Mucous discharge during pregnancy - normal or pathological?
In the early stages of gestation, the discharge is colorless and odorless, sticky, and the consistency is viscous, thick, reminiscent of snot or raw chicken protein. Rarely contains tiny inclusions with light clots. Abundant mucous secretions contribute to the closure of the cervical canal, due to which the child is protected from the action of pathogenic microorganisms from the genital tract. At week 10, the expectant mother notices the appearance of a snot-like secretion with a nagging pain in the lower abdomen due to the fact that the uterus changes position.
The second trimester is characterized by a change in the properties of the discharge: at the 15th week of pregnancy, the woman notices that it becomes less viscous, slimy and more abundant due to the intense production of estrogen. At 20-21 weeks, the secretion becomes grayish, liquid and of a uniform consistency. By the 23rd-24th, false contractions appear along with milky discharge, which the expectant mother may mistake for the onset of premature labor.
In the 3rd trimester, the mucus becomes viscous and jelly-like or watery, but experts do not consider either option to be a pathology. At 28-29 weeks, the secretion becomes less abundant, maintaining a uniform structure and transparency. At week 30, the amount of mucous secretions increases, increasing noticeably by week 33, when maximum blood filling of the organs of the reproductive system occurs.
If bloody layers are found in the mucus, severe pain appears in the lower abdomen and then heavy bleeding occurs, these symptoms may be a manifestation of premature placental abruption. At 34 weeks of gestation, the volume of discharge decreases and becomes more slippery, similar to snot.
Even when pregnancy proceeds without any pathology, a certain time before the expected birth, the expectant mother notices changes in the nature of the vaginal discharge. At 38-39 weeks, snot-like mucus with a pinkish-red tint is produced. Don't be alarmed: this is a plug coming off, signaling the imminent approach of labor.
In the third trimester, at the onset of 40-41 weeks, the secretion acquires a yellowish tint, which is considered normal.
Why mucus forms - possible reasons
Normal discharge for the gestation period is synthesized by glands located in the uterine cavity and surrounding the cervix.
Hormonal changes
After fertilization, progesterone begins to be produced, which is responsible for the physiological development of the baby in the early stages and ensures the formation of the baby’s organs and systems. At the beginning of pregnancy, under the influence of the hormone, changes in vaginal discharge occur, which is why it is viscous, viscous and thick.
In the second trimester, estrogen production increases, and mucus becomes more abundant, but of a more watery consistency. If throughout the entire period it is transparent, does not have an unpleasant odor, foreign impurities or inclusions, this indicates the normal course of pregnancy.
What does the color of the discharge indicate?
When vaginal discharge has a structure, shade and smell unusual for the norm, they are called pathological. Let's take a closer look at what disorder the color of the mucus indicates.
White color
They are considered physiological when they do not contain pathological impurities or unpleasant odors. From the 12th week, progesterone acts on the production of secretions, and on the 13th week the amount of secretions increases, but does not contain any foreign odor and does not cause itching or burning. If the secretion is abundant, it contains whitish inclusions that resemble cottage cheese and smell like beer, the expectant mother suffers from vaginal candidiasis. Thrush often occurs at 8-9 weeks and will need to be treated to prevent complications.
Yellow
At 6 and 7 weeks, leucorrhoea of this shade is considered normal if it is uniform in structure and is not accompanied by pain, itching, or foul odor. Yellow discharge may indicate the action of external factors - wearing underwear made of synthetic material, using panty liners with fragrances, failure to maintain regular hygiene of the external genitalia.
Also, yellowish mucus indicates an advanced inflammatory process, usually at the purulent stage of the pathology. