that it will turn into cancer and insist on treatment, others claim that it will “resolve on its own” and nothing needs to be done. It is clear that such a discrepancy does not inspire optimism, but it did not arise by chance. There are very clear reasons for such diametrically opposed opinions. They are connected with the term “erosion” itself. Let’s make a reservation right away: the term “erosion” can only be used at the initial stage of the examination. Underneath it lies many (more than twenty) diseases with completely different treatment tactics. Having heard such a doctor’s verdict, it is important to understand only one thing: an examination is necessary until this term is replaced by others that reflect the true picture of the disease.
What is cervical erosion?
To better understand this issue, you first need to take a short excursion into anatomy. The uterus has a cavity that communicates with the external environment through the cervical canal (cervical canal), the main functions of which are protection against infections and ensuring that sperm enter the uterine cavity precisely during the period of ovulation, i.e. when the egg is released from the ovary and conception becomes possible. The cervical canal is 3–4 cm long.
It opens with an external opening (throat) into the vagina, and an internal opening into the uterine cavity.
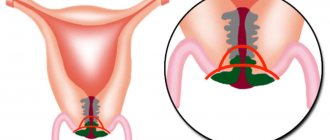
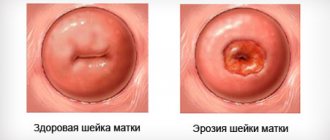
Its inner layer (cylindrical epithelium) produces mucus. It is formed by just one row of cells tightly adjacent to each other and has a bright red color due to the close arrangement of blood vessels. On the vaginal side, the cervix is covered with stratified squamous epithelium of a pale pink color. So, sometimes the junction of the columnar epithelium of the cervical canal and the multilayered epithelium is displaced, and it can be seen from the outside on the cervix. During a routine gynecological examination “in the speculum,” the only thing that the doctor can see is a red area around the opening of the cervical canal, which is perceived as a tissue defect or erosion (from the Latin “erosio” - corrosion, destruction). The area of redness may be small or spread over the entire surface of the cervix. What is hidden under “erosion”? True cervical erosion , i.e. mucosal injury is rare. Its appearance is associated with mechanical impact (for example, during extreme sexual intercourse). Without treatment, such damage can heal on its own within a month or develop into pseudo-erosion (see below). Some infections, such as herpes and trichomoniasis, can also cause true mucosal damage. During pregnancy planning, true erosion requires further examination for infections and observation until healing.
Congenital ectopia
The term “ ectopia ” (from the Greek ektopos - displaced) means the appearance of any tissues in unusual places.
In the case of the cervix, the junction of the squamous and columnar epithelium shifts to the outer surface of the cervix. This condition can normally be observed during adolescence, pregnancy, and the use of hormonal contraceptives. Menstrual irregularities due to hormonal problems can contribute to the appearance of ectopia. Ectopia is detected by chance, during a routine examination, does not bother the woman in any way and is not a precancerous condition. It can go away on its own or transform into pseudo-erosion. During pregnancy planning, no action needs to be taken, you just need to monitor her condition.
Ectropion is an ectopia that occurs as a result of trauma to the cervix during childbirth, abortion, and various gynecological interventions. The term means turning inside out and reflects the mechanism of occurrence of this defect. Cervicitis is inflammation of the cervix. Various sexually transmitted infections, such as chlamydia, myco- and ureaplasma, trichomonas, viruses (primarily papillomavirus and herpes), vaginal dysbiosis (colpitis, bacterial vaginosis and thrush) lead to the development of inflammation in the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix, causing it to turn red, which can also look like erosion. When planning a pregnancy in such cases, you will definitely have to undergo treatment to get rid of the infection that caused cervicitis.
Pseudo-erosion
Pseudo-erosion is the most common condition.
