Currently, uterine fibroids are among the most common pathologies of the female reproductive system. In most cases, patients undergo surgical treatment because this is considered the most effective treatment option. This method of treatment includes hysteroscopy.
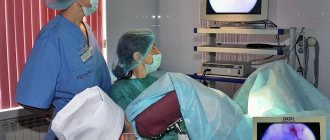
Hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive method of surgical treatment that allows you to monitor the progress of the operation visually.
Services table
| Service name | Price |
| Promotion! Initial consultation with a fertility specialist and ultrasound | 0 rub. |
| Repeated consultation with a fertility specialist | 1,900 rub. |
| Initial consultation with a reproductologist, Ph.D. Osina E.A. | 10,000 rub. |
| Hysteroscopy | RUB 22,550 |
| Ultrasound gynecological expert | RUB 3,080 |
| Therapeutic and diagnostic laparoscopy (difficulty category 1) | 65,500 rub. |
| Therapeutic and diagnostic laparoscopy (difficulty category 2) | RUB 82,200 |
| Program "Women's Health after 40" | RUB 31,770 |
Today, several types of hysteroscopy are used. This is hysteroscopy using an electric knife or a laser. Mechanical myomectomy.
What is fibroid?
Myoma is a hormone-dependent formation that begins to develop when two important hormones are imbalanced - progesterone and estrogen . To say that fibroids are a tumor is not entirely true. This formation has signs of a tumor, but in fact it is not one; it is largely a benign tumor formation.
Despite its benign nature, fibroids can not only cause a woman a lot of trouble and complications, but also in very rare cases can change its status to malignant. Therefore, it cannot be ignored .
Myoma begins its development in the growth zone, which is localized near a thin-walled blood vessel.
The growth rate of education can be either low or very high. Sometimes fibroids are multiple.
The causes of myomatous formation are precisely problems in the hormonal background of a woman, but there are also a number of provoking factors that can give impetus to the development of pathology:
- irregular sexual activity, lack of childbirth and lactation;
- ovarian diseases, endocrine diseases;
- stress and hard physical work;
- sedentary lifestyle and excess weight;
- chronic diseases;
- mechanical damage - abortions, curettage, surgical interventions;
- genetics.
NOTE!
In some cases, fibroids may begin to develop during pregnancy; such cases are especially common during late pregnancy.
Removal of a submucosal node
Depending on the category of complexity from 62,000 – 95,000 rubles.
Included in the price:
the operation, anesthesia, histological examination of the removed specimen, medications, food and hospital stay.
20-40 minutes
(duration of operation)
Indications
- submucosal myomatous nodes that deform the uterine cavity (on a thin base and interstitial-submucosal), no more than 5 cm in diameter.
Contraindications
- general inflammatory diseases (flu, sore throat, pneumonia, acute thrombophlebitis, pyelonephritis, etc.)
- severe somatic disorders incompatible with surgical treatment
- acute inflammatory diseases of the external and internal genital organs.
For small tumors, there are no symptoms at all. As soon as the tumor begins to grow due to decreased immunity or exacerbation, the patient is faced with the following manifestations of pathology:
- Acute pain that decreases with the onset of menstruation.
- The volume of menstruation and duration increase significantly.
- Bloody spotting appears regularly.
- The functioning of the sphincters of the large intestine and bladder is disrupted.
- The abdominal circumference expands.
- It is impossible to get pregnant for a long time.
Tissue necrosis gradually increases as blood flow to the uterus is significantly reduced. This is due to the appearance of twisting and pulling on the leg due to the growth of nodes. In this case, experts immediately prescribe surgical treatment, since otherwise the uterus will have to be completely removed due to tissue death.
Causes
Experts around the world cannot name the exact cause. It is known that pathology manifests itself even in the embryonic period.
During adolescence, the appearance of nodes can be triggered by an imbalance in the hormonal system (a significant increase in progesterone or estradiol).
Some experts are inclined to believe that the pathology is associated with tissue hyperplasia, and the node is not a tumor.
The following reasons can cause the development of a submucosal node:
- Taking oral contraceptives without medical supervision and testing.
- Imbalance in the hormonal system.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Psychological trauma and severe stress.
- Heavy operations with serious damage to the tissues of the reproductive and genitourinary systems.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Reluctance to become pregnant before age 35.
- Sexually transmitted infections.
- Hypertension.
Node types
There are 3 types of nodes:
- Submucosal - grows into the uterine cavity from muscle tissue and is accompanied by the growth of the mucous layer.
- Subserous - grows towards the abdominal cavity from the uterus.
- Intramural - located in the muscles of the uterus partially or completely.
In this case, submucosal nodes are divided into 4 types:
- The neoplasm is localized on the stalk without penetration into the myometrium.
