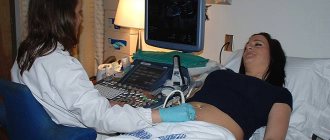
Often, in the process of diagnosing various gynecological diseases, doctors prescribe hysteroscopy. This is a minimally invasive method that allows you to obtain reliable information about the state of the reproductive system. On what day of the cycle hysteroscopy is performed is decided by the gynecologist, taking into account the exact purpose for which these manipulations are performed.
What is hysteroscopy of the uterus and why is it needed?
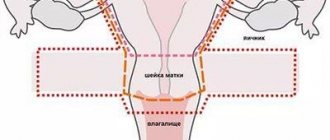
Hysteroscopy of the uterus is a procedure that allows you to examine the internal cavity of the organ using a hysteroscope (optical system). It is needed to implement a targeted biopsy - taking a section of the mucous membrane and other material for the purpose of examining neoplasms (benign, malignant).
Kinds
The following types of such procedure are distinguished:
- diagnostic;
- surgical;
- test.
Diagnostic hysteroscopy
Another name is office. This endoscopic examination of the uterus is done when it is necessary to diagnose pathology and confirm a preliminary diagnosis.
Peculiarities:
- carried out on an outpatient basis;
- does not require anesthesia;
- Local anesthesia is allowed.
Sometimes diagnostic and treatment hysteroscopy (resectoscopy) is required. This method is used to determine the type of disease and its simultaneous treatment.
Surgical hysteroscopy
This type involves surgical intrauterine intervention, in which:
- additional equipment is used;
- tissue integrity is compromised;
- Local or general anesthesia is used.
In this case, it is possible to perform an operation for:
- elimination of pathological processes in the uterine area;
- removal of polyps;
- elimination of adhesions and other neoplasms.
Control
The purposes of control hysteroscopy may be:
- monitoring the patient’s recovery process;
- determining the effectiveness of the prescribed procedures;
- timely detection of complications and relapses of diseases.
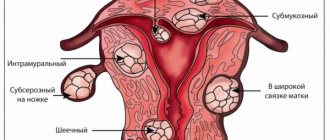
What does hysteroscopy show?
Hysteroscopy shows:
- Submucosal myomatous nodes. The hysteroscope reveals round, light pink tumors with smooth borders. At the same time, the question of the possibility of their excision is being resolved.
- Uterine polyps and diffuse type hyperplasia. Using an optical device, you can see growths of the endometrium, an increase in the thickness of the mucosa and the presence of folds. Polyps can be numerous or single, hang into the uterus and have a pale pink color.
- Internal endometriosis. It is visible in the form of white spots from which blood leaks.
What is a hysteroscope?
A hysteroscope is a device that has a small rectangular body with two taps. They are connected to hoses for supplying gas or liquid under pressure.
The device is equipped with:
- telescopic system;
- lighting system;
- eyepiece
Thanks to this, it is possible to study:
- cervical canal;
- isthmic department;
- uterine cavity.
There are several types of such tools:
- operating;
- diagnostic;
- hysteroresectoscope.
Depending on the type of hysteroscope, its diameter may differ, as well as the entrance angle of the field of view, its direction and working length.
Operating principle of an operating hysteroscope
Diagnostic hysteroscope (photo)
Hysteroresectoscope
Treatment after hysteroscopy
The duration of therapy varies from five to seven days. In this case, drugs are used in the form of tablets.
In the case of manipulations during inflammatory processes in the uterus, anti-inflammatory and antibiotic drugs are prescribed. Even before the procedure, 1000 mg of Cefoperazone or Ceftazidime is administered intravenously. After 12 hours and a day later, the drug is administered again without changing the dosage. If such therapy is not possible for some reason, then broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed.
During the same period, you need to use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Piroxicam or Ibuprofen).
In case of excision of synechiae in the cavity of the reproductive organ, a spiral is installed in the uterus for two months. This significantly reduces the risk of relapse. An alternative option is to insert a silicone balloon or a special catheter for just one week. During this period, the woman needs to take antibiotics.
After the catheter or balloon has been removed, and throughout the entire period of use of the intrauterine device, hormonal therapy is used. It lasts at least two months. After removal of the septum from the reproductive organ, antibacterial agents (Cefuroxime or Ceftazidime), as well as estrogen-based medications, are prescribed.
