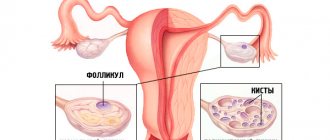
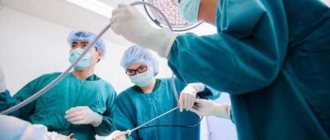
Laparoscopy of the ovaries is prescribed for cysts, ectopic pregnancy, and inflammation. Nulliparous patients worry whether ovulation will occur after surgery. Statistics say that egg maturation stops in every fifth girl after laparoscopy.
There are two types of laparoscopic intervention - emergency and planned. Doctors perform emergency surgery in the following cases:
- rupture of an ovarian cyst;
- pathologies of the reproductive system.
Reference!
During laparoscopy, several micro-incisions are made. A laparoscope with a video camera at the end is inserted into one of them, and a manipulator is inserted into the other. Carbon dioxide is released into the abdominal cavity to separate the organs from the abdominal surface for better vision.
If we talk about the planned operation, it is carried out when:
- removal of adhesions;
- uterine fibroids;
- infertility;
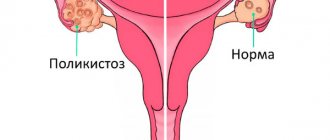
- PCOS;
- removal of fallopian tubes;
- hysterectomy;
- formations of a benign type;
- sterilization.
Laparoscopy is a popular method of surgery because the recovery period is short and the stitches are less noticeable due to their small size.
Reasons for absence
There are situations when there is no ovulation after laparoscopy. All causes are divided into two types - pathological and physiological. In some cases, the egg does not mature due to some problem. These could be diseases of the heart, thyroid gland, or uterus.
Striving for perfection, girls try to lose as much weight as possible. Taking these actions, they do not even suspect that a sharp weight loss affects fertility. When body weight is below normal, the follicle simply does not form. As a result, problems with menstruation begin.
Important!
A similar situation arises with excess weight. With obesity, there is a hormonal imbalance, sometimes due to this polycystic disease occurs, so the ovulatory period does not occur.
As for physiological reasons, girls who are breastfeeding should not wait for ovulation. This group also includes women who... Then the lack of ovulation can be attributed to menopause.
Each woman experiences up to three anovulatory cycles per year. The older you get, the more often an egg does not form. In this regard, it is recommended to become pregnant before the age of 30.
Do you always follow doctors' orders?
Yes, they know us better.
43.38%
Not always, because more information can be obtained from other women in labor.
20.31%
I comply, but I check reviews and advice from various mothers.
36.31%
Voted: 325
Often the cause of failures is the use of hormonal medications, such as those that contain estrogen.
Stimulation of ovulation in polycystic ovary syndrome
Stimulation of ovulation in polycystic ovary syndrome has its own characteristics. Depending on the severity of the process, the doctor chooses a short or long protocol. A short protocol is preferable in young girls. In women with profound hormonal imbalances, it is preferable to perform ovarian stimulation using a long protocol.
Drugs for stimulating ovulation in polycystic ovary syndrome also have their own characteristics. Typically, the scheme for stimulating ovulation in polycystic disease includes the use of several types of drugs:
Considering the fact of tissue resistance to its own insulin and the presence of excess body weight, it would be rational to carry out metabolic therapy in preparation for stimulating ovulation.
Metabolic vitamin therapy differs slightly in the composition and volume of recommended drugs:
- Antiestrogenic drugs are used - Clomiphene, Clostilbegit. The dose of drugs is selected by the doctor individually in each case. In small doses, these drugs stimulate the production of one's own FSH and LH; in large doses, they suppress the synthesis of one's own gonadotropins, which allows complete control of hormone levels in a woman's body.
- A combination of antiestrogenic drugs with a gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist is preferable.
- When carrying out a short protocol, along with Clostilbegit, the follicle growth stimulator Gonal-F can be used.
