Sometimes a pregnancy has to be terminated. This happens at the request of the woman, due to medical or social reasons. There are several methods used to free the uterus from fetal material. In the early stages, drug interruption, vacuum aspiration or curettage (curettage) are most often used. But despite the difference in technology, they give the same effect and also have similar consequences. For example, the temperature often rises after an abortion. Only a doctor can tell what this is connected with and whether it has any health risks. And it is important for a woman to notice extraneous symptoms in time and seek medical help.
How to clean
Any cleaning of the uterus - during bleeding, during examination or after childbirth - is performed only in a hospital setting.
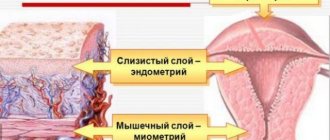
The top layer of the uterine lining, called the functional layer, is removed - the one that is naturally shed during menstruation. The basal layer is not affected. Intravenous anesthesia is neglected only when cleaning the uterus is carried out after childbirth - due to bleeding or a lobule of placenta left in the uterine cavity. At this time, the cervix is dilated enough so as not to cause pain in the woman.
In other cases, anesthesia is performed before the expander is inserted. Then several probes are inserted into the cavity in turn - they expand the neck to the required size. Direct scraping is carried out with a spoon on a long handle, called a curette. The detached endometrium is sent to the laboratory for examination. If a hysteroscope is inserted during the diagnostic process, the procedure takes from 40 minutes to an hour; Blind cleaning takes 15-20 minutes.
Cleaning the uterus in case of endometriosis or suspected cancer is carried out in two stages - first the cervical canal is scraped, and then the uterine cavity. All received materials are examined as separate samples.
To clarify the diagnosis, curettage is prescribed in the following cases:
- with the appearance and enlargement of myomatous nodes;
- before operations to remove fibroids;
- to monitor pathological changes in the endometrium;
- if malignant processes are suspected.
For therapeutic purposes, the procedure is carried out for the following diagnoses:
- to remove polyps;
- elimination of endometrial hyperplasia;
- when post-abortion or postpartum complications occur;
- with heavy bleeding.
If the procedure is carried out as planned, then they try to schedule it before the menstruation is due. Only in this case can the negative consequences of surgical intervention be reduced.
Vacuum method
There are 2 types of vacuum cleaning: machine and manual. Manual is used more often - it is safer.
The procedure is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- Dilatation of the cervix is carried out in the same way as with regular curettage, only local anesthesia is often performed, the patient does not fall asleep;
- After determining the length of the uterus with a special probe, an aspiration tube is inserted into it, attached to a syringe - with the manual method, or an electric aspirator - with the mechanical method;
- When the catheter rotates, material for diagnostics is collected or the uterine cavity is cleaned.
Indications for vacuum cleaning:
- termination of pregnancy before 5 weeks;
- in case of spontaneous abortion to remove parts of the fertilized egg;
- correction of an error after a conventional abortion - this reduces the risk of damage to the basal layer of the endometrium;
- removal of placental tissue after delivery;
- accumulation of fluid or blood in the uterine cavity with a hematometer;
- uterine bleeding.
The method cannot be used when a woman has myomatous nodes, inflammatory diseases of the gynecological organs of infectious etiology, with endometriosis and ectopic pregnancy, if the woman had an abortion or cesarean section less than 8 months ago.
Despite the fact that the vacuum method is considered the most humane and causes less damage to the reproductive organs, its complications are similar to the adverse consequences that arise after conventional curettage.
These include:
- inflammatory processes;
- perforation of the body and cervix;
- secondary infertility.
If a woman has the opportunity to choose a scraping method, then preference is usually given to vacuum. A very important indicator is the answer to the question: “After cleaning the uterus, how many days does the bleeding last?” . After the procedure performed using a vacuum, bleeding continues from 5 days to a week.
After normal curettage - at least 2 weeks.
Nuances of diagnostic curettage
Since diagnostic curettage is essentially a surgical intervention, preparation for it is carried out in the same way as for a conventional operation.
