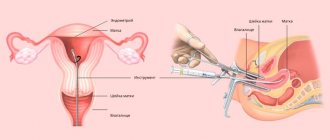
Cervical biopsy is one of the effective methods for diagnosing cervical cancer at an early stage of its development. It should be noted that cervical cancer is in seventh place in the list of the most common cancer pathologies in women.
The main cause of cervical cancer is HPV (human papillomavirus).
Depending on the patient’s age, expected diagnosis, medical history (presence of cervical erosions, history of childbirth, presence of surgical gynecological interventions, etc.), a cervical biopsy can be performed using a Pap test (Papanicolaou smear for cytological examination) , conization of the cervix, targeted puncture biopsy, etc.
The decision about which
biopsy is preferable is made by the gynecologist.
Indications for cervical biopsy
If pathological processes in the pelvis are suspected, diagnostic procedures are prescribed. Initially, a visual examination of the genital organs is carried out, and a smear is taken for flora . In order to make an accurate diagnosis, ultrasound monitoring and colposcopy . These procedures help to find the pathological area, but its structure can only be determined using a biopsy. It is usually carried out in the following cases:
- cervical erosion;
- formation of condylomas;
- hyperkeratosis;
- polyps;
- pathological changes in the structure of the lower segment of the organ.
Before the biopsy, an extended colposcopy is performed. It involves treating the cervix with various reagents. Depending on the reaction of the pathological cells, a decision is made to perform a biopsy. The following parameters are considered direct indications for its implementation:
- detection of iodine-negative or acetowhite spots during extended colposcopy;
- the presence of keratinized areas of epithelium on the cervix;
- detection of genital warts or polyps during examination;
- the presence of atypical cells as a result of cytological examination.
What is a loop biopsy
This biopsy method is also called electroexcision. The essence of the procedure is to excise pathological areas with a special instrument, which is shaped like a loop. The loop-shaped nozzle is mounted on a metal rod connected to a handle, which is attached directly to the main unit of the device.
A loop biopsy machine generates a high-frequency current that is conducted to the loop, heating it to high temperatures. It is with this loop that excision of tissue is carried out, which will subsequently be subjected to histological examination.
The main goal of the procedure is to confirm or refute an oncological disease, since a biopsy is primarily performed for histological examination of the changed tissues.
Among the advantages of the technique are the following:
- simplicity and accessibility;
- relatively low cost;
- sufficient volume of material obtained.
But loop biopsy has disadvantages. After manipulation, a large scar forms on the cervix, which can cause the inability to conceive and bear a child normally. Therefore, the procedure is not prescribed to nulliparous patients, as well as women who are planning another pregnancy. In general, this method is considered highly traumatic and is therefore used only in extreme cases.
Contraindications
A biopsy is a surgical procedure, so you should be aware of the restrictions before performing it. In case of pathological processes in the pelvis, the procedure is prohibited. First, the source of inflammation is eliminated. It is also not recommended to do a biopsy during menstruation , if there is a blood clotting disorder and during pregnancy .
Biopsy technique
The procedure is performed at the beginning of the cycle, namely in the period from 5 to 7 days . The principle of its implementation is based on taking part of the tissue for research. The complexity of the biopsy depends on how large the lesion is. The method of implementation is selected based on the clinical picture of the disease. The patient’s health condition is taken into account and possible risks are weighed. Some types of procedures perform not only diagnostic, but also therapeutic functions. The following methods are distinguished:
- puncture;
- endocervical;
- electrosurgical;
- knife;
- trepanobiopsy.
puncture
This method is considered the simplest. It is carried out in the gynecological office as part of a routine examination. The procedure does not involve the use of general anesthesia. It takes no more than a minute. The doctor plucks off a suspicious piece of tissue . Minor discomfort may be present at this point.
Endocervical
Unlike other diagnostic methods, endocervical biopsy examines not the cervical tissue, but the mucus lining the cavity . It is scraped out using a medical instrument - a curette . In this case, local anesthesia is used. Unpleasant sensations are present only at the time of administration of the anesthetic injection.
Electrosurgical
This technique is divided into laser and radio wave biopsy. Its advantages include a low likelihood of complications. The rehabilitation period takes 2-3 days. At this time, the woman may experience slight bleeding.