- It is rational to combine hormonal therapy with vitamin therapy:
- From days 1 to 14 of the cycle the following is used: Folic acid 400 mcg once a day;
- Glutamic acid 1 g 2 times a day;
Pyridoxine and thiamine are taken alternately every other day!
- Pyridoxine 5 mg once a day;
Thiamine 25 mg once a day.
- Tocopherol 200 mg 1 time per day;
- Potassium iodide 200 mg per day;
- Lipoic acid 0.25 mg 3 times a day;
- Cocarboxylase IM 2 ml once a day.
The scheme for stimulating ovulation with Clostilbegit for polycystic ovary syndrome is approximately the following:
- From 5 to 9 days of MC the drug is taken.
- from the 11th day of MC, ultrasound of the uterus is regularly performed to monitor the growth of the follicle.
- in the middle of the cycle, a special injection is given to ensure that the follicle ruptures and the egg comes out.
- maintenance therapy with progesterone is prescribed so that the egg develops normally. Afterwards, the results are checked using ultrasound diagnostics.
Stimulation of ovulation with folk remedies for polycystic ovary syndrome is especially popular as an adjuvant in the absence of a response to drug stimulation. The most used are:
- boron uterus for polycystic ovary syndrome is one of the most popular remedies. The plant contains vitamins and organic acids and has a powerful anti-inflammatory effect.
- It is recommended to prepare nettle roots as soon as you have discovered this disease. The alcohol infusion is taken 30 drops before meals.
- It is recommended to drink mint tea at night if you have problems with polycystic disease.
Don’t despair if you don’t get pregnant after the first cycle of stimulation. This occurs in only 60% of women. If the second and third attempts fail, then you need to return to the stage of preparation for stimulation and re-pass the examination and follow all the recommendations.
What do you need to remember?
- Ovulation after ovarian laparoscopy in most cases is restored on its own.
- If everything is in order, then the egg matures already in the first cycle after the operation, which means you can get pregnant.
- Ovulation after laparoscopy may be absent due to excess weight, hormonal imbalance, or poor quality of the operation.
- If ovulation does not occur, the gynecologist prescribes an ovarian stimulation protocol.
- A maximum of three stimulations can be made in a row.
- Gynecology: national guide / ed.: V. I. Kulakova, I. B. Manukhina, G. M. Savelyeva. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2011. - 1088 p.
- Endoscopy in gynecology / V. I. Kulakov, L. V. Adamyan. - M.: Medicine, 2000. - 384 p.
- Puchkov K.V., Politova A.K. Laparoscopic operations in gynecology: monograph. – M.: MEDPRACTIKA, 2005. – 212 p.
Unfortunately, not all women manage to get pregnant “easily and simply”, without delays and problems. Various gynecological diseases become an obstacle to motherhood, and in such cases medicine comes to the rescue. Laparoscopic surgery, which can be performed both because of the inability to get pregnant, and because of the treatment of any gynecological pathology, is one of the methods that helps to become a mother. But on the other hand, patients who have undergone this manipulation have a lot of questions: when can they get pregnant, what is needed for this, whether the operation will cause infertility, and others.
Stimulation
If ovulation does not occur after surgery, you should consult a doctor. First, he will prescribe a course of tests and studies that will confirm that the woman can become pregnant and it will not harm her. You need to do a pelvic ultrasound and take a blood test for hormones. This is the first stage of stimulation - preparatory.
In the second stage, hormonal imbalance, if present, is restored. If the patient is overweight or, conversely, underweight, then a weight adjustment program is prescribed. Often at this stage a woman becomes pregnant; it is enough just to get her health in order.
The third stage is the stimulation itself with medications. There are several basic schemes; the gynecologist selects the protocol individually, adapting to the specific patient. The woman’s medical history, age, and weight are taken into account. Also, in some cases, the doctor may prescribe a repeat laparoscopy.
