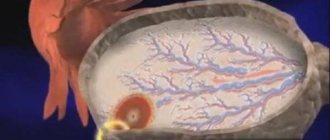
Organ structure
The organ is made up of connective fibers tightly intertwined with arteries, capillaries and vessels. On average, the volume of one ovary is 8 cm3, but during the menstrual cycle this size may change.
The ovaries are located on the sides of the pelvis. They connect to the fallopian tubes. The feeling of pain in the ovaries after menstruation makes itself felt because the ligaments with these tubes are penetrated by nerve fibers.
These organs can undergo changes throughout life, in particular, there are two types of development of changes:
- Irreversible – release of the follicle and maturation of the egg;
- Regular – changes within one menstrual cycle.
What are the main recommendations?
Regardless of the diagnosis, doctors recommend adhering to the following basic recommendations:
- avoid stressful situations;
- do not lift heavy objects;
- temporarily abstain from sexual intercourse and monitor your well-being;
- take a warm bath if there are no contraindications.
It is better to give preference to a balanced diet. Give up bad habits.
From this video you can learn about the causes of pain in the ovaries:
Pain after menstruation
Before menstruation begins, a woman's hormonal background undergoes several changes. The corpus luteum actively produces estrogen, the body prepares for future fertilization. When fertilization does not occur, menstruation begins. And after they are over, the hormonal levels return to normal.
It is during these days that symptoms of chronic diseases and pathological changes may appear. These include:
- Displacement of the reproductive organs - it can be a consequence of active drug therapy for infertility, hormonal contraception, or is a congenital anatomical feature. When using hormonal drugs, the reproductive organs increase slightly in size and can put pressure on neighboring organs and mucous membranes penetrated by nerves.
- Instability of psychological state. Since the menstrual cycle does not pass without changes in hormonal levels, a woman may experience despondency, insomnia, anxiety, and fear. Depressive conditions can cause a decrease in the activity of hormonal organs. In this case, the ovaries can suddenly become ill and calm down just as quickly if the root cause is eliminated.
- Endometriosis. This disease is characterized by excessive separation of the uterine endometrium and its growth. At the same time, the endometrium can end up in both the fallopian tubes and the ovaries. This can cause pressure on the nerve networks from the inside.
- Ectopic pregnancy. Despite the fact that menstruation has finally begun, the development of the fertilized egg in the fallopian tube often makes itself felt much later.
- Peritonitis. Inflammatory foci in the abdominal area are manifested by the fact that after menstruation the entire area of the lower abdomen hurts. Peritonitis occurs against the background of diseases that worsen during menstruation - cysts, neoplasms, hemorrhages into the ovarian cavity.
What treatment
Treatment is selected on an individual basis. The doctor takes into account: the patient’s age; main diagnosis; existing contraindications.
Treatment consists of prescribing medications. The patient may be recommended medications:
- hormonal to stabilize hormone levels;
- painkillers to improve well-being;
- anti-inflammatory to eliminate the inflammatory process;
- antibacterial drugs to suppress pathogenic microflora;
- vitamin and mineral complexes to stabilize well-being.
Self-selection of medications is strictly prohibited. If the pain is severe, call an ambulance. Do not take medications until the doctors arrive. Otherwise, the symptoms will be erased and making a diagnosis will be difficult.
Pain on the left
Common reasons why pain may occur in both ovaries after the end of menstruation have been listed. Some patients complain that the ovary on the left and only one hurts.
Even when the disorders listed above affect both ovaries, some of them may be localized and affect the left one. This area of the peritoneum contains the intestines and urinary system. Therefore, pain in the left ovary can become a symptom:
- Oophoritis is an inflammation that most often affects the left ovary; the pain is paroxysmal;
- Cysts are accumulations of fluid in a small oval that puts pressure on the ovary;
- Apoplexy - effusion of blood into the ovarian cavity.
In this case, the symptoms and pain are more pronounced than with a similar diagnosis for the right organ, since the intestine is located nearby. The pain will be more pronounced when the intestines are swollen and feces pass through it.
Ovarian pain before menstruation
Many girls do not have problems with their periods, but there are those who suffer from irregular periods. The ovaries may hurt before menstruation, and the reasons for this are varied. One of them is hypothermia, which has a negative effect on the condition of the appendages by developing inflammation in them.
To accurately determine the cause of the pathology, you should consult a gynecologist. Only a specialist, based on the clinical picture, can accurately name the cause of pain.
A fairly common aspect of pain is cysts on the ovaries. They are fluid-filled neoplasms. They often appear if the follicle is overripe. In a normal state, it matures and ruptures, however, if this does not happen, a cystic formation appears in its place.
The main causes of pain in the appendages:
- hormonal disbalance;
- neoplasms;
- atypical location of the ovaries.
Pain on the right
If the right ovary hurts after menstruation, the reasons may be hidden in the same diseases as for the left one. But there are several conditions that are more typical for the right ovary and pain in it:
- Apoplexy is damage to blood vessels in the right ovary due to infection, inflammation, or heavy physical activity. Most often it occurs in the right ovary due to the fact that it is fed by a large artery.
- Appendicitis - developing inflammation of the appendix can also cause pain in the area of the right ovary.
Also, pain for both ovaries can also occur due to an increase in the size of the uterus, which puts external pressure on the organs and displaces them somewhat. This condition is accompanied by acute pain and requires medical attention.
What pathologies may be
It is important to distinguish natural pain from pathological pain in time. This can only be done in a hospital using diagnostics.
The patient may be diagnosed with the following abnormalities:
- inflammatory process;
- cyst rupture;
- adhesions;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- inflammation of the appendix.
The sign does not always indicate gynecological diseases. There is a possibility of damage to the genitourinary system. It is strictly forbidden to independently select medications to eliminate the disorder. This will lead to poor health.
