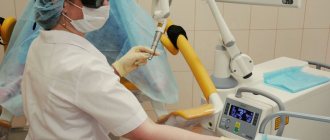
About the procedure
Many couples at the planning stage of a baby face problems.
A woman comes to the gynecologist's office with suspected infertility.
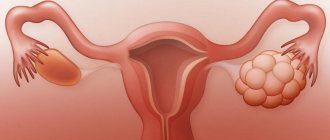
Biomaterial is taken from the ovaries for further examination.
A biopsy accurately determines the reasons for failed attempts at conception. In addition, the nature of the formations and the presence of a malignant tumor are established. However, doctors do not turn to this method very often, only in extreme cases.
Why is an ovarian biopsy performed?
Ovarian biopsy is a diagnostic method used for some pathologies of the appendages. Most often, it is necessary in the presence of cysts, tumors and other neoplasms, or prolonged absence of conception. It is an accurate way of making a diagnosis and is often used in combination with instrumental types of research.
Why is the procedure needed?
An ovarian biopsy is performed strictly for medical reasons. It is recommended for patients with suspected pathology of the appendages. This procedure is popular among women with established infertility without visible health problems. Most often, a biopsy of an ovarian cyst or tumor is performed to identify the type of formation and the presence of malignant cells in it.
Order of conduct
The total duration of the study is from 10 to 30 minutes. Stages of an ovarian biopsy:
- Placing the patient on the couch. If necessary, connect the devices necessary to monitor its condition.
- Immersion in anesthesia or administration of drugs for local anesthesia.
- Performing punctures on the abdominal cavity.
- Insertion of the laparoscope and other instruments.
- Capture the biomaterial with forceps and remove it.
- Carrying out electrocoagulation in the presence of bleeding, applying internal sutures.
- Removing instruments and applying external sutures.
Source: https://TvoiYaichniki.ru/diagnostika/biopsiya
Kinds
In gynecological practice, there are four types of procedures. They differ from each other in the purpose of the examination and the way it is carried out. The main types are as follows:
- laparoscopic biopsy. The biomaterial is collected by a doctor during a minimally invasive operation. The method is absolutely painless and informative,
- sighting. Tissue is taken through vaginal penetration. The doctor performs all manipulations under the control of a hysteroscope and colposcope,
- aspiration. The contents of the organ or tumor are sucked out. To do this, the doctor uses a regular syringe,
- intial. The organ being examined is excised using a scalpel.
The most popular methods are laparoscopic and aspiration. The latter differs in the absence of a rehabilitation period. In this case, the patient will not have to stay in a hospital for a long time.
Indications and contraindications
Indications for a biopsy in women are pathologies that could not be cured with drug therapy or hormonal treatment.
These include:
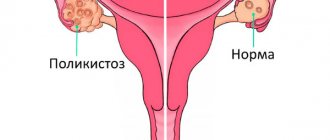
- identification of additional shares,
- polycystic disease,
- fibroma,
- papillomas,
- infertility,
- multiple cysts,
- suspicion of tecomatosis,
- developing oncology.
Attention! Indications may also include disruptions in the menstrual cycle if previously prescribed treatment has not borne fruit.
If we talk about contraindications, there are also many of them. Doctors include the following factors in this category:
- inflammatory processes,
- excess weight,
- colds or infectious diseases suffered less than 1.5 months ago,
- individual intolerance to certain types of drugs,
- the presence of cardiac pathologies,
- acute and chronic renal failure,
- poor blood clotting.
In emergency cases, a puncture is taken, despite the presence of contraindications. The attending physician bears full responsibility for what happens.
Preparation stages
Before the biopsy, the doctor prescribes a comprehensive examination, which includes an X-ray of the lungs, general blood and urine tests, taking a smear for vaginal microflora, determining the presence of antibodies to HIV, testing for hidden viruses, syphilis and hepatitis.
There are certain rules for preparing for a biopsy. Typically, a week before the procedure, the patient needs to give up dieting, eating fatty, spicy and salty foods. You should strictly adhere to the basics of proper nutrition. In addition, physical activity and sexual contact are excluded.
If possible, smokers are advised to give up their addiction for a while. It would be a good idea to stop drinking alcohol and caffeinated drinks. It is better to coordinate the use of previously prescribed medications with your doctor in advance, perhaps he will review the dosage. By the way, he needs to be informed about the presence of chronic diseases, if any.
Important! The patient should refuse food and water 6-8 hours before the biopsy to prevent bloating.