Important! You can stimulate the ovaries a maximum of three times in a row. They need rest to recover. Otherwise, there may be ovarian depletion.
In total, a woman can have up to six stimulations throughout her life. If this does not help the couple have children, then this method is considered ineffective and other methods are proposed: surrogacy, donor eggs, IVF. The proposed method depends on the problems of a particular couple.
Unfortunately, stimulation of egg maturation also has side effects: weight gain, hormonal disorders, multifollicular ovaries. The most serious consequence is hyperstimulation syndrome.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
First of all, it is worth noting that with laparoscopic access, the surgeon sees much wider and more accurately the organs on which he operates due to multiple optical magnification of the given area. Other advantages should be noted:
- low trauma to organs (they do not come into contact with gloves, air and gauze swabs);
- minor blood loss;
- short periods of hospital stay (no more than two to three days);
- there is practically no pain (except for a feeling of distension in the abdomen in the first or second days after the operation, until the gas is absorbed);
- absence of rough scars, except for the places where the holes were sutured;
- quick rehabilitation period (does not require bed rest);
- low probability of formation of postoperative adhesions;
- the possibility of simultaneous diagnosis and surgical treatment;
Painful ovulation after laparoscopy
BeTeshka is your assistant in pregnancy planning
* Dear friends! Yes, this is an advertisement, you have to spin like that!
Ovulation after laparoscopy
Girls, hello everyone! I didn’t find a similar thread, just someone who got pregnant after lapara. I don't think I'll repeat it. Tell me how it was, if anyone encountered it.
Almost 2 weeks ago I had a laparoscopy, a cyst of almost 6 cm was removed (appeared while taking clostilbegit), adhesions were removed and the right ovary turned out to be polycystic (they said it didn’t work at all).
No additional treatment was prescribed, they said there was no indication for it and it could be planned immediately in this cycle.
But on top of that, before the operation, judging by the graphs, I never had ovulation (there is no difference in temperature (I’ve been measuring for more than a year)). Now I only take vitamins. The days drag on like rubber for a schedule to finally emerge, all the while waiting for a miracle. Girls who also did not ovulate before the operation, did it improve and how quickly?
Causes of painful ovulation in women and ways to relieve pain
The female body is designed in such a way that ovulation occurs approximately on days 12-14 of the menstrual cycle. This process is characterized by the rupture of the dominant follicle and the release of an egg ready for fertilization.
This can happen painlessly, but there are times when ovulation causes discomfort. According to gynecologists, pain during ovulation is normal.
However, there are situations where painful ovulation may indicate the presence of a disease.
The photo shows the moment the egg leaves the dominant follicle.
Causes of painful ovulation
- Stretching and subsequent rupture of a section of the ovary during ovulation. Increased contractility of the uterine tubes, trying to draw in a free egg. Together with the egg, fluid enters the abdominal cavity from the canal, which irritates the parietal peritoneum. The increasing size of the follicles puts pressure on the egg before ovulation, which provokes pain. Chronic inflammatory processes, which can result in adhesions. They create obstacles to the normal contraction of the tubes, which leads to pain. Endometriosis. Ectopic pregnancy or threatened miscarriage.
Pain during ovulation is considered normal in the following situations.
- After childbirth . Since inflammatory processes occur during childbirth, after them ovulation may be accompanied by constant pain. After a cesarean section, adhesions may form, which also leads to pain during the ovulation period. To treat painful ovulation after childbirth, you need to carry out a series of procedures to find out whether the pain is dangerous. This could be a vaginal ultrasound, laparoscopy, blood test, etc. It is better to contact a specialist with the test results. After stopping birth control . The process of ovulation after stopping the use of contraceptives feels exactly the same as always. Pain may occur at first and last a short period, so no specific treatment is prescribed in such a case. Over time, this process will normalize and the pain will go away. After laparoscopy . Pain after laparoscopy will go away over time; it is normal. No medical intervention is required.