The presence of the disease is unlikely when the symptom is mild and short-lived. A woman should monitor her well-being.
Cyst and neoplasms
Any of the ovaries can be subject to cyst formation. Most often, the cyst affects the left side, but doctors find it difficult to answer what these statistics are related to.
The formation of a cyst occurs due to the inability of the egg to be released and the thickening of the ovarian membrane. The organ can hurt both before and after menstruation. Additionally, the cyst is accompanied by symptoms such as increased urination, nausea, menstrual irregularities, and slight bleeding in the middle of the cycle.
A discovered cyst requires constant gynecological monitoring, treatment, and sometimes immediate removal is required if it increases in size and interferes with the functioning of other organs.
Diagnostic methods
With ovarian diseases, it is impossible to make a diagnosis on your own, since similar symptoms occur in many diseases. Pain of any kind in the lower abdomen is a reason to consult a gynecologist. He examines and prescribes
Microflora smear
examination:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- blood tests - general, hormones;
- Analysis of urine;
- vaginal smears for microflora;
- PCR for infections, immunological tests.
If necessary, it may be necessary to introduce a contrast agent into the uterus and study its distribution - hysterosalpingography, examination of the ovaries using an endoscope - diagnostic laparoscopy, tomography.
Apoplexy
A fairly serious disorder, which may be accompanied by pain after menstruation, is bleeding. It occurs due to vascular damage, excessive physical activity, as a complication of inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs.
Most often observed in the right ovary. Symptoms of apoplexy are sharp pain in the ovary throughout the menstrual cycle, which can radiate to the lower back, groin, and rectum. Pale skin, dizziness, vomiting and nausea, chills and increased body temperature may also indicate organ apoplexy.
If pain develops, body temperature increases, and the condition becomes worse, immediate help is required to prevent the development of intra-abdominal bleeding.
Causes and symptoms of enlargement of the right appendage
What does the ultrasound diagnosis “enlarged right ovary” mean? An organ exceeding the permissible size does not always indicate pathology. Normally, it can increase during lactation (due to a large amount of prolactin in the body), during ovulation or adolescence.
It happens that an enlarged appendage indicates a “problem” in the body’s functioning and requires an early visit to the gynecologist. The causes of the pathology are:
- long-term and continuous use of hormonal drugs,
- constant nervous shock, emotional tension, depressed mood,
- sudden weight loss in a short period of time,
- obesity,
- improper functioning of the endocrine system.
In addition, the right appendage in girls may increase due to the following diseases:
- Inflammatory processes localized in the pelvic organs. Sometimes the infection is asymptomatic and then becomes chronic. An increase in the size of the ovary in women provokes the formation of infiltrate and adhesions. In advanced cases, the uterus and appendage are palpated as one organ.
- Cervical erosions. The inflammatory process caused by pathogenic microorganisms sometimes moves to the ovary, located on the right or left, and causes its enlargement.
- Presence of cystic neoplasms. The size of the appendage often exceeds the norm when it is affected by a cyst, the diameter of which is more than 3 cm. Ultrasound is used for accurate diagnosis.
- Existing malignant tumors of the pelvic organs (enlargement of the ovary is sometimes observed during its metastasis). It is possible to detect deviations by palpation only in the last stages of the pathology.
- Appendicitis, which is due to the fact that the right appendage and appendix are actually adjacent to each other.
If a woman’s right ovary enlarges, the pathology may be accompanied by unpleasant symptoms:
- bloody discharge outside the cycle,
- pain during sexual intercourse and when urinating,
- purulent vaginal discharge.
White discharge after ovulation
This page contains the most popular posts and comments from our users on the topic “White discharge after ovulation.” This will help you quickly get an answer to your question, and you can also take part in the discussion.
Girls, tell me, is this normal? Ovulation was 06/04/15. In the morning, an ultrasound confirmed... In the afternoon of this day, the stomach began to pull (like before menstruation). And so it was for a day! The doctor said it's normal after ovulation. Yesterday 06/06/15 (I apologize for such details) I saw pink-brownish discharge on my panties, one large drop. This morning there is quite a bit of that too. What can it do.
yeah, not vomiting, but like a lump in the throat and almost the whole day... dizziness... that time there was a miscarriage somewhere around that time, I didn’t feel that bad. and here it’s really cruel) well, that means the baby is fine there, he’s giving signs)))
3 days after ovulation, there is such a thick creamy white discharge, why is this? Could it be that this is a sign that conception was successful?
Type "G"
- Infertile mucus, progesterone-dependent. Forms a clot in the lower parts of the cervix, closing it hermetically. Protects against bacteria, viruses, sperm. Cloudy, thick, does not crystallize. Does not have soda ions. 90% consists of water. Gives a “dry” feeling.
Type "L"
- Semi-fetal mucus, estrogen-dependent. Formed along the entire length of the cervix. Crystallizes in the form of fern leaves. Its functions: elimination of defective sperm, nutrition of sperm, their maturation. Sperm can remain in this mucus for up to six days. Supports fetal mucus. Contains 95-96% water. Gives a “wet” feeling.
Type "S"
— Fetal mucus, estrogen-dependent. It is produced by the upper glands of the cervix. Fills the entire uterus and tubes, and pours out. Its functions: possible
Source
Sex with ovarian inflammation
Acute oophoritis or a period of exacerbation of its chronic format is a contraindication for sex. When the glands are damaged during friction, women experience not just discomfort, but real pain.
During this period, many patients do not experience sexual desire, which is explained by psychological and physiological discomfort.
Inflammation of the ovaries is a serious gynecological pathology that requires adequate treatment for the condition. That is why, when pain appears in the lower abdomen, a woman needs to consult a gynecologist and undergo a course of therapy.