Types of endometrial biopsy
The endometrium is the mucous inner layer of the uterus, which undergoes cyclic changes under the influence of female sex hormones. In accordance with the menstrual cycle calendar, the structure of the endometrium is different. The structure of the mucous layer is affected by many factors, for example, pathology of the ovaries and endocrine system. It is by studying these changes that the doctor can determine the true cause of the problem.
Depending on the purpose of the diagnosis, one of the acceptable biopsy methods is selected. The methods have various contraindications, indications that are taken into account by the gynecologist for a particular diagnosis. In modern medicine, several methods of endometrial biopsy are used for diagnostic purposes:
- classic biopsy - curettage of the inner surface of the uterus for diagnostic and treatment purposes;
- pipel biopsy - improved aspiration using low-traumatic instruments (flexible tube - pipel);
- vacuum aspiration – a vacuum aspirator is used to collect the endometrium;
- CUG - partial sampling of the mucous layer in the form of trains (scraping with strokes).
Hysteroscopy uses targeted biopsy, which makes it possible to obtain mucous tissue in areas with the most obvious structural changes, determined by visual examination.
Progress of the procedure
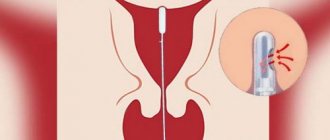
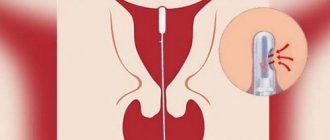
Pipelle biopsy of the endometrium is a planned intervention. It is performed on an outpatient basis and lasts 5–10 minutes.
The woman takes a comfortable position in the gynecological chair, after which the doctor inserts a special speculum and fixes the cervix. The pipel is a thin flexible probe with a diameter of 2–4 mm, so its insertion does not require preliminary dilatation of the cervix, as with diagnostic curettage.
In most cases, the procedure is painless. Sometimes, at the time of insertion or aspiration of the mucous layer of the uterus, a woman may feel short-term discomfort for 2-3 minutes, reminiscent of a nagging pain in the lower abdomen during menstruation.
There is a piston inside the pipel probe. When the piston is pulled toward itself, negative pressure is created at the opposite end of the tube, and endometrial tissue enters it. More often, the material is aspirated from several areas of the uterine mucosa. After this, the probe is carefully removed and the vaginal speculum is removed.
The aspirated tissue is placed in a container or on a glass slide and sent with an accompanying document to the histological laboratory with the obligatory indication of passport data and the day of the menstrual cycle.
Contraindications
Sometimes a biopsy may be delayed for some time or contraindicated:
- Severe anemia.
- Pregnancy.
- Infectious diseases of the genital organs in the acute or chronic stage.
- Pathological processes associated with circulatory disorders - risk of bleeding.
- Infectious diseases - intestinal infections, colds, etc.
- Taking certain medications - anti-inflammatory, anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents.
Results of the procedure
The period for performing a laboratory test for pipell biopsy of the endometrium is from 7 to 14 days. Depending on the purpose of the study and the suspected diagnosis, the following may be performed:
- routine microscopic examination of the tissue of the inner layer of the uterus;
- study using immunohistochemistry (IHC).
The cost of IHC is higher, and the information content of a biopsy with such a study is better. The result depends on the day of the menstrual cycle when the biopsy was performed, since the condition of the inner layer of the uterus changes depending on the level of female hormones (progesterone and estrogens).
Based on the results of the study, the doctor can draw conclusions about the presence of processes such as:
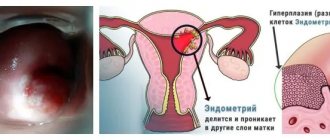
- chronic endometritis (inflammatory process in the uterus) with its type of inflammation and degree of fibrosis;
- benign hyperplastic processes of the inner layer of the uterus - polyps, endometriosis;
- precancerous and malignant degeneration of the uterine mucosa.
The condition of the tissue of the inner layer of the uterus, thickness, ability to implant an embryo, and response to hormonal treatment are also determined.
Preparation for the procedure
Endometrial biopsy is a procedure that requires preliminary preparation, including testing. So, the mandatory list includes:
- general blood and urine tests;
- analysis for sexually transmitted and blood-borne infections (syphilis, HIV, hepatitis);
- determination of Rh factor, blood group;
- coagulation study;
- vaginal smears;
- pregnancy test (human chorionic gonadotropin).
Once all contraindications have been excluded and the date for the biopsy has been set, the woman should prepare physically. Two days before the scheduled day of the study, it is recommended to refrain from any douching, insertion of vaginal tampons, and it is necessary to abstain from sexual activity. If you regularly take anticoagulants, the drugs should be stopped a week before the biopsy. When prescribing a biopsy by curettage, general anesthesia is usually used. To avoid negative consequences after anesthesia, you should avoid eating and drinking liquids after dinner before the procedure the next day.
Before the procedure, the woman must remove hair from the genital area; in the presence of varicose veins, elastic bandaging of the lower extremities is performed to prevent thromboembolism.
What happens after a biopsy is performed?