The main symptom is pain that occurs in the middle of the cycle. This condition is commonly called painful ovulation syndrome. Pain can appear on both the right and left in the lower abdomen in the ovarian area.
It is important to note that in different cycles this pain may move from one side to the other. The pain may last for several minutes or may last throughout the day. The pain is acute or dull. The pain is always approximately the same, therefore, after a while, the woman experiences a familiar feeling and guesses that the ovulation period has begun.
It is important to remember that the ovulation period is the best time for conception.
How to relieve pain
After you are convinced of the symptoms of painful ovulation, you can try to relieve the pain yourself. Doctors say that the pain that accompanies ovulation is considered acceptable, and no treatment or medical intervention is needed.
It is recommended to reduce the usual physical and mental stress and, if necessary, take a pain reliever (Ibuprofen, No-spa, Ketoprofen). Taking a warm bath with aromatic oils or a warm compress on the lower abdomen will also help reduce pain.
If ovulatory syndrome brings serious discomfort, then the gynecologist has the right to recommend contraceptive drugs that block ovulation. However, such medications are contraindicated in women who are planning a pregnancy.
When to see a doctor
You should go to a doctor for examination if the following symptoms accompany ovulation occur.
- The painful sensations do not go away after ovulation is completed, the intensity of the spasms increases, and painkillers do not help. The pain is cutting, stabbing, aching in nature. A sign of serious problems is acute pain in the abdominal area. This may indicate the presence of appendicitis, ectopic pregnancy, adhesions or peritonitis. The pain is accompanied by dizziness and fainting. Painful sensations are transferred to other organs, for example, to the hypochondrium (indicates the presence of gastritis, pancreatitis, hepatitis), under the arm or shoulder blade (indicates cardiovascular diseases), in the groin (inflammatory processes in the pelvic area are possible).
If at least one of these symptoms appears, you should immediately consult a doctor. The specialist, after assessing the test results and performing a pelvic ultrasound, will make a diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Hi all! We were planning a child, but in the third year of planning we were diagnosed with adhesions in the tubes! It's a shame to the point of tears.
I sympathize with all the girls who have a similar diagnosis! A couple of months ago I had a laparoscopy, I had the most optimistic expectations that I would cross the threshold of the hospital after discharge and I would already be a healthy person! This was not the case: periodic nagging pain; it stings like an electric shock, now in one side, now in the other, I can feel any rustle in the pelvic area, and ovulation has become so painful that I can’t sleep at night... Anyone else too?
I was offered to stimulate ovulation so that several eggs would hatch in both ovaries at once, thereby increasing the chances! But I’m afraid of something: I can barely “hatch” one egg, and if there are several at once, they will probably just tear me apart...
Please advise, has anyone had personal experience?
//www. my-bt. ru/talk/post21963.html
//appendicit-simptom. ru/content/ovulyatsiya-posle-laparoskopii
//woman-l. ru/prichiny-boleznennoj-ovulyacii/
//m. baby. ru/answers/planning/category-4718015/question-243395997/
Source: //live-academy.ru/boleznennaya-ovulyaciya-posle-laparoskopii/
Why is ovulation painful?
If you suddenly start experiencing pain symptoms mid-cycle, it may be due to painful ovulation. Don't worry too much - 20% of sexually mature women experience abdominal pain every month during ovulation.
Why does it hurt so much?
Ovulation is the phenomenon of the release of a mature egg from the ovary into the abdominal cavity. For most women, this is still a painless process, which is accompanied by additional signs:
- increase in basal temperature,
- breast swelling,
- increase in the density and amount of discharge.
Pain during ovulation can be mild, or it can be very strong and acute.
It is quite natural if you want to know why this happens and why exactly you experience painful symptoms at the stage of ovulation. It is immediately worth noting that painful ovulation is a permissible condition of the body and special treatment is not needed, unless you have confused the symptoms and your appendicitis has worsened.