Rules
Initially, the surgeon makes 2-3 punctures in the abdominal area. The location is selected based on which ovarian material is needed for analysis. The following is the action plan:
- a camera with a flashlight and a special laparoscope with forceps are inserted,
- the appendage is grabbed and fixed,
- the second puncture provides access to the capsule and stroma,
- if heavy bleeding occurs, the electrocoagulation method is used.
The puncture can be taken using a needle with a diameter of 2 millimeters; it is inserted into the peritoneum. A syringe with a pre-prepared saline solution is attached to the surgical instrument. The latter is necessary for irrigating the affected area. The contents are sucked out with a needle.
The second method of performing a biopsy involves the following steps:
- several punctures are performed on the right or left, depending on the affected ovary,
- , a flashlight and an operating laparoscope with forceps are inserted inside
- is captured and held in a certain position,
- electrocoagulating forceps are inserted into the second puncture to supply current with open brooches, as a result of which the blood flow stops,
- the problem area is irrigated with saline solution ,
- spot coagulation is done with closed brooches if individual areas continue to bleed,
- The area is inspected for about five minutes. If no problems arise, the instruments are removed from the cavity, and sutures are placed at the puncture sites.
There are cases when the patient cannot lie on the operating table. Then, under the control of special equipment, a needle is inserted into the ovary. In this case, the woman is put under general anesthesia, and sometimes local anesthesia is used.
Reference! Neoplasm tissue or fluid located in the peritoneum serves as biosamples. The first is taken in rare cases, since there is a high degree of danger of the spread of metastases.
As a rule, in oncology, the analysis is done after the tumor is removed.
Ovarian biopsy in women: what it is, how it is performed, results
An ovarian biopsy is an operation performed to diagnose neoplasms, during which doctors obtain ovarian tissue and send it to study its structure and composition. This diagnostic method is effective and low-traumatic.
Early diagnosis of cancer through biopsy significantly increases the chances of successful treatment and the ability to have children in the future. Read on to learn more about how a biopsy is taken and why it is done, as well as about the methods of conducting it, contraindications, indications, research and other issues related to this diagnostic method.
Why do a biopsy?
Many couples experience failed attempts to conceive. To identify the causes of infertility in women, biological material is taken from the organ for further examination of the improper functioning of the ovaries.
An ovarian biopsy allows you to most accurately determine the reasons for unsuccessful attempts at conception, as well as identify the nature of neoplasms and the presence of cancer cells in the tissue sample taken. However, specialists resort to this diagnostic method in exceptional cases.
Types of biopsy in gynecology
In gynecological practice, the following types of biopsy of the appendages are used, which make it possible to diagnose malignant, benign and precancerous neoplasms:
- Laparoscopic biopsy. The method is used in most cases to take a biopsy from the ovaries through an operation during which small incisions are made in the patient's abdomen.
- Aspiration biopsy. The method involves sucking out the contents from the organ using a regular syringe.
- Incisional biopsy. The tissue required for research is excised with a scalpel.
- Targeted biopsy. Biomaterial is taken from the epithelium of the cervix under the control of a colposcope or hysteroscope.
Doctors use these methods for diagnosing ovarian pathologies in extreme cases, but if this occurs, laparoscopic and aspiration biopsies are performed.
Taking material with a syringe
Indications
A biopsy is indicated for women with the following pathologies that have not responded to drug or hormonal treatment:
- fibroids;
- presence of additional shares;
- papillomas;
- PCOS, polycystic formations;
- infertility;
- suspicion of tecomatosis;
- ovarian cancer.
In cases where there is no effect from stimulating therapy prescribed to regulate the menstrual cycle, menstrual irregularities are also an indication for the procedure.
Contraindications
Epididymal biopsy is not recommended in the presence of the following contraindications due to the high risk of complications:
- inflammatory processes in the appendages;
- overweight and obesity;
- previous infectious and cold diseases less than one and a half months ago;
- intolerance to certain drugs.
The procedure is strictly contraindicated for pathologies:
- hearts in the stage of decompensation;
- lungs in the stage of decompensation;
- liver in acute or chronic form;
- blood clotting (hemophilia).
In emergency cases, a biopsy can be performed on persons with contraindications under strict control over the life and health of the patient.
Preparing for an ovarian biopsy
Preparatory actions standards: ECG, fluorography, general and biochemical tests, identification of blood group and Rh factor, flora smear, PCR for hidden infections and viruses, antibodies to HIV, hepatitis and syphilis.
