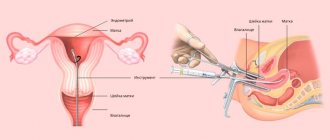
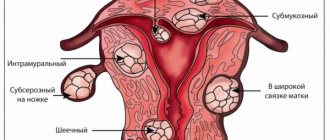
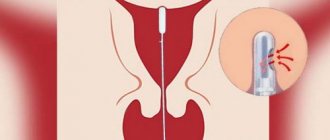
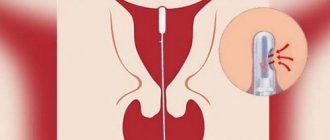
Histological examination of the endometrium is the most informative method for diagnosing most gynecological diseases.
But it requires direct collection of a sample taken from the lining of the uterus. Therefore, such procedures were previously performed quite rarely, since in all respects they resembled a full-fledged surgical intervention. This was due to manipulation technology, since literally fifty years ago doctors obtained a section of the endometrium only mechanically - with the help of scraping. The procedure was somewhat reminiscent of a surgical abortion, only performed for a different purpose. Even the instruments for performing a biopsy of the inner membrane were similar - cervical dilators, as well as a sharp small curette.
Everything changed with the active introduction of the aspiration version of manipulation, which makes it possible to collect material for analysis blindly. In gynecological practice, a polymer uterine probe has appeared that easily penetrates the cervical canal without preliminary expansion. Nowadays, taking aspirate from the uterine cavity is carried out in two ways - using a syringe or pipette biopsy.
Indications
Recently, these manipulations have become widespread for various indications:
- Approximate and initial diagnosis for suspected various diseases of the uterine body. This manipulation can be performed to diagnose conditions such as uterine cancer, endometrial hyperplasia, chronic endometritis, various variants of abnormal conditions of the uterine cavity - hematometer, serosometer.
- Routine examination before various gynecological procedures and operations. An endometrial biopsy is performed before IVF, insemination, and stimulation of ovulation in women with infertility.
In gynecological patients, this manipulation is performed as a primary stage before planned operations, for example, before removal of uterine fibroids, pelvic floor plastic surgery. Previously, separate diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity was used for these purposes, but in recent years in most cases there is no need for such a traumatic examination.
- Diagnosis of the causes of infertility in women. In this case, endometrial tissue can be obtained for histological examination. This is important for assessing the usefulness of the endometrium, its correspondence to the phase of the menstrual cycle, and the presence or absence of an inflammatory response.
- Monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of treatment for a particular condition. An aspirate from the uterine cavity can give an answer as to whether prescribed medications help, for example, for endometrial hyperplasia, or whether chronic endometritis has been treated with antibiotics.
Now let's look at each type of aspiration biopsy separately.
Taking an aspirate from the uterine cavity for cytological examination
Taking an aspirate from the uterine cavity is a diagnostic procedure, the purpose of which is to study the cellular composition of the obtained material. This inexpensive study allows you to quickly and easily identify pathological conditions of the organ.
Compared to diagnostic curettage, aspiration in gynecology is a more gentle and safe method, since the procedure does not damage the thin mucous membrane of the uterine cavity and complications are less likely to be observed.
- 1 Definition
- 2 Indications
- 3 Preparation
- 4 Procedure
- 5 Consequences
Definition
The uterus is a hollow organ lined internally with endometrium (mucous membrane). Normally, there is no fluid inside it. Sometimes ultrasound shows the presence of free secretion, which may indicate a pathological process.
If the gynecologist suspects that a woman has diseases associated with the reproductive organ, a cytological examination of the aspirate from the uterine cavity is performed. In simple terms, the doctor must extract the contents from the organ and send it for analysis.
The necessary biomaterial is obtained in several ways:
- manual - using a syringe and a flexible probe;
- electric - a special electric suction is used;
- pipel biopsy - using a tube with a piston.
