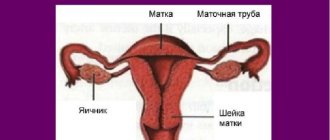
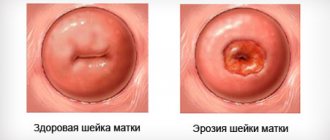
Argon plasma coagulation of the cervix
Argon plasma coagulation of the cervix is practiced by gynecologists in the treatment of many diseases of the female reproductive system, such as erosion or dysplasia, lycoplasia, and is also shown as an effective means for stopping uterine bleeding. Also, using this method, you can successfully remove papillomas and condylomas from the walls of the maca and vagina.
Cauterization of cervical erosion with argon
Pregnancy
Cauterization of cervical erosion with argon does not have any negative effect on the distensibility of the cervix. Therefore, the intervention not only does not in any way reduce the ability to get pregnant, but also does not complicate the birth process.
You can begin sexual activity one and a half months after the intervention. And planning a pregnancy is already in 3-4 months. This is general information. But a more precise favorable period for conception can be determined by a doctor individually.
The cost of the intervention can vary significantly depending on the region.
The meaning of the procedure: should it be done when planning a pregnancy?
When planning a pregnancy, every woman should undergo an examination and, if a particular disease is detected, undergo a course of treatment. In some cases, for nulliparous women, doctors recommend this particular treatment method to combat erosion or to remove a polyp, to prevent the formation of scars.
After it, as noted earlier, there are no scars left, the recovery period is fast - you can plan a pregnancy in 1-2 months. The presented procedure, without leaving scars, will ensure good stretching of the walls of the uterus during pregnancy and childbirth.
Factors of occurrence and symptoms
The reasons for the formation of a defect are quite diverse, which causes the appearance of a specific type of erosion. In reality, erosion can occur at any age. An erosive spot is diagnosed in both young girls and older women.
The most common causes of erosion include:
- onset of sexual activity in adolescence;
- infections that may be caused by having multiple partners or ignoring barrier contraception;
- use of chemical spermicides;
- injuries of the cervical epithelium during abortion, childbirth, curettage;
- hormonal changes.
Indications and contraindications
The treatment method using argon plasma coagulation is used for the following indications:
1. Neoplasms of epithelial origin - papillomas or condylomas. 2. Myomas and leukoplakia. 3. Diagnosis of pseudo-erosion and ectopia. 4. The course of cervicitis, which is not amenable to drug therapy. 5. For various mechanical and chemical damage.
Through this medical procedure, doctors remove benign, pathological tumors, most often localized in the vulva, genitals or anus.
Regarding existing contraindications, the procedure is not performed if:
1. Acute inflammatory process, pathology of a systemic nature. 2. For bleeding of unclear theology and poor blood clotting. 3. When diagnosing cancer of the female genitourinary system.
Video
The Internet is full of various content about what argon plasma coagulation is during cesarean section; videos that can be found and viewed usually last no more than three minutes and provide a brief informative summary of the procedure, taking into account all the indications and contraindications. A specialist from the Mediton clinic talks about the colossal effect of argon plasma ablation, focusing the attention of the audience on the fact that its use is the most minimally invasive method of intervention that exists today. An interested viewer and future patient, after watching the video, will also be able to familiarize themselves with the design of the argon-containing device with which the surgical intervention will be performed.
Preparation
Before the procedure, the woman undergoes an examination on a gynecological chair, and also undergoes a series of laboratory and instrumental examinations:
- colposcopy.
- testing for STDs, smear for vaginal microflora.
- PCR for the presence of chlamydia and ureaplasmosis.
- examination for the presence of HPV cancer stamps.
- General analysis of urine and blood.
- taking an HIV test.
- Ultrasound.
Afterwards, the procedure itself is carried out from the 5th to the 11th day of the menstrual cycle.
Stages
The intervention is carried out in three stages. They cannot be neglected. This includes preparation, the actual manipulation and the recovery period. The success of the intervention depends on the thoroughness of their implementation.
Preparation
Cauterization of erosion with argon requires the same preparation as any other type of coagulation. It is necessary that the intervention be carried out on days 5-7 of the cycle, because this way healing will occur faster. Before performing the manipulation, you need to make sure that there is no inflammation, fungi, or viruses. To do this, a number of analyzes are carried out:
- Smear;
- Cytology;
- Biopsy;
- Analysis for sexually transmitted infections;
- Colposcopic examination.
Proper and comprehensive preparation is necessary to determine the scope of intervention. And also in order to promptly identify contraindications to intervention in the patient. In addition, the need to promptly diagnose and treat inflammation, the presence of which can lead to a risk of infection during coagulation, plays a significant role.
Soreness
The procedure is completely painless. There is no direct contact of the epithelium with the equipment, therefore the discomfort during the intervention is minimal. Moreover, there are very few nerve endings in the cervix. But at the patient’s request, the doctor can administer local anesthesia, which is applied externally.
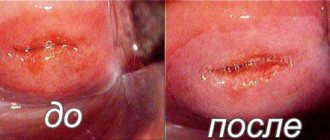
Scab (white area)
Duration
The duration of the intervention depends on the size of the erosion. In some cases, one sensor installation is sufficient, in others – several. Treatment of one zone to which the waves are directed takes 7-12 minutes. Together with installing the colposcope, setting up the equipment, etc., the entire procedure takes from 20 minutes to half an hour.
Technique
The intervention is carried out as follows:
- The patient is located in a gynecological chair;
- A neutral electrode is placed under her buttocks;
- An extended colposcopy is performed;
- The sensor is inserted into the vagina so that its working surface is half a centimeter away from the affected area;
- Using pedals, the doctor activates the device, setting the desired treatment depth;
- A torch of argon plasma appears;
- After the required time of exposure to the area, the torch coagulates it, and the area acquires a sandy tint.
Carrying out the procedure
The patient is placed in a gynecological chair, which already has a special neutral electrode - the cervix is treated with an antiseptic, and then the treatment procedure itself is carried out. The main thing at this moment for a woman is to relax the vaginal muscles and not tense.
During the procedure, the woman does not feel severe pain - a slight tingling and nagging pain in the lower abdomen, as during menstrual flow. The procedure takes from 2 to 8 minutes, depending on the area of treatment of the affected area. Upon completion, the woman should lie down in a chair for a while, relax and calm down.
Pregnancy after laparoscopy: is it true that the procedure increases the chances of conceiving a child?
Can echohysterosalpingoscopy reveal the cause of female infertility: read more.
Hysterosalphingography (HSG) or checking the patency of the fallopian tubes - we identify the cause of infertility:
Argon plasma coagulation
The most common method of tissue dissection and coagulation is electrosurgical. Other methods of dissection and hemostasis during endovideosurgical operations are rarely used, leaving electrocoagulation dominant [1].
At the turn of the 20th century, the first works appeared that showed the use of high-frequency electric current to destroy biological tissues. Back in 1890, A. d'Arsonval showed that alternating current passing through the human body causes a thermal effect, but there are no neuromuscular reactions [2].
Electrocoagulation was introduced as a treatment method by Doyen as early as 1909. In Russia, V.N. became a pioneer in the field of electrosurgery. Shamov, who a little later (in 1910-1911) used high-frequency currents in the treatment of malignant tumors in the clinic at the Military Medical Academy [3,4].
The next stage in the development of electrosurgery was the creation of a high-frequency current generation unit, which received mass production thanks to G. Cushint and V. Bovy in 1926 [3,4].
It is possible to cause tissue destruction by creating cellular heat when an electrical impulse passes through the cell. Tissue proteins coagulate when heated to 43 °C, but their destruction is reversible. Vaporization of intercellular and boiling of tissue fluids occurs at a temperature of 55-70 °C; changes in the structure sought in this case are based on cellular micro-ruptures. Complete denaturation of the protein, boiling off of the liquid and, as a result, dehydration of tissues is observed at a temperature of 100 °C. Prolonged exposure to thermal effects leads to carbonization or charring, and subsequently to the combustion of tissues with the formation of smoke. To measure the depth of the impact of coagulation, histologists use the term “coagulation necrosis,” which characterizes the space between coagulated and intact tissue. The magnitude of thermal necrosis has a direct impact on the degree of inflammatory changes in the wound, the intensity of postoperative pain and the rate of wound healing [5].
In modern surgery, methods of cutting tissue and stopping bleeding using effective energies are widely used, united under the term “surgical energy”. Significant adjustments have been made to the tactics of organ-preserving methods of hemostasis. Well studied: mono- and bipolar methods of electrocoagulation [6]. In recent years, numerous scientific works and publications have appeared on the use of argon plasma coagulation in surgery.