- The tumor partially penetrates the muscles of the uterus.
- More than 50% of the neoplasm tissue penetrates the myometrium.
- There is no muscle tissue between the mucosa and the tumor.
Depending on the severity and tissue necrosis, specialists prescribe radical or organ-sparing surgery. If it is possible to preserve the uterus and reproductive function, then the following is prescribed:
- Embolization of the uterine arteries.
- Hysteroresectoscopy.
- FUS ablation.
- Myomectomy.
When choosing a surgical operation, medical history data, as well as the type of tumor, are taken into account.
If tissue necrosis is significant and the node has grown deep into the muscle, then complete removal of the uterus is performed using extirpation by laparotomy or hysterectomy by laparoscopic endoscopy.
To achieve a better result, the following medications are prescribed in parallel with surgical treatment: immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, hormonal, hemostatic.
How is a submucosal node removed in CELT?
- Painless
The operation is performed under general anesthesia, i.e. completely painless for the patient. - Under visual control,
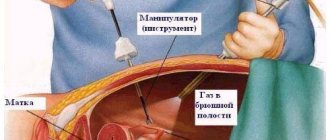
the operation is performed using an endoscope - a hysteroscope (this is an optical tube with different viewing angles with a diameter of 7 mm and a set of special instruments), which is inserted through the vagina and cervical canal into the uterine cavity. - Effective
After a detailed examination of the cavity, layer-by-layer removal of the submucosal nodes of fibroids is performed using an electric loop and careful hemostasis. The possibility of combining competent preoperative preparation (reducing nodes and the risk of bleeding) with high-quality tumor resection techniques allows preserving the uterus and the reproductive potential of patients.
Why do they trust us and choose the CELT clinic?
- The CELT Clinic has unique experience in treating uterine fibroids using different methods since 1993
- Extensive experience of gynecologists and the latest equipment guarantee results and a minimum number of complications
- The absence of queues for treatment allows you to prescribe and perform surgery as quickly as possible
Prevention
To avoid the growth of submucosal nodes, you need to follow 5 rules:
- Take hormonal contraceptives only as prescribed by a doctor with regular monitoring of your health using tests.
- Get pregnant before age 35.
- Do not delay treatment of acute and chronic diseases of the reproductive system.
- Don't have an abortion.
- Undergo diagnostics and gynecological examination at least once every six months.
If there is a suspicion of the development of pathology, then there is no need to self-medicate or use traditional methods. This will only worsen the condition and accelerate the growth of the tumor, which in the future can lead to infertility. Immediately contact a specialist for a comprehensive diagnosis.
Doctors performing submucosal node removal:
How is the difficulty category determined?
The difficulty category depends on:
- on the size, type and location of the node (the ratio of the volume of the node in the cavity to the volume of the node in the muscle of the uterus),
- from a history of operations on the cervix and body of the uterus,
- from hormonal age (reproductive or postmenopausal),
- on the degree of obesity,
- on the presence and severity of concomitant diseases. The category of complexity is determined by a gynecologist during a consultation after collecting an anamnesis, examination and evaluation of the examination results.
What type of diagnostics accurately detects tumors?
To detect tumors with 100% accuracy, you need to undergo an MRI or CT scan with contrast. These methods find the smallest nodes at the initial stage, making it possible to begin treatment earlier.
Is special preparation needed before surgery?
The evening before the operation, before a light dinner, take a herbal laxative or do a cleansing enema. On the morning of the operation, you are allowed to take medications prescribed by your doctor; you can take them with a small sip of water (other drinks, food and chewing gum are excluded).
Is conservative treatment possible?
No, all over the world complete removal of submucosal nodes is performed using surgery. Taking anti-inflammatory and hormonal drugs is an addition to the main treatment strategy.
Is reproductive function preserved after surgery?
If you start treatment on time and avoid tissue necrosis due to weakened blood flow and suppuration, you can partially remove the tumors and preserve reproductive function. With severe necrosis and tumor penetration into the muscle tissue, complete removal of the uterus is required.
Are there possible complications after the procedure?
Extremely rarely (less than 0.1%) during surgery, perforation of the uterus is possible, which is sutured laparoscopically (through punctures of the anterior abdominal wall). After surgery, inflammation of the uterus may develop.
To prevent this complication, antibacterial therapy is carried out during surgery and in the early postoperative period. Thanks to the extensive experience of our doctors, complications are kept to a minimum.
Postoperative rehabilitation
In the postoperative period, to prevent complications, it is recommended to limit usual physical activity for 2-3 weeks and abstain from sexual activity for 2 weeks. Upon receipt of the results of a histological examination of the removed specimen, an individual program for further treatment is determined (examination by the attending physician 2-4 weeks after surgery).