Indications for the procedure
Indications for modern hysteroscopy of the uterus are suspicions of:
- the presence of pathological processes in the endometrium or damage to the myometrium;
- tumors in the uterus and other formations that are abnormal in nature;
- abnormalities in the development of the uterus;
- the presence of inflammation after natural childbirth or cesarean;
- the presence of remains of embryo fragments after an abortion or foreign bodies in the uterine cavity;
- postpartum complications.
The study may also be prescribed for:
- infertility;
- spontaneous termination of pregnancy;
- bleeding during postmenopause;
- irregular menstrual cycle;
- the need to diagnose the endometrium;
- hormonal disorders.
On what day of the cycle is it carried out?
The procedure is carried out after menstruation has already ended. Hysteroscopy is not performed during menstruation. As a rule, the patient is examined on the 5th–10th day of the cycle.
A woman’s physiology is designed in such a way that with the onset of the first phase, the thickness of the endometrium is minimal. During this period, the uterine cavity is well visualized, all defects are clearly visible, blood loss is minimized, and polyps and other neoplasms can be easily removed.
For the purpose of a detailed study of the functional characteristics of the endometrium, hysteroscopy is also prescribed on the 15th–18th day of the cycle. If emergency diagnosis is necessary, the day the procedure is performed is not important, but in any case it should be a period without menstruation. During critical days, the study turns out to be uninformative.
From the moment of menopause, the procedure can be performed absolutely any day. The main condition is that there is no uterine bleeding during this period.
Contraindications
Contraindications to treatment or diagnosis:
- changes in the endometrium or genital tract that are inflammatory in nature;
- the patient’s pregnancy (regardless of the period);
- copious uterine discharge;
- narrowing of the cervical canal, or cervix;
- malignant tumor (cancer);
- infectious diseases;
- severe forms of liver or heart disease (in which the introduction of anesthesia into the body is strictly contraindicated).
Menstruation after the procedure
When performing a procedure to identify pathologies of the cervix and reproductive organ, the arrival of menstruation after hysteroscopy can be expected at the usual time. Sometimes there is a delay in regulation ranging from three days to two weeks. A slight delay in menstruation is normal.
If endometritis was curetted during hysteroscopy, then the date of the operation should be considered the first day of the cycle. Critical days should occur 28–30 days after this.
Violation of the cycle, changes in the volume, shade and smell of discharge indicate problems in the body. If such symptoms appear, you should immediately go to a medical facility.
How to prepare for the procedure?
To prepare for the procedure, a woman needs to undergo a number of studies:
- Take blood tests (general, biochemical, coagulogram), as well as urine tests. All results must be received no earlier than two weeks before surgery.
- Be examined for syphilis, hepatitis, HIV infection.
- Determine Rh factor and blood group.
- Take smears (at the doctor's discretion).
- Do fluorography, electrocardiography of the heart (one month before the examination).
- Conduct an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs and colposcopy.
- Visit your doctor and get notified for a hysteroscopy.
Before the study, a woman needs to independently carry out the following preparation:
- eat only those foods that are easy to digest and do not cause gas formation;
- the day before hysteroscopy, do not have dinner, but you should drink liquid (non-carbonated);
- do an enema before going to bed;
- in the morning, before the procedure, limit your intake of water and food;
- no smoking.
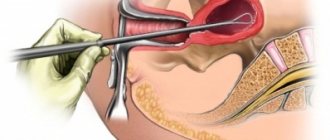
Technique and how hysteroscopy is performed
The research technique looks like this:
- For examination, the patient should sit on the gynecological chair in the usual position. When it is necessary to administer anesthesia, the anesthesiologist applies a drip system for the administration of medications necessary for the procedure.
- Then the external genitalia, vagina and uterus itself are treated.
- After this, to gain access to the organ, a special gas is injected into the abdominal cavity, raising the abdominal wall above the organs.
- Next, the doctor slowly widens the cervical canal using instruments of various diameters.
- If foreign bodies are detected, they are removed using a clamp that is inserted through the hysteroscope channel. If there are suspicious areas on the uterus, a targeted biopsy is performed.
