Such a tragedy for women as infertility, in most cases is caused by polycystic ovary syndrome or PCOS. Medicine claims that the disease cannot be cured by currently available means, but the manifestation of the disease can be significantly mitigated: restoring the menstrual cycle and ovulation by cauterizing the ovaries. Ovarian cauterization is a minimally invasive, safe operation during which the doctor cauterizes the cysts on the ovary.
When is ovarian cauterization prescribed?
Any surgical intervention must be justified. This treatment method is used when drug treatment is ineffective, ineffective, or life-threatening.
In the case of ovarian cauterization, there are several reasons for the manipulation:
- history of polycystic ovaries,
- lack of results from drug treatment,
- infertility,
- growth of cystic formations to large sizes.
If a woman has been undergoing treatment for a long time, and the diagnosis of infertility remains in the medical history, the most effective way to become pregnant is ovarian cauterization. This is a much safer option than resection. After surgery, the likelihood of adhesions and other complications occurring is minimal. After 3-4 days, the woman returns home and can return to her normal rhythm of life.
Preparatory measures
Preparation for electrocautery is the same as for traditional laparoscopy. Typically, such a surgical procedure is easily tolerated by patients, but there is still a need for preparation.
Before prescribing electrocautery, the patient should take part in the following studies:
- General blood analysis.
- Coagulogram aimed at analyzing blood clotting.
- Test for sexually transmitted infections, including HIV.
- General medical examination.
- Fluorography.
- ECG.
- Gynecological smear for microflora analysis.
The need for these measures is due to reinsurance in the occurrence of postoperative complications. For example, if blood clotting is poor, the patient cannot be prescribed electrocautery. In this case, she must take drugs that strengthen red blood cells.
The day before surgery, you are prohibited from eating. The only permitted product is low-fat kefir. You can drink water without restrictions.
An important preparatory procedure is an enema. Its purpose is to cleanse the intestines. In hospital settings, this procedure is used twice: in the evening, before bedtime, and in the morning, a few hours before surgery.
Drinking alcohol 4 days before electrocautery of the ovaries is strictly prohibited. It is also recommended to refrain from smoking during the preparatory stage.
Consequences of the procedure: pros and cons
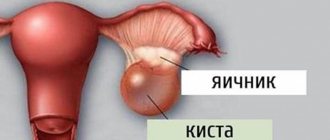
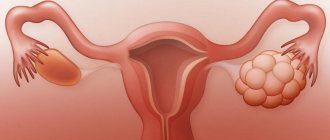
With polycystic disease, the egg maturing in the ovary cannot be released for fertilization, since the walls of the follicle are too dense. As a result, over time, many follicles form on the ovary, they fill with fluid and turn into cysts. The ovary also increases in size.
Important! The main advantage of cauterization is its minimal invasiveness.
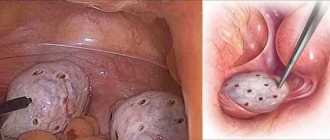
Violation of the integrity of the follicles, cleansing of accumulated fluid and restoration of ovarian function is carried out through small incisions. The operation is performed under anesthesia using special instruments and equipment. 3 pinholes are made in the abdominal cavity, after which small sutures remain, which are quickly and painlessly tightened. Another plus is complete control of all manipulations. This is achieved through the use of a camera, which displays the image on the screen. Every movement of the specialist is under visual control.
As for the disadvantages, they are related to the very essence of the surgical operation. No one is immune from blood loss or damage to other internal organs. The likelihood of adhesions in the pelvis does not completely disappear. This operation also does not promise to completely get rid of polycystic disease.
Treatment of PCOS using electrosurgery
Polycystic ovary syndrome is a common condition that interferes with the normal process of follicle maturation. Even if the egg develops normally, during ovulation it is not able to leave the organ because the follicular membrane is too thick. As a result, a cystic bladder filled with fluid is formed. Over the course of several cycles, the same situation is repeated: the ovary cannot ovulate normally, and many cysts appear in it. For this reason, a woman is unable to become pregnant. There is no treatment for polycystic ovary syndrome as such, however, there are a number of measures that allow patients with this diagnosis to successfully conceive a child. If drug therapy does not help, surgery is used.
Please note: Electrocauterization of polycystic ovaries is a highly effective method that allows manipulation with the least trauma to the genital organs. Recovery after surgery is quite fast, which allows the woman to start planning a child in the near future. This method is technically similar to conventional laparoscopy, in which instruments are inserted through small punctures.
In order for the egg to be released and fertilized, four types of surgical intervention can be performed:
- electrocautery, which involves the destruction of cystic tissue;
- electrodrilling, in which cyst cavities are removed using electric current;
- decortication, which allows you to cut off the top layer of the capsule with an electrode;
- wedge resection, the purpose of which is to cauterize the follicular cyst.
The method of surgery is determined by the doctor, who takes into account the complexity of PCOS and the general condition of the patient.
We recommend you learn: Polycystic ovary syndrome symptoms
How does the procedure work?
