Many girls dream of getting pregnant, but desire alone is not enough to successfully fertilize an egg. The right approach will increase the chances of having a baby. The most appropriate time is the ovulatory period. The arrival of ovulation and early pregnancy can be determined using basal temperature, since it is influenced by hormonal levels. Basal temperature during menstruation can determine not only cycles, but also show gynecological diseases and abnormalities in the functioning of the reproductive organs.
Measuring basal temperature helps determine the day of ovulation
What is basal temperature
Basal temperature during pregnancy, before and after menstruation, as well as during menstruation, is the lowest temperature indicator that is measured during sleep or rest. It acts as an indicator that varies depending on the changes that have occurred in the female body on a hormonal background.
Correct use of a thermometer and compliance with the basic rules of measurement will allow you to determine:
- the beginning of the ovulatory cycle;
- ovulation date;
- ovarian productivity;
- preparing the uterus for pregnancy.
If the temperature during menstruation is normal, then this is the first step towards successful conception.
BT in the first phase of the cycle
The first phase of the menstrual cycle is called follicular, or menstrual.
The first day of the cycle is considered the first day of menstrual bleeding. Typically, the temperature in the follicular phase is low, less than 37C in the rectum.
The duration of the phase is about 14 days. The end of the first phase corresponds to the moment the egg leaves the follicle - ovulation. Before ovulation, BT normally decreases, and after it increases, which is due to the production of the hormone progesterone by the corpus luteum. The corpus luteum forms at the site of the ruptured follicle and produces progesterone within 10-12 days.
How to measure correctly
The use of a basal thermometer is common not only to determine the best days of pregnancy, but also during it. The girl should continue to keep a schedule and fill it out daily. Such information is necessary to monitor the condition of the fetus. Controlling the temperature will allow you to timely identify deviations during the baby’s development or begin timely treatment of inflamed organs (if any).
Measurements must be taken daily
Temperature during pregnancy and menstruation is measured the same way:
- Measurements must be taken at the same time every day.
- You must select one of the places to fill out the chart: vagina, oral cavity or rectum.
- The thermometer should be used immediately after sleep.
- When waking up, minimize movements and even conversations.
- The beginning of the procedures is the first day of the cycle.
- Use only one thermometer.
- Fill out the schedule carefully.
- In case of illness, stress or poor health, mark the days on the schedule.
- Do not measure temperature during the day, in the evening, or at any time of day other than the morning. If you missed the morning measurement: either skip the recording, or go to bed after lunch for at least 6 hours, then take the measurement in the same way as in the morning.
Many girls, when they become pregnant, begin to measure their temperature several times a day. You shouldn't do this because it constantly changes throughout the day, especially during physical activity.
Ura||
BASAL TEMPERATURE, MENSTRUAL CYCLE
1. In the second phase, the temperature does not rise above 37. Does this mean that there is no ovulation/pregnancy is impossible
No, that doesn't mean it. In the second phase, the normal temperature is 36.8C, and sometimes even lower. It is the temperature difference between phases that is important, not its absolute values.
2. The temperature jump in the second phase is unclear, spread over days
It does not matter. And this is not a sign of lack of ovulation or egg deficiency
3. Is a drop in temperature in the middle of the second phase a sign of the death of the zygote?
No. And it must be remembered that fluctuations in BT by fractions of a degree within the normal BT of the second phase are not a decrease. 37.1-36.9 is NOT a decrease in BT.
4. What does it mean if BT is monophasic?
Firstly, this may mean an incorrect interpretation: considering a slow rise, BT below 37.0, fluctuations in BT within the second phase as monophasic. And this is not true. Secondly, BT may be measured incorrectly - later than 8 am, for example. Thirdly, presenting the results in the form of a graph with an arbitrary scale sometimes masks the presence of phases. And even if all the measurement rules are strictly followed, the BT is still monophasic, and this does not always mean the absence of ovulation. There are people whose BT data, measured according to all the rules, do not coincide with the data of ultrasound monitoring of the follicle, the onset of ovulation and pregnancy. I have a case of an ideal pregnancy with BT up to 8 weeks = 36.6. Didn't measure further
5. How to measure BT correctly?
In the morning, at the same time every day, from 6 to 8 (depending on the time of year), without getting out of bed (the usual getting up at night does not count, it is important not to get up just before the measurement), 5 minutes with a mercury thermometer in a straight line intestine at a depth of approximately 5 cm. You can fall asleep with a thermometer; it will fall out and keep the temperature level until you wake up.