- The patient undergoes general urine and blood tests;
- does fluorography;
- the smear results and cytology diagnostic materials must be indicated in the referral;
- specific - blood for biochemistry, coagulation, group, HIV and syphilis;
- An ultrasound examination is required;
- A cardiogram may be required...
Other tests and studies are at the discretion of the doctor. Surgery is prescribed 2-3 days before the menstrual cycle. Before the operation, you should not eat or drink for 8 hours.
Women are warned in advance: sexual rest is necessary for a month after curettage. When deciding to undergo surgery, women try to find out how long after the operation their periods will begin? After the vacuum method, if there is no hormonal imbalance, menstruation begins no later than 30 days later.
It is impossible to say when menstruation will come after a diagnostic curettage performed manually - it depends on the individual reaction of the body to the procedure. As soon as bleeding begins, you need to analyze how your menstruation is progressing. Both scanty and profuse bleeding are considered abnormal. Menstruation is considered heavy when pads have to be changed every 3 hours, or even earlier. Scanty, dark-colored periods signal the onset of the inflammatory process.
All these signs are a good reason to see a doctor. The second period should pass without complications and the menstrual cycle is finally restored by 3-4 months after curettage. In the same way, it is impossible to clearly answer when you can become pregnant after cleaning the uterus. It all depends on the reason for which diagnostic curettage was performed. In case of spontaneous termination of pregnancy, it is necessary to conduct a thorough examination of the reasons that caused this phenomenon and carry out treatment. It is not rational to get pregnant earlier than after 8-12 months - this can lead to recurrent miscarriage.
Diagnostic curettage was performed to remove the fertilized egg during a frozen pregnancy.
Frozen pregnancy can be caused by infectious diseases; disorders of the endocrine system, autoimmune diseases.
After eliminating the infection, you can plan to conceive in 2-3 months; it takes 2-3 years to restore the functioning of the endocrine system. In case of autoimmune diseases, the onset of pregnancy is at the discretion of the attending physician and you need to be prepared for the fact that you will have to bear a child under strict supervision.
When cleaning of the uterine cavity has been prescribed for diagnostic purposes and the general condition allows you to bear a child, you can approach conception as soon as the inner layer of the endometrium has sufficiently recovered. This usually takes 3 to 6 months.
You need to keep in mind: after cleaning the uterus, the body requires a recovery period. Conception in the first month after curettage rarely leads to a successful birth - the body has not yet recovered enough, the hormonal balance has not been restored, and it is very likely that the course of pregnancy will not be successful.
If pregnancy does occur and it is desired, it is necessary to register as early as possible.
Cleaning the uterus after childbirth is a gynecological procedure that can be prescribed by a doctor for diagnostic purposes or for therapeutic purposes (termination of pregnancy, after a miscarriage, to remove a frozen embryo or after childbirth). Cleaning is carried out manually (mechanically) or using vacuum methods. In both cases, local anesthesia or general anesthesia can be used.
Vacuum cleaning is a modern effective method of removing the contents of the uterine cavity to free the mucous layer of the organ from blood clots or remnants (pieces) of the placenta, carried out without damaging the cervix and its walls. There are many indications for this procedure. We will consider those cases when cleaning is prescribed in the postpartum period.
Often, cleaning the uterus after childbirth is a complication associated with the lack of natural release of the placenta and fetal tissue, which cannot be ignored, as it is dangerous for the woman’s health. Many people are afraid of this procedure, but it is not as scary as it might seem. In any case, it’s no worse than childbirth itself (and you’ve already experienced that). In addition, doctors prescribe cleaning only in extreme cases, when it comes to the possibility of more serious complications, the consequences of which can be quite complex, even fatal. Therefore, there is no need to be afraid or refuse the procedure. You just need to figure out what's in front of you.
Indications for cleansing in the postpartum period
As a rule, after the birth of a baby, a woman remains in the maternity hospital under the supervision of doctors for another 5 days, and this is necessary so that the gynecologist can assess the mother’s condition and determine:
- her body temperature;
- condition of the birth canal;
- discharge from the uterus;
- the condition of the sutures (if any had to be placed after a cesarean section or as a result of ruptures);
- general well-being of the woman.