On the day after the examination, slight bleeding may be observed from the vagina. For 2–3 days after the procedure, pain in the lower abdomen and spotting brown discharge may appear. After a pipel biopsy of the endometrium, the patient can immediately return to her usual lifestyle. For a week after the procedure, it is recommended to refrain from sexual intercourse, physical activity, visiting the bathhouse and sauna, taking baths, as well as using tampons, suppositories and douching. In some cases, taking antibacterial drugs may be indicated.
At what phase of the menstrual cycle is an endometrial biopsy performed?
Depending on the day of the menstrual cycle at the time of the biopsy, the histological picture of the endometrial tissue will differ. Therefore, the duration of the procedure is determined individually, depending on the expected diagnosis.
So, if it is necessary to determine the causes of anovulation, infertility, cycle disorders, a biopsy is prescribed on the first day of the cycle or 1 day before the start of menstruation.
In the case of physiological features in the form of heavy bleeding during menstruation, it is better to perform a biopsy between 5-10 days of the cycle. A biopsy for bleeding not associated with the menstrual cycle should be performed within the first 2 days after its onset. If necessary, the study can be carried out several times during the cycle.
In the 2nd half of the cycle, that is, between days 17-25, a biopsy is performed to determine the effectiveness of hormone therapy. If the doctor suspects the presence of malignant lesions, then the study is carried out on any day of the cycle.
Indications for pipell biopsy of the endometrium
The study is prescribed by a gynecologist after a preliminary consultation if the following indications exist:
- spotting that is not associated with menstruation;
- uterine bleeding in the postmenopausal period;
- heavy, prolonged menstrual bleeding;
- disruptions of the menstrual cycle;
- prolonged bleeding after delivery or termination of pregnancy.
In addition, an endometrial biopsy is performed in preparation for in vitro fertilization (IVF) and if thickening of the uterine mucosa is detected during ultrasound diagnostics. Also, based on the results of the study, it is possible to determine the cause of problems with conception and pregnancy.
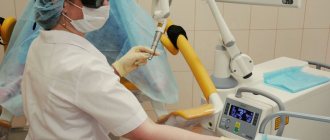
Curettage
The classic method is to collect the endometrium with a curette. During the procedure, the cervix is dilated and fixed, then the surgeon uses a sterile curette to scrape the mucous layer.
As a rule, the procedure is performed under general anesthesia. In this case, intravenous or mask anesthesia is more often used. In this regard, a woman should undergo a preliminary examination, if necessary, stop taking certain medications, and not take food or water after 6 pm the previous day.
Curettage is performed for hyperplasia of the mucous membranes, pathological bleeding, non-developing pregnancy, or suspected neoplasm.
Aspiration biopsy
In this case, the collection of material for research is carried out using vacuum aspiration. Aspiration curettage is less traumatic than classical. During the procedure there is no need to dilate the cervix, and there is virtually no pain. In case of increased sensitivity, short-term drug anesthesia can be used.
Preparation for vacuum aspiration involves avoiding douching, sanitary tampons, and sexual intercourse for 3 days before the procedure. In the evening before the biopsy, it is recommended to do a cleansing enema. Since during manipulation there is a risk of infection of the uterine tissue, measures are taken to eliminate infectious and inflammatory processes in the uterine cavity.
An aspiration biopsy is performed to diagnose uterine pathologies. A disadvantage of the procedure is the relatively smaller volume of material for research than with classical curettage.
Pipelle biopsy
The Pipelle biopsy method is carried out according to a similar scheme with aspiration, but using a special thin tube with a diameter of 3 mm. The method does not require expansion of the uterus, is low-traumatic and does not lead to the development of complications.
The procedure can be performed on an outpatient basis, the preparation is the same as before aspiration. A Pipel biopsy is performed using a special Pipel tip, which is inserted into the uterine cavity. Next, when the piston is activated, a fragment of the endometrium is separated for biopsy.
As a result of this procedure, no wounds are formed on the mucous membranes, which reduces the risk of infection, and the biopsy is painless. Pipelle biopsy is recommended for young women who have not yet given birth to diagnose endometrial pathologies, identify the causes of infertility, and determine hormonal receptors.
CUG biopsy
During CUG biopsy, the cervical canal is not dilated. The surgeon removes the endometrium in thin strips along the entire cavity using a small curette. A procedure is prescribed to identify the body's response to hormone therapy, determine the degree of maturation of the mucous membranes at physiological hormonal levels during the cycle (several biopsies are assumed at different phases).
CUG biopsy is a low-traumatic and safe manipulation in which a slight sampling of the endometrium is carried out in the form of thin strokes. Sufficient information content is ensured by collecting several strips of mucous membrane from different areas of the uterine cavity.
Advantages of pipel biopsy
Compared with other minimally invasive diagnostic methods, pipell endometrial biopsy has a number of advantages:
- the procedure is painless (the examination is performed under local anesthesia);
- minimal risk of damage to the walls of the uterus;
- the possibility of collecting biomaterial from hard-to-reach places of the uterus;
- fast recovery;
- safety of the procedure (the study does not have a pathological effect on the body);
- minimal risk of complications;
- relatively low cost of the procedure.