Why is ultrasound prescribed for cervical erosion?
An obstetrician-gynecologist may prescribe an ultrasound examination for cervical erosion for the following reasons:
- If a woman is pregnant and is bothered by vaginal discharge, the length of the cervix and the condition of the internal os of the uterus are determined using an ultrasound. If the cervix does not shorten and the pharynx remains closed, then it can be assumed that the discharge is caused by erosion.
- If “bad” erosion is diagnosed and there is a suspicion of cervical cancer.
- A gynecological examination of virgins does not allow us to diagnose many things, so an ultrasound examination is performed.
If, after a gynecological examination “on the chair”, erosion was detected, a good specialist will prescribe a colposcopic and cytological examination. Colposcopy is performed using a colposcope - this is a device that has the same principle of operation as a microscope. The colposcope enlarges the epithelium of the cervix, allowing the doctor to determine the presence of “bad” cells.
Cytological examination is carried out by taking a smear on the surface of the cervix. A smear is taken on a gynecological chair using a cervical stick. Another name for this test is a Pap smear.
Diagnosis of the disease
This disease manifests itself quite specifically in a woman’s body. Often it practically does not appear. Only sometimes is it possible to detect it by signs such as spotting after sexual intercourse. That is why, in order to detect the development of this disease as early as possible, it is necessary to undergo regular preventive examinations.
If a specialist discovers the presence of any defects in the cervical area, then most likely the woman will be prescribed a colposcopy.
This procedure is a special examination using a special device that allows you to diagnose erosion.
Such an examination is painless and does not require special preparation measures.
If during such an examination the doctor finds a changed area, he will take a small sample of tissue for analysis. This is necessary in order to identify erosion at an early stage.
In addition to these two procedures, the doctor may prescribe the following studies:
- Ultrasonography.
- Flora smear.
- Cytological examination.
- Blood analysis.
Completing such studies will help make the diagnosis as accurately as possible.
Is cervical erosion visible on ultrasound?
Many sources say that it is possible to see erosion on an ultrasound. However, such a judgment is erroneous; ultrasound will not show cervical erosion! Even if some changes are noticeable, they will not be the basis for making a diagnosis.
If you can see cervical erosion without an ultrasound, then why look for additional diagnostic methods. Moreover, it is completely uninformative, because it cannot show pathological changes in cells.
The procedure for detecting cervical erosion is as follows: a woman comes to see a gynecologist and during a routine examination using gynecological speculum, erosion is detected. The next thing that should concern the doctor and the patient is how dangerous the erosion is. In order to find out, a woman must have a cytological smear and undergo a colposcopy; no one will immediately send her for an ultrasound!
Preparing for an ultrasound
Preparing for an ultrasound will depend on how it is done. There are two main ways in which female internal organs are examined:
- Transvaginal, examination of organs is carried out through the vagina with a special sensor.
- Transabdominal - the study occurs through the anterior abdominal wall.
For general preparation, it is necessary to exclude foods that cause increased gas formation. This list of products includes legumes, dairy products, yeast bread, carbonated drinks, etc.
If a few days before the ultrasound the patient had an x-ray using a contrast agent (barium), then false results may appear on the “ultrasound”. The ultrasound specialist should be warned about this.
When performing a transabdominal ultrasound, you should fill your bladder - drink 1 liter of fluid in half an hour, or do not empty your bladder for two hours. In emergency situations, fluid is infused through a catheter.
With the transvaginal technique, it is necessary to empty the bladder. If the examination is carried out using two methods, then initially it is done transabdominally, then the woman is sent to the restroom, after which it is examined transvaginally.
Some women suffer from flatulence and constipation; they are advised to take activated charcoal or other appropriate medications a few days before the test. On the day of the ultrasound, it is better to eat 10-12 hours before the procedure. The intestines, “bloated” with gases, pinches the uterus and prevents you from seeing some of its parameters.
How they do it
Transabdominal ultrasound of the uterus and other female organs is carried out as follows: the patient lies down on the couch, laying a diaper on it, and releases the lower abdomen. The ultrasound doctor applies a special gel to the sensor and to the patient’s stomach, then he places the sensor on the lower abdomen and begins to move it. The procedure is absolutely painless, only cold gel can cause an unpleasant sensation; it takes from 5 to 20 minutes.
A transvaginal ultrasound differs in that the woman needs to undress to the waist. The doctor puts a special condom (which the patient must purchase in advance) onto the sensor, applies a special gel to it and inserts it shallowly into the vagina. The procedure is painless, because the tip of the sensor has a diameter of no more than 3 cm, the patient practically does not feel it.
If a girl has never had sexual intercourse, then she will not be examined using the transvaginal method; in extreme cases, if dangerous diseases are suspected, it can be done transrectally through the anus.