Biomaterial analysis is carried out in cytological and histological laboratories within 1-3 days. In an emergency, it can be done in a few hours.
Procedure
Today, a vacuum in gynecology is created using a small compressor, which is started with certain parameters. A thin probe is attached to the device, sucking the biomaterial into a special container.
In general, the procedure for selecting biomaterial looks like this:
- The woman sits on a gynecological chair, and the gynecologist inserts a speculum into the vagina.
- Then the cervix is irrigated with a solution of local anesthetic to relieve unpleasant painful sensations.
- Then a catheter is passed through the cervix into the uterine cavity and the doctor pumps out the contents of the uterus.
- The cervix is treated with an antiseptic, and the woman is freed from the gynecological speculum.
- The manipulation takes only 2-5 minutes and takes place within the walls of the antenatal clinic.
In a pipel biopsy, instead of electric suction, a disposable, sterile, flexible catheter with a piston is used. It is easily inserted through the cervical canal into the uterine cavity and eliminates perforation of the organ wall. The technology for collecting biomaterial is the same as with the previous method.
Aspiration. Source: my-sunshine.ru
Many patients ask whether taking aspirate from the uterine cavity hurts or not. Any doctor will assure you that this procedure is completely painless. Some women feel slight discomfort in the lower abdomen associated with the creation of negative pressure in the uterine cavity. There is no pain.
Consequences
While examining the obtained contents of the uterine cavity, the laboratory technician evaluates its appearance, color and structure. Afterwards, a morphological study is performed using a microscope, which will show the structure of endometrial cells. All visible characteristics of the cells compared to normal values are recorded.
The interpretation of the result may describe the characteristic features of decreased endometrial activity - atrophy, or accelerated growth and strengthening of its function - hypertrophy and hyperplasia. The detection of atypical cells that differ in structure from the norm indicates the presence of a malignant neoplasm.
Immediately after taking the aspirate, the patient can go home. In the first days, a woman may feel slight cramping pain in the lower abdomen. If they cause discomfort, then you can use No-shpa or Spazmolgon. Light discharge from the genital tract should disappear after two days. In some women they are not observed at all.
Sexual activity after aspirate is postponed for 10 days to avoid infection of the uterine cavity. When self-healing of the organ occurs, you can resume intimate intimacy, but still use barrier contraceptives.
You should immediately consult a doctor in the following cases:
- if a few days after the procedure the temperature rises;
- if the discharge does not stop for 5-7 days;
- if heavy bleeding begins;
- if there is weakness and unbearable pain in the lower abdomen;
- if after 4-7 days purulent vaginal discharge appears.
In general, this procedure is safe, informative, painless and does not require hospitalization of the patient in a hospital or special training. The risks of developing infection and complications after it are minimal, and there is also no negative impact on the woman’s body.
Source: https://uterus2.ru/disease/aspirat-iz-polosti-matki-chto-eto-takoe.html
Vacuum biopsy
This is an older method, which, in addition to diagnosing the condition of the endometrium, has been and continues to be used to terminate short-term pregnancies and also to clean the uterine cavity from blood clots, hematometers, serozometers, remnants of the fertilized egg after abortion, and postpartum lochia when they are delayed.
Source: vashamatka.ru
The essence of the method is to use the principle of a vacuum cleaner. A vacuum aspirator is an electrical device consisting of a compressor, a thin aspiration probe or catheter inserted into the uterine cavity, and a container for the resulting aspirate.
This is the type of aspirator that is also used to terminate early pregnancies.
The aspiration procedure is as follows:
- The patient lies on the gynecological chair in a standard position.
- The cervix is brought out in the speculum, fixed with forceps, using a button probe, the doctor passes through the cervical canal and inserts a catheter into the uterine cavity.
- The catheter is fixed, the doctor presses the pedal of the device, the “vacuum cleaner” creates negative pressure and the tissues of the uterine cavity are sucked into the container.