Source: https://www.celt.ru/napravlenija/gynec/uslugi/udal-submukoz-uzla/
Kinds
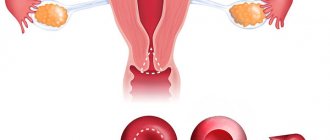
There are 5 types of fibroids, which are distinguished by the nature of their growth and location:
- intermuscular or submucosal - develops in the muscle layer. This form accounts for more than half of all cases.
- submucosal – the growth of the formation is directed towards the endometrium;
- subperitoneal – fibroids are located under the outer membrane of the reproductive organ;
- retroperitoneal – the formation grows from the lower parts of the uterus or from the cervix;
- interligamentous – localized between the uterine ligaments.
Experts separately consider formations that have a leg. Myoma without a stalk is called diffuse.
The cellular composition of fibroids also has its own classification:
- simple fibroids are a benign formation, with no mitosis;
- proliferating - this formation is also benign in nature, but the number of muscle cells in it is greater, and slight cell division is observed;
- presarcoma - mitosis is almost 80%, while the cellular structures are atypical and with heterogeneous nuclei.
Can fibroids resolve on their own? Read here.
Diagnostic methods
Early diagnosis of myomatous formation is very important for the selection of more gentle therapy .
Failure to consult a doctor in a timely manner may result in the impossibility of conservative or minimally invasive treatment of the disease.
Diagnostic measures are based on the following:
- Anamnesis collection . The doctor listens to the woman’s complaints, finds out whether the woman has had childbirth, abortion, surgery, and so on. Takes into account family history.
- Gynecological examination . In the gynecologist's chair, you can diagnose large nodes, and also see that the uterus is enlarged in size.
- Ultrasound . This diagnostic method provides a large amount of information. Ultrasound can be transabdomial or transvaginal.
- Blood test for hormones . Considering that myomatous formation directly depends on hormonal levels, this analysis is extremely important. In addition, sometimes the doctor refers the patient to analyze adrenal and thyroid hormones. Biochemical and general clinical blood tests are mandatory.
- CT, MRI;
- Hysterectomy, laparoscopy , biopsy .
- PCR, radiography.
The extent of research will be carried out by the doctor, based on the clinical picture and medical history of the woman.
It is very important to differentiate myomatous formations from endometriosis, since the symptoms of these ailments are very similar.
Technique of the procedure
Office hysteroscopy can be performed on an outpatient basis if there is a one-day hospital stay and the possibility of urgently transferring the patient to the gynecological department (if complications develop). Planned hospitalization is indicated for nulliparous women, postmenopausal women, and also in the presence of serious somatic pathology.
An endoscopic examination of the uterine cavity is performed under anesthesia. Diagnostic procedures can also be performed under local anesthesia, but according to women, this is not the most pleasant procedure. A patient who has agreed to local anesthesia feels pain when the cervix dilates and cannot always withstand such unpleasant sensations. Anesthesia is beneficial not only for the woman, but also for the doctor. While the patient is unconscious, the doctor can calmly perform all the manipulations, detect fibroids and take material for histological examination. Removal of the node is carried out only under anesthesia.
Hysteroscopy of uterine fibroids
Hysteroscopy is not only an examination of a woman’s reproductive organs, but it is also possible to perform surgery using a special device called a hysteroscope.
Prescribed when:
- the presence of polypous formations in the mucous membrane of the cervical canal or in the endometrium;
- various types of tumors in the uterine area;
- endometriosis;
- adhesions in pipes;
- other ailments of the reproductive system.
For myomatous formations, hysteroscopy is prescribed for:
- precise determination of the location of the formation;
- determining the type of formation and its size;
- removal of fibroids by mechanical, laser or electrosurgical methods;
- control over hormonal treatment, as well as during the rehabilitation period after surgery.
This intervention is minimal, but despite this, it is quite effective..
The procedure is carried out as follows. Through the hysteroscope tube, instruments are inserted into the uterine cavity that the surgeon will need to excise the tumor, scrape it, or collect the necessary material.
The intervention is performed under intravenous general anesthesia.
Useful video
Even more interesting:
Ulcers due to thrush in women
Pits on fingernails reasons photo
From the video you will learn what hysteroscopy is:
Hysteroscopy is an endoscopic method for examining the uterine cavity. The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis or in a gynecological hospital and allows you to identify various pathological conditions of the reproductive organ. In the diagnosis of submucous uterine fibroids, hysteroscopy plays a decisive role and is performed on all patients, regardless of age and reproductive status.