If, 2-3 days after birth, upon visual examination and measurement of the fundus of a woman’s uterus, a weak (or complete cessation) of its contraction is noted, then the doctor may resort to an instrumental examination in a gynecological chair or refer the patient to an ultrasound of the pelvic organs to examine her for possible the presence of placenta particles, membranes or large blood clots in the uterus. If any are detected, then intravenous injections are first prescribed to stimulate uterine contractions and facilitate the passage of the placenta from the reproductive organ. Such a complication arises in the case of strong fusion of the placenta with the uterus, which does not allow the tissues to come out freely in the second phase of labor. And the presence of foreign tissue in the uterus becomes:
- firstly,
it is a breeding ground for microorganisms, and their active reproduction can cause purulent inflammation; - secondly,
the cause of a significant decrease in the contractility of the uterus, which ultimately leads to infection and the development of serious postpartum consequences.
If droppers do not help, then this is an indication for cleaning the uterus, since further development of purulent processes and toxic poisoning of the body as a whole immediately prohibit breastfeeding (since the infection gets into the breast milk through the bloodstream) and threatens the patient’s health .
How is the procedure carried out?
The postpartum cleansing procedure is usually performed under anesthesia and is technically similar to an abortion after an unwanted pregnancy. To avoid painful shock, both general and local anesthesia can be used. However, when carrying out vacuum cleaning, a woman may not be afraid of getting microtraumas and other similar complications, and therefore the procedure is carried out under local anesthesia - the patient does not feel pain, but may experience characteristic unpleasant sensations for curettage.
The operation takes place according to the following “scenario”:
- Preoperative examination of the woman’s genital organs - their external and internal treatment with antiseptics (ethyl alcohol and iodine)
- Gradual dilatation of the cervix using dilators of different diameters.
- A cleansing procedure during which all blood clots and afterbirth residues are removed. The vacuum is created using special equipment, the operating principle of which resembles the operation of a vacuum cleaner. During the cleansing procedure itself, “everything unnecessary” and the upper epithelial layer of the walls of the organ are removed from the uterus.
The procedure lasts about half an hour.
Rehabilitation period
After cleaning, the uterus resembles an open bleeding wound, and therefore the woman continues to be under the supervision of doctors for several more days. At this time, she is prescribed individual drug treatment appropriate to the characteristics of her body:
- antibacterial therapy (injections)
- to prevent exposure to clots previously present in the uterus and possible infection; - taking medications that stimulate uterine contractions;
- treatment of the external (if necessary, internal) genital organs
with an antiseptic solution and drugs for rapid recovery.
After the cleansing procedure, a woman experiences discharge, which can last up to 10 days and resembles menstruation. The strongest ones are observed in the first hours after the operation, then they decrease, and after 5-6 days they change, becoming brown. By the end of the decade they disappear completely.
While there is discharge, a woman is contraindicated:
- Using tampons.
- Douching.
- Excessive physical activity and any sports.
- Lactation. This is due to drug treatment, which can affect the composition of milk and harm the baby’s health. In addition, the woman feels unwell and may not be able to care for the child. Upon completion of the course of treatment, the woman can resume breastfeeding.
At first, after cleansing, a woman may feel a nagging pain in the lower abdomen, which decreases as the amount of discharge decreases.
However, if the discharge lasts longer than 10 days, has an unpleasant odor and a strange color, or is completely absent, then this should be brought to the attention of the attending physician.
Possible complications
Despite the safety of the procedure itself, like any operation, vacuum cleaning of the uterus after childbirth can cause some complications that, unfortunately, cannot be predicted:
- Damage to the walls or cervix.
- Severe blood loss.
- Infection of the genital organs.
- Inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs.
- Formation of adhesions.
- Fusion of tissues in the uterine cavity.
- The occurrence of hormonal and endocrine disorders.
- Failure of the menstrual cycle.
- The occurrence of infertility.
If complications arise after surgery, doctors select appropriate treatment.
The curettage procedure for a frozen pregnancy involves removing the unwanted contents of the woman’s uterus. The operation is also performed after abortions, as a result of various pathologies of the uterus and miscarriages. In most cases, the cleansing is successful, but women are always worried about the main question: is it possible to get pregnant again? Gynecologists claim that a few months after the procedure, a woman is able to conceive a child.