Plasma is produced by passing gas through an electrical discharge generated by electrodes located in the plasmatron. One of the main requirements for plasma systems in surgery is the stable production of plasma with minimal gas volumes to eliminate the risk of embolism.
Exposure of biological tissue to an ionized high-temperature gas flow leads to the appearance of a thermal damage zone, which includes three layers: 1) carbonized (charred tissue); 2) spongy necrosis; 3) a zone of compact necrosis in which there are partially damaged cells [7].
A high-frequency electric current enhanced by an argon flow provides tissue dissection and coagulation. The non-contact effect on tissue is carried out by passing a flow of ionized argon through an active electrode, to which a high voltage is applied, due to which dissection and coagulation are not accompanied by the formation of smoke [8]. It is known that plasma energy is characterized by high-temperature regimes.
When the microplasmatron exits the nozzle in the form of a beam of jets, its temperature at the epicenter is several thousand degrees (3000–12000 °C), but in the area of contact of the plasma with the tissue does not exceed 100 °C. This prevents evaporation and causes a drying effect. At the same time, 2–3 mm away from the plasma jet, the air temperature is about 30 °C, which allows the surgeon to freely manipulate in the depths of the surgical field without fear of damaging nearby tissues. Thanks to the non-contact effect of high-frequency current, the possibility of “welding” the fabric onto the active part of the instrument is eliminated.
Dissection and coagulation in this case is carried out by radio frequency waves produced by an electric generator through an ionized argon flow. A distinctive feature of this type of energy is the minimal zone of necrosis, which is achieved by continuous gas supply, which reduces tissue temperature. Being inert, argon helps reduce combustion, which means it minimizes carbonization of biological tissues. Depending on the exposure and operating mode, the penetration depth varies from 0.1 to 3 mm. The method was developed specifically for hemostasis during surgery on parenchymal organs, as well as destruction of pathological structures [9].
An arc of argon plasma is formed between the working part of the plasmatron manipulator and the area of the tissue surface that has the lowest electrical resistance. During coagulation, the impedance increases, which promotes the movement of the argon plasma arc to areas of lower resistance. The action is repeated until the entire treated surface is evenly coagulated. Overheating and carbonization are minimal, since the flow of inert gas displaces oxygen from the affected area and prevents combustion.
Due to the properties of flow around tissue, APC allows coagulation in hard-to-reach places, while the direction of the instrument tip does not matter [9].
Guided by the principle of preserving the maximum volume of functioning tissue during operations, we can highlight the main advantages of APC:
- non-contact coagulation;
- objectively controlled depth of tissue coagulation no more than 3 mm;
- activation of repair processes as a result of neoangiogenesis.
The disadvantage of this method is the possibility of hemostasis during bleeding from vessels with a diameter of no more than 1.5 mm.
Numerous advantages outweigh the disadvantages of the hemostasis method under discussion. Argon plasma coagulation can be considered as an alternative method for effectively stopping bleeding, allowing maximum preservation of healthy functional tissue [10].
Author:
Obstetrician-gynecologist, Ph.D. Khamzin Ildar Zakirovich Instagram: dr_khamzin
Any use or copying of article materials is permitted only with the obligatory indication of active links to the author’s page https://www.instagram.com/dr_khamzin and the website https://www.tiaramed.ru/
Bibliography:
- Titov, D.S. Argon plasma energy in the treatment of benign tumors and tumor-like formations of the ovaries: diss… Cand. honey. Sci. - M., 2021. - 142 p.
- Brill, AI Bipolar electrosurgery: convention and innovation. / AIBrill // Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. - 2008. - Vol. 51, No. 1. - P. 153–158.
- Frew, J. W. Performing surgery with a single electron: electrosurgery and quantum me mechanics. / JW Frew // ANZ J. Surg. - 2009. - Vol. 79, No. 10. – P. 680–682.
- Vender, JR Effect of hemostasis and electrosurgery on the development and evolution of brain tumor surgery in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. / J.R.Vender, J.Miller, A.Rekito // Neurosurg. Focus. - 2005. - Vol. 18, No. 4. - P. 93.
- Safronova, D.A. Reproductive health of women after organ-preserving operations on the ovaries: dis. ...cand. honey. Sci. — M., 2011.—130 p.
