Surgery to remove the ovaries is carried out for a number of reasons that provoke dysfunction of the ovary and threaten the woman’s life. These reasons are:
— tumors and neoplasms;
- complicated inflammation of the ovaries and appendages (adnexitis);
- rupture of an ovarian cyst (ovarian apoplexy);
- ectopic pregnancy;
- a tumor in the mammary glands, which is formed under the influence of ovarian hormones;
Most often, the operation involves removing one ovary. If an ovary is removed on a woman of childbearing age, then most often after the operation she will experience symptoms of menopause. They appear a few days after the operation and get worse every month. In this case it is observed :
- Sharp increase in heart rate;
- Feeling hot;
- Vaginal dryness;
- Urinary problems;
- Fatigue, decreased mood;
- Migraines, dizziness.
Pain after removal of the ovary is often accompanied by postoperative bleeding, inflammatory processes, and elevated body temperature in the first days after surgery. Sometimes pain after surgery can be a symptom of infection in the tissue during surgery. Pain in the first days after surgery spreads throughout the entire pelvic area. The pain is girdling, sharp, cutting. There is an increased body temperature, general weakness of the body, pain intensifies when walking, urinating, defecating. After removal of the ovary, the risk of adhesions in the pelvic cavity increases.
Pain after removal of ovary and leucorrhoea
Pain after removal of the ovary is most often associated with the postoperative period and surgery. In this case, women experience bleeding. Leucorrhoea is not profuse and is observed for several days after surgery. Also, spotting may occur several times within a month after surgery for three to four days. This is due to the removal of the ovary and menstrual irregularities. This type of leucorrhoea and pain is normal.
The disorder is heavy bleeding and severe pain in the area of the removed ovary, which lasts more than three days. In this case, an increase in body temperature, dizziness, and loss of appetite observed These symptoms may indicate infection during surgery and severe tissue inflammation. The infection provokes a strong increase in temperature, stabbing, sharp pain in the side from the side of the removed ovary. In this case, dark red or scarlet discharge with an unpleasant, pungent odor is also observed.
Consequences of tubal removal
Removing the fallopian tubes is called a salpingectomy. The most likely complication after salpingectomy is an increased risk of infertility. So, if one fallopian tube is removed, the likelihood of a desired pregnancy is significantly reduced - up to 50 percent. has, then a subsequent conception may again result in an ectopic pregnancy.
After removal of the fallopian tubes, no reconstruction is carried out - it simply does not make sense. The fact is that the fallopian tube is normally capable of contracting (peristalsis), and thanks to this, a fertilized egg can move along the tube to the uterus, but with plastic surgery of the fallopian tube, this is, alas, impossible to achieve. It is noteworthy that after removal of the fallopian tube, menstruation will occur regularly, but provided that the ovaries are functioning normally.
After surgery to remove the fallopian tubes, pain often remains. Pain in the pelvic area in such cases indicates the formation of adhesions in this place.
Salpingectomy is sometimes prescribed to prepare a woman's body for in vitro fertilization (IVF) - this procedure helps ensure the woman's safety from an ectopic pregnancy. But it should be noted that removal of the fallopian tubes negatively affects the process of follicle maturation and ovulation. Therefore, in each specific case, the need to remove the fallopian tubes is determined only by a doctor. Typically, surgery to remove the fallopian tubes is performed when the hydrosalpinx is large or if it has existed for six months or more. The size of the inflammatory formation helps to establish the pelvis.
Recovery after fallopian tube removal
Rehabilitation after salpingectomy consists of adequate anti-inflammatory therapy. This therapy is necessary to ensure that the second fallopian tube remains as patent as possible. As a rule, after surgery, absorbable drugs are prescribed - vitreous, aloe, as well as physiotherapeutic procedures - such as electrophoresis.
To prevent the formation of adhesions after removal of the fallopian tube, the cheapest and simplest method is physical activity, as well as an early start in eating.
Hello Svetlana.
If the healing process after surgery proceeds without complications, then complete healing of damaged tissues and restoration of the body occurs in 3 to 6 weeks. During this period, when a woman who has undergone surgery to remove the fallopian tube is undergoing rehabilitation, it is extremely important to follow all the doctors’ recommendations, carry out the prescribed measures and manipulations that are necessary for the fastest and smoothest recovery.
In addition to recommendations aimed at speeding up the healing process, there are also restrictions, neglect of which can cause significant harm. Strict restrictions, for example, include physical activity and sexual contact.
Physical activity after removal of the fallopian tube
Physical activity after surgery to remove the fallopian tube is strictly prohibited. There can be no talk of any stress, sports, and especially hard physical work in the first 2 to 3 weeks after the operation.
Returning to usual physical activity in sports is possible only with the permission of a doctor, and this process should be gradual and very slow. Starting with minimal loads, you can gradually and very carefully return to your usual standards.
If we talk about hard physical work, then if possible you will have to give it up altogether - this will preserve your health, because you are a young woman who cannot destroy her body with unbearable physical exertion. In the first month after surgery, you certainly should not experience intense stress or do hard work. The question of resuming work will shock any doctor, because for at least 3 months a woman should not lift weights exceeding 3 kg.
If there is no opportunity to refuse work, then you will have to reduce your workload to a minimum in order to avoid the development of complications and health problems. This does not mean at all that after surgery to remove the fallopian tube, everything is strictly prohibited for you. No! But after such health problems, it is necessary to take into account the fact of the operation, disruption of the reproductive system, functioning of the body, etc. There are certain medical recommendations that it is better for a woman to adhere to, so as not to end up on the surgeon’s table again.
Sex life after fallopian tube removal
The main reason why sexual intercourse after gynecological operations is prohibited is the likelihood of infection. After the operation, both general and local immunity decreases; the body is not able to withstand the attacks that it can withstand on ordinary days. In addition, after surgery, a wound surface remains in the body (at the site of removal of the fallopian tube), and 2 weeks is quite enough for tissue regeneration in the absence of medical contraindications.
However, you should not start sexual activity at your own discretion, because... The specialist should conduct an examination and make sure that the healing process was successful and there are no signs of infection or any other complications. Oral sex is not subject to the restriction, so married couples are given a very real opportunity not to experience a lack of sexual pleasure.