Theoretically, a woman can become pregnant after suffering a frozen pregnancy in the next cycle, only for this it is necessary to find out the reasons that provoked fetal fading. Otherwise, it is possible that the loss that occurred will happen again.
In order to have an idea about this pathology, you should know the pattern of its appearance: after its fertilization, the egg is attached to the walls of the inner mucous membrane of the cervix, after which the fetus begins to develop. If fertilization does not occur, the endometrium changes, is rejected and comes out along with menstrual bleeding. When, for one reason or another, in the first trimester of pregnancy problems arose with the development of the embryo, which led to a limitation of its viability, then in this case, removal should be carried out exclusively surgically. One of the most common manipulations in this case is curettage (gynecological cleansing or curettage). The essence of the procedure is to remove the upper functional layer of the uterine mucosa and, depending on how professionally the operation was performed, the duration of the woman’s postoperative recovery will depend, as well as the likelihood of complications.
Today, cleansing is carried out during the diagnosis and treatment of many diseases of the internal genital organs of women. In this case, not only special instruments are used, but also medications that dilate the cervix.
In order for a full-fledged pregnancy to occur without complications after cleaning during a frozen pregnancy, it usually takes several months for the complete recovery of the injured organ.
In medical practice, curettage is carried out using two technologies:
- separate, in which the cervical canal is first cleaned and only after that the uterus itself. To establish an accurate diagnosis, the resulting analysis is sent for cytological examination. An analogue of the separate curettage procedure today is hysteroscopy. This minimally invasive examination uses a special device, a hysteroscope, which is inserted into the uterus, allowing you to monitor the progress of the work. Thanks to this low-traumatic method, a woman can think about her next pregnancy within a month after cleansing;
- conventional curettage is a more traumatic procedure, as it is performed blindly. To quickly restore the organ, the operation is performed 2-3 days before the start of menstruation.
Reasons for fever after abortion
If all the necessary requirements for the conditions for abortion are met, a healthy woman after an abortion usually returns to normal temperature on the third day after the intervention.
But, unfortunately, sometimes the temperature not only does not decrease, but has a steady tendency to increase. The reasons for this reaction of the body may be different.
One of the main reasons for an increase in temperature after an abortion is the leaving of unremoved parts of the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity. Abortion is a blind operation. And no matter how professional the doctor is, due to the developmental characteristics of the fetus and the individual structure of the uterus, a similar situation can always arise. As a result, decomposition of the remains of the fertilized egg begins, which is accompanied by suppuration and the development of a septic process, leading to an increase in temperature.
Another possible reason for an increase in temperature after an abortion may be an exacerbation as a result of the operation of dormant chronic infections - chronic gonorrhea, chlamydia, gardnerellosis, etc.
Indications for cleaning
Cleansing the uterus is performed for several reasons. Largely in order to take scrapings for examination if certain diseases are suspected. Curettage is also done to remove tumors, eliminate complications after abortions, miscarriages or frozen pregnancies.
Indications for curettage:
- changes in the internal mucous membrane of the uterus (hyperplasia and other local formations);
- polyps;
- intermenstrual bleeding and during menopause;
- pathologies of the cervix;
- frozen pregnancy;
- miscarriage;
- intrauterine adhesions, endometriosis.
In some cases, as prescribed by a doctor, before performing a curettage operation during a frozen pregnancy, the patient needs to have her blood tested to determine its coagulability, a smear for flora, and an analysis to detect infections of the genital organs.
2 days before surgery, you should stop having sex, douching, and using intimate hygiene products. It is recommended to wash only with warm water. Vaginal suppositories, tablets or sprays can only be used as prescribed by a gynecologist. Immediately on the eve of the operation and before it is performed, you should try to refuse food and drink. This is necessary for normal anesthesia.
What is the scraping procedure?
The duration of the operation is no more than 30 minutes. It is performed under general anesthesia; after the administration of intravenous anesthesia, the patient falls asleep within 2 minutes. To fix the uterus in a stationary state, the doctor inserts a gynecological speculum into the vagina and fixes it using a special instrument. After dilation of the cervix, curettage is performed with a curette - a special surgical instrument.