Knife
An extended or knife biopsy is performed using a medical scalpel. Unlike other methods, it involves the collection of not only pathological, but also healthy cells . This allows you to identify potential lesions. It is carried out not only for diagnosis, but also for the treatment of existing tumors. During the operation, general anesthesia is used. Extended biopsy can be circular or wedge-shaped .
Trephine biopsy
A distinctive feature of the technique is taking material from several areas at once , which allows you to get an overall picture of the disease. It is practiced for multiple foci of pathology. The procedure is carried out using a special instrument - trephine . It has the shape of a long tube, hollow inside and pointed at the end. Trephine biopsy allows not only to detect pathological cells, but also to determine their nature.
Features of symptoms and procedure, contraindications
The discharge after the biopsy should be as follows:
- not too abundant;
- have a bloody appearance;
- do not continue for a long time.
If the consequences of the procedure are of this nature, there is no need to worry. About 10 days will pass, and the woman will be able to return to her usual lifestyle. As a rule, the test is performed in the first 13 days of the cycle to minimize the likelihood of complications.
The recovery period differs with different techniques for examining patients. The radio wave method is the safest and is not accompanied by prolonged discharge. Wedge-shaped, circular, as well as curettage techniques are characterized by a longer and more pronounced nature of symptoms during the rehabilitation period.
Excluding contraindications is an important point when preparing for diagnosis.
- tumor diseases of unknown etiology;
- acute inflammation and infections;
- intolerance to anesthesia (for techniques that require pain relief);
- blood diseases accompanied by reduced clotting.
Before the procedure, the doctor will definitely examine the patient and perform the necessary tests according to indications.
Types of procedure
Biopsies are divided into several types depending on the instrument used. The intensity of pain varies in each case. The following types of procedure are distinguished:
- sighting;
- radio wave;
- wedge-shaped;
- circular;
- aspiration;
- laser;
- conchotomous;
- trepanobiopsy.
Sighting
As part of the colposcopic examination, a targeted biopsy of the cervix is performed. A small amount of abnormal tissue is removed using a special needle . The collection is carried out on a gynecological chair. It only takes a few seconds. During this time, the woman feels only a small prick in the cervical area. The procedure is carried out when the area of growth of pathological cells is small.
How is curettage performed?
Surgery is often performed in the second phase of the cycle to reduce the risk of bleeding. The woman sits in a special chair. Before carrying out the manipulation, the doctor sanitizes the woman’s genital tract. After this, a local anesthetic is administered. When the anesthesia takes effect, the doctor begins cleaning.
A gynecological speculum of the required diameter is inserted into the woman’s vagina. The passage of the cervical canal is also expanded using special devices. After expansion, a special curette is inserted into it, similar to a spoon-knife with pointed edges. It is used to remove the functional layer, while the basal layer remains unaffected. As necessary, tissue is collected for cytological and histological examination.
In case of endometrial lesions, the uterine cavity is first cleaned, and then the cervical canal is curetted. The duration of the procedure is about 40 minutes. The tissues obtained during collection are analyzed separately. The results of the cytological examination will be received no earlier than the 10th day.
How the research is carried out
The diagnostic procedure is performed in a sterile room using special medical instruments. Depending on the complexity of the technique, the biopsy is performed on an outpatient basis or in a hospital. The patient is first introduced to the technique of the study. Before the procedure, it is necessary to undergo tests to exclude the presence of contraindications.
Outpatient
When performing a biopsy in a antenatal clinic, the cervix is not anesthetized . The procedure is performed in several stages:
- The girl sits in the gynecological chair.
- Using a speculum and a special mirror, the doctor assesses the condition of the cervix.
- The vaginal cavity is irrigated with an antiseptic. If necessary, local anesthesia is used.
- A piece of tissue is separated with a medical instrument.
This may cause discomfort. Immediately after the procedure, the patient goes home. Next time she should come for an examination on the date prescribed by the doctor. If necessary, the biopsy is repeated.
In a hospital setting
The woman is admitted to the hospital if the woman needs time to recover after the biopsy is completed. After intravenous anesthesia or spinal anesthesia, it is not possible to go home immediately. The woman remains in the hospital for up to two days. During this time she is under the supervision of medical personnel. After discharge from the hospital, the patient must visit the gynecologist at the agreed time.
Who gets a cone biopsy?