Other rehabilitation factors
Naturally, in the postoperative period, the doctor should prescribe a gentle diet, excluding salty, hot, spicy foods. Alcoholic drinks are also strictly prohibited. Physiotherapy may also be recommended in the required number of courses. Physiotherapeutic measures will help speed up wound healing and regeneration of damaged tissue. It is also worth consulting with your doctor about taking vitamin and mineral complexes. The most popular are vitamin preparations such as “Multi-tabs”, “Vitrum”, etc.
Sincerely, Natalia.
In terms of frequency of occurrence, the tubal form of ectopic pregnancy is in first place. That is why the issues of its prevention, as well as treatment, are so relevant. Given the absence of specific symptoms in the early stages, tubal ectopic pregnancy in 80% of cases is detected at later stages, when emergency surgical intervention is necessary.
Modern techniques in obstetric and gynecological practice make it possible to perform organ-preserving operations that sharply reduce the risk of developing infertility in a woman. Unfortunately, there are often situations when preservation of the fallopian tube is impossible for a number of reasons. If the course of an ectopic pregnancy is complicated by a ruptured tube and intra-abdominal bleeding, then an operation is performed to remove the ectopic pregnancy with cutting off the fallopian tube.
Those methods of removing the fallopian tube that are used today are used quite selectively, taking into account the characteristics of a particular clinical case.
The main indications for removal of the fallopian tube include:
- in case of extensive damage (rupture) of the fallopian tube;
- to stop massive intra-abdominal bleeding;
- if the woman herself does not want to have children in the future.
If an ectopic pregnancy was spontaneously terminated due to rupture of the fallopian tube with subsequent bleeding, then emergency surgery is performed.
Preoperative preparation in this case includes intravenous administration of special solutions, determination of blood type and Rh factor, and a gynecological examination.
The main goal of emergency surgery is to stop bleeding as quickly as possible. In this case, a laparotomy technique is used (dissection of the anterior abdominal wall), as a result of which it becomes possible to quickly stop bleeding from a ruptured tube, followed by its removal. In this case, the fallopian tube is removed only after the bleeding has completely stopped and blood pressure has normalized.
An important point is to assess the condition of the ovary on the affected side. If there are no changes in it, then the fallopian tube is removed while preserving the ovary.
To maximize the preservation of a woman’s reproductive function, atraumatic medical instruments are used during laparotomy, as well as special suture material.
If the woman’s condition is satisfactory and there are no corresponding contraindications, then it is possible to remove the ectopic pregnancy. Laparoscopic removal of the fallopian tube is performed using special instruments to minimize traumatic effects. Such instruments include an electrocoagulator, stitching devices and ligatures.
Pain after ovary removal and infertility in women
Many women are frightened by the thought that after the removal of one ovary, pregnancy does not occur. However, this is not the case. Of course, if two ovaries were removed, then pregnancy, alas, will not occur naturally. But even one ovary can fully cope with all the functions necessary for conceiving a child. Pain after ovary removal is normal if it lasts for a few days immediately after surgery. If pain after removal of the ovary torments a woman for quite a long time, this may indicate the presence of complications after the operation, which can lead to infertility in women. During surgery, the genitals may become infected and an inflammatory and adhesive process may develop. All this has an extremely negative effect on the functioning of the ovary, which can lead to infertility. Therefore, if the pain after removal of the ovary lasts long enough and is severe, then you should immediately consult a gynecologist to exclude the development of complications.
Removing an ovary or two at once (oophorectomy) is not often performed by doctors, since such a drastic measure requires very compelling reasons. This could be cancer, ovarian rupture, or ectopic pregnancy. If it is possible to save at least one ovary, the doctor will definitely do this, since the consequences of the operation for the woman in this case will not be so critical.
Pain after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, why the stomach hurts and the ovary pulls after surgery
Removal of cystic tumors using laparoscopy is a fairly simple and painless operation, so the recovery process in the postoperative period is quick. However, some women experience pain after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst. Painful sensations are rare, but still tend to bother the patient for some time.
The lower abdomen may linger for several days. As a rule, unpleasant sensations do not pose a threat to the patient’s health. In most cases, they go away without any treatment. But it is still worth remembering that sometimes prolonged pain after surgery should cause concern in a woman.
In what cases does such a symptom remain the norm, and when is it necessary to visit the treating gynecologist as soon as possible?
Painfulness of the procedure
Although some patients experience ovarian pain after laparoscopy, the procedure itself is completely painless. The surgery takes place under general anesthesia. Anesthesia is administered intravenously. If general anesthesia is prohibited for any reason, local anesthesia is used.
A pain relief method is often used in which the medication is injected between the discs of the spine. Therefore, during the removal of the cyst, the patient feels almost nothing, even if she is conscious.
In modern medical practice, the most effective methods of pain relief are used, so there will be no pain during the procedure. We recommend you find out: If pain in the ovaries begins when sneezing
Pain syndrome after surgery
Many patients are frightened not so much by the laparoscopy process itself, but by the pain syndrome in the postoperative period. In reality, there is no reason to be afraid of this.
The fact is that pain in the lower abdomen after laparoscopy is quite rare. Unpleasant symptoms in this case are less intense than after surgical removal performed by the cavity method.
Their nature and source after lapara may vary. So, unpleasant sensations arise:
- in the area of incisions;
- in the chest and shoulders;
- lower abdomen.
Pain in the operated area most often appears immediately after surgery, while the patient is recovering from anesthesia. Doctors call it postlaparoscopic syndrome.
In this case, the nature of the pain after elimination of the cystic neoplasm is quite clear: it occurs due to injury to the soft tissues, genitals and abdominal cavity. It is especially acute at the puncture sites through which the endoscope was inserted.
Sometimes after laparoscopy, pain is localized in the upper abdomen, although surgeons do not touch this area during the operation.
Please note: About 95 percent of patients after lapara complain of quite severe postoperative pain. According to research, their intensity on a 100-point scale often reaches sixty points. Most often, this is how patients feel in the first hours.
Having completely recovered from anesthesia, women rated them at thirty points. After laparoscopy, the right ovary or left appendage hurts severely, most often for one day. After the same amount of time, the discomfort in the area of the stitches disappears.