At the end of the operation, the doctor treats the cervix and vagina with an antiseptic solution, and so that the bleeding stops quickly and the uterus contracts, ice is placed on the woman’s stomach. In some cases, vacuum aspiration is used to remove a non-viable embryo. After this, the gynecologist sends the scraping taken for laboratory testing. Histological analysis of a frozen pregnancy allows us to find out the reasons for what happened. The next pregnancy after vacuum cleaning can be planned no earlier than 3 months later.
The patient is not recommended to have sex for the next 2 weeks. The fact is that the endometrium is injured, the uterus is open for some time after manipulation, so the risk of pathological infections is extremely high. In addition, sexual intercourse can cause acute pain for several weeks after cleansing a frozen pregnancy.
Temperature after medical abortion
Many women are interested in the following questions: What should be the normal temperature after a medical abortion? How long can a fever last? What temperature is dangerous?
We will try to answer these questions in the current section.
Low-grade fever (37.0-37.5 C) after a medical abortion can persist for several weeks and should not cause alarm, and does not require treatment. This temperature is maintained due to the increased content of progesterone in the woman’s blood. Progesterone after termination of pregnancy may remain elevated for another 10-14 days, but its concentration gradually decreases to a minimum level.
Your attention should be drawn to the fact that a rise in temperature above 38.0 C and persistence of high numbers for more than 1 day may be evidence of an infectious-inflammatory process.
Therefore, if this symptom appears, consult a gynecologist as soon as possible. You should not try to bring down the temperature with medications or other means - your efforts will only delay the diagnosis of the inflammatory process and aggravate the condition of the body. If comprehensive treatment of the infectious-inflammatory process is not started on time, it threatens such a serious complication of abortion as infertility. Moreover, adequate and timely therapy practically reduces to zero the possibility of developing infertility.
10-14 days after the start of bleeding, you must contact a gynecologist for a control ultrasound. This is necessary to ensure that parts of the fertilized egg have completely left the uterine cavity.
The preservation of fragments of the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity or the presence of blood clots is a favorable substrate for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms, which can lead to serious consequences.
10, total, today
We draw your attention to the fact that this website is for informational purposes only and under no circumstances constitutes a public offer as defined by the provisions of Article 437 (2) of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Complications after cleaning
If cleaning during a frozen pregnancy was carried out in compliance with all the rules, then, as a rule, there are no postoperative complications. However, an incorrectly performed curettage procedure can lead to complications such as:
- tear of the cervix as a result of the forceps slipping. For large tears, sutures are necessary;
- punctures and injuries to the uterus also require suturing;
- as a result of curettage, blood may accumulate in the uterus, and this sometimes leads to infection of the organ;
- if antiseptic requirements are violated and there is no antibiotic therapy, an inflammatory process may occur in the uterus. The first sign of inflammation is a high temperature after cleaning;
- risk of endometrial damage with inability to further recovery;
- poor-quality curettage of polyps, in which the pathology is not completely removed and requires a repeat operation.
Why does fever occur after an abortion?
1. Cell destruction during abortion. The body's response is the release of special substances that irritate local tissues. In the human brain there is a zone responsible for maintaining normal temperature (hypothalamus). An increase in temperature begins when the neurons of the hypothalamus begin to be washed by blood containing a huge number of molecules released from damaged cells. These substances are foreign. Getting into the thermoregulatory center, they cause an increase in temperature after an abortion.
2. Blood entering the pelvis. The fallopian tubes communicate with the pelvic space. During an abortion, a large amount of blood is lost. If it gets inside the pelvis, irritation of the peritoneum may occur. The inflammatory process covers internal organs. Inflammation is accompanied by high fever.
3. Incomplete abortion. Mini-abortions are now common. They are performed in the early stages of pregnancy. They are carried out carefully with a vacuum aspirator, without injuring the cervix. But there is a danger that part of the fetus may remain inside the uterus. The probability of this is high and it happens more often than with medical abortion. The inflammatory process begins, accompanied by high temperature. Only a doctor who will perform additional curettage of the uterine cavity can help.