- Palanker, DV Electrosurgery with cellular precision. / D. V. Palanker, A. Vankov, P. Huie // IEEE Transact. Biomed. Engineer - 2008. - Vol. 55, No. 2. - P. 838–841.
- Kulagin, V.A. The use of a plasma scalpel in the treatment of hemorrhoids: abstract. dis. ...cand. honey. Sci. - Smolensk, 2001. - 16 p.
- Morris, M. L. Electrosurgery in gastrointestinal endoscopy: principles to practice. / MLMorris, RDTucker, THBaron [et al.] // Am. J. Gastroenterol. - 2009. - Vol. 104, No. 6. - P. 1563–1574.
- Khamzin, I.Z. Organ-conserving operations in patients with benign ovarian tumors. State of ovarian reserve when using modern methods of hemostasis: abstract. dis. ...cand. honey. Sci. - M, 2021. - 25 p.
- Khamzin, I.Z. The influence of argon plasma coagulation on the ovarian reserve during organ-preserving operations on the ovaries / A.A. Solomatina, I.Z. Khamzin, V.A. Strygina, O.V. Bratchikova, M.Yu. Tyumentseva // Issues of gynecology, obstetrics and perinatology - 2016. - No. 15(5). — P. 20-25.
Equipment for agro-industrial complex
Universal argon coagulator (Efa) An innovative argon, radiofrequency and high-frequency electrosurgical device.
Find out the price
Innovative argon, radio frequency and high frequency electrosurgical device.
To favorites
Comparing to
ARC 350 Electrosurgical unit with wide functionality, simple operation and four instrument connectors. Maximum power 350 W. Convenient touch control panel with an intuitive interface. Preset program settings. Indicator of the connector on which the settings are currently being adjusted. The device is easy to clean.
Find out the price
Electrosurgical device with wide functionality, simple controls and four connectors for instruments. Maximum power 350 W. Convenient touch control panel with an intuitive interface. Preset program settings. Indicator of the connector on which the settings are currently being adjusted. The device is easy to clean.
To favorites
Comparing to
ZERTS Multifunktion The only gynecological combine in the world that combines the maximum of necessary tools in one ergonomic body.
Find out the price
The only gynecological combine in the world that combines the maximum of necessary tools in one ergonomic body.
Add to favorites
Compare
Recovery
Complete restoration of the reproductive system after argon plasma coagulation takes 2 months - during this period of time, copious vaginal discharge mixed with blood is possible. Unpleasant nagging pain in the lower abdomen may also bother you.
Throughout the recovery period it is important:
- do not have sex for at least 3-4 weeks, and after that - practice protected sex with condoms.
- It is mandatory to observe the rules of personal hygiene.
- Avoid overheating and hypothermia, do not lift weights and get involved in strength sports.
There is no need to take special medicinal formulations; the only thing is that doctors can prescribe suppositories to restore the vaginal microflora.
Argon plasma coagulation during caesarean section
Today, when performing a cesarean section, doctors resort to argon plasma coagulation - this will allow wound healing due to deep heating of the wound, reduction of collagen fibers due to heat treatment.
In addition, this method allows you to reduce blood loss and improve the recovery period by reducing pain. Moreover, due to the fact that the procedure has a parallel, antibacterial effect, it reduces the need for antibiotics and reduces the risk of developing purulent foci of inflammation and sepsis.
Reviews
The opinions of many patients regarding this procedure are very positive.
- Anna. Not long ago, a doctor diagnosed me with an extensive erosive neoplasm in the cervical area. He said that it is best to resort to argon plasma coagulation - since I have never given birth, this is the most optimal method of treating erosion. It was scary, but I was afraid in vain - they quickly cauterized it and after half an hour I went home, 3 days later for a follow-up examination.
- Tamara . My erosion, so to speak, “came out” after my second baby - my gynecologist advised me how to quickly and painlessly remove it. Using argon plasma coagulation is quick, effective, and there are practically no negative consequences. Everything went great - thanks to the doctor.
- Tatiana. The argon plasma coagulation procedure itself, which the doctor prescribed for me to remove polyps, took place in just 5 minutes - there was a little tingling and pulling in the lower abdomen, but that’s okay. This is better than curettage - thanks to the doctor for choosing such a modern method.