Since the vaginal cavity has a different environment than the cervical canal, the area of ectopia is damaged and becomes inflamed when an infection occurs. In response to this effect, epithelial cells rapidly divide, trying to close the resulting wound surface. Actively dividing cells can turn into both columnar and squamous epithelial cells. The area of such cell transformation is called the “transformation zone”. While it is active, there is an increased risk of the appearance of atypical cells, i.e. development of cervical cancer. But in 99.9% of cases, the transformation does not lead to the appearance of atypical changes and ends with the formation of multilayered squamous epithelium. Therefore, uncomplicated pseudo-erosion , like ectopia, requires observation and treatment of concomitant gynecological diseases (infections, cycle disorders, etc.). Problems begin when proper transformation is disrupted by other factors, primarily the addition of the human papillomavirus (HPV). The insidiousness of human papillomavirus infection lies in the fact that it does not manifest itself in any way and the existence of the virus in the body can only be determined through tests. At the same time, it can cause dysplasia (atypical changes in the epithelium) and cancer of the cervix and rectum.
Based on this criterion, all HPVs are divided into types of low, medium and high oncogenic risk. HPV types 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59 and 68 are high-risk varieties. Changes in the cervix, characteristic of the human papillomavirus, always alert the doctor, because women who have this virus for a long time have a 65 times greater risk of developing cervical cancer than those who do not have it. However, the presence of a high-risk virus in the body does not mean that a woman will necessarily develop cancer. Additional factors must be present for cells to become malignant.
But the fact of detection of HPV of high oncogenic risk against the background of existing pseudo-erosion of the cervix is a reason for active treatment before pregnancy. This can be either conservative therapy or surgical removal of lesions. What the treatment will be is determined individually. Unfortunately, in very rare cases, cervical cancer can be hidden under the guise of “erosion”. Therefore, a woman planning a pregnancy, regardless of the nature of the “erosion,” must be thoroughly examined before conception.
Cervical cancer can be aggressive while expecting a baby and often requires termination of pregnancy with removal of the uterus. If cancer is detected in a timely manner at an early stage, a 100% cure is possible using technologies that make it possible in the future to become pregnant, carry and give birth to a healthy baby.
Diagnosis of cervical erosion
Any diseases of the cervix may not manifest themselves for a long time. In some cases, women complain of discharge, pain during sexual intercourse and slight spotting after it. If, when examining a woman on a gynecological chair, the doctor detects redness (spots) on the cervix, then the following examinations will need to be carried out:
- Colposcopy is an examination of the vaginal part of the cervix using a special microscope - a “colposcope”, which allows you to identify the nature of the lesion in the cervix and, if necessary, take an analysis or biopsy. The procedure is carried out in the same way as a regular examination on a gynecological chair. A special speculum is placed in the vagina, and the doctor examines the cervix under a directed light mounted on a colposcope. The procedure does not take much time - it lasts only 10–20 minutes. There is no need for special preparation for colposcopy; before the procedure, you should abstain from sex, the use of vaginal medications, tampons, and douching for 1–2 days. This test is not done during menstruation.
- Cytological examination or PAP test. During a cytological examination, the structural features of the cells of the surface and canal of the cervix are studied under a microscope, as a result the cytologist makes a conclusion about the presence or absence of inflammation or atypical changes, i.e. dysplasia. A smear for this study is taken with a special instrument - a spatula or brush during an examination on a gynecological chair or colposcopy.
- Flora smear. Using this method, you can identify the inflammatory process (by the number of leukocytes), detect some types of infection (fungal, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, bacterial vaginosis). If there are changes in the cervix, be sure to perform a test for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) - chlamydia, myco- and ureaplasma, herpes virus, HPV, the detection of which requires special research methods. Tests for STIs are taken from the cervical and urethral canal. These infections must be treated, since any of them worsens the course of cervical diseases and can lead to infection of the fetus, as well as placental insufficiency and oxygen starvation of the fetus.
- A cervical biopsy is a procedure in which a small piece of tissue is removed from the cervix to be tested for dysplasia or cancer. A biopsy is considered a minor surgical operation, so before it is performed it is necessary to undergo general tests and a smear for flora. And in order to reduce discomfort during the procedure, local anesthesia is first given before it.