4. Individual intolerance to drugs. With the medical method of termination of pregnancy, an increase in temperature can be caused by individual intolerance to the drugs.
5. Infections. Sexual infections (chlamydia, gonorrhea) can also cause fever. Abortion suppresses the immune system, as a result of which microorganisms (causative agents of the disease) are activated.
Menstruation after curettage
The first menstruation after cleansing a frozen pregnancy appears, as a rule, after a month and a half, but this parameter completely depends not only on the woman’s health, but also on her individual menstrual cycle. Only if a woman has undergone a medical termination of pregnancy (abortion) will it take more time to restore the reproductive functions of her body.
A serious reason to visit a gynecologist is the fact when, as a result of curettage, the patient observes heavy or scanty bleeding, accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen and high body temperature.
A situation in which, after curettage, the menstrual cycle is not restored within 3 months should also be a reason to contact the gynecological department. It should be remembered that after cleaning with the removal of a non-viable fetus, heavy menstruation may last longer than usual. And their complete absence in this case speaks of a serious pathology.
Additional diagnostics
To say exactly why the temperature increased after termination of pregnancy, it is necessary to conduct an additional examination. The woman will have to undergo laboratory and instrumental tests, the results of which are necessary for the doctor to make a correct diagnosis. These include the following:
- Complete blood count (leukocytosis, increased ESR).
- Blood biochemistry (acute phase indicators, coagulogram, immunoglobulins).
- Bacteriological analysis of secretions.
- Determination of microflora sensitivity to antibiotics.
- Ultrasound of the uterus.
In most cases, this is enough to determine the problem causing the temperature increase. Based on this, the doctor will formulate a treatment strategy to eliminate the pathology and give recommendations for subsequent life. And in order to prevent further abortions, a woman should be reminded of the importance of contraception as an effective method of planning pregnancy.
Termination of pregnancy can be perceived by the body in different ways. In some cases, everything goes more or less successfully, and health is quickly restored. However, some women can take years to bring their body back to normal. Their health was so seriously compromised. Factors that influence the consequences after an abortion include the timing of the woman’s pregnancy, the method of abortion, based on the timing at which the pregnancy can be terminated, and the qualifications of the doctor performing the operation. But the main factor will always be the woman’s health and how quickly her body starts the rehabilitation process.
The article “” provides a list of diseases and circumstances in which abortion is extremely undesirable. In those cases, a woman needs to think carefully about whether it is worth exposing her body to serious risk. If a pregnant woman has firmly decided to terminate an unwanted or unsuccessful pregnancy, she should be aware of the possible consequences after an abortion. General (also given in the article “”) and specific, such as fever after an abortion, pain in the lower abdomen after an abortion, nausea after an abortion, pain in the chest after an abortion and others. This article will talk about which consequences after an abortion are normal and which are a symptom of complications.
Recovery after cleansing a frozen pregnancy
The rehabilitation period after the curettage procedure in some cases drags on for several months. In the first days after successful surgery, the patient can be discharged home. In this case, the gynecologist prescribes certain antibiotics and painkillers. Upon arrival from the hospital, it is better for a woman to remain in bed for 24 hours; additional physical activity during this period can lead to blood loss.
In the first weeks after surgery to remove a non-viable fetus, doctors advise abstaining from sexual intercourse. It is also important to know that pregnancy can occur almost immediately after cleaning the uterus. Therefore, if conception is undesirable, then take care of contraception.
You should immediately consult a doctor if:
- a few days later your body temperature rose to 38 degrees;
- bleeding increased;
- menstruation does not end within 2 weeks;
- antispasmodic drugs do not eliminate severe pain in the lower abdomen;
- vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor.
Cervicitis
The reason for the increase in temperature - sometimes to very significant levels - after cleaning (curettage) of the uterine cavity is inflammation of the vaginal segment of the cervical canal.
In addition to high fever, the disease is characterized by the appearance of vaginal discharge. They can be either mucous or contain purulent impurities. In addition, the pathology is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, as well as significant discomfort accompanying the process of urination.
