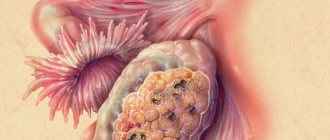
How long people live with stage 3 ovarian cancer depends on how much the woman’s body is affected by metastases. The size of metastases reaches 2 cm. But even with such a serious diagnosis, a woman has a chance to survive if the operation and course of chemotherapy were successful. In some cases, patients are completely cured of the disease and continue to live as they did before the tumor was discovered.
Survival depends on the technology of therapy and the implementation of procedures on time. From a medical point of view, the effectiveness of treatment does not depend on whether the patient has stage 1 or 3 ovarian cancer.
Symptoms of pathology
In the first stages of the disease, there may be no signs. Stage 3 ovarian cancer is accompanied by striking symptoms:
- sudden weight loss – often occurs as a result of lack of appetite;
- pathological discharge from the vagina - the presence of blood clots, foreign impurities;
- pain in the lower abdomen - increases during sexual intercourse, defecation, physical activity;
- asymmetry of the lower abdomen - occurs with large tumors, ascites;
- indigestion - nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea;
- general exhaustion of the body;
- increased frequency of urination.
When these symptoms occur, a woman often confuses ovarian cancer with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
At this stage, patients have menstrual irregularities. Such a symptom can occur even with the development of the first degree of the disease. At stage 3, the following disturbances in the course of menstruation are possible:
- complete absence of menstruation;
- frequent intermenstrual bleeding;
- the course of the cycle with a frequency of several months;
- frequent and heavy menstruation;
- scanty hemorrhages;
- severe, almost unbearable pain during the onset of menstruation;
- pronounced premenstrual syndrome.
The most common type of ovarian cancer is adenocarcinoma, which begins to actively metastasize already at stage 3.
Irregularity of menstruation is caused by the presence of a tumor on the appendages. Additionally, the disorder is facilitated by hormonal imbalance, which often occurs when the ovaries fail. This is also possible in the presence of a hormone-producing malignancy.
Diagnostic methods
Extensive testing is required to make a diagnosis. With its help, the type of pathology, type of tumor, and degree of disease are determined. A woman must undergo the following diagnostic methods:
- survey - determining the nature of menstruation, the severity of symptoms and how long ago they developed, the type of gynecological diseases suffered, the presence of ovarian cancer in relatives;
- gynecological examination - assessment of the condition of the internal genital organs, their size, pain, type of vaginal discharge;
- blood and urine tests - obtaining a picture of the general condition of the body;
- study of hormonal levels;
- biopsy of tumor tissue followed by histology - necessary to accurately determine the type of formation;
- blood tests for tumor markers - detection of malignant cells;
- Pelvic ultrasound – examination of internal organs, measuring the size of the tumor, studying its type and extent of spread, the presence of metastasis in nearby organs and lymph nodes;
- diagnostic laparoscopy - puncture of the abdominal cavity is performed if it is difficult to make a diagnosis;
- fluorography – detection of metastases in the lungs.
During the diagnostic process, the pathology is differentiated from benign tumors and cysts, uterine fibroids, endometriosis and ectopic pregnancy.
This is a standard list of procedures that must be completed. If it is difficult to make a diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe additional types of examinations. Most often, this is necessary if there is the formation of metastases in distant organs and lymph nodes.
Causes
Not everything is known about the causes of this disease. However, today there are a number of factors that, one way or another, can influence the likelihood of developing this disease.
- A risk factor is hyperestrogenism - excessive production of estrogen in the first phase of the monthly cycle. Ovarian tissue is sensitive to the effects of hormones, and hormone stimulation can provoke active cell proliferation and their malignant degeneration. Hyperestrogenism is also observed during hormonal therapy of menopause , as a consequence of stimulation of superovulation during IVF or egg donation. Since adipose tissue also has hormonal activity, obesity can also cause hyperestrogenism .
- Another risk factor is a long reproductive period with constant ovulation. This is observed with early onset of puberty and late menopause, in the absence of pregnancy and refusal of natural feeding.
- The risk of developing ovarian carcinoma is doubled in people with breast cancer.
- An important factor is heredity and genetic disposition. The risk increases if cancer was diagnosed in first-degree relatives.
- Also, some scientists note that a risk factor is the high content of animal fats in the diet, which is typical for developed countries.
How to cure ovarian cancer at stage 3
Treatment of stage 3 ovarian cancer involves the use of several therapeutic methods. The most effective of them are surgery and chemotherapy. Most often they are used in combination to enhance the therapeutic effect.
Stage 3 therapy must be combined with proper nutrition - for ovarian cancer, the diet should consist only of easily digestible foods. Patients are recommended to eat low-fat soups, boiled or baked vegetables, and fruits. Fatty, salty, fried, smoked, and alcohol are prohibited. Following a diet for stage 3 ovarian cancer can alleviate the course of the disease and eliminate the symptoms of gastrointestinal dysfunction.
Carrying out the operation
Surgery is usually performed after a course of chemotherapy. It is possible to assign one of several types of operations:
- oophorectomy - removal of one or both affected ovaries;
- panhysterectomy - removal of the uterus and its appendages;
- extirpation - involves the removal of all female genital organs, including the cervix and omentum.
Most often, one of the last two methods is used for adnexal cancer. In this case, not only the affected, but also healthy genital organs are removed. This is necessary to prevent recurrence of the disease.
If there is a need for further reproductive capacity, they try to leave the woman with the uterus and one appendage. Nevertheless, the optimal option is considered to be complete removal of organs, since during the course of this disease there is a high risk of its transition to stage 4 with subsequent death.
Recurrence of the pathology is most likely after removal of only one affected appendage.
Positive effects of surgery for oncology of the appendages:
- complete removal of a malignant tumor or significant reduction in its size;
- elimination of metastases close to the ovaries;
- increasing the survival rate from stage 3 ovarian cancer;
- preventing further development of oncology;
- reducing the risk of distant metastasis.
Surgical intervention is performed by laparoscopy or laparotomy.
The first is used for small tumors and when it is necessary to remove only one ovary. The laparotomy method is more common. When it is carried out, the best view of the internal organs opens, which improves the quality of the intervention and allows the removal of nearby metastases. Laparoscopy is more popular in the treatment of stages 1 and 2 of the disease.
Immediately after surgery, doctors install a special drainage for several days to prevent abdominal dropsy.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy can be given both before and after surgery. Its most common use is in both cases. Positive effects when used before surgery:
- prevention of metastasis to distant organs;
- complete elimination of small metastases;
- reducing the size of the tumor or stopping its growth;
- reducing the number of malignant cells in the body.
Survival prognosis
The favorable prognosis depends on many reasons. The highest chance of long-term remission of stage 3 ovarian cancer is in the presence of the following factors:
- complete course of treatment;
- strict adherence to all medical recommendations;
- presence of childbirth and full breastfeeding;
- slow-growing malignant tumor;
- absence of metastases or their minimal number;
- young age;
- damage to only one appendage;
- a tumor that does not grow into neighboring organs;
- absence of concomitant chronic diseases.
Unfortunately, with the development of stage 3 ovarian cancer, women are not able to live for a long time. Under favorable conditions, the survival rate is no more than 35% over a five-year period. The ten-year life expectancy for stage 3 ovarian cancer does not exceed 5-7%.
You can reduce the risk of relapse after stage 3 treatment by regular follow-up with a specialist after treatment. This makes it possible to detect recurrent tumor formation in the early stages and begin timely treatment. You need to visit a doctor as often as possible, and it is necessary to undergo a complete diagnosis of the body. This is especially important for women during menopause - natural hormonal imbalance at this age can provoke a recurrence of ovarian cancer.
Treatment with folk remedies
Ovarian cancer should never be treated with folk remedies. In this case, such treatment leads to delay and can be life-threatening, since precious time will be lost. Therefore, no advice given by this or that forum can be a guide to action. However, on resources like “Oncobudny” and others, you can find many practical recommendations about nutrition and psychological perception of the disease, which can be very valuable for women with cancer.
Prevention measures
Prevention involves careful monitoring of your own health. To do this, you must follow the following rules:
- visiting a gynecologist 1-2 times a year;
- annual hormonal tests, ultrasound examination of the genital organs;
- taking medications only after consulting a doctor;
- use of barrier methods of contraception;
- regular sex life;
- physical activity 2-4 times a week;
- balanced diet;
- avoidance of abortion;
- timely treatment of all pathologies.
Particular attention should be paid to the health of women at risk for developing cancer:
- genetic predisposition – presence of adnexal cancer in relatives;
- early onset of menstruation;
- late onset of menopause;
- absence of childbirth;
- late birth of the first child;
- a history of gynecological and endocrine diseases;
- lack of sex life.
It is impossible to completely prevent pathology. Preventative measures help reduce the risk of its occurrence. Regular visits to the doctor are necessary to monitor sexual health and early detection of all diseases.
A woman with symptoms of stage 3 ovarian cancer should see a doctor as soon as possible. The latter must prescribe courses of chemotherapy and surgery. The earlier treatment is started, the greater the chance of increasing the five-year survival rate. To prevent the disease and detect it in a timely manner, all preventive measures must be followed.
Consequences and complications
Ovarian cancer is a dangerous disease that can lead to the development of metastases , and in the absence of adequate and timely treatment, death.
anemia and leukopenia may develop . Kidney disease is also likely to develop. Chemotherapy increases the risk of toxic hepatitis .
After therapy, there is also a risk of re-development of the tumor, so constant preventive monitoring is very important.