Cervical erosion and pregnancy
Most often, with erosion, pregnancy proceeds normally and healthy children are born. However, there are still certain nuances: Pregnancy aggravates the degree of dysplasia, worsening the course of the disease. Cervical erosion is a favorable background for the development of infection. The wound surface becomes infected, the aggressive environment that forms during inflammation can “melt” the lower part of the amniotic sac and lead to the rupture of amniotic fluid, which means miscarriage or premature birth. Cervical erosion is one of the causes of isthmic-cervical insufficiency, in which the cervical canal opens slightly and can no longer perform its “obturator” function, keeping the fetus inside the uterus and preventing premature termination of pregnancy. During childbirth, the eroded cervix stretches less easily and ruptures more easily, which increases the likelihood of bleeding and stitches after childbirth. For pregnant women with erosion, doctors often prescribe preventive treatment to prevent the exacerbation of the disease, while the choice of drugs that can be used during pregnancy is very limited. If erosion is accompanied by inflammatory processes, antiviral drugs or antibiotics are prescribed. It becomes clear that in order to avoid such problems during pregnancy, you need to be treated before conception.
Treatment of cervical erosion
There is an opinion that nulliparous girls and women for cervical erosion .
This is not entirely true. Treatment tactics, as we have already said, depend on the diagnosis hidden under the guise of “erosion”. In young nulliparous women, cervical ectopia and pseudo-erosion without inflammation really only require observation. Any inflammation of the cervix must be treated with antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory drugs. Dysplasia most often requires surgical removal or the use of special “destructive” methods – “cauterization”. The classic method is diathermocoagulation: an electric current that, in contact with tissue, leads to a burn. This method of treating erosion is still used, but if a woman is planning a pregnancy in the near future, it is not the best choice. The fact is that due to deep damage to the tissue of the cervix and its deformation, problems with bearing the baby and during childbirth are possible in the future. Now there are many modern methods that do not lead to the appearance of rough scars that prevent the dilation of the cervix during childbirth.
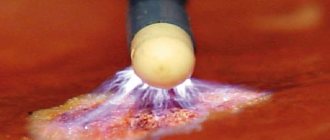
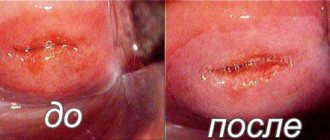
This includes laser coagulation (removal using a targeted low-intensity laser beam), cryodestruction (the erosion site is frozen with liquid nitrogen), and chemical coagulation (treatment of the cervix with special preparations that remove irregular epithelium). During these procedures, the squamous epithelium does not suffer and quickly covers the area of erosion. The most gentle and modern method of treatment is radio wave. The influencing factor is a radio wave. “Unnecessary” cells are not cauterized, but simply evaporate, so side effects are minimal. In case of severe extensive lesions, removal of part of the cervix surgically or using an electric or radio knife (conization) can be used. But after conization, pregnancy is often accompanied by the threat of termination, and childbirth is carried out by caesarean section. Having carried out timely treatment of cervical erosion at the stage of preparation for pregnancy, a woman has every chance to safely carry and give birth to a healthy baby.
General recommendations after cauterization
The recovery period after the cauterization procedure is approximately 2 months. The main task for a woman when asked: what to do after cauterization of cervical erosion is to exclude possible bleeding from poorly healed wounds.
Therefore, no matter how the specialists eliminate the problem, every patient should know what is not allowed after cauterization of cervical erosion:
- First of all, you need to protect yourself from physical activity and heavy lifting.
- For a month (ideally, the attending physician will tell you the period for resuming sexual activity), it is recommended to exclude sex, even with a regular partner.
- In order not to provoke bleeding, it is forbidden to take a hot bath (this also includes visiting swimming pools, saunas, baths). A moderately warm shower is best for maintaining personal hygiene.
- The use of tampons damages the vaginal microflora, so their use should be avoided for 2 months.
- Do not engage in active sports. Only after a month, the doctor may allow light gymnastics or yoga.
The recommendations should be followed until complete recovery, which will be confirmed by a specialist at the next examination.