Causes of pain during ovulation:
- Due to the large size of the follicle, stretching appeared, followed by a slight rupture of the ovarian capsule at the time of ovulation;
- Irritation of the peritoneum as a result of the release of the egg from the follicle and a small amount of blood fluid from the ovary, which is eventually absorbed;
- Intense peristalsis of the fallopian tubes, which try to draw in the egg released from the ovary.
Very rarely, pain at the time of ovulation can cause a disease, for example, adhesions in the abdominal organs, endometriosis or fibroids. But, in addition to unpleasant ovulation, there should be other signs of these diseases.
- Spontaneous pain in the middle of the menstrual cycle against the background of good health;
- Pain can be observed on the right or left side above the pubis, depending on which ovary is functioning;
- It can radiate to the groin area and pelvic bones;
- Minor weakness, nausea, cramps, migraine can complement the pain;
- The duration of pain varies - from a few minutes to two days, but not longer.
Unbearable pain (especially with fever and vomiting) is a reason to consult a doctor. It would be good if there were records of the conditions of previous ovulations: how long the pain lasted, on what day of the cycle, the nature of the sensations.
Does pain affect conception?
Pain during ovulation and its first signs are harmless and do not initiate the appearance of gynecological diseases. The only thing that can be depressing is the discomfort during and after sex.
Interesting: Cloudy, light urine in a child
You could postpone having sex until more favorable days, but if you are interested in conceiving a child, then sex is necessary.
Doctors recommend regular sex throughout your cycle to increase your chances of conceiving. If you have sex every 2-3 days, then active sperm will definitely be in the right place and will carry out conception.
The period when cervical mucus is thicker and more slippery along the path of sperm and causes conception.
What to do to get rid of pain:
- Reduce emotional and mental stress, relaxation and peace;
- Do not make sudden movements;
- Heat on the lower abdomen (heating pad, warm bath) will relieve spasm of smooth muscles;
- Eat foods rich in plant fiber (nuts, cereals, apples, carrots, cabbage, beets and others). This will reduce irritation of the intestinal wall after bowel movement;
- Resort to the help of painkillers and antispasmodics (No-spa, drotaverine, analgin and others);
- Treatment with physiotherapy and exercise therapy;
- Apply vitamin and herbal therapy.
Protection with oral contraceptives saves you from painful ovulation, since when taking hormonal pills, ovulation does not occur at all. The doctor may prescribe hormones to prevent ovarian rupture.
Does childbirth affect ovulation?
If pain appears after childbirth, then you need to be wary of dyshormonal disorders and endometriosis.
Sometimes regular pain during ovulation begins precisely after childbirth or after suffering an inflammatory process in the organs of the reproductive system. Symptoms also occur after surgery, such as appendicitis.
This is due to the fact that the ovarian membrane becomes denser and ovulation occurs under great pressure inside the vesicle, the egg has to break its way through, and as a result, spotting occurs.
With severe hemorrhage, fluid accumulates in the pouch of Douglas, irritating the posterior wall of the uterus and rectum. The whole stomach, lower back and lower back seem to hurt.
After a cesarean section - an operation performed when complications arise during natural childbirth - adhesions often form, and subsequent ovulations are also painful.
Hormonal levels often change after childbirth. Until the body recovers from childbirth, ovulation will be painful.
What needs to be done to find out whether painful ovulation is dangerous and whether other causes affect the body after childbirth:
- taking anamnesis;
- medical examination, gynecological examination;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity in different phases of the cycle;
- blood analysis;
- vaginal ultrasound;
- study of hormonal levels;
- laparoscopy.
Operations that result in adhesions:
- Abortions, miscarriages;
- Caesarean section during childbirth;
- Laparoscopy;
- Cyst removal;
- Abdominal surgery in the peritoneal region or pelvic organs.
Consult a doctor in a timely manner, especially if, in addition to unpleasant ovulation, there is vomiting, fever, bleeding, and loose stools. The causes must be identified and treatment prescribed!