In this case, pain may remain if the seam is injured or pressure is applied to its area.
After lapara, many women feel pain in the chest and shoulders. This is due to the fact that during surgical removal of the cyst, carbon dioxide is introduced into the abdominal cavity. This is necessary for its expansion.
As a result, some internal organs and the diaphragm are compressed. Unpleasant sensations from this may occur for the first few days after surgery. This symptom is not very pronounced, so it is tolerated quite normally by patients.
The introduction of carbon dioxide most often brings only discomfort and inconvenience.
IMPORTANT! If you have sharp or cutting pain that affects the lower abdomen and does not disappear for too long, you should visit a doctor, as this indicates the presence of a complication. In emergency cases, accompanied by ongoing severe pain in the ovaries, urgent hospitalization is carried out.
Causes of pain in the postoperative period
In some patients, after laparoscopy, the ovary is pulled, while in others, quite severe abdominal pain is observed. The reason that such sensations appear may be:
- adhesions;
- too rapid resumption of sexual activity during the period of recovery of the body (the first month after elimination of the ovarian cyst);
- the course of inflammatory processes in the genital organs;
- failure to maintain personal hygiene after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst;
- formation of internal bleeding due to suture divergence;
- infection during or after surgery;
- significant physical activity and lifting heavy objects;
- rupture of the ovarian membrane.
It is worth remembering that the larger the cyst and the more advanced the disease, the more difficult the operation is and, accordingly, the longer the recovery period. Pain caused by laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst is quite common.
However, if the pain is accompanied by fever, dizziness, nausea and vomiting, or acute pain that radiates to the lower back or lower abdomen, it is recommended to immediately consult your doctor or call an ambulance.
The stomach should not be pulled for longer than a few days.
How to relieve pain
In modern medical practice, after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, specialists tend not to use painkillers. The fact is that the unpleasant sensations are not too pronounced to require the use of anesthetics. They are prescribed only in rare cases when it is really necessary.
As a rule, painkilling injections are administered once during the process of the patient coming out of anesthesia. Doctors are in no hurry to use pain-blocking medications because they interfere with the timely detection of complications that arise during the recovery period.
This may be a relapse of cyst development after laparoscopy, organ rupture, inflammatory process and other pathological complications. Important! If twelve hours after removing the cyst using the laparoscopic method, the patient experiences acute pain, this is not normal.
In this case, additional diagnostics are required.
We recommend you find out: Can menstruation be delayed after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst?
Recommendations in the postoperative period
In most cases, surgical treatment of cystic neoplasms does not require long-term recovery. However, if the operation is not very successful, the patient may experience severe pain.
Sometimes the cause of its appearance is an incorrect lifestyle: lifting weights, active sports, washing in the bathroom. Until the sutures heal, general hygiene should be observed and the operated area should be treated daily with antiseptics.
To avoid unpleasant nagging pain in the lower abdomen, it is not recommended to resume sexual relations earlier than after three weeks.
Complications caused by laparoscopic intervention are rare, however, if there is too much pain in the lower abdomen, fever, or the formation of purulent discharge on the surface of the suture, it is worth visiting a doctor.
Please note: On the first day after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, women often experience general fatigue and weakness, so it is advisable to maintain bed rest. You should return to your normal lifestyle, including sports, no earlier than after a month.
To avoid complications and discomfort in the appendage area, it is recommended to gradually increase the load. It is important to avoid sudden movements, lifting weights of more than three to five kilograms and long trips in the first month.
It is worth doing everything possible to maintain the integrity of the stitches and prevent them from becoming infected. It is recommended to temporarily avoid tight and tight clothing. It is better to choose loose clothes that will not put pressure on the genitals.
Do not panic if in the first month after laparoscopic treatment, menstruation is more painful and heavy than usual.
You should consult a doctor if:
- the temperature reaches 37.5 degrees and lasts more than one day, and there are no other diseases;
- the pain in the lower abdomen has become too intense and sharp;
- vomiting and nausea continue for several hours;
- the stitches are red or there is pain in their area;
- There is unusual and noticeable weakness, dizziness, and confusion.
If at least some unusual signs appear, it is better not to delay consultation with your doctor.
: What to do if your stomach hurts after laparoscopy
Source: https://ProYaichniki.ru/lechenie/laparoskopiya/boli-posle-laparoskopii-kisty-yaichnika.html
Changes in the body
The importance of the ovaries for a woman’s body is very difficult to overestimate.
They are responsible for several vital functions:
- Vegetative. It is thanks to the ovaries that during puberty a girl acquires characteristic feminine features - roundness of shape, softness of skin, lack of hair on the face and body, and a gentle voice. The ovaries begin their work during the adolescent’s first menstruation and end after the onset of menopause.
- Hormonal. The ovaries produce in a certain mode two hormones necessary for the maturation of the egg and the subsequent maintenance of pregnancy - estrogen and progesterone.
- Childbearing. It is the ovaries that produce eggs ready for fertilization.
The normal functioning of all body systems gives a woman health, beauty, emotional stability and the ability to conceive and bear a healthy baby.
Reference.
When even one ovary is removed, the production of hormones is sharply disrupted, the number of ovulations decreases, appearance deteriorates and sudden mood swings appear.
If the doctor decides to remove the ovaries on both sides, the woman is completely deprived of the required estrogenic influence. She experiences early post-operative menopause, also called post-castration syndrome.
For women over 50 years of age who are already approaching the natural end of their menstrual cycles, the operation does not have such severe consequences as for young girls of childbearing age.
With the onset of natural, age-related menopause, the body gradually adapts to a decrease in hormone production and the cessation of egg ripening. After the operation, artificial menopause in women is usually extremely difficult.
Hormonal background
If only one ovary is removed, the body adapts after some time, transferring all functions to the second appendage, and the woman will experience only a short-term decrease in the amount of hormones released.
After some time, the background, supported by drug therapy, will be restored, and the woman will even be able to plan a pregnancy.
If both ovaries are removed, the production of estrogen either sharply decreases or disappears altogether, since the organ that produces them no longer exists.
Contraindications for salpingectomy
Surgical intervention for fallopian tubeectomy is carried out using two methods:
- Laparotomy
. This technique involves abdominal dissection (up to 15 cm). - . The operation is carried out using an endoscope; three small incisions are made to carry out the instrumentation.