- The doctor removes the instruments and treats the vagina and cervix with antiseptics. The procedure is over.
The resulting tissues are fixed depending on their quantity. If there is a good, abundant aspirate, the biopsy can be placed in formaldehyde and sent for histological examination. When the aspirate is scanty, histology is usually uninformative. It is better to place such a biopsy on a cytological slide and send it for cytological examination of the cellular composition.
The manipulation, as a rule, is carried out without general anesthesia under local anesthesia; the cervix is injected at certain points with a solution of novocaine or lidocaine. In young women who have given birth naturally, the procedure is sometimes carried out quietly without anesthesia at all, causing the patient a moment of minor discomfort. Manual aspiration
The meaning of the procedure is generally similar, only instead of electrical power, manual force is used to “suck out”. A manual aspirator is a kind of large syringe with a tight piston and a container for collecting the resulting tissue.
Endometrial aspiration biopsy: how it is performed, preparation, whether it hurts or not, consequences
Endometrial aspiration biopsy, or Pipelle biopsy, is an easy-to-use, informative method of gynecological diagnostics that allows you to establish an accurate diagnosis and refrain from conducting more serious and painful studies. The procedure is considered minimally invasive and quick.
The examination itself lasts no more than 5 minutes, the entire appointment takes up to 20 minutes. To collect the endometrium, the gynecologist uses a pipel - an instrument in the form of a plastic tube with a diameter of 3-4 mm with side holes and a piston.
By pulling the piston, cells necessary for histological examination enter the tube.
Indications and contraindications
Endometrial aspiration biopsy is performed only as prescribed by a doctor. Such diagnostics can identify many different diseases. Most often it is prescribed for:
- Endometriosis.
- Infertility.
- Detection of polyps in the uterus.
- Endometrial hyperplasia (thickening of the mucous membrane) of the uterus.
- Unstable menstruation.
- Continuous bleeding after childbirth or abortion.
- Chronic endometritis.
- Miscarriage.
- Pathologies during menopause.
Pipelle biopsy will be indicated in preparation for in vitro fertilization (IVF). The results of the analysis will allow you to find out the condition of the endometrium before starting the use of hormones.
Contraindications to aspiration biopsy are: pregnancy at any stage, acute infectious and inflammatory diseases of the uterus and appendages, poor blood clotting (for example, hemophilia), severe cervical stenosis.
Benefits of the procedure
Experts highlight the following undeniable advantages of endometrial aspiration biopsy:
- Simplicity and painlessness.
- High information content.
- There is no need for general anesthesia.
- Atraumatic (uterine tissue is not damaged, the risk of inflammation is minimal).
- The ability to obtain material from hard-to-reach areas of the organ.
- It is performed without dilation of the cervix.
After endometrial aspiration biopsy, the patient can leave the clinic almost immediately.
Preparation
Aspiration biopsy does not require lengthy or complex preparation. Before the examination, it is recommended to take a smear for vaginal microflora, standard blood tests, and undergo an ultrasound of the female genital organs.
At the preliminary consultation, the gynecologist will definitely ask about all the medications the patient is taking. It is especially important to know if among them there are anticoagulants - medications that thin the blood. On the eve of the study, the specialist may cancel them.
It is important to perform a pregnancy test before aspiration biopsy and make sure it is negative.
You should also keep a menstruation calendar and know the phase of the cycle, because the study can be scheduled for different periods. If chronic endometritis is suspected, the diagnostic procedure is carried out in phase 1 of the menstrual cycle (from the first day of menstruation until ovulation, while the egg matures). In all other cases, endometrial aspiration biopsy is performed any day.
It is recommended to abstain from sexual intercourse, use tampons, and limit physical activity for three days. It’s a good idea to stick to proper nutrition and maintain hydration.
Features of the event
Aspiration biopsy is performed on an outpatient basis, in a specially equipped room. After the patient is placed on the gynecological chair, the doctor examines the vagina, then carefully inserts a special speculum, opening the cervix.