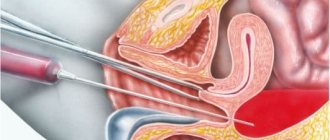
Cauterization takes place under general anesthesia, as it is a painful procedure. In the abdominal cavity, women make 2 or 3 holes with a diameter of no more than 1-2 cm. Through them, a backlit camera and a coagulator, as well as a clamp, are inserted into the abdominal cavity. Using a clamp, the ovary is fixed in the desired position, and with the help of a laparoscope, incisions are made on the ovary. To make it more convenient for the doctor to work, carbon dioxide is injected into the abdominal cavity, which improves visibility.
Using a needle-shaped coagulator, the doctor makes small incisions on the surface of the ovary up to 5 mm deep. The number of such incisions can reach 20. Gradually, accumulated fluid comes out of the cyst cavity. The ovary quickly decreases in size, this can be seen by the end of the manipulation. After similar manipulations on the second ovary, instruments and carbon dioxide are removed from the abdominal cavity. The specialist applies stitches, and the woman is returned to the ward for recovery and rehabilitation.
Features of electrocautery
Electrocauterization of the ovaries restores the function of the gonads, malfunctions of which prevent patients from becoming full-fledged women capable of becoming pregnant and bearing a child.
As a result of cauterization and dissection of the surface of the organs with a hook or electrode, the follicular fluid of the cyst pours out through the holes made (in total, “cuts” are made from 7 to 20, the number depends on the stage and severity of the disease), the ovaries decrease in volume and begin to function correctly in the near future .
The recovery period after the intervention is quick, the risks of complications and adhesions are minimal.
Rehabilitation stage
After the operation, the woman remains under doctor's supervision for several more days. After discharge, to fully restore strength and function of the reproductive system, the woman must follow the doctor’s recommendations. Typically, a rehabilitation course includes:
- taking vitamins and immunostimulating drugs,
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle, giving up cigarettes and alcohol,
- refusal of physical activity,
- proper sleep and rest,
- taking hormonal and ovulation-stimulating drugs.
In order for the rehabilitation course to be complete and give good results, you can undergo sanatorium-resort treatment in specialized institutions.
Ovulation after ovarian cauterization
Any surgical intervention in the functioning of internal organs can provoke disturbances in their functioning. So, after cauterization of the ovaries, the menstrual cycle may be disrupted. Your period may not come as scheduled. This is considered normal. In the first month after surgery, a woman is recommended to have an ultrasound scan every 2 weeks to monitor the condition of the ovaries.
If the operation is successful, ovulation occurs within 2-3 weeks. The egg is successfully released from the ovary and is ready for fertilization. Ovulation usually occurs while taking special medications.
Important! Doctors recommend refraining from open sexual intercourse in the first cycle after surgery.
If the leading specialist did not give recommendations on taking medications, and ovulation occurred on its own, this is a good sign indicating that cauterization is effective and there is a good chance of getting pregnant.
Recovery period (when to see a doctor) after transposition
After the operation, the patient remains in the intensive care unit for some time. Analgesic drugs are prescribed to relieve pain. If the pain does not subside, you should inform the medical staff.
When undergoing laparoscopic transposition, the patient can return home the next day. The criteria for allowing discharge are:
- Ability to eat regular food.
- Normalization of intestinal function (this is determined by medical staff).
- Possibility to urinate.
- Ability to walk independently.
- No severe pain.
You can carry out your daily activities at home, excluding excessive physical activity and lifting weights exceeding 5 kg. You can take a shower already on the first day after the intervention, protecting the suture area.
If you have the following symptoms, you should consult a doctor:
- Temperature rise above 38.5 degrees.
- Abdominal pain that does not go away after taking painkillers.
- Swelling and tenderness in the lower extremities.
- Prolonged constipation (no bowel movements for more than 3 days) or diarrhea.
- Breathing disorders, shortness of breath.
Ovarian cauterization and pregnancy
When can you try to get pregnant after ovarian cauterization? Theoretically, ovulation and fertilization of the egg can occur already in the first cycle. However, doctors recommend maintaining an interval of at least 2 months to allow the woman’s reproductive system to fully recover. But each individual case is individual. The doctor monitors the woman’s condition and the restoration of ovarian function. In general, cycles 3-6 are considered the best periods for conception.
This is why a woman should monitor ovulation in each cycle using tests. You cannot delay conception, since polycystic disease in most cases returns after 1-3 years.
Ovarian cauterization is an effective and safe method of treating infertility in polycystic disease. For some women, this is their only chance to become a mother. The only other way is IVF.
Reviews
Margot, 32 years old, Yaroslavl Had cauterization 4 years ago. I got pregnant after 2 cycles, but the pregnancy froze at 8 weeks. The second time we managed to conceive only after 1.5 years. Now the baby is already one year old. Svetlana, 26 years old, Moscow. I’ve been married for 4 years, we wanted a child right away, it didn’t work out, it turned out that I have polycystic disease. I was treated for a long time, had ovarian stimulation several times - all in vain, now I’m preparing for surgery, I really hope that this is the solution. I read a lot of reviews about ovarian cauterization and pregnancy. Opinions vary, as do the results. Tatyana, 36 years old, Sevastopol, gave birth to her eldest daughter and son without any problems, but when they decided on a third baby, there was no way. I went through an examination and found several cysts on my ovaries, and my hormones were not all right. The recommendations include cauterization. Everything went quickly and painlessly, now I’m recovering and we’ll try again.