The laparoscopic method is very well tolerated, complications are rarely observed during its implementation, and it causes minimal trauma to the woman’s body. The recovery period does not take much time, and the woman very quickly returns to her usual lifestyle.
However, there are some contraindications that limit the use of this surgical technique.
These include:
If laparoscopic surgery is not possible, abdominal surgery (laparotomy) is used.
Preparing for surgery
Before surgical treatment for fallopian tubeectomy, a woman must undergo a comprehensive examination.
She is prescribed:
The essence and conduct of the operation
If there are no contraindications, preference is given to the laparoscopic method of surgical intervention. Such an operation is possible if the clinic has the necessary equipment and the gynecologist has the skills to use this technique.
But if a rupture of the fallopian tube occurs with subsequent hemorrhage into the retroperitoneal space, this poses a threat to the patient’s life (peritonitis develops). Then they resort to laparotomy. This condition requires urgent surgery.
Operation tactics:
The same sequence is followed when performing laparoscopy, with the difference that the blood that accumulates in the peritoneal cavity is not collected and, as a result, is not transfused to the sick woman after the operation.
If we compare these two types of surgical treatment, it can be noted that laparoscopy has certain advantages:
- The operation is low-traumatic and does not cause psychological discomfort.
- After it is completed, there is a short period of rehabilitation (the woman is discharged from the hospital on the 5th day).
- After the operation there are no significant scars left on the skin.
Complications after tubal removal
Undesirable consequences sometimes occur after a fallopian tubeectomy. They help to increase the postoperative recovery period.
Typically this may occur:
Rehabilitation period after ectomy
After this operation, the main priority in the rehabilitation period is to prevent the appearance of adhesions and keloid scars.
To do this, a woman needs:
After surgical therapy, vaginal discharge usually occurs. This is a normal process if they do not contain purulent contents.
With rapid adaptation of the body, after several days the woman begins the menstrual cycle (it can have a longer duration). If its onset is accompanied by large blood losses, a blood transfusion and curettage of the uterine body may be prescribed. Early menstruation is not a sign of the development of a dangerous pathology.
Egg relocation after fallopian tubeectomy
This development of menstruation is rare. Usually they come on time and occur in a normal rhythm. Very rarely, it takes a couple of months for them to recover. This should not cause a feeling of anxiety, because it is not a pathology.
It should be noted that if the menstrual cycle has not returned within 3 months, this is a serious reason to visit the doctor. Since the appearance of such a symptom may mean that surgical therapy has led to a failure of the proper functioning of the endocrine system.
Consequences of a fallopian tube ectomy
The body of the uterus and the fallopian tubes have a common innervation; their blood supply is carried out using the same vessels. Also, they are connected by one bra.
As a result, when a fallopian tubeectomy sometimes occurs, the normal functioning of the adrenal cortex and thyroid gland changes.
With hormonal imbalance, the following may appear:
These symptoms may intensify before the onset of menstruation.
In some women, after surgery, after 3 months, the menstrual cycle may change. It may alternate with irregular periods.
The ovary, from the side of the removed fallopian tube, becomes sclerotic. This is clearly visible on ultrasound.
Some women may experience changes in the mammary glands:
- Their coarsening begins.
- Hypertrophy is noted.
- The thyroid gland enlarges.
- Sometimes weight gain occurs, and male-type hair growth occurs (hair grows on the face and body).
This clinical picture may be intensified if surgery was performed for an ectomy of two tubes.
Stories from our readers!
“The gynecologist advised me to take natural remedies. We settled on one drug - which helped cope with hot flashes. It’s such a nightmare that sometimes you don’t even want to leave the house to go to work, but you have to... Once I started taking it, it became much easier, I even feel like some kind of internal energy has appeared. And I even wanted to have a sexual relationship with my husband again, otherwise it was all without much desire.”
Rehabilitation
The severity and duration of the postoperative period depends on factors such as:
- type of operation (laparoscopy or laparotomy);
- patient's age;
- presence of concomitant diseases;
- number of ovaries removed.
After laparoscopy, a woman can be discharged for home treatment with recommendations within three to four days. Laparotomy requires medical observation in a hospital for at least a week.
In the hospital, in addition to antibacterial therapy, the woman will be prescribed daily treatment of the sutures; after discharge, they will need to be carefully cared for at home.
The doctor will also prescribe hormonal medications, vitamins, estrogen-containing medications (including herbal decoctions) and sedatives that can reduce the severity of “post-castration” syndrome.
The onset of sexual activity is allowed no earlier than one and a half to two months after the operation.
At the same time, the woman will be able to return to work and start playing sports - walking, light gymnastics, and dancing will help strengthen the body after surgery and make it easier to survive hormonal imbalances.
Pain in the lower abdomen
The first few weeks after surgery, minor pain at the site of the removed organ is a completely natural phenomenon. Even after the body has fully recovered, nagging small unpleasant symptoms may appear from time to time. In some weather-sensitive women, the site of the operation “sinks” when the weather changes, extreme fatigue or physical activity.
Important!
If your side hurts a lot even a month or more after removal of the ovary, you should see a doctor. It is possible that adhesions have formed that require treatment.
Temperature
After laparoscopy, the temperature, even in the first days, rarely rises above the subfernal level.
Since the woman is at this time in the hospital under the supervision of doctors and is prescribed antibacterial therapy, there is no need to worry.
Abdominal surgery entails more severe consequences - in the first days after it, the temperature can rise to 38 degrees.
It makes sense to worry if after discharge the temperature rises, accompanied by symptoms such as:
- the increase is sharp and above 38°C;
- the wounds do not heal well, their edges are red, the inside is festered;
- obvious symptoms of an infectious disease appeared - wheezing in the lungs, aches, pain in the eyes;
- pain in the area of the suture or the removed organ does not go away or becomes more intense.
In all these cases, you need to see your doctor as soon as possible.
It is necessary to call an ambulance and immediately take the patient to the hospital if the following signs appear in addition to a high temperature:
- sudden profuse sweating, accompanied by strong heartbeat and dry tongue;
- chills to the point of trembling;
- vomiting or severe nausea;
- severe headaches.