Often, for a more comfortable examination, the cervix is treated with a local anesthetic solution. At this stage, proceed directly to the biopsy. Through the cervical canal, the tip of an instrument, a pipel, is inserted into the uterine cavity. In order to collect the endometrium, the piston is pulled back.
It creates negative pressure, creates a vacuum, and tissue cells are released into the plastic tube. Carefully turning the pipel, the doctor removes it from the cervical canal. After this, the material is sent to the laboratory for histological examination.
The duration of endometrial aspiration biopsy is about 20 minutes. Processing information and preparing a conclusion takes 1-2 weeks.
Period after the procedure
After a pipel biopsy, women often feel satisfactory and there is no need for hospital observation. You may experience discomfort, similar to menstruation, for 24-48 hours after the procedure.
In the first days, there may be various types of bleeding from the vagina. During this period, it is necessary to abstain from sexual intercourse.
After 3-4 days, intimate relationships can be resumed, making sure to use contraception.
After aspiration biopsy of the endometrium, menstruation occurs on time or with a delay of up to 7-10 days. If the delay is longer, you should consult your gynecologist. It is also important to tell your doctor if you feel unwell in general, fever, dizziness or fainting.
Research results
If no pathology is detected, then the results of the study will indicate that the mucous layer corresponds to the phase of the female cycle and age, and no signs of atypia were found.
If we talk about pathological conditions, then diagnostics allows us to identify:
- Endometritis.
- Underdevelopment of the endometrium or its atrophy.
- Discrepancy between the thickness of the mucous layer of the uterus and the day of the cycle.
- Atypical endometrial hyperplasia.
- Hyperplasia (glandular-cystic or simple diffuse).
- Adenomatosis (precancerous condition).
- Degeneration of the endometrium into a malignant tumor.
Additional examinations are possible if any disease from the list above is detected. The doctor will talk about this in detail during the consultation. If the biopsy provides enough data to establish an accurate diagnosis, then treatment will be prescribed.
Possible complications
During aspiration biopsy, only sterile, disposable instruments are used. The procedure follows a standardized protocol in compliance with all aseptic rules.
During the study, no surgical manipulations (incisions, sutures, etc.) occur. That is why the risk of complications is minimal.
It is important to understand that the diagnosis does not affect the ovaries and their work, and does not affect future pregnancy.
Despite this, aspiration biopsy, like other medical procedures, has several unpleasant consequences. Typically, patients report moderate pain in the lower abdomen, slight discharge, sometimes mixed with blood, headache, and increased body temperature. Inflammatory processes rarely develop in the uterus and appendages.
Pipel biopsy is a proven and safe diagnostic method. The accuracy of determining pathology and various types of disorders is up to 90%. The resulting tests make it possible to assess the condition of the mucous membrane, identify malignant cells and the causes of disorders of the reproductive organs.
Source: https://www.euroonco.ru/glossary-az/aspiratsionnaya-biopsiya-endometriya
Advantages and disadvantages
Let's start with the positive points:
- Low invasiveness and almost complete absence of trauma to the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity, in contrast to separate curettage of the uterine cavity and hysteroscopy. This is very important and relevant for young nulliparous women, patients planning pregnancy, because the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity is one of the fundamental factors for the successful onset and course of pregnancy.
- There is no need for general anesthesia, and, therefore, no risks of anesthesia and its possible complications.
- Simplicity and speed. Unlike hysteroscopy, these methods are widespread, available in almost every institution, and are not expensive.
- No need for hospitalization or hospital stay.
In the USA, this kind of manipulation is called “office” or “office” because it is carried out not in a hospital, but in a purely outpatient setting - on a regular gynecological chair in a regular gynecologist’s examination room, and does not require special training, anesthesia and sick leave.
That is, the woman undergoes this procedure and can return to work, to the “office”. Few complications. Considering its minimally invasive nature, the procedure has virtually no serious complications, unlike RDV or hysteroscopy.
