Increase in general body temperature during menstruation
Gynecologists believe that during menstruation the temperature may rise slightly. At this time, the body experiences stress and a slight loss of fluid occurs. An increase of no more than 37.3 degrees is considered normal. This is due to fatigue and weakness of the body. If the elevated temperature does not normalize after rest or exceeds the set value, it is necessary to be examined to determine the cause.
Among the common causes of pathological increase in temperature during menstruation are:
- Infectious diseases of the genitourinary system. During menstruation, the cervix opens, acting as a gateway for infection. The internal environment promotes the development of pathogenic microflora. It is recommended to refrain from swimming in bodies of water and having unprotected sex, which is associated with an increased risk of contracting infections during menstruation. This risk is also increased in women who use tampons.
- Intestinal inflammation. For many women, menstruation is accompanied by stool problems (diarrhea or constipation). There are many reasons: hormonal disorders, gastronomic preferences, unusual foods. The problem is more acute in patients suffering from chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Gynecological diseases. On critical days, the body is weakened and in a stressful state, so chronic processes may worsen.
- Pregnancy. Usually in this case they talk about a low rise in temperature, but the initial stages of gestation are different. The body perceives the new condition as a disease.
- Climax. Postmenopause is accompanied by sweating, hot flashes, and increased temperature.
What processes occur during menstruation
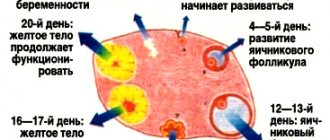
Throughout the entire menstrual cycle, the female body intensively prepares itself for a possible pregnancy by producing a hormone called progesterone. But if conception does not occur, the body also begins to intensively get rid of this hormone, producing another type of hormone - prostaglandins. They are the very harbingers of the onset of menstruation.
The endometrial vessels of the uterus begin to narrow, due to which its overall blood supply decreases. Over time, the mucous membrane of the uterus separates from it and exfoliates. It is her remains that can be seen in the discharge along with the blood that has accumulated as a result of ruptures of small vessels. This process is gradual: some parts of the mucous membrane with blood may come out in the first days of menstruation, others may come out only at the end of menstruation, which is why the menstrual period can vary. At the same time, a new shell begins to form to replace the old one, thereby making this process cyclical.
Critical days are fraught with a number of unpleasant sensations for women:
- nausea and fever;
- unpleasant smell of discharge;
- pain in the lower abdomen. Often women also complain of ovarian pain during menstruation. This is due to the fact that during menstruation the uterus contracts more frequently. You can cope with these painful sensations through medications, but before using them it is best to consult a doctor.
An important guarantee of good health for every woman is hygiene. It is during menstruation that the greatest attention should be paid to it.
Increased with PMS
Premenstrual syndrome is a normal reaction to changes in the body, which include the following symptoms:
- stomach ache;
- swelling of the limbs;
- swelling of the mammary glands;
- dizziness;
- mood swings;
- rash;
- vomit;
- weakness;
- nausea;
- bloating in the abdomen;
- back pain.
Temperature changes are among the symptoms of premenstrual syndrome. In teenagers and young women, this is associated with hormones, and later with diseases in the body.
With an atypical form of pathology, measurement indicators can reach 38-39 degrees. In this case, you need to contact a gynecologist and endocrinologist.
Basal temperature
Basal temperature (BT) is used to determine ovulation. The highest level during the day is set during sleep. BT is measured while lying in bed after a long rest. Changes in its indicators indicate the presence of inflammation, hormonal abnormalities and help determine the quality of ovulation.
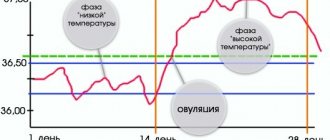
The norm is within 36.9-37.2 degrees. It rises to 37 degrees after the onset of ovulation and remains at this level until the onset of menstruation. 1-2 days before bleeding it drops lower and continues to fall.