Some ultrasound rooms are equipped with two monitors. As a result of this, the patient can simultaneously observe her internal organs with the doctor.
Methods of carrying out
Ultrasound examination can be performed in several ways:
- Transabdominal (through the stomach). The method is used if it is not possible to insert the sensor intravaginally (during pregnancy, in virgins, with certain diseases of the vagina).
- Through the skin of the perineum. The method is used for virgins, children with pathologies of the uterine cervix or with vaginal atresia.
- Transvaginally (through the vagina). A small sensor is inserted directly into it. The method is indicated for everyone who is sexually active in the early stages of pregnancy or at 38-40 gestational weeks.
- The sensor is inserted transrectally into the anus. The method is used mainly for virgins.
Any of the listed methods has its own characteristics and prohibitions. The optimal method is prescribed by a doctor after a prior consultation.
What are they watching?
The most favorable time for an ultrasound is the first week after menstruation. Using ultrasound, the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, bladder, and intestines are examined. Obviously, the uterus can be examined with a transabdominal ultrasound, but cervical erosion can only be approximately seen transvaginally.
Ultrasound can detect the following diseases - fibroids, endometriosis, polyps, uterine and cervical cancer, ovarian cysts and inflammation of the ovaries, abnormal development of the genital organs. At a short stage of pregnancy, the transvaginal method makes it possible to eliminate the possibility of developing an ectopic pregnancy in a timely manner.
The length of the cervix is measured transvaginally; this parameter must be known if a shortening of the length of the cervix is suspected in a pregnant woman. The bladder is examined in the same way.
A woman should come for an ultrasound if she experiences pain during intimate relationships, has no menstruation, or has a problem conceiving a child. As a rule, a woman will be referred for an ultrasound by a gynecologist after an examination on a “chair”, but, as mentioned above, cervical erosion is easily detected on this chair. For this reason, the gynecologist will refer a patient with erosion for additional studies, but not for an ultrasound.
Indications and prohibitions
An examination of the cervix is done simultaneously with the diagnosis of the pelvic organs, so the indications are largely common:
- pain (of any intensity) in the lower abdomen;
- menstrual irregularities;
- uterine bleeding;
- infertility or suspicion of it;
- endocrine diseases;
- urinary disturbance;
- the appearance of discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- preventive examination;
- postoperative control;
- suspicion of inflammation;
- preparation for surgery.
Ultrasound is also indicated during pregnancy to determine the length of the cervix and its closure. The technique has almost no contraindications, except for the choice of diagnostic method.
Transvaginal examination should not be performed on virgins and women with vaginal defects. Examination immediately after surgery is not recommended.
Transabdominal has no contraindications, but if a woman cannot hold back urination, then diagnosis becomes very difficult. Transrectal ultrasound is not performed after surgery on the rectum or during inflammatory processes.
Pros and cons of ultrasound examination
Ultrasound has a huge number of advantages compared to other diagnostic methods. For example, a picture after an X-ray can be misinterpreted due to the fact that the patient was moving, but “ultrasound” allows you to examine organs in their usual rhythm. In addition, the undoubted advantages of ultrasound examination are the following factors:
- Availability. The ultrasound procedure, even on a paid basis, is accessible to most citizens; in addition, the appropriate devices are available in almost all medical institutions.
- Information content. Due to the fact that the sensor is located directly next to the organ, its changes are easily detected.
- Harmlessness. For this reason, it is prescribed to pregnant women and children.
- The research takes little time.
- There is no need for anesthesia.
Disadvantages include lower image quality than with MRI and CT, distortion of the information received due to the size of the sensor and the heterogeneous environment (human organs are a heterogeneous environment), the need for certain preparation (dieting, drinking water, etc.)
Etiology of the disease
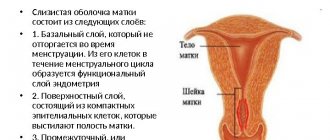
The endometrium includes the following two layers:
- The first layer is functional.
- The second is basal.
The first layer peels off at the end of the menstrual cycle, and the second layer allows the creation of a new functional layer that begins the menstrual cycle again.
The main etiological factor is damage to the uterine mucosa. However, the damage itself is not dangerous; the danger is posed by viruses and virulent microorganisms that have penetrated inside the uterus. Let's figure out what are the main reasons for infection entering the uterus.
So, inflammation develops due to the following reasons:
- Incorrect douching.
- Complicated abortion and childbirth.
- Sexual intercourse during the menstrual cycle.
- Performing instrumental studies, in particular laparoscopy.
Now that we’ve sorted out the etiology, let’s move on to the main symptoms of the pathology.