The cervix is a high-risk area prone to cellular changes in the tissue. The risk increases with infection with the human papillomavirus. Long-term infections contribute to the development of cancer. At your annual examination, your doctor will take a smear from your cervix for testing. Its goal is to detect precancerous conditions, so-called CIN neoplasia, as early as possible. There are three types of neoplasia:
- CIN I is a mild dysplasia that requires simple observation by a gynecologist. In most cases, it spontaneously regresses or does not develop.
- CIN II and III - moderate and severe dysplasia, a high class of precancerous lesions. They may also disappear or never change, especially in younger women. However, 5 to 12% of them degenerate into invasive cancer after 10 to 15 years of evolution.
If the smear results are questionable or cancerous changes are found, a cone biopsy may be performed for further diagnosis or therapy, that is, removal of a cone-shaped piece of tissue from the cervix.
How to Prepare for a Cervical Biopsy
Before conducting a diagnostic study tests are taken for HIV, syphilis, gonorrhea, hepatitis, mycoplasmosis, trichomoniasis, etc. Blood clotting is also assessed and a vaginal smear for the presence of inflammation. In order to successfully carry out the procedure, the following rules are taken into account:
- Three days before visiting a gynecologist, you should not douche, use tampons or vaginal suppositories.
- When choosing anesthesia, an allergic reaction test is performed.
- Sexual contact should be avoided three days before the biopsy.
- If general anesthesia is used for pain relief, food intake is stopped 12 hours before surgery.
- On the recommendation of a doctor, sedatives are taken.
- Documents confirming the patient’s consent to surgical interventions must be signed.
If an inflammatory process or infection is detected during preparation for the biopsy, the diagnosis is postponed for a certain time. The procedure is carried out after treatment and repeated tests. It is imperative to notify your doctor about the following facts:
- previous surgical experience;
- allergies to medications or food;
- high or low blood pressure;
- tendency to bleed;
- thromboembolism or deep vein thrombosis.
Postoperative period
Mild pain may be felt after surgery. Complete healing usually takes six weeks. Bleeding may occur two to three weeks after surgery. If bleeding lasts longer, you should contact your doctor.
Tampons should not be used for the first four weeks after the procedure. Also during this period you should avoid:
- taking baths;
- swimming;
- intensive sports training;
- lifting weights;
- sexual acts.
The postoperative period of cervical conization requires regular
colposcopic control, usually every three to four months for two years. If not all modified cells were removed during conization, which is extremely rare, a repeat cone biopsy is performed. In severe cases, a hysterectomy is required.
Possible complications
If you follow your doctor's recommendations during the recovery period, the likelihood of negative consequences occurring is low. If you do not follow hygiene standards, you can cause infection to enter the wound. As a result, signs of an inflammatory process . Increased physical activity during the recovery period is fraught with severe bleeding . It is necessary to urgently contact a gynecologist in the following cases:
- purulent discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- high body temperature;
- sharp abdominal pain;
- the duration of bleeding exceeds a week.
The likelihood of developing complications increases the presence of chronic pathologies of the liver and kidneys. Elderly women are at risk. With autoimmune diseases, bleeding disorders and obesity, the likelihood of unpleasant consequences is higher. If the rules for selecting an anesthetic drug are not followed, an allergic reaction . It manifests itself in the form of hives and itching sensations.
, scars may remain on the cervix . They pose a danger to bearing a child in the future. Therefore, for nulliparous women, more gentle diagnostic methods are selected. These include radio wave, conchotomic, laser and puncture types of biopsy.
Causes of bleeding and preventive measures
During the procedure, the integrity of the mucous membranes and underlying layers of the cervix is partially disrupted. After the biopsy, there is a period of recovery and healing, which may be accompanied by various adverse reactions and disorders, including bleeding.
The doctor must inform each patient about such consequences of the manipulation, as well as indicate possible more serious complications. During the recovery period after a biopsy, each woman should follow a number of recommendations that will significantly reduce the period of spotting.
These include the following:
- Use sanitary pads, which should be changed every 3 hours.
- Don't douche.
- Do not use tampons.
- Refuse to visit public places such as bathhouses, saunas, swimming pools, and open reservoirs.
- Avoid intense physical activity.
- For the period specified by the doctor, refuse sexual intercourse.
- Do not take medications that contain acetylsalicylic acid, which thins the blood and increases its secretion.
- It is prohibited to use medications in the form of vaginal suppositories and ointments.