How to measure BT
Basal temperature indicators are widely used during pregnancy planning. It unambiguously determines how well the reproductive system functions, helps to calculate the date of ovulation with an accuracy of the day, and indirectly indicates possible violations. To do this, you need to measure it over several months and enter the data into a calendar. It is important to evaluate whether ovulation occurs in each month and what the difference is in the readings between the phases.
Measurements are taken every day at the same time. BBT can be measured through the rectum, vagina or orally.
Rectal and vaginal measurements should be taken within the first 5 minutes, and in the oral cavity - 3 minutes. It is recommended to use mercury thermometers. It is best to take measurements at 6-8 am.
You should consult a doctor if you experience the following symptoms:
- lack of ovulation for several months;
- low temperature lasts the entire cycle;
- high temperature in the second part of the cycle with a negative pregnancy test result;
- increased temperature during the menstrual period;
- menstrual cycle less than 20 days;
- high BT readings for several months.
To determine the cause of the pathology, a gynecological examination, ultrasound, and blood, urine, and stool tests are prescribed.
During menstruation, a slight increase in temperature (up to 37.5 degrees) is normal.
Reading time: min.
Daily fluctuations in BT
Measurement of bt in early pregnancy should be carried out at the same hours in the morning. Such indicators can be trusted, since the body has rested, and no external factors have yet been able to influence it. Physical activity, eating, emotions, even wearing clothes inherent in wakefulness inevitably change its meaning. Usually, the basal temperature in the early stages of pregnancy rises above 37.3 degrees during the day, but this does not hide any threat. At this time, its values can change every hour under the influence of the already mentioned factors.
By the end of the day, the body “digests” everything accumulated during the day, but is already preparing for rest. However, taking measurements at this time of day is also pointless. The indicator will still be high, and it is impossible to understand whether this is caused by natural causes or health problems. In the early stages of pregnancy, basal temperature in the evening is usually about 1 degree higher than normal. An informative measurement at this time will be if the woman slept for at least 5 hours during the day. But it is unlikely that anyone will follow such a strange regime for all 12 weeks of the initial stage.
Basal temperature after menstruation
Women should know what basal temperature should be after menstruation. The sequence of changes looks like this:
- before the arrival of a new monthly cycle, the BT indicator decreases slightly;
- on the days of menstruation it should not increase sharply;
- the day before the end of menstruation, BT drops to approximately 36.3 - 36.4;
- basal temperature immediately after menstruation remains at 36.5 - 36.8.
The basal temperature after menstruation on the 9th day can drop sharply, and then rise again. The day when it drops sharply is precisely the day when the oocyte is released. At this time there is the highest probability of conception.
Women should remember that if before the expected new menstrual cycle BT increases slightly and remains the same further, then pregnancy can be assumed.
There are cases when the temperature may change after menstruation:
- with insufficiency of the corpus luteum;
- if there were inaccuracies in the measurements - for example, a woman got up before measuring BT, she had coitus (it must be at least 8 hours before measurement);
- if there was stress;
- if measurement procedures occur at different times (the permissible deviation in measurement time is half an hour).
How to measure temperature correctly to determine pregnancy
The most accurate readings will be when the thermometer is inserted rectally. The thermometer can be either electronic or mercury, depending on personal preference. Below are the basic rules on how to measure basal temperature to determine pregnancy:
- When planning pregnancy, measuring basal temperature should be done daily in the morning at a certain time after sleep, lasting more than six hours. You should not leave bed or sit up suddenly after waking up;
In addition, frequent walking during night rest distorts research data.
- During the daytime and evening hours, quite strong fluctuations in BT occur due to stress, increased activity or simple fatigue. There is no need to recheck morning measurements during the day and evening, as this is not informative;
- The temperature is measured with a mercury thermometer for 6-10 minutes, with an electronic one - from 2 to 3 minutes or until a sound signal;
- For clarity, it is best to start taking measurements and plotting the graph from the day your menstruation begins. This will allow you to see the temperature difference during the transition from one phase of the cycle to another and evaluate hormonal levels;
- For the convenience of taking measurements, you can use a regular paper sheet, a printed template, or applications that automatically build graphs based on the entered data.
For your information. The following factors influence BT indicators:
- alcohol;
- sex a few hours before the measurement procedure;
- stress;
- infectious diseases;
- too warm sleeping place, for example, from a heating pad;
- hypothermia of the lower extremities.
If any of the listed factors took place, it is worth making a note about it.
Standards for temperature readings by phase
With this method, body temperature at rest is recorded, measured rectally. Knowledge of the main indicators, measurement techniques and rules for constructing a temperature curve is of great importance for obtaining an up-to-date graph.
First phase: basal temperature after menstruation
- In the first half of the cycle, the basal temperature after menstruation remains at 36.2-36.5°, in some cases 36.7°. Duration: approximately from 1 to 11 days (with a 28-day cycle). At this time, a certain amount of estrogen in the blood creates the most favorable conditions for the growth and development of the dominant follicle.
- From days 12 to 16, there is first a decrease of 0.1-0.2°, which means a rapid exit of the cell, and then an increase of 0.4-0.6°, which confirms the fact that the liquid vesicle with the cell has ruptured. It is for this moment that the temperature is measured, since this is the only segment of the cycle, only a day long or a little more, when conception is most likely.
Second phase: high basal temperature for conception
- The second phase is characterized by a temperature of 37.0-37.3°, but not higher than 37.5°. In this case, progesterone acts, which is necessary to create favorable conditions for conception and pregnancy.
The difference in basal temperature after menstruation and before between phases during a normal cyclic period is 0.4-0.6°.
When are atypical readings possible after menstruation?
Basal temperature 36.9° after menstruation
A basal temperature of 36.9° after menstruation may indicate a lack of the first phase hormone, which causes an increase in temperature indicators. But perhaps this is just the individuality of a given organism, if such values are recorded monthly. For example, in a completely healthy woman, after the numbers in the first part of the graph are 36.1-36.2°, in the second segment the values are 36.8-36.9°.
Basal temperature after menstruation 36.8
Basal temperature after menstruation is 36.8 and an increase in its values after ovulation, but with a discrepancy of 0.4°, is not recognized as pathology. This condition is called hyperthermic and is defined as a normal individual symptom.
It is believed that the normal average temperature fluctuations are as follows:
- From the first to the last day of menstruation, the decrease occurs from 37 to 36.3-36.5°;
- Before ovulation, depression decreases by 0.1-0.2°;
- After the cell is released, within 3 days the increase to 37.0-37.3°;
- In the second phase it stays at 37.0-37.4°;
- 1-2 days before menstruation, decrease to 36.8°;
- If there is no decrease and if there is a delay, we can talk about pregnancy.
Why do you need a schedule?
A BT chart during early pregnancy is necessary if a woman seriously decides to monitor this indicator. As the fetus develops, various changes occur in the mother's body, mainly related to hormones. It is not surprising that basal temperature is also unstable in the early stages of pregnancy, the graph will prove this. Usually it looks like this:
- On the day of fertilization of the egg, the value balances between 36.4 and 36.7 degrees;
- Over the next 3-4 days it rises by 0.1 degrees daily and reaches 37;
- For another 2-3 days, the basal temperature remains the same;
- On the day of implantation of the fertilized egg into the uterine mucosa, it decreases to 36.5-36.6 degrees;
- Over the next 2-3 days, the indicator values gradually rise, reaching 36.8-37 degrees;
- For about 2 weeks, the numbers on the thermometer can fluctuate from 36.7 to 37.1. But the values should not be lower than those observed on the day of ovulation.