In addition, it is recommended to follow the rules:
- For a week, give up diets, junk and fatty foods, observing the principles of proper nutrition during the week.
- For five days, completely eliminate physical activity, including sexual intercourse.
- Avoid alcohol and coffee and, if possible, smoking.
- A week in advance, consult a doctor about the medications the patient is taking.
- Use only medications approved by your doctor.
- 6-8 hours before the procedure, completely refuse food and water to avoid bloating.
Be sure to notify your doctor about chronic and recent illnesses.
How is the procedure performed?
An ovarian biopsy is performed as follows:
I. 2-3 punctures are made on the patient’s abdomen, depending on which ovary material is needed: the left or the right. A camera with a flashlight and an operating laparoscope with forceps are inserted, the appendage is grabbed and held in a stationary position.
Through the 2nd puncture, the capsule and stroma are captured with biopsy syringes. If severe bleeding occurs, electrocoagulation is performed. If there is difficulty in viewing due to significant bleeding, the abdominal wall is punctured with a needle (2 mm).
A syringe with saline solution is attached to the needle, which is used to irrigate the diseased area. The contents are then sucked out with a needle.
II. 2-3 punctures are made on the patient’s abdomen, depending on which side the diseased organ is located on: left or right. A camera with a flashlight and an operating laparoscope with forceps are inserted, the ovary is grasped and held in a stationary position.
Through the 2nd puncture, electrocoagulating forceps with open brooches are inserted and current is applied. The blood stops. The affected area is irrigated with saline solution. Point coagulation is performed using closed brooches of individual bleeding areas.
They inspect the area for about 5 minutes and, if everything is in order, the instruments are removed and the punctures are sutured.
III. If the patient cannot be operated on for some reason, a needle is inserted into the ovary under the control of CT equipment or ultrasound through a puncture biopsy.
General anesthesia or local anesthesia is used. Samples may be taken of fluid inside the peritoneum or tissue from the tumor itself. The latter sample is taken extremely rarely due to the existing danger of the malignant tumor spreading to other organs.
The biopsy itself for cancer is usually performed after the tumor is removed. The duration of the biopsy varies from 15 minutes to 2 hours.
Recovery
The recovery period after ovarian biopsy is short. The patient can be discharged within 24 hours. Sick leave is given for 1-3 days. Physical and sexual rest for a month is recommended.
You may experience some pain for several days after the procedure. In this case, it is allowed to use painkillers. You can usually remove the bandage from a puncture or stitches after a day, and take a shower too, but this is individual.
Methods for studying biomaterial
The taken material is examined using microscopic technologies. The resulting tissue or liquid is sent for two types of diagnostics:
- Cytological. Cell structures are studied in detail. The biopath is placed on glass and examined through a microscope. The nature of the neoplasm is determined: malignant, precancerous, inflammatory, etc. A simple and quick study, however, the reliability is reduced compared to histological diagnosis.
- Histological. Tissue sections are studied. They are placed in a special solution and paraffin, then stained and sections are made: the cells and their areas are better distinguished under a microscope.
The patient receives a conclusion in 5-14 days. Urgently sent research results are ready in 40 minutes.
results
The following is found in the biopsy:
- Final diagnosis. It is the basis for formulating a diagnosis. Start choosing a treatment regimen.
- Indicative answer. Allows you to identify a range of possible diseases for diagnosis and establish the only correct diagnosis. They begin additional examinations to narrow the range of possible diseases.
- Descriptive answer. Indicates a lack of information, material or a presumptive diagnosis. The presumptive diagnosis is checked and, if necessary, additional examinations are prescribed.
The result can also be affected by factors such as untimely placement of the biomaterial into a fixative or taking material from outside the affected area. The result of a normal biopsy is the absence of cellular changes.
Consequences and possible complications
The ovary is surrounded by a large number of blood vessels, which can be damaged due to an error by an inexperienced doctor or a sudden movement of the patient during diagnosis. Therefore, the most common consequences are bleeding and increased pain, which go away fairly quickly. An extremely rare consequence is death (1:10,000).
The following complications may occur:
And symptoms:
- increase in temperature;
- increased amount of vaginal discharge;
- increased pain in the lower abdomen;
- the appearance of nausea and vomiting.
If the above symptoms appear or complications are suspected, it is recommended to immediately contact a medical facility.
Ovarian biopsy in children
Malignant tumor conditions that arise in childhood account for about 1% of other tumor processes. The most common neoplasm in adolescents is benign teratoma. After it - adenoma.