There are two forms of cervicitis. The gradation depends on which tissues of the cervical canal were involved in the pathological process.
- When the vaginal part of the cervical canal becomes inflamed after curettage of the uterus, a woman develops exocervicitis.
- If, after cleaning, inflammation of the inner surface of the cervical canal of the uterus begins, then we are talking about endocervicitis.
The main cause of the disease is tissue damage during uterine curettage, which is subsequently joined by nonspecific infectious agents. The development of inflammation after cleansing and the accompanying rise in body temperature can be provoked by:
- staphylococci;
- coli;
- streptococci, etc.
After cleaning (scraping) the uterine cavity, the female body becomes more vulnerable to various types of infections as a result of decreased immune defense.
In addition to its own opportunistic flora, inflammation and fever are caused by pathogenic microorganisms. Pathogens such as chlamydia, mycoplasma and ureaplasma, viruses can provoke cervicitis when open sexual activity begins after cleansing earlier than recommended by the doctor. The disease also becomes more active if the infection has progressed before the cleansing. Failure to comply with the principles of rational antibiotic therapy leads to cervicitis and a rise in temperature after cleaning.
Symptoms
As a rule, after injury to the cervix during curettage and the addition of a secondary infection, a woman develops acute cervicitis. In addition to the increase in temperature, the following symptoms appear:
- copious mucous and even mucopurulent discharge;
- presence of dull pain in the lower abdomen.
During a gynecological examination - a few days after curettage - swelling and redness of the cervix are noted.
If an increase in temperature is typical for all types of cervicitis, then the accompanying symptoms depend on the pathogen and the current state of immune defense.
- For the gonorrheal form, an acute course is typical - high body temperature, significant purulent discharge with a pungent odor.
- With chlamydial cervicitis, the symptoms are somewhat blurred, but the temperature still rises.
- When a herpetic infection forms, the cervix becomes loose, covered with ulcers and becomes very red.
- Trichomonas cervicitis is characterized by the appearance of small hemorrhages on the surface of the mucosa.
Discharge after cleansing a frozen pregnancy
Since the curettage procedure requires immediate surgical intervention, it almost always entails tissue damage that requires long-term recovery. This is why patients are often haunted by discharge after cleansing a frozen pregnancy.
There is no need to panic in this case, since gynecologists call this condition normal and a completely natural process. A woman’s recovery time will depend entirely on her physiological characteristics and usually postoperative bleeding lasts no more than one week. A month after the curettage procedure, if the restoration of the uterus goes according to plan, the bloody smear completely stops.
After being discharged from the hospital, the operated patient should monitor the abundance of discharge and its nature. If the pad becomes completely saturated with blood in less than 60 minutes, then you should inform your gynecologist about this. A consequence of infection of the uterus may be an unpleasant odor that accompanies the discharge. Such consequences usually overlap with sharp pain in the lower abdomen, and in this case it is impossible to delay a visit to the doctor. The specialist is obliged to find out the nature of the discharge and the reasons that provoked it. Are they a consequence of the inflammatory process in the uterus, or is it just a post-operative phenomenon.
In order to avoid unpleasant consequences after cleansing, women are advised to more carefully monitor their health and its signals. Hypothermia, stress and any physical activity are extremely contraindicated.
Symptoms
As in other situations, the origin of a particular symptom can only be determined by conducting a full diagnosis. And it starts with fairly simple methods. First, the doctor determines what is bothering the woman and details her complaints, and then conducts a clinical and gynecological examination. According to the anamnesis and thermometry performed by the woman on her own, the temperature after an abortion can be of a different nature:
- By size: subfebrile (37–38 °C), febrile (38–39 °C), pyretic (39–40 °C) and hyperpyretic (above 40 °C).
- By type of curve: constant, laxative, hectic.
- By duration: short-term, long-term.
Of course, a feverish state has a negative impact on everyday life. The woman’s general well-being deteriorates, which is expressed in the following:
- General weakness.
- Headache.
- Increased fatigue.
- Sweating.
If the temperature is low, then these symptoms may be absent or mild. But you should pay attention to other signs that indicate processes in the uterus itself.