Contraindications
In the treatment of cervical diseases, laser coagulation is the most effective high-tech method. It allows you to safely get rid of formations, eliminating serious consequences. But like any laser therapy, it has its contraindications, these are:
- acute inflammation of the genitourinary system;
- postpartum period;
- pregnancy;
- genital infection;
- malignant formations;
- growth of erosion to the length of 2/3 of the cervical canal;
- frequent bleeding.
Any remaining damage after the procedure heals very quickly. This method does not cause the formation of scars and crusts on wounds.
IMPORTANT: restoration of the vaginal lining lasts from 1 to 3 months, so start planning your pregnancy no earlier than this period.
Recommendations after electrical, nitrogen and chemical cauterization methods
After performing procedures using similar methods, most women experience aching pain in the lower abdomen. To eliminate it, doctors recommend taking painkillers: Spazmalgon, No-shpa.
During the regeneration process, dead tissue will come out, spotting bloody discharge, and over time, the shade of the discharge will become lighter. Ideally, such discharge stops after two weeks. Therefore, it is important to carefully observe hygiene of the intimate area to prevent infections from entering unhealed wounds.
Examination of a woman
Most women have a negative attitude towards the examination procedure. Metal speculums are inserted into the vagina for examination. They are cold, so the muscles narrow and the instrument enters tightly. Then it is better to use plastic mirrors. A light is then directed to the cervix and examined. If redness or uneven color is detected, the doctor performs a colposcopy and takes smears for the flora.
To make an accurate diagnosis, you need to undergo cytological and histological examinations. To check for malignancy, a small piece is cut off from the damaged area. Next, after receiving the biopsy result, the doctor will prescribe the correct treatment. First you need to take a smear. When infections are detected, they are treated, and then the erosion itself. It happens that after the infection is cured, the problem disappears on its own.
Recommendations after laser cauterization
Laser removal of erosion, although considered an effective method that leaves behind minor wounds, is still advisable, for a better healing process, to use medications: Depanthol, Methyluracil.
Folk remedies have a positive effect on the recovery process. For daily washing, you can use herbal infusions. Flowers (dry or fresh) of medicinal chamomile and calendula are best suited. For 1 tbsp. l. half a liter of boiled water is added to the herbs and infused for half an hour.
In emergency cases, the use of tampons with medicinal herbs is allowed.
In addition to the main treatment after cauterization of cervical erosion, it is worth paying attention to the general condition of the body. It is recommended to strengthen the immune system with the help of fortified preparations.
Symptoms of erosion and preparation for treatment
Usually the disease is asymptomatic. The woman is not worried about anything. The disease can be detected during a gynecological examination.
However, excessive discharge of a pathological nature may be a cause for concern. Normal vaginal discharge is present in small quantities and does not have an unpleasant odor. They are transparent or whitish. In cases of an increase in the amount of discharge, a change in color, or the appearance of an unpleasant odor, you should consult a doctor.
At the appointment, the gynecologist performs an examination on the chair. Before doctors learned to use colposcopy to examine the cervix, the diagnosis of “erosion” was very vague. It meant the presence of slight redness on the mucous surface. Colposcopy allows you to examine the female genital organs under a special medical microscope. If necessary, an extended colposcopy is performed. Then, before the examination, the cervix is treated with a special solution, which allows visual detection of pathology. If the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor chooses the appropriate treatment.
Treatment after cauterization
As mentioned earlier, healing after cauterization, on average, occurs after 2 months.
For faster recovery of the body, it is recommended to take biological supplements and use vaginal suppositories. Especially the use of anti-inflammatory suppositories after cauterization of cervical erosion has a positive effect on the woman’s body. Thanks to the active substances included in the vaginal suppositories, the drug promotes rapid healing after the cauterization procedure. The epithelial layer is intensively restored, and the metabolic process in the body is accelerated.
Also, as an anti-inflammatory, antiviral drug, experts prescribe Epigen spray, which helps accelerate regeneration and relieves itching.
During rehabilitation, some patients may be diagnosed with diseases: bacterial vaginosis, mycoplasmosis. In this case, the doctor will prescribe a course of antibiotics.
It is worth remembering that only a specialist has the right to prescribe any treatment after cauterization of cervical erosion. All medications have a number of contraindications for use, which means self-medication can lead to unpleasant consequences.