The disadvantages of manipulation are:
- There is no “eye control”, that is, the procedure is, in principle, carried out blindly, in contrast to hysteroscopy, in which a biopsy can be taken under visual control, from the most suspicious area.
- Orientation of diagnosis. As a rule, in serious cases, for example, when cancer cells are detected in an aspirate from the uterine cavity, a clarifying diagnosis is indicated - hysteroscopy.
- Lack of significant therapeutic effect - that is, with aspiration biopsy it is impossible to stop the bleeding or remove the polyp. At most, vacuum aspiration can empty the cavity of liquid, blood, and exudate. When
- With pipel biopsy, a therapeutic effect is generally impossible due to the extremely thin diameter of the probe.
Pipelle endometrial biopsy - how and why they take aspirate from the uterus
Pipe endometrial biopsy is a procedure during which the doctor, using an instrument of the same name (a pipe is something like a very thin plastic syringe with a diameter of 3 mm without a needle), takes endometrial cells (the inner mucous layer of the uterus) from the patient for analysis. Histological, or more precisely, cytological analysis of a sample of the obtained tissue can show cancerous and precancerous changes in uterine cells, a chronic inflammatory process (of the endometrium), and identify dyshormonal changes.
The material is collected in the gynecologist’s office without the use of anesthesia. Typically this takes about 10 minutes .
The effectiveness of this method of taking cell material from the uterus is quite high. However, it is significantly lower than during curettage (scraping) of the uterus, when the entire endometrium is taken for analysis.
However, the pipell method makes it possible to diagnose endometrial cancer and hormonal disorders in the early stages. It is recommended for young and nulliparous women in simple situations when there is no suspicion of cancer, for example, before removal of uterine fibroids.
During the procedure, the doctor does not expand the cervix using medical instruments, and therefore does not injure it. This is a big plus.
If we compare pipel biopsy and hysteroscopy, then each method has its own advantages. With conventional hysteroscopy, the doctor can visually examine the uterine cavity and remove tumors in it. Take material from a certain area for analysis. Paypel - the procedure is simpler, faster and does not require general anesthesia, but is carried out “blindly”.
At the same time, there is a method of office (mini) hysteroscopy, which is performed without dilation of the cervix and without anesthesia, but the doctor sees everything and can take the tissue for histology. This research is deeper and more effective.
Back to contents
Indications and contraindications for endometrial aspiration
Endometrial cell analysis is performed to diagnose uterine abnormalities and rule out various diseases.
Your doctor may take a biopsy to:
- find the cause of postmenopausal bleeding or abnormal uterine bleeding;
- detect or exclude endometrial cancer;
- assess fertility (ability to conceive a child);
- check the response of the endometrium to hormonal therapy.
Do not take aspirate from the uterus in the following conditions:
- pregnancy;
- inflammation of the pelvic organs;
- cervical or vaginal infection;
- cervical cancer;
- cervical stenosis (severe narrowing of the cervix).
Back to contents
What painkillers should you take before the procedure?
Whether or not it is painful to undergo a pipel biopsy depends on the woman’s pain threshold, the skill of the doctor and the presence or absence of pain relief. Since the procedure is carried out on an outpatient basis, in any antenatal clinic, intravenous anesthesia is not advisable.
Ibuprofen , 30-60 minutes before the procedure . It will provide an analgesic effect. “No-shpa” before this , since it is a good antispasmodic, the uterus will not contract too much and painfully and will open more easily for the insertion of a pipel.
In addition, the doctor can use lidocaine spray , sprinkle it on the cervix, this will also somewhat reduce pain.
Sometimes there is a need to take a mild sedative. It may cause drowsiness, so you should not drive until the effects have completely worn off. Ask a friend or family member to drive you home after the procedure.