During the operation, surgeons examine the second ovary and, if in doubt, perform a biopsy, although this happens very rarely. Ovarian oncology in children and adolescents accounts for 0.2% of the total number of patients.
Diagnosis in girls is based on the results of the following examinations:
- inspection;
- Ultrasound;
- MRI and CT;
- general blood and urine tests;
- laparoscopy.
These examinations are usually sufficient to make an accurate diagnosis.
By trusting an experienced doctor, you can say with a 100% guarantee that the procedure will be successful, without consequences or complications.
Source: https://oyaichnikah.ru/diagnostika/biopsiya.html
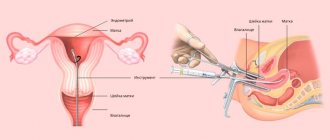
Cyst examination
Before puncturing the cyst, the patient is sent for a comprehensive examination.
It consists of the following stages:
- Ultrasound of the genital organs,
- ECG,
- CT,
- blood donation for tumor markers,
- general urine and blood tests,
- examination by a radiologist.
There are also contraindications:
- inflammatory processes,
- pregnancy,
- breastfeeding period,
- allergic reaction to medications,
- intolerance to anesthesia.
The duration of the procedure depends on the amount of internal contents of the cyst. Typically, indicators range from 15 to 40 minutes. All manipulations must be carried out only in a medical institution. The decision to conduct an analysis is made only by the attending physician.
The methodology here is as follows:
- all actions are carried out when the woman is on the gynecological chair during the administration of local anesthesia,
- inserts a sensor with a long needle into the vaginal area It helps eliminate fluid from the cyst area,
- the affected area is displayed on the screen of the ultrasound machine to monitor what is happening, and the nurse constantly monitors the woman’s blood pressure.
Important! A long needle must be fixed on one area of the tumor. The examination of the collected liquid is carried out in the laboratory by microbiologists.
Ovarian biopsy in women - how and why the procedure is done, features
Modern diagnostics make it possible to determine the structure of a neoplasm at the earliest stages, and one of such methods is an ovarian biopsy in a woman. It is prescribed exclusively by a doctor when tissue growths of unknown etiology are detected.
When prescribed or indications
For many, biopsy is associated exclusively with cancer, although this diagnostic method is actively used to identify benign tumors. As a rule, an ovarian biopsy is part of a comprehensive diagnosis, including ultrasound, blood tests, CT and some other studies.
Indications for ovarian biopsy are determined at the discretion of the doctor, but the main ones include:
- Examination in connection with identifying the causes of infertility.
- The presence of neoplasms of unknown etiology. It is important to determine the structure of the problem area in a timely manner. A biopsy is prescribed for suspected polycystic disease, fibrosis, papilloma and oncology.
- Preparatory activities for the upcoming operation.
- Tracking the dynamics of treatment, including those with a diagnosed malignant tumor.
An ovarian biopsy allows one to examine part of the biomaterial taken from a potentially problematic area, and this need arises mainly when tissue growths are detected on ultrasound. The fact that they differ from normal tissue structures on ultrasound is noticeable, but it is also important to find out which cells are included.
Features of the biopsy
The diagnostic procedure may differ slightly in the methodology used. The technique depends on the main indication for the biopsy, the location, size of the problem area, if any tumor is detected, as well as the general health of the patient.
In practice, the following methods of collecting material are often used:
- Laparoscopy using instruments to remove tissue fragments.
- Taking a puncture through a special syringe or aspiration biopsy.
- Incisional and excisional biopsy. It involves taking material by directly cutting off the problem area or by excision of the entire tumor.
For diagnostic purposes, when there are no direct indications for making incisions, laparoscopy and the aspiration method are predominantly used.
Laparoscopic biopsy
The most common method of collecting biomaterial is laparoscopy. Minimally invasive surgical intervention that does not involve abdominal excision of tissue . Three punctures are made, a special endoscope is placed in one of them so that you can monitor the process and view all actions on the monitor, and the necessary instruments are inserted into the other two.
The approximate scheme for performing an ovarian biopsy using laparoscopy is as follows:
- Use of local or general anesthesia. If a woman has health problems and her condition needs to be monitored during surgery, then the appropriate equipment is connected.
- Formation of punctures. Their location is determined depending on the ovary that needs to be examined. Usually three punctures are made, their diameter does not exceed 1.5-2 cm.