The graph of basal temperature during pregnancy in the early stages should include not only the numbers of the indicator and the days of the cycle, but also the accompanying circumstances. BT values can be affected by illness, medication, and stress. The attending physician should learn about each of them in order to have a complete picture of the development of pregnancy.
Diagnosis of the disease according to schedule
Deviations from normal temperature values occur in the event of any disease. Inflammatory processes are the most common.
Basal temperature after menstruation 37°
A basal temperature after menstruation of 37° is an identifying sign of endometritis, inflammation of the uterine mucosa. If it decreases slightly on the eve of critical days, an increase is observed on the first day of menstruation and can persist until their end and beyond. If you find such a picture on the chart, you should contact a gynecologist in order to get rid of the problem in time.
Basal temperature after menstruation 37.1-37.0°
With inflammation of the appendages, a basal temperature after menstruation of 37.1-37.0° is also characteristic. It rises sharply to these numbers, lasts for several days and then drops just as sharply. In such cases, you can incorrectly calculate the day of ovulation, mistaking this jump for it if it happened on the 9th or 11th day. With this disease, in the second phase of the cycle, the temperature will show values above normal, which again will require medical intervention to avoid complications.
Possible reasons for deviations and errors
A high basal temperature after menstruation, which lasts only one day, does not pose a particular threat, since it is clear that not a single inflammation goes away in a day. Therefore, you need to look for other reasons.
If the rules are not followed
There may be measurement errors. We remember that measurements are carried out taking into account clear rules:
- After 6 hours of restful sleep;
- At the same time;
- Without getting out of bed or making sudden movements;
- One thermometer, prepared in the evening;
- Stand for 5-7 minutes or until a beep sounds if using electronic.
Other factors
External factors can also influence the result:
- Stressful situation the day before;
- Insomnia or interrupted sleep;
- Physical stress, fatigue;
- Cold;
- Sexual intercourse less than 8 hours before measurement;
- Flight, change in climatic conditions.
Some skeptics believe that the basal temperature chart is not accurate enough, since many factors influence the temperature, which makes analytics difficult.
But with its help, many women were able to plan their pregnancy by calculating the optimal time for effective intercourse. Even if it is not informative enough in terms of determining early pregnancy, but by the points of the graph indicating what the basal temperature is after menstruation, at the time of ovulation, and before them, one can judge the hormonal balance that supports a woman’s reproductive function, notice deviations in time and take appropriate measures.
Pathological causes
It happens that an increase in temperature at the beginning of menstruation is associated not with physiological, but with pathological factors that require immediate identification and elimination. It is necessary to consult a doctor if the thermometer shows 38–39 °C, and menstruation is accompanied by a sharp deterioration in health.
Inflammation of the appendages
Adnexitis is an inflammatory process in the pelvis, affecting the ovaries. Develops as a result of hypothermia, a sharp decrease in immunity, in combination with sexually transmitted infections. It manifests itself as a rise in temperature to subfebrile levels, a pulling sensation in the lower abdomen, radiating to the lower back, and weakness. As the disease progresses, the temperature may become higher and the pain may intensify. Sometimes the patient requires urgent care in a hospital setting.
Endometritis
An inflammatory process in the uterine cavity, spreading to its upper layer (endometrium). It occurs as a consequence of a recent termination of pregnancy, spontaneous abortion, or diagnostic uterine curettage. An infection can also develop after using drugs to induce a miscarriage if the fertilized egg has not completely left the uterus. Remains of embryonic tissue can fester, causing an acute bacterial infection.
Conclusion
Thus, what the basal temperature should be after menstruation depends on the characteristics of the female body in each specific case. You can focus on the average standards with which we introduced you. It is important to follow the rules for measuring and plotting.
A two-phase curve with a visible pre-ovulatory decline, an increase in the second period of the cyclic process and a decline before menstruation is considered normal. The absence of the latter indicates the presence of pregnancy if the increase lasts more than 18 days after ovulation.
«>