The most severe pain is felt at the moment of taking material for research. The uterus reacts to the doctor’s actions with spasm. The pain is similar to what happens shortly before the critical days. Some women feel dizzy and have stomach pain. This is called a vasovagal reaction.
Back to contents
How to prepare for an endometrial biopsy and on what day it is performed
Endometrial biopsy during pregnancy can lead to miscarriage. Tell your doctor if you are or are likely to be pregnant. Your gynecologist will ask you to take a pregnancy test before the biopsy to make sure there is no pregnancy.
Sometimes it is necessary to record your menstrual cycles before the biopsy so that your doctor can schedule the procedure on the most appropriate day.
If this is a woman of reproductive age, then most often an intrauterine biopsy is prescribed on the 25-26th day of the cycle , that is, 2-3 days before the critical days.
In case of infertility, when abnormalities of the luteal phase are considered to be the culprit, the procedure is recommended for the second half of the cycle. With this pathology, a woman ovulates, but by the time the fertilized egg enters the uterus, the endometrium is too thin and cannot “receive” it. This feature is successfully detected by histological analysis.
After menopause, the test is taken any day.
24 hours before diagnosis you cannot:
- use sanitary tampons;
- insert vaginal suppositories and tablets;
- douche;
- have sex.
Before the manipulation begins, you will be asked to sign a consent form stating that you understand the risks and agree to this.
Talk to your doctor about the need for a biopsy, its risks, what results may be obtained, and what they mean for you specifically.
Back to contents
How it all happens
You will be asked to lie down on a gynecological chair. The doctor will perform a manual examination of the uterus. Then he will insert a speculum into the vagina to straighten its walls and open access to the cervix. It will be fixed in a comfortable position using a clamp. Everything will be treated with antiseptic. After fixing the cervix, you will feel discomfort; pressure on the rectum is normal.
Your doctor will insert a thin, flexible tube into your cervical canal. It will go a few millimeters into the uterus. It will then pull the piston towards itself to create a suction effect. The entire procedure usually takes about 10 minutes.
The tissue sample will be placed in a liquid and sent to a laboratory for analysis. Results will be ready in approximately 7-10 days.
After the procedure, you will have some bloody vaginal discharge. Don't forget to take a sanitary pad with you. Blood may appear for several days, until the start of menstruation, if the biopsy was taken shortly before its expected start.
For several hours, pulling sensations in the uterine area and spasms are considered normal. You are allowed to take a painkiller.
Back to contents
Consequences and complications of the procedure
Sometimes a woman does not wait for the result of a histological examination because too few endometrial cells were submitted for analysis. This happens when the endometrium is thin or the material collection technique is violated. In this case, you will have to agree to curettage of the uterine cavity.
Rarely, an inflammatory process provoked by taking an aspirate can occur. It can be avoided if you take the test when you are healthy and get a good result from a gynecological smear on the flora beforehand. A very rare complication is perforation of the uterus with an instrument.
Signs of trouble are:
- increased body temperature;
- increased bleeding;
- severe abdominal pain;
- vaginal discharge with a putrid odor.
Taking a biopsy does not affect the duration of the menstrual cycle. Does not lead to delayed menstruation and infertility.
You will be able to get pregnant almost immediately after the procedure, unless your attending physician has a different opinion on this matter.
Back to contents
Recommendations from gynecologists
On the day of the aspiration biopsy, you should not expose yourself to heavy physical activity, play sports, or lift weights. Until the bloody and spotting discharge disappears completely, you should avoid taking a bath. At the same time, sexual activity should be interrupted.
Back to contents
Endometrial aspiration biopsy results - transcript
We present here some of the terms that doctors write in their conclusions.
Normal endometrium in the proliferation phase
- corresponds to the first phase of the menstrual cycle.
Normal endometrium in the secretory phase
- corresponds to the second half of the cycle.
Endometrial atrophy
- thin endometrium due to age-related changes (decreased production of sex hormones) or injury to the germ layer as a result of rough curettage.