When is cauterization prescribed?
This method of surgical intervention is used when the pathology is in an advanced form. Cauterization is also used if the patient does not respond to conservative treatment and cases of re-inflammation constantly occur.
In addition, surgery is performed in cases where the area of spread is large enough and simple therapy does not help in this situation.
Are women interested in when erosion is cauterized? A doctor can prescribe this procedure only if there is no doubt that the tumors on the cervix are not malignant.
In addition, cauterization is performed only when the infection does not spread to the internal canal of the organ.
Cauterization of erosion
Consequences after cauterization
The more common consequences of cauterization are aching pain, discharge and swelling of the vulva.
Pain in the abdominal area is considered normal and usually goes away quickly.
Minor liquid discharge is also a natural stage, due to the process of rejection of destroyed tissue. A cause for concern should be heavy discharge, possibly due to damage to the blood vessels of the cervix. In this situation, the doctor prescribes hemostatic drugs.
The detection of greenish or yellow discharge, accompanied by an unpleasant odor, after cauterization indicates the development of inflammation. Therefore, you should immediately seek help from a specialist.
Doctors may highlight unpleasant consequences associated with scars formed after cauterization, which can negatively affect the pregnancy (premature birth, termination of pregnancy).
Despite a fairly large list of prohibitions and consequences after cauterization, it is impossible to refuse treatment for erosion. Treating the disease at home will only worsen the situation. Therefore, the right decision would be to contact a specialist who will prescribe the proper method to eliminate the problem. And strictly following the recommendations after cauterization of cervical erosion will help speed up the stages of recovery.
Biopsy
To find out whether the erosion is benign or not, a biopsy is done. This is a procedure that is performed 5-7 days after the menstrual cycle, after menstruation has ended. Before it starts, swabs are taken to make sure there are no infections. A biopsy is a procedure in which tissue is removed to look for precancerous cells. Although a biopsy is considered surgery, it is not something to be afraid of. This happens almost painlessly and quickly. When performing a biopsy, anesthesia is not used, unless the doctor may treat the cervix with lidocaine. At the doctor’s command, a breath is taken, and at this moment, material is taken for analysis using a radio knife. During the process, the patient only experiences a tingling sensation. After the biopsy, you must adhere to the following rules:
- abstain from sexual activity for two weeks;
- it is necessary to do douching daily;
- exclude physical activity.
Disease prevention
It is better to prevent a disease than to treat it later. This is why it is so important for your health to follow the rules of prevention:
- Firstly, it is necessary to observe the rules of personal hygiene. Daily water procedures, clean linen. During your menstrual cycle, it is a good idea to shower not only in the evening, but also in the morning.
- Secondly, you should lead a correct lifestyle. Indiscriminate change of partners has a bad effect on the health of the female genital organs. The microflora of the vagina undergoes constant changes. The risk of acquiring a sexually transmitted disease increases significantly.
- Thirdly, contraception. If conception is not planned, you need to think about it in advance. Abortion has an extremely negative impact on a woman's health. The cervix is grossly injured. The chance of acquiring erosion increases several times.
- Fourthly, visiting a gynecologist should occur at least twice a year. The earlier the disease is detected, the easier it is to cure it.
How long does it take to treat: recovery time
The duration of the procedure is from 7 minutes (laser vaporization) to several hours (complex cases of cauterization and surgical removal).
Recovery time:
- with diathermocoagulation – 9-10 weeks;
- cryodestruction – 7-9 weeks;
- laser vaporization – 6-7 weeks;
- chemical cauterization – 7-9 weeks;
- Cauterization with radio waves – 4-6 weeks.
After cauterization, suppositories are usually prescribed for ectopia. Doctors recommend abstaining from sexual activity for a month after the procedure.
It is necessary to follow all doctor's recommendations. If you pay insufficient attention to your health, complications and relapses are possible.
Although erosion can be a warning sign of cervical cancer, it can be successfully treated. Remember that any disease is easier to treat in the early stages. Visit your gynecologist regularly, without delaying “for later” if you have complaints. Your health is in your hands!