Important! You should consult a doctor if you notice any suspicious symptoms.
Important! You should not be afraid of minor bleeding and light spotting after a biopsy in the first 10 days. Excessive bleeding is a dangerous symptom indicating the development of complications.
What diseases can be detected
Histological examination gives an idea of the structure of the cells of the cervix. With its help, background, precancerous and cancerous pathologies are diagnosed. The background nature of the course is the following diseases:
- cervicitis;
- papillomas;
- ruptures and fistulas;
- erosion;
- polyps;
- endometriosis.
Such ailments do not develop into cancer, but under the influence of certain factors they act as its basis. Precancerous conditions include dysplasia, adenomatosis and leukoplakia. The probability of degeneration into a malignant tumor is 50%. The procedure can also be used to diagnose early and late stages of cancer.
Process description
The biopsy procedure is painful, so it is performed under local anesthesia. The entire process of taking a piece of tissue is controlled using colposcopy. It begins as a regular gynecological examination, in addition to which the vagina is treated with an antiseptic. The cervix is lubricated with Lugol's solution containing iodine so that colposcopy reveals pathological tissues, they are paler in color, and they will be taken for analysis.
Using a scalpel, like a knife, a wedge is excised from the suspicious area. The removed fragment must contain changed and healthy tissue. Sometimes the entire affected segment is removed in the form of a wedge or triangle, then diagnosis is combined with treatment.
After the bleeding has stopped, several stitches are placed on the injured area. The removed area in formaldehyde solution is sent for examination.
For complete reliability of histological examination, damage to a piece of tissue should be minimal. That is why cutting off a piece with a scalpel has an advantage over a conventional biopsy, when deformation and compression of the material is possible.
We will call you back
Leave your phone number
Discharge after cervical biopsy
During the procedure, part of the epithelium is damaged, so bleeding may occur . They usually last no more than three days. However, abundant and prolonged symptoms indicate the development of complications. There should also or discharge with purulent contents . The color depends on the antiseptic used. When treated with iodine or brilliant green, the vaginal secretion will change color. After 2-3 days everything returns to normal. The following menstruation occurs with normal frequency and intensity.
What not to do after the procedure
During recovery, a woman is subject to certain prohibitions regarding her lifestyle. Violation of recommendations slows down the healing process and increases the risk of complications. After a biopsy you cannot:
- practice sexual contacts;
- lift heavy things (weighing more than 3 kg);
- visit swimming pools, public reservoirs, saunas and baths;
- use tampons and medications intended for vaginal administration (suppositories, ointments, douching, etc.);
- exercise.
Sexual life should be excluded for at least a week. If there are complications, the period of abstinence is extended to 21 days. The possibility of playing sports is determined on an individual basis. Abdominal exercises are especially prohibited.
Pathologically dangerous
In addition to quite dangerous uterine bleeding, you should consult a specialist if the following problems occur:
- the discharge has an unpleasant odor;
- the discharge is bright scarlet or dark brown in color;
- the discharge is not abundant, but its duration is more than 3 weeks;
- there are purulent inclusions in the discharge;
- blood discharge comes out in copious clots.
The reasons for the appearance of pathologically dangerous discharge may be:
- mechanical damage to the walls of the uterus during the procedure;
- rupture of the existing seam;
- slow healing of injuries;
- inflammatory processes;
- premature onset of menstruation due to cyclic disruptions;
- disregard for specialist recommendations.
The cause of complications after a biopsy test can also be insufficient qualifications of the doctor.
Before carrying out the procedure, the specialist is obliged to familiarize the patient with a number of contraindications and personally verify that the woman does not have them.
How to speed up cervical healing
Medications for internal and local use help to hasten the onset of the recovery process. In order to prevent inflammation, antimicrobial agents are prescribed: Ornidazole or Metronidazole . To strengthen local immunity, Genferon suppositories . To avoid scar formation, vaginal suppositories Depanthenol . Their use begins on the 10th day after the procedure, during the period when tissue regenerative processes begin. To relieve pain, No-shpa or Paracetamol . If there is a risk of infection, Terzhinan suppositories .
Taking vitamin complexes . Hygienic procedures should be carried out without the use of aggressive cleaning agents. It is acceptable to use foams and gels with a neutral pH and without fragrances. It is advisable to wear cotton underwear and use sanitary pads.