These symptoms may indicate the onset of a severe inflammatory process; they are life-threatening for the woman.
Pain after laparoscopy: abdomen, navel, right side and lower abdomen
Laparoscopy is the most gentle type of surgery. The postoperative recovery period is easier, and the likelihood of complications is minimal.
Pain after laparoscopy is mild. They decrease after 12-24 hours. Most often, patients complain that they have pain in the chest or stomach after laparoscopy. To distinguish normal from pathology, it is necessary to pay attention to the intensity and nature of pain.
Pain during the procedure
Laparoscopic surgeries are becoming popular. They are increasingly used in gynecology, when removing stones in the gall or bladder, as well as when removing abdominal organs. The operation is performed through several small punctures of soft tissue.
Progress of the surgical intervention:
- The patient is given anesthesia.
- 3-4 punctures are made on the anterior abdominal wall, through which a surgical instrument and camera are inserted.
- The abdominal cavity is filled with argon or carbon dioxide to expand the intra-abdominal space.
- An image is displayed on the monitor, the surgeon observes all his manipulations.
- After the operation is completed, the instruments are removed and sutures are applied to the punctures. If the surgical intervention is complex, for example, removal of the uterus, then drainage is left in the wounds for 1-2 days. In this case, sutures are applied for 5-6 days.
Before going on the operating table, patients are concerned about the progress of laparoscopy and whether it hurts. No. The operation is performed under local or general anesthesia, so the person does not feel any manipulation.
More often, general endotracheal anesthesia is used, in which the patient is put to sleep. He regains consciousness after the end of the operation.
Local (epidural) anesthesia is done less frequently, only if there are contraindications to general anesthesia.
An anesthetic substance is injected into the spine, the patient does not feel anything below the area where the anesthesia was injected. Very rarely discomfort is possible, but these are isolated cases.
Unlike laparotomy (cavity surgery), laparoscopy is much easier to tolerate. In some cases, the patient is discharged from the hospital the very next day. Analgesics, NSAIDs and lidocaine are used to relieve pain.
Causes of pain after surgery
Painful sensations appear after surgery in all patients. Compared to laparotomy, the pain is minor and goes away much faster. The severity of pain largely depends on the patient's pain threshold.
More often, pain occurs in those places where punctures were made, as well as:
- in the abdominal area;
- near the navel (when filled with gas, the umbilical ring stretches);
- in the chest, in the side, under the ribs, in the shoulder area;
- in the throat;
- in the genital area.
During the first 12 hours, the most pronounced pain is observed. If epidural anesthesia was used during the operation, the person experiences pain in the lumbar region.
Pain after laparoscopy occurs for the following reasons:
- Injury to soft tissues and internal organs with a surgical instrument. In this case, pain is felt in the area of the incisions.
- Stretching, as well as irritation of the abdominal cavity with carbon dioxide, which was introduced during the operation. Up to 3-4 liters of gas are pumped into the patient’s stomach. After the anesthesia wears off, the intensity of pain increases. The patient feels severe pain in the upper abdomen, in the back, under the ribs, and the shoulder may even hurt. Some people who have laparoscopy have difficulty breathing. This is caused by the compression of the diaphragm. It may be painful for a person to straighten up.
- The use of a tube through which the patient breathes during surgery. This tube is inserted into the throat and anesthesia is delivered through it. After using it, the patient feels a sore and sore throat, but does not experience any particular discomfort.
The intensity of pain depends not only on the pain threshold, but also on the indications for surgery. If the pain does not subside, the temperature rises after laparoscopy, the suture festers, and tension in the abdominal wall is felt, then you need to contact a surgeon. These are symptoms of an infectious process.
You should also seek medical help in the following cases:
- cutting pain in the lower abdomen;
- redness of the seam;
- blood in the incision area;
- difficulty urinating;
- dizziness, headache, weakness;
- fainting.
Acute pain in the first 12 hours is not normal. This is a sign of a failed operation.
Abdominal pain
Patients often complain of pain in the upper abdomen, even if this area was not affected during the operation. The reason was described above. But you need to know how your stomach hurts after laparoscopy.
Painful sensations appear 2 hours after the operation, when the anesthesia stops working. The pain is severe, sometimes you cannot do without analgesics. More than 70% of patients rated the severity of pain at 30 points out of 100. Pain disappears after 12-24 hours.
It is impossible to determine where the pain is localized, whether the intestines, stomach or liver hurt. Sudden movements can cause abdominal pain. Unpleasant sensations should subside after three days, and disappear by 5-6 days. If this does not happen, you need to consult a doctor.
Pain in the upper abdomen, side and under the ribs always occurs when internal abdominal organs are removed. The peritoneum is stretched, the walls are irritated by carbon dioxide, and therefore painful sensations appear.
Accordingly, pain after removal of the gallbladder is localized in the abdomen, hypochondrium, side, as well as in places of punctures and incisions.
After surgery to remove an organ of the digestive tract, pain persists for more than a month until the functioning of the digestive system normalizes.
The pain syndrome can be relieved with analgesics - “Spazmalgon” or “Ketanov”. If it does not go away 2-3 months after laparoscopy, then this indicates adhesions.
Pain in the suture area after surgery
After the anesthesia wears off, patients most clearly feel pain in the area of the incisions. It decreases after 12-24 hours. The occurrence of severe pain several days after surgery may be associated with the development of complications. In this case, you need to consult a doctor.
The puncture sites heal quickly, since their size is only up to 1.5 cm. They heal for 7-14 days, it all depends on the puncture site. The sutures in the navel area take a long time to heal, and the likelihood of suppuration is high.
During the first week after laparoscopy, the suture hurts. Normally, the following signs appear:
- It's a dull pain;
- abdominal pain;
- slight suppuration and redness of the incision site;
- bloating.
Such unpleasant sensations should subside within 7-14 days; it is during this period that the sutures are removed. If self-absorbable threads are used during the operation, they disappear within 5-7 days. The punctures heal completely after 30 days.
Is it painful to remove stitches after surgery?
If this is done on time, the wound does not fester, there are no complications, and the threads do not grow into the skin, then there will be no pain. The patient may experience discomfort from the instrument, but not pain.
Only a doctor should remove threads; you cannot do it yourself. It is important to go to the hospital within the specified time. If the suture material grows into the skin, then removing it will be painful.