The results are recorded in the columns: date, day of the cycle, BT, special circumstances (different measurement time, unusual rises at night, sexual activity the day before, menstruation, ailments, headaches, bowel movements, rise in general body temperature, taking medications (except daily - vitamins)
Do not draw graphs or interpret the BT yourself! Especially using Internet data. If you doubt the doctor’s interpretation, check ovulation in more objective ways - ultrasound monitoring of the follicle and endometrium
6. Is it possible to measure basal temperature in the mouth, in [email protected] #$%&, with an electronic thermometer
No. An electronic thermometer, in addition to the fact that it can err unpredictably, is too sensitive, and if you plot a graph, the fluctuations will be very pronounced and you will be upset when you see a “fence” instead of the correct BT
Basal temperature is the temperature of the blood of a sleeping body. Of course, it can be measured in [email protected] #$%& and in the mouth and armpit, taking into account the temperature difference on the skin and mucous membranes. But only in the rectum it changes cyclically, depending on the function of the ovaries (which is what we want to determine by measuring BT) - hormones synthesized by the ovaries flow through the ovarian veins and create cyclical fluctuations in BT. Due to the peculiarities of the blood supply to the ovaries, these cyclic fluctuations are detected only rectally. Sometimes they are so pronounced that they can be determined when measuring body temperature in another place, sometimes even the general body temperature in the armpit changes cyclically - but this is not a rule and does not always happen, you cannot rely on these data in such a delicate matter as determining ovulation - this is just only measuring body temperature. And the determination of ovulation is based on measuring basal rectal temperature, i.e. blood temperature in the ovarian vein. Don't do useless things. If there is no possibility or desire to measure rectal temperature, do not measure BT at all. There are other, more objective methods for determining ovulation
7. What cycle length is considered a delay?
More than 15 days 2 phases. The total length of your cycle does not matter, even if you have never had delays or they always meant pregnancy. If according to BT the length of the second phase is less than 15 days, no matter what the length of the cycle, doing the test is useless.
8. Are late ovulation and a long cycle signs of egg deficiency? Does this require treatment?
No, it is not and does not require it.
9. Is it necessary to correct the short/unexpressed/absent second phase with duphaston/utrogestan?
No. The second phase is a consequence of the first. The presence or absence of the corpus luteum and the level of progesterone secreted by it depend on the usefulness of the egg, which matures in the first phase, and the occurrence of ovulation. If medical intervention is required, it is only in relation to the first phase and ovulation. Taking duphaston can mask the inferiority of the second phase, but will not be able to eliminate it and make the failed ovulation complete and increase the chances of pregnancy. Duphaston is taken during the ovulatory cycle to support a possible pregnancy.
10. On what days should I take duphaston if I have an irregular cycle?
According to BT and ultrasound monitoring - in the second phase. Not necessarily from the first day, you can delay the start of taking it, but just don’t start it before ovulation, because it can block ovulation. In no case should you take duphaston blindly from days 16 to 25 of your cycle, even with a regular cycle - you need to track the beginning of the second phase and start duphaston no earlier. And they stop taking duphaston on the first day of menstruation. If it is canceled earlier, it may cause termination of the pregnancy.
11. On what day should I donate blood for progesterone if I have an irregular cycle?
According to ultrasound and BT data - on days 5-7 of the second phase
12. Does duphaston affect BT
As a rule, no. But in some sensitive people it can affect both BT and the length of the second phase (cause a delay). Most likely, this is not the influence of the hormone itself, but the psychological effect of active pregnancy planning.
13. What does it mean when BT data does not coincide with data from other methods of determining ovulation?
BT is not an objective method, it is quite indirect even with absolutely correct measurement and interpretation, which is rare. Ovulation tests based on determining the concentration of LH in the blood are also biased - it can increase for reasons not related to ovulation. The definition of cervical mucus, fern symptom, etc. is also biased. Ultrasound monitoring of the follicle and corpus luteum is quite informative, but it is difficult to differentiate the luteinization syndrome of a non-ovulated follicle (although this syndrome does not occur so often as to refuse ultrasound monitoring because of it). All the same, today ultrasound monitoring, especially with determining the level of hormones during follicle growth (LH, FSH, estradiol) and in the middle of the second phase (estradiol, progesterone), remains the most informative of the not very expensive methods - of course, if it is done by a qualified specialist a good device with a vaginal sensor.
The most accurate method of verifying ovulation is laparoscopy in the second phase and determining the stigma - the place where the egg leaves the ovary.
14. Is it necessary to measure BT during pregnancy, is it possible to judge the well-being of pregnancy from it?
The rise in BT in the second phase and during pregnancy is caused by high levels of progesterone secreted by the corpus luteum. During pregnancy, the corpus luteum is supported by the hormone hCG, secreted by the chorion, the membrane of the embryo. Even if the embryo dies, until a complete miscarriage occurs, the membrane remains in the uterus, and therefore the pregnancy test will be positive and the BBT will be high. They cannot be used to judge the viability of the embryo. Therefore, there is no need to simply measure BT and, even more so, worry about its decrease from 37.1 to 36.9! Such fluctuations in BT are an error in the method, and not a real “decrease,” just as reverse fluctuations are not an increase.
How does the indicator change during menstruation?