Norm
So, in the period after a surgical or medical abortion, the uterine cavity heals and menstrual function is restored. This is accompanied by certain changes in the body that cannot be ignored. Firstly, you should immediately reassure women by saying that an increase in temperature to 37.5 °C is the norm. It can be like this from several days until the onset of the first menstruation. Secondly, common signs will be:
- Bloody vaginal discharge, gradually decreasing.
- Discomfort in the lower abdomen or mild nagging pain.
- Unpleasant sensations in the chest.
These symptoms are due to the restoration of the size of the uterus and the removal of endometrial remnants, as well as changes in hormonal levels that occur as soon as the body becomes aware of the termination of pregnancy. Pain and discharge may last about 10 days, but they certainly tend to decrease and pass. Therefore, a woman should not worry about them, but she must undergo a control gynecological examination so that the doctor can assess how the recovery process is proceeding after an abortion.
The normal course of the post-abortion period is characterized by a slight increase in temperature, but this reaction cannot persist after the first menstruation.
Incomplete abortion
Among the complications of artificial termination of pregnancy, incomplete abortion should be noted. This is a situation when the remains of the fetus (usually its membranes) are retained in the uterine cavity. In this case, the organ cannot contract adequately, which leads to the following:
- Prolonged bleeding (usually more than 2 weeks).
- Drawing or cramping pain in the abdomen.
- Increased body temperature.
Upon palpation, the uterus has a soft consistency and dimensions exceeding the norm for the period after an abortion. This creates additional risks for a woman's health, as it can lead to progressive blood loss, disorders of the blood coagulation system and infection. Therefore, a woman with similar symptoms should contact a medical facility for re-evacuation of the uterine cavity.
Endometritis
If the temperature after an abortion rises above 38°C, this is a sure sign of the development of infectious inflammation in the uterus. This can be facilitated by the use of non-sterile instruments (more often in cases of criminal termination of pregnancy) or non-compliance with personal hygiene rules after manipulation. And the direct source of endometritis is a microbial factor: Escherichia coli, streptococcus, staphylococcus, etc. Inflammation of the uterus is accompanied by the following changes:
- Pain in the abdomen and lower back.
- Vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor.
- Hyperthermia.
- Violation of general health.
The uterus is painful and enlarged on palpation. And the bleeding, which should have ended, still continues. In such a case, the woman requires hospitalization with antibacterial therapy.
Respiratory infection
It also happens that the spotting has stopped, the pain in the lower abdomen does not bother you, and your period has already arrived, but a fever has appeared. Then, most likely, you should look for the cause among extragenital diseases. Quite often after an abortion, various respiratory infections are observed, the appearance of which is associated with a decrease in the immunological reactivity of the body. But then, along with the elevated temperature, completely different symptoms appear:
- Runny nose, nasal congestion.
- Sore throat.
- Cough.
They indicate an inflammatory process in the upper respiratory tract, but if not treated in a timely manner, the process can spread lower: into the bronchi or lungs.
Taking into account all the symptoms – gynecological and general – helps to identify the problem in a timely manner and suggest the cause of the fever.
Conception after a frozen pregnancy
A woman who has suffered a frozen pregnancy must plan a new conception with all responsibility. First of all, you need to find out what led to such sad consequences; for this, partners must undergo examination to identify genetic and hormonal disorders, as well as infections of the reproductive system.
Such an examination should include:
- blood sampling to determine progesterone and estrogen levels;
- smear for flora and presence of infections;
- ultrasonography;
- histological analysis of uterine tissue;
- genetic research on partner compatibility.
Pregnancy immediately after cleansing cannot be planned until certain problems are identified that led to the death of the fetus. Only after the partners have undergone appropriate treatment will the doctor recommend favorable timing of conception.
You can significantly reduce the likelihood of negative consequences by adjusting your lifestyle:
- Stop smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
- Avoid radiation, including x-rays, exposure to chemically active substances, and potent medications.
- Establish proper nutrition: take multivitamin complexes, rest and do gymnastics.
Pregnancy after cleansing is a serious test for both women and men. It is very important to overcome your psychological barrier, work on yourself, lead a healthy lifestyle, avoid stress and try to get pregnant again.