Hysteroscopy for uterine fibroids can be not only a diagnostic, but also a therapeutic procedure. If a small or medium-sized node is detected, located in the uterine cavity on a thin stalk, the doctor can immediately remove the tumor and save the woman from the problem. To remove other formations using a hysteroscopic approach, preliminary medical preparation is required.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of hysteroscopy are:
- high accuracy;
- duration – from 5 to 45 minutes;
- recovery period 2 days;
- no need for additional equipment to simultaneously remove pathological formations with diagnostics;
- no scars;
- preservation of menstrual and reproductive function.
The disadvantages of this procedure are the possible consequences after such an intervention.:
- bleeding - may occur if the uterine vessels are damaged during the procedure;
- infection - possible if septic and antiseptic rules are not followed;
- damage to the cervical canal;
- perforation of the uterus is a very rare complication that is possible with low qualifications of the doctor;
- Air embolism is a rare but very dangerous condition when air enters the uterus through a tube.
IMPORTANT!
In order to minimize the risks of consequences of hysteroscopy, it is necessary to carefully approach the issue of choosing a clinic and a specialist who will perform the procedure.
Symptoms
At the initial stages, fibroids do not manifest themselves in any way and make themselves felt only when their size reaches 20-60 mm. Clinical manifestations are:
- nagging and cramping pain in the lower abdomen that is not associated with menstruation;
- problems with conception;
- miscarriages;
- increased bleeding during menstruation;
- menstrual irregularities;
- an unjustified sharp increase in the abdomen.
If the above symptoms appear, you should consult a gynecologist.
Danger of disease
If you ignore the symptoms and do not consult a doctor promptly, uterine fibroids can lead to the following complications:
- heavy uterine bleeding, causing anemia;
- a sharp increase in tumor size;
- decreased uterine tone, which leads to blood loss after childbirth;
- degeneration of fibroids into sarcoma;
- hydronephrosis and pyelonephritis;
- miscarriages;
- malnutrition, fetal hypoxia.
Preparing for surgery
Before surgery, the woman is prescribed a course of hormone therapy. The woman must also pass all the necessary tests, ECG, ultrasound, colposcopy.
Before the operation, it is necessary to cleanse the intestines (with an enema or take a laxative), get rid of hair on the genitals and empty the bladder . You can eat at least 7 hours before surgery, and drink 4 hours before surgery.
You should avoid sexual intercourse two to three days before surgery. It is best to carry out the procedure on days 5-7 of the menstrual cycle, since during this period the endometrium is as thin as possible and will not interfere with the doctor .
Contraindications
Despite the minimal intervention, hysteroscopy is still an operation, and naturally there may be contraindications for it:
- oncological processes in the cervical region in a severe stage;
- pregnancy;
- cervical stenosis;
- serious diseases of the liver, kidneys and cardiovascular system;
- heavy bleeding;
- inflammatory diseases of the reproductive organs;
- viral and bacterial diseases.
Postoperative period
During the intervention under general anesthesia, the patient remains in the hospital for at least two hours.
If necessary, the patient may be kept in the hospital for a longer time. As a rule, discharge is carried out the next day after the intervention.
During the postoperative period, the following discomfort may occur::
- Malaise and fatigue that disappear within a day after the intervention;
- An increase in temperature to subfebrile levels, which also decreases on its own during the day;
- Pain in the lower abdomen, relieved by taking painkillers recommended by a specialist;
- Vaginal discharge of a spotting nature. As a rule, this is a mucous discharge mixed with blood and clots. This phenomenon can be observed for several days.
After hysteroscopy, doctors recommend:
- abstain from intimacy for a month;
- do not use tampons or douche for a month;
- do not take baths for three weeks, do not go to the sauna, bathhouse or swimming pools;
- do not overwork yourself physically;
- To wash, use only warm water and a neutral intimate hygiene product.
In general, all discomfort disappears after a week.
Breakthrough bleeding, the presence of purulent discharge, intense pain, the presence of spasms, a sharp increase in temperature above 38 degrees - this is a signal of developing postoperative complications . In this case, an urgent visit to a doctor is necessary.
As for the cost of hysteroscopic intervention, it consists of the price of the operation itself and the days that the woman will stay in the hospital after the intervention. It must be said that the difference in prices is due to the different equipment of the clinics.
Modern hysteroscopic equipment is considered quite expensive, so prices in clinics with such endoscopic equipment will be higher.
Complications
Correctly performed removal of fibroids during hysteroscopy of the uterus does not lead to complications. If contraindications were not taken into account or the procedure was performed incorrectly, the following complications may arise:
- fever due to infection;
- the occurrence of abdominal pain;
- metrorrhagia and prolonged bleeding from the genital tract;
- damage to the uterine wall, up to perforation and the development of peritonitis;
- the appearance of scars on the wall of the uterus due to rough and ineptly performed manipulation.