A low or high temperature during menstruation is not a terrible phenomenon, since it depends on several factors and changes with each cycle. The main thing is that it does not go beyond the norm.
Temperature depends on cycle stage
Information is given for a regular menstrual cycle:
- Primary follicle formation. The temperature should not be less than 37 C, and when moving into the second phase of the cycle, not less than 37.4 C.
- Pre-ovulatory period. At this time, estrogen levels rise and affect the temperature. It should correspond to numbers from 36.5 to 36.9 C. If it is higher, then this indicates estrogen deficiency.
- Ovulation. The basal temperature during this period should be around 37 C. In case of a low indicator, there is a risk of anovulation. In this case, the temperature ranges from 36.5 to 36.9 C. It is worth noting that there may be several such periods in 365 days, and this is not a concern. But if it repeats from menstruation to menstruation for several months, this indicates abnormal disorders in the female body.
- Postovulatory period. In this case, the temperature drops to 37-37.2 C. If it fluctuates by 0.3-0.4 C, this may be estrogen-progesterone deficiency.
This video talks about measuring basal temperature during menstruation:
This is standard information provided by clinical trials. No conclusions can be drawn based on the indicators.
Each organism is unique and has its own characteristics, so only a qualified doctor can provide accurate information.
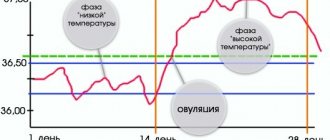
Indicators during ovulation
An unusual basal temperature before or during your period may indicate a number of problems. But measurements on other days are no less indicative. Normally, the next morning after the release of the egg, a woman observes an increase in temperature. It can be either sudden or gradual.
For some, on the very first day it increases by 0.4 degrees, for others this difference increases in 2-3 days. Both of these situations are completely acceptable. In the case when the rise in values takes more than 3 days, one can suspect the inferiority of the egg released from the ovary or a lack of estrogen. As a rule, it is almost impossible to get pregnant in such a cycle.
Based on this, we can conclude: a sharp rise in body temperature in the middle of the cycle indicates the onset of ovulation, a drop at the end on the eve of menstruation indicates the absence of pregnancy. Experts advise monitoring fluctuations in basal temperature before menstruation (a week). This way, various pathologies can be excluded.
To make the method more informative, the values of basal temperature before menstruation are included in a graphical representation. To draw up a graph that will help identify the period of increased temperature before menstruation, you will need a pen and a sheet of squared paper. You need to draw coordinate axes, where one axis (x) depicts the order of the days of the cycle, and the vertical axis (y) is the rectal temperature for each day. The 37°C mark is best marked with a dividing line. It will symbolize the difference between the phases of menstruation.
Why is the temperature higher than normal?
High temperature during menstruation can vary from 37.5 to 38.5. Experts note that for some women the norm was 38 C, and no negative connotations were observed. But any temperature fluctuation may indicate gynecological diseases or inflammatory processes in the body.
It is impossible and even dangerous to independently determine the cause of this phenomenon, therefore, when maintaining a personal schedule of the menstrual cycle and detecting deviations, you must consult a specialist.
It is very important to visit a doctor on time
Pregnancy and its effect on BT
Conceiving a child and the process of bearing it is associated with monthly cycles and has a great impact on all systems and organs inside the female body. Naturally, this cannot but affect fluctuations in basal temperature.
Therefore, if you systematically take measurements, it will not be difficult for you to determine the onset of pregnancy.
However, for this, as has been repeatedly said, the requirements for the measurement process and the subsequent construction of the graph must be correctly observed.
The appearance of pregnancy will cause certain changes in your schedule:
- Temperatures will exceed 37 degrees Celsius and will remain at this level for at least three days more than in previous months. That is, if before this temperature jump (that is, before the onset of ovulation) 12 days had passed since the last menstruation, and this month 16-17 have already passed, we should talk about the fact of conception.
- Pay attention to the number of temperature fluctuations during the menstrual cycle. The usual schedule consists of two waves, and pregnancy will be reflected on it in the form of an additional, third surge.
- Basal temperature is at a high level for more than three weeks - this is pregnancy.
When the temperature is below normal
The temperature on the first day of menstruation should not be less than 37 C. In many cases (except for individual characteristics) it indicates a complication of the pregnancy. A low temperature is a reason to visit your doctor. But this does not mean that you need to immediately run to the hospital. It is worth waiting a couple of hours and measuring the temperature again, if the indicator is the same, only in this case contact a specialist. The fact is that hormonal levels are not always stable and estrogen and progesterone constantly change their values, affecting temperature.
When will measurements be meaningless?
Measuring BT values should not be carried out if:
- you have a delay in menstruation and want to determine the onset of pregnancy;
- after unprotected sex when you think you are pregnant.
- if you have not taken regular measurements for at least three months before the delay. Information obtained after a single procedure will not give you anything;
- if you want to use the calendar method of birth control. It will simply not be effective, so it will not be suitable for those people who do not want to have children.