- At the end of the procedure, gynecologists scrape the uterus (cervix and its cavity), and then remove the patient from the state of anesthesia.
Is it painful?
Reviews from patients indicate that there is nothing to be afraid of, because there is no pain when performing this manipulation. There is also nothing terrible in surgical intervention, because anesthesia is used.
The possibility of using anesthesia depends on:
- general condition of the patient;
- approximate time of the procedure;
- the presence of concomitant ailments in the patient;
- the likelihood of developing allergies to certain drugs;
- expected complications during the procedure.
How long does it last?
A diagnostic examination takes about 5–25 minutes.
The duration of the procedure depends on:
- method and technique used by the doctor;
- specialist experience;
- the complexity of each specific situation.
How often can I do it?
If office research is necessary, there are no restrictions on their frequency and quantity. As for intervention through surgery, hysteroscopy should be performed after it no earlier than six months later.
Reviews about hysteroscopy
According to the services Irecommend.ru and Otzovik.com, more than 90% of women leave positive reviews about hysteroscopy. The advantages of this procedure for the patient include speed, high sensitivity of the method, assistance with IVF, and minimal discomfort. The disadvantages of HS include the relative high cost of the method, the presence of contraindications and possible complications, and the need in some cases for subsequent hormonal treatment.
Read
Also:
- What is cervical erosion
- Curettage of the uterus - all about the procedure
- Anatomy of the uterus: location, structure and functions
- Glandular hyperplasia of the endometrium - what is it?
- Fallopian tube laparoscopy
- What is uterine rabies - a disease or a rumor?
What to do after the event?
The procedure is low-traumatic due to the absence of tissue incisions, so rehabilitation is usually quick and easy, however:
- During diagnostic (therapeutic) hysteroscopy, special monitoring of the patient is not required. You can return to your normal rhythm of life the very next day after the procedure.
- Women who are at risk of infectious complications, as well as during surgical hysteroscopy, are prescribed prophylaxis with antibiotics. Sometimes the doctor prescribes antifungal agents.
After the operation:
- Douching and using tampons are prohibited;
- You should avoid sexual intercourse for several weeks (depending on the complexity of the procedure);
- you need to refrain from visiting the bathhouse and swimming pool;
- Physical activity should not be allowed.
If severe pain is present, you can take painkillers. In cases where the bleeding does not stop for a long time, specialized medications are indicated (after consultation with a doctor).
Symptoms
With single adhesions of the uterine cavity there are no symptoms. Their presence can only be determined during a hysteroscopic examination and mostly becomes an incidental finding.
If adhesions block the cervical canal, the symptoms are as follows:
- absence of menstruation - blood does not flow due to obstruction of the canal;
- pain in the lower abdomen.
Blood accumulates in the uterus. It is thrown into the fallopian tube.
Another complaint may be infertility. It is diagnosed if, within 12 months of regular sexual intercourse with a fertile partner, without using contraception, pregnancy does not occur.
Consequences
Patients may experience some unpleasant consequences:
- painful sensations;
- discharge;
- temperature increase.
Painful sensations
Possible painful sensations:
- spasms;
- the appearance of aching pain in the lower back;
- discomfort in the ovarian area.
If sharp, unbearable sensations occur, you should definitely consult a doctor; as a rule, he will prescribe painkillers.
Discharge
Features of discharge after hysteroscopy:
- Spotting discharge is considered normal, and may appear even after a diagnostic examination:
- if curettage was performed, the amount of blood should be similar to that typical for normal menstruation;
- The duration of bleeding is about 4–7 days.
Temperature increase
If the body temperature after hysteroscopy is slightly elevated (37–37.2), this is considered normal. The inflammatory process is indicated only by a significant increase 2–3 days after the procedure.
What is the price?
The cost of the procedure is shown in the table:
| Region | Cost, rub | Firm |
| Moscow | from 2800 | "Medical Center Family Clinic" |
| Chelyabinsk | from 880 | "Oncology clinic EVIMED" |
| Krasnodar | from 1500 | "Best Clinic" |
| Saint Petersburg | from 6 250 | Consultative and Diagnostic Center of the Military Medical Academy |
| Ufa | from 2700 | Maternity hospital No. 3 |
All the pros and cons
The pros and cons of the procedure are given in the table:
| pros | Minuses |
|
|