Examination before laparoscopy
Before laparoscopy, as before any other surgical operation, it is necessary to undergo a certain examination, the list of which includes:
- examination of the patient on a gynecological chair;
- complete blood count (with platelets and leukocyte count);
- general urine analysis;
- blood clotting test;
- blood chemistry;
- blood group and Rh factor;
- blood for hepatitis, syphilis and HIV infection;
- gynecological smears (from the vagina, cervix and urethra);
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs;
- fluorography and electrocardiography;
- spermogram of the husband in case of laparoscopy for infertility.
Contraindications
Laparoscopic surgery, like laparotomy, has a number of contraindications. Absolute contraindications are:
- diseases of the cardiovascular system in the stage of decompensation;
- cerebral hemorrhage;
- coagulopathies (hemophilia);
- kidney and liver failure;
- malignant diseases of the pelvic organs greater than grade 2 plus the presence of metastases;
- shock and coma of any etiology.
In addition, laparoscopic surgery is prohibited for “its own” specific reasons:
- incomplete and inadequate examination of spouses in the presence of infertility;
- the presence of sexual and general acute and chronic infectious diseases or in case of recovery less than 6 weeks ago;
- subacute or chronic salpingoophoritis (surgical treatment is carried out only for acute purulent inflammation of the appendages);
- pathological indicators of laboratory and additional examination methods;
- 3 – 4 degree of vaginal smear purity;
- obesity.
Laparoscopy: chances of pregnancy
There is a chance of pregnancy within a year after laparoscopic surgery in 85% of women. How long after laparoscopy is pregnancy possible (by month):
- after 1 month, 20% of women report a positive pregnancy test;
- 20% of patients become pregnant within 3–5 months after surgery;
- within 6 to 8 months, pregnancy was registered in 30% of patients;
- by the end of the year, the desired pregnancy occurred in 15% of women.
However, there are still 15% of women who have undergone laparoscopy and never become pregnant. In such situations, doctors recommend not to delay the wait, but to resort to IVF. After all, the longer the time passes after the operation, the less likely the chances of conceiving a child become.
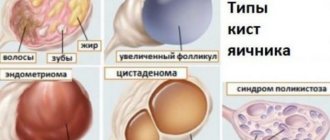
After laparoscopy for an ovarian cyst, pregnancy should also not be rushed. Laparoscopic removal of an ovarian cyst is performed very carefully; only the ovarian cyst itself is removed, leaving healthy tissue behind.
Let's work together to make the unique material even better, and after reading it, we ask you to repost it on a social network convenient for you. net.
INDICATIONS FOR LAPAROSCOPY
There are two types of laparoscopic intervention: planned and emergency. An emergency type of intervention is carried out in the following cases:
- ectopic pregnancy;
- apoplexy;
- ovarian cysts;
- in the presence of pathological abnormalities of the reproductive system.
These are the main indications that require urgent surgical intervention. The following indications for elective surgery are:
- Endometriosis. After removal of endometriotic adhesions, pregnancy occurs in 65% of cases.
- Uterine fibroids. In the initial stages of the disease, drug treatment is possible, but if it does not produce results, surgical intervention is performed.
- Infertility. Often, if there are adhesions in the fallopian tubes, it is possible to cure the pathology through laparoscopic surgery. Infertility can be treated, but it all depends on the cause of the disease.
- Removal of fallopian tubes. After such an operation, a woman loses the opportunity to conceive a child.
- Hysterectomy. A pathology that requires removal of the uterus, as a result of which the woman also loses her ability to reproduce.
- Benign neoplasms. When the size of benign neoplasms increases, surgery is required to remove them.
- Sterilization. During this operation, the woman loses the opportunity to become pregnant. This procedure is useful if a woman does not want to become pregnant.
The presence of these indications requires laparoscopic intervention. Today this method is very popular due to factors such as safety, high recovery rate and efficiency.