- Carrying out basic manipulations of collecting materials using instruments placed through two punctures. Illumination and control of actions passes through another puncture, where a compact endoscope is placed.
- Additional actions. During the operation, bleeding may occur due to vascular damage, to prevent which electrocoagulating type instruments are used. Simultaneous removal of the tumor and cauterization are also practiced, which is also carried out by laparoscopy.
The stages of ovarian biopsy using laparoscopy can be adjusted depending on the situation. Sometimes you have to irrigate the area under study to clear it of blood and take biomaterial. Additionally, auxiliary instruments are used and sutures are applied.
After laparoscopy, it takes several days to recover; the procedure is performed in a hospital setting, so the patient is monitored for some time. The percentage of complications is minimal; no scars remain after such surgery.
Aspiration biopsy
The material collection option does not involve any cuts or punctures. A special needle is directed directly to the pathological area. All actions are controlled by an ultrasound sensor, which helps to accurately reach the problem area without damaging the surrounding tissue. Fragments of the tumor are removed using a syringe, creating a kind of vacuum or “suction” of the material.
Incisional and excisional biopsy
This type of study takes place during open surgery. With such manipulations, a significant part of the problem area is cut off, for example, simultaneously with the removal of a tumor, cyst or other neoplasm.
Tissues removed for examination are sent to a laboratory, where the examination can be carried out using several methods.
The most informative is histological examination, which allows one to accurately identify mutated cancer cells and determine other structural changes.
In some cases, a cytological method is used, which involves studying the composition of cells under a microscope.
How to prepare
If we consider the preparatory stages for ovarian biopsy, they concern both the patient himself and the medical staff. It is necessary for doctors to conduct a comprehensive examination and exclude contraindications.
To do this, a woman takes an OAM, a general blood test, a biochemical type, for tumor markers, viruses, infections, and may also require the results of fluorography and an electrocardiogram.
Ultrasound findings are often the basis for referral for a biopsy, so a repeat ultrasound examination may not be required immediately before the procedure.
The patient also needs to prepare for the upcoming diagnosis. To do this you will need:
- Sexual abstinence for at least a week.
- Limit physical activity and, if possible, avoid stressful situations.
- 5-7 days before surgery, adhere to proper nutrition. Heavy and unhealthy foods can cause various reactions that complicate the biopsy process. Such undesirable consequences of an improper diet include flatulence and gastrointestinal disorders.
- Consult your doctor regarding the medications you are taking. It is important not to take uncontrolled medications before a biopsy, as they can affect blood clotting and other processes, the disruption of which can lead to unforeseen situations during surgical interventions.
- 5-6 hours before the main procedure, food intake is excluded.
Not only the quality and accuracy of the biopsy, but also the percentage of possible complications depends on compliance with the above rules. The woman may be given other recommendations by the doctor on how to follow the preparatory steps.
Feelings after an ovarian biopsy
The rehabilitation period after an ovarian biopsy is short, the woman quickly returns to her usual lifestyle, but for this you need to follow the doctor’s recommendations . Typically, the doctor prescribes the following rules:
- Limiting physical activity, visiting swimming pools, saunas, baths.
- Sexual rest. The period is set by the doctor depending on the complexity of the procedure performed and the identification of the pathological process.
- Treating seams or puncture marks with special antiseptic agents, maintaining personal hygiene.
- Taking prescribed medications, including antibiotics, if there is a risk of developing infectious reactions.
In rare cases, complications from the manipulations may occur, and they are manifested by pain in the ovaries, lower abdomen, as well as suppuration of the sutures, and increased body temperature. If after the biopsy you notice a deterioration in your health, or there are signs of the development of inflammatory or other pathological processes, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Ovarian biopsy allows us to identify pathologies that are almost impossible to detect using hardware methods. There is no need to be afraid of this procedure, as it is carried out painlessly due to anesthesia, and in most cases it is safe.
Source: https://gormons.ru/zhelezy/yaichniki/biopsiya-yaichnika-u-zhenshhin-kak-i-zachem-delayut-protseduru-osobennosti/
Rehabilitation
The rehabilitation period, if the laparoscopic approach is used, does not exceed 30 days.
The patient can go home within three days after the procedure.
She will experience the painful sensations themselves for about a week and a half.
General recommendations for recovery:
- You should consult a doctor if pain increases,
- in the first week after the biopsy, antibacterial agents are taken to avoid suppuration,
- for two weeks you need to stop inserting tampons into the vaginal area as a means of hygiene during menstruation,
- lifting heavy objects is prohibited,
- You cannot have sex during the entire rehabilitation period,
- the seams are treated daily with antiseptics,
- It is prohibited to visit the sauna and bathhouse, you cannot take a bath, only showers are allowed.