Hyperplasia without atypia
- excessive growth of the uterine mucosa (normally, its maximum thickness in women of reproductive age on days 19-23 of the cycle is 21 mm), there is no risk of cancer at this time.
Endometritis
- acute or chronic inflammatory process of the uterine cavity, one of the causes of infertility.
Hyperplasia with atypia
- not yet cancer, but there is a bad trend, treatment and further observation are required.
Adenocarcinoma
- malignant tumor, cancer.
Back to contents
Real reviews
In order not to be unfounded, we present several reviews of women from the social network.
Source: https://viskablivanie.ru/pajpel-biopsiya-endometriya-kak-i-zachem-berut-aspirat-iz-matki.html
Preparation
Although the procedure is called “office”, a minimum examination is still required before it:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs, so that the doctor understands the picture and indications for the procedure, as well as in case of any structural features of the genital organs in this patient - for example, a bicornuate uterus or a septum in the uterus.
- General blood and urine tests to exclude acute inflammatory processes in the body.
- Gynecological smear for flora to exclude an inflammatory process in the vagina.
- A smear from the cervix for atypical cells - oncocytology.
Forecast
After aspiration of contents from the uterine cavity, a woman may notice slight bleeding, reminiscent of menstruation. The next period should be expected no earlier than in 25-35 days. The next bleeding can be either less profuse and short-lived, or more intense.
After vacuum aspiration of the reproductive pelvic cavity, you must visit a gynecologist and perform an ultrasound scan after 2 weeks. Additional examination is necessary to assess the condition of the endometrium and confirm that there are no membranes left in the uterus (in case of termination of pregnancy).
In most cases, the intervention is well tolerated and has no negative consequences. However, complications such as hormonal imbalance, infection, bleeding, and secondary infertility cannot be completely excluded. Planning the next pregnancy after the procedure is allowed no earlier than six months later. This time is necessary for the body to restore strength and hormonal levels.
Complications
Complications with this type of procedure are extremely rare, but it is important to know the possible ones:
- Perforation of the uterine walls with instruments or a probe is an almost casuistic situation, since in this version of manipulation there are no sharp, hard instruments, as in hysteroscopy or RDV.
- Secondary infection is acute or chronic endometritis, which can occur due to poor smears in the patient and violation of aseptic rules.
In conclusion, I would like to say that aspirate from the uterine cavity is an excellent alternative to surgical diagnostic methods, a real salvation for patients with contraindications to anesthesia and invasive procedures.
Share:
Contraindications
The patient needs to understand what aspiration of the uterine cavity involves. By creating negative pressure, the contents and endometrium are removed from the uterus.
Vacuum aspiration involves a preliminary examination to exclude possible contraindications. If any are detected, the manipulation is postponed until they are eliminated or eliminated altogether. In this case, the woman’s condition must be assessed, each pathological case is considered individually. Contraindications to the procedure are:
- congenital or acquired malformations of the reproductive organ;
- acute diseases of the pelvic organs or exacerbation of chronic pathologies;
- infectious processes of different localization, including colds;
- pregnancy developing outside the uterine cavity;
- fibroids causing deformation of the cavity;
- the patient's serious health condition;
- previous termination of pregnancy performed less than six months ago.
The question of the possibility of minimally invasive intervention during breastfeeding is decided individually.
After the procedure
Aspiration biopsy of the endometrium is a low-traumatic method, complications after which develop extremely rarely. However, to avoid negative consequences, after the procedure, doctors give patients the following recommendations:
- abstain from sexual intercourse for 3–5 days;
- wash regularly;
- change underwear daily;
- do not visit saunas, swimming pools;
- do not swim in open waters;
- avoid hypothermia.
On the recommendation of a gynecologist, local antiseptics in the form of suppositories or douches are used to prevent infectious complications.
In rare cases, discomfort in the lower abdomen or slight bleeding may occur within 1–2 days after taking the aspirate.