Shoulder and chest pain
This type of pain occurs very often because carbon dioxide is introduced into the abdominal cavity. It expands the peritoneum, but compresses the internal organs. Within 1-2 days after laparoscopy, there is pain in the collarbone, chest, left or right side, under the ribs. But the pain is moderate, it is easily tolerated without taking painkillers. It's more of an uncomfortable feeling.
After removal of the gallbladder or appendicitis, the shoulders hurt, the right side hurts, the back on the right side hurts, as well as the upper abdomen. The most pronounced pain is at the puncture sites.
Why does the shoulder and neck area hurt after laparoscopy? The neck, shoulders and chest hurt in almost all patients who have undergone this type of surgery.
This is due to the introduction of carbon dioxide, which is released through the lungs for several days after surgery. This is why the neck, collarbone, throat and other parts of the body hurt.
The most intense pain is the first two days after surgery, as well as during movement.
Pain in the genital area
Women often have to undergo laparoscopy due to gynecological diseases. This type of surgical intervention is used for the following purposes:
- diagnosis of genital diseases;
- tube removal for ectopic pregnancy;
- treatment of endometriosis;
- removal of ovarian cysts, adhesions, fibroids or fibroids, as well as the uterus;
- treatment of inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs.
Laparoscopy is also common among men with diseases of the genital organs. After laparoscopy of an inguinal hernia, men experience minor pain that goes away after 2-3 days. The pain radiates to the lower abdomen, side, lower back or sacrum.
After surgery, there is a high risk of complications. There is a risk of damaging nearby organs with the laparoscope. These are the intestines, liver and stomach.
Complications after laparoscopy are indicated by sharp cramping pain.
Pain in the lower abdomen after genital surgery in women is the most common. Other types of pain after laparoscopy in gynecology:
- the navel or the entire stomach hurts;
- pulling in the lower abdomen;
- the postoperative suture hurts;
- pain is felt in the right side, closer to the ribs;
- chest, shoulders, lower back hurt.
The localization of pain depends on the disease.
After laparoscopy to remove an ovarian cyst, pain in the lower abdomen and bloating occur. Painful sensations may bother the patient for 7 to 30 days. The most severe pain after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst is felt in the first day. There is also severe pain at the puncture sites.
Do not be alarmed if your ovary hurts after laparoscopy. This is normal, since when a cyst is removed, soft tissue is injured. You need to be wary if the pain becomes cutting. It is acute, the pain in the ovaries increases. In this case, hospitalization is required.
After laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes for an ectopic pregnancy, the lower abdomen will drag for at least a month. But such pain is mild. It should not cause discomfort or lead to loss of ability to work. Painful sensations may intensify with sudden movements. After laparoscopy of the uterus, it is painful to write and also to defecate.
Other characteristic pain syndromes
Very often, patients experience back pain. Pain syndrome occurs due to epidural anesthesia. The pain is mild and may bother the patient for several months after surgery. Sometimes my back hurts because of carbon dioxide.
After anesthesia, the whole body may ache, muscle weakness, dizziness and headache may be felt. If an anesthetic substance was injected into a vein, your arms may hurt, and after a couple of days your legs may hurt. Pain in the limbs can occur when carbon dioxide enters the vascular bed.
If a nerve is damaged by a surgical instrument, the patient's skin hurts or there is no sensitivity of the skin at all. The pain should go away over time. If this does not happen, then adhesions may be the cause.
Pain relief in the postoperative period
Laparoscopy is an operation with the least severe pain syndrome in the postoperative period. Immediately after surgery, the puncture sites are injected with an analgesic so that after recovery from anesthesia the patient does not feel severe pain.
Narcotic analgesics (opiates) are rarely used because they cause a number of side effects. They also quickly relieve pain, which interferes with the timely diagnosis of postoperative complications. If acute pain occurs after 12 hours, then this is not the norm.
In the first days after surgery, doctors may prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They not only relieve pain, but also eliminate foci of inflammation.
The most popular are “Ketanov” and “Ketotifen”. To relieve pain after laparoscopy to remove a cyst in the ovary, NSAIDs and non-narcotic analgesics are used simultaneously.
But you shouldn’t get carried away with painkillers, they negatively affect your health.
After laparoscopy, pain can be localized in different parts of the body, but it is not as severe as after abdominal surgery. This benefit is especially important for patients with a low pain threshold.
Source: https://DiagnozPro.ru/skopiya/laparoscopy/boli-posle-laparoskopii
Nature of the discharge
A slight brownish discharge after surgery is normal and usually lasts no more than three to four days.
White discharge with cheesy inclusions, a sour smell, accompanied by itching in the vagina, indicate the onset of thrush. This disease is a consequence of antibacterial therapy and is easily treated in a few days with suppositories or tablets prescribed by a doctor.
You should be concerned if the discharge turns yellow with greenish impurities and inclusions of blood - this indicates that an infection has begun at the site of the surgical intervention.
Important!
If pus appears in the discharge, or it acquires a sharp, unpleasant odor, you should immediately consult a doctor and get tested.
Can tubal plastic surgery replace them?
In gynecological practice, the term “tubal plastic surgery” is known. It is very often performed when partially removing damaged sections of the fallopian tubes.
Complete restoration of the fallopian tubes does not make any sense. Since a normal fallopian tube has the ability to contract. This property is necessary so that the fertilized egg can move through the tube to the uterus.
After plastic surgery, the fallopian tubes do not have the ability to contract, which means it will be impossible for the egg to move through them.
Partial tubal plastic surgery, when only individual damaged areas are replaced, is important for the female body. With such operations, depending on their complexity and the volume of replaced tubal tissue and the successful course of pregnancy, the rate is 40–90%.
In the female body, the fallopian tubes play a very important role. It lies in the reproductive function of the female body, and is a connecting link between the body of the uterus and the appendages.
However, some pathological conditions may be a reason to remove the fallopian tubes.
Many experts indicate that the consequences of such intervention can disrupt menstruation, and as a result, hormonal disruptions occur.
What medications should be used?
In the postoperative period, the woman is prescribed antibiotics to prevent suppuration, drugs to maintain microflora (Hilak forte, Lactobacterin), and vitamins for immunity.
The main therapy is hormone replacement.
Women over 50 years of age who have already experienced menopause are not prescribed medications; younger patients must strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations and take courses of estrogens and progestins.
The pills are designed to replace lost hormonal function of organs.
Today, drugs are able to provide the patient with the necessary hormones and make the postoperative period as easy as possible.
Hormonal therapy can prevent a sharp deterioration in appearance and reduce mood swings.
Bandage
In some cases, to protect the sutures, reduce pain and maintain internal organs, the patient after a laparotomy is prescribed to wear a bandage.
Pregnancy
After removing one of the ovaries, while fully maintaining all the functions of the second, it is quite possible to become pregnant naturally.
The eggs continue to mature, hormonal function weakens, but remains intact.
In some cases, in order to successfully conceive or maintain an existing pregnancy, the patient will be prescribed additional hormonal medications.
Reference.
After removal of two ovaries, natural pregnancy is impossible - the woman has no eggs.
But if the uterus and tubes are preserved, the patient may be offered to undergo an IVF procedure with the participation of a donor egg and partner’s sperm.
Main functions of the fallopian tubes
The fallopian tubes connect to the body of the uterus in the upper section, on the other hand they join the ovaries.
How to get rid of women's disease? Irina Kravtsova shared her story of curing thrush in 14 days. In her blog, she explained what medications she took, whether traditional medicine was effective, what helped and what didn’t.
With the help of this organ, two functions are performed, without which pregnancy cannot occur:
- Preparing and providing a place for a fertilized egg.
- Ensuring the movement of the egg into the uterus, where it attaches to the wall of the uterus and the subsequent development of the fetus.
Nutrition for recovery
After removal of the ovaries, it is necessary to follow a diet that is aimed at solving several problems:
- gaining excess weight;
- mood swings, depression;
- acute lack of hormones;
- weakness of the body after surgery.
To prevent obesity, it is necessary to completely eliminate foods that combine industrial sugar and fat - ice cream, cakes, pastries, frozen yogurt, pastry creams and muffins.
You can replace them with honey, dried fruits, fresh fruits and berries.
You can consume chocolate in small quantities - high quality and no more than two or three slices per day.
The following product groups should also be excluded:
- fast food;
- fat meat;
- sharp salty cheeses;
- industrially produced canned and smoked meats.
Be sure to include in your diet:
- salads from fresh vegetables (cabbage, carrots, beets, herbs, cucumbers);
- flaxseed oil and seeds - they will alleviate hormonal deficiency;
- low-fat fish;
- fruits and berries;
- nuts;
- poultry and eggs;
- whole wheat bread;
- fermented milk products - preferably from a trusted manufacturer or farm products that do not contain artificial hormones.
Reference.
After consultation with a gynecologist, you can include herbal teas with sage, boron uterus and red brush in your diet. These herbs contain natural phytohormones that can greatly facilitate the body's recovery process.
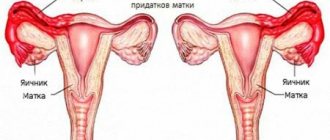
Unilateral or bilateral removal of the ovary (oophorectomy) is not a common operation, as it is performed according to a limited number of indications. Sometimes the ovary has to be removed together with the fallopian tube, less often - with the uterus.
The importance of the ovaries for the female body cannot be overestimated. They are responsible for three main functions:
— Vegetative, thanks to which girls undergo puberty and a “feminine” appearance is formed. The ovaries “turn on” during puberty and function until menopause.
- Hormonal. The ovaries secrete two determining hormones in a cyclic manner: estrogen (in the first phase) and progesterone (in the second phase). The rhythmic production of ovarian hormones is regulated by the hypothalamus and pituitary gland located in the brain.
- Generative (childbearing). The ovaries produce fertilizable eggs throughout the reproductive period.
The full and adequate performance of all these functions by the ovaries ensures a woman’s health and the possibility of motherhood.
The ovaries are a paired hormonal gland. The completely identical structure and functioning of the right and left ovaries testifies to the wisdom of nature, which prudently decided “just in case” to make this organ a pair. It is thanks to this decision that the removal of the right ovary allows a woman to realize the function of childbearing at the expense of the remaining left ovary, and the removal of the left ovary is compensated by the remaining right one.
The ovary (each) has a dense connective tissue outer shell; under it in the cortical layer there are many small underdeveloped follicles containing the same undeveloped eggs. One of these follicles (they are called primordial) becomes fully mature over a period equal to one menstrual cycle, and the egg inside it reaches the development necessary for fertilization. The full development of the follicle and egg, respectively, is ensured by estrogens. A mature follicle (Graafian vesicle) bursts by the middle of the cycle, and the egg leaves it (ovulation), moving through the abdominal cavity to the fallopian tube - the site of potential fertilization. If fertilization does not occur, the egg dies within two days, and in the ovary, from the remnants of the burst Graafian vesicle, a corpus luteum is formed, capable of synthesizing progesterone. When the corpus luteum is destroyed (shortly before menstruation), under the influence of a sharp decline in hormones, the endometrium is rejected, and menstrual bleeding begins.
Thus, the menstrual cycle is conventionally divided by the period of ovulation into two phases of equal duration - follicular (first) and luteal (second). All changes that occur in the follicular phase occur with the participation of FSH of the pituitary gland (follicle-stimulating hormone), and in the luteal phase the pituitary gland secretes LH (luteinizing hormone).
Similar cyclical structural and hormonal processes continue throughout the reproductive period.
The most common diagnosed ovarian pathology is hormonal dysfunction, when, due to improper hormonal secretion, the cycle is disrupted and/or infertility develops. As a rule, such disorders are corrected with the help of hormone therapy. The ovary is removed only in situations where its presence is associated with life-threatening consequences, for example, bleeding, septic complications, large tumors, and the like.
As a rule, unilateral removal of the ovaries leaves a woman the chance of motherhood. Pregnancy after removal of the ovary is possible, but its likelihood, for obvious reasons, is reduced.
Serious consequences are provoked by bilateral oophorectomy, since the body is deprived of proper hormonal influence and enters a period of artificial premature menopause.
Therapy after removal of the ovaries is intended to correct hormonal imbalances in order to eliminate menopausal disorders.
Reasons for spay removal
Any clinical situation in gynecology is considered by specialists from the perspective of organ preservation, especially in patients during the reproductive period. Therefore, each surgical intervention to remove the uterus or appendages has very clearly defined indications.
The decision to remove an ovary is made:
— In case of an emergency, when the ability to preserve the health (and sometimes life) of the patient is directly related to oophorectomy.
These primarily include purulent processes in the appendages. In patients with weakened immune defense mechanisms, infectious inflammation quickly spreads in the area of the fallopian tubes and ovaries, followed by the formation of a circumscribed, pus-filled formation, which, if ruptured, can cause septic shock. It is not always possible to eliminate such a purulent infiltrate in isolation, so the affected ovary must also be removed.
Surgery to remove an ovary
Removing the left ovary and removing the right ovary are technically the same.
In emergency situations, when there is no possibility for detailed diagnosis, the decision to remove the ovary is made directly during the operation, when the situation is assessed visually.
The nature of the operation depends on the specific clinical situation, which requires the surgeon to solve the main issues:
— To what extent will the intervention be performed, that is, one ovary is removed or both; The uterus and tubes remain or are removed.
— Which surgical technique to choose.
In fact, all existing techniques are divided into gentle, laparoscopic, and abdominal. With the abdominal technique (laparotomy), the abdominal cavity is opened layer by layer; with the laparoscopic technique, instead of a large incision, several small holes appear on the abdominal wall.
During the operation, the ovary is cut off from the muscular-ligamentous frame that supports it, and the resulting peritoneal defect is closed with a broad uterine ligament.
Depending on the technique and volume, the operation time varies from one to four hours, and the subsequent number of days spent in the hospital does not exceed five days.
Early therapy after removal of the ovaries begins in the hospital. Usually it does not differ from that for other gynecological operations, but it has some features. Since the ovaries serve as a source of sex hormones, and their amount depends on age, with bilateral oophorectomy it is necessary to determine the degree of need to compensate for hormonal deficiency through medication. Hormonal rehabilitation after removal of the ovaries is necessary for patients who have not entered menopause.
Pain during the procedure
Laparoscopic surgeries are becoming popular. They are increasingly used in gynecology, when removing stones in the gall or bladder, as well as when removing abdominal organs. The operation is performed through several small punctures of soft tissue.
Progress of the surgical intervention:
- The patient is given anesthesia.
- 3-4 punctures are made on the anterior abdominal wall, through which a surgical instrument and camera are inserted.
- The abdominal cavity is filled with argon or carbon dioxide to expand the intra-abdominal space.
- An image is displayed on the monitor, the surgeon observes all his manipulations.
- After the operation is completed, the instruments are removed and sutures are applied to the punctures. If the surgical intervention is complex, for example, removal of the uterus, then drainage is left in the wounds for 1-2 days. In this case, sutures are applied for 5-6 days.
Before going on the operating table, patients are concerned about the progress of laparoscopy and whether it hurts. No. The operation is performed under local or general anesthesia, so the person does not feel any manipulation.
Consequences after removal of ovaries
Negative consequences after removal of the ovaries can be conditionally classified into functional and organic.
Organic are associated with the removal of the organ as such, when its absence provokes the appearance of postoperative consequences. One of them is pain syndrome. Pain after removal of the ovary in the early period is associated with minor changes in the topography of the pelvic organs: they shift slightly and the apparatus that fixes them “stretches,” causing pain. As a rule, after two weeks (or earlier) these pains stop.
Unfortunately, sometimes pain after removal of the ovary is provoked by an adhesive process that cannot be completely eliminated. More often, adhesions form against the background of inflammatory phenomena, when inflammatory exudate appears in the pelvic cavity; over time, it becomes viscous and thick, so it literally “glues” adjacent tissues, disrupting their proper mobility. Early rehabilitation after removal of the ovaries involves the prevention of inflammatory and, accordingly, adhesive processes.
The most serious consequence of oophorectomy, especially in young patients, is a complex of functional disorders. Their severity is determined by the number of removed ovaries. Unilateral oophorectomy leaves the patient the opportunity to have her own sex hormones and also realize reproductive function. More often, after the removal of one ovary, dishormonal disturbances occur, which can be compensated for.
If both ovaries are removed, the woman is artificially deprived of the necessary estrogenic influence, and a condition similar to menopause occurs, called post-castration syndrome. Unlike natural menopause, when the body has the ability to gradually adapt to the attenuation of the hormonal function of the ovaries, menopausal syndrome of artificial origin is quite difficult.
Life after spaying
The most favorable clinical situation is observed after the removal of only one ovary, since the remaining one begins to compensate for the changes that have occurred.
Two or three weeks after bilateral oophorectomy, the first symptoms of artificial menopause appear: neurovegetative disorders (72.8%), metabolic and endocrine disorders (11.2%), psycho-emotional abnormalities (16%). The lack of proper estrogenic influence on the mucous membranes of the genital tract provokes their premature “aging” with the development of atrophic changes.
Post-castration syndrome is manifested by hot flashes, increased sweating (especially night sweats), headaches, unstable blood pressure, chills, cardiac dysfunction (arrhythmias). There is also deformation of the psycho-emotional sphere (irritability, tearfulness, insomnia, decreased memory and attention, drowsiness, etc.).
Since estrogenic influence extends to almost the entire female body, many systems react to their absence, and the list of symptoms of artificial menopause can be very extensive.
The situation when a woman panics during premature menopause is quite understandable and understandable. However, it should be noted that although it is unpleasant, it is not a death sentence. Moreover, not all women endure this period with difficulty, since its course is always individual and depends on the state of health in general and gynecological health in particular. The greatest severity of negative symptoms occurs in the first two years after removal of the ovaries, and then the body partially compensates.
Rehabilitation after removal of the ovaries involves hormonal therapy. The drugs are selected in such a way as to imitate the natural hormonal background and maintain it until the onset of natural menopause.
When a woman finds out that she is going to have an oophorectomy, she is often concerned about whether pregnancy is possible after removal of the ovary. If only one ovary is removed, pregnancy is possible if the second ovary, tube and uterus are preserved. With bilateral oophorectomy, natural conception is, unfortunately, impossible.