If the patient follows all the doctor’s instructions, the risk of complications is minimal.
Introduction
The risk of developing ovarian cancer (OC) is 1.7% and occurs mainly during the postmenopausal period [1].
The probability of developing OC during reproductive age does not exceed 0.01%. The majority of ovarian tumors are of germ cell origin (30%), borderline tumors are detected in 21%, epithelial carcinomas in 28%, Krukenberg tumor in 3%, and other types of neoplasms in 8% [2, 3]. Among all tumor processes in pregnant women, OC ranks 5th after cervical, breast, thyroid cancer and Hodgkin's lymphoma [1]. The prevalence of OC increases with age, amounting to 0.2–1.4 cases up to 20 years, 1.8–2.2 cases at 20–29 years, 3.1–5.1 cases at 20–39 years, 40-49 years old - 9.0-15.2 cases, 50-59 years old - 21.8-28.3 cases, 60-69 years old - 36.2-41.5 cases and after 70 years old - 47, 6–56.7 cases per 100,000 women [1].
During pregnancy, on average, 0.2–2% of ovarian tumors are diagnosed, and approximately 1 to 6% of them are malignant [2, 3]. There are not very many publications on the topic of ovarian cancer during pregnancy. According to a large study conducted from 1958 to 2007, OC was verified in 41 pregnant women [4]. The average age of the patients was 32.6 years (from 23 to 46 years), the stage of the disease was established in 39 cases: FIGO I in 59%, FIGO II in 5%, FIGO III in 26%, FIGO in 10% IV.
Epithelial ovarian tumors account for 50% of all tumors in pregnant women, germ cell tumors account for one third, and the remainder are stromal and other types of tumors (sarcoma, metastatic tumors).
About 50% of epithelial ovarian tumors found during pregnancy are of low malignant potential, and the remaining 50% are invasive. Epithelial ovarian tumors with low malignant potential during pregnancy can change their ultrastructure; morphological examination can reveal atypical signs characteristic of invasive cancer (nuclear polymorphism, anisocytosis, multifocal microinvasion). According to some studies, 8 out of 10 serous neoplasms diagnosed during pregnancy showed microscopic signs of a malignant process, which regressed after childbirth [5–7].
Biomaterial analysis
The biomaterial is subject to research in laboratory conditions. To do this, biologists use one of the diagnostic methods:
- cytological. Cell structure assessed through a microscope. This method allows doctors to determine what the actual nature of the ovarian tumor is. The positive aspects are that the analysis does not require much time, but the information content is low,
- histology. Tissue sections are analyzed in a special solution, where their color changes.
You usually have to wait 14 days for the analysis. If the fence was of an emergency nature, then all manipulations can be completed within a few hours.
The second method is mainly used for analysis.
Possible results
The results of a biopsy do not always help the doctor make an accurate diagnosis. At the same time, in most cases the information content of the method is high.
Gynecologist-obstetrician 6 years of experience A final diagnosis is made if the reliability of the obtained material is high, a preliminary diagnosis is made if it is impossible to accurately determine the type of illness. It allows you to reduce the list of diseases to a few of the most likely ones. In the case of a small data set, a descriptive answer is given. This situation occurs when the biomaterial was collected incorrectly.
Useful video on the topic:
Positron emission tomography (PET)
To detect cancer, this test injects glucose labeled with a radioactive substance intravenously. The radioactive substance will accumulate in malignant tumors, since they are characterized by increased consumption of glucose (sugar) compared to healthy tissues. The scanner detects these deposits.
This test is very useful for identifying tiny clusters of cancer cells. PET can be used in some cases to detect metastases from ovarian cancer.
When combined with CT (PET-CT), the value of the study increases. This test is especially good at detecting cancer metastases.
Complications
The risk of complications with this type of analysis is high. The situation is often aggravated by improper preparation for analysis, lack of personal hygiene, and neglect of existing contraindications.
A few days after the intervention, certain symptoms are observed:
- jumps in body temperature,
- blood secretion accompanied by clots,
- general weakness,
- migraine,
- nausea and frequent vomiting.
Attention! If the patient notices the above signs, she should immediately report them to the doctor. Self-relief of symptoms is strictly prohibited, since it indicates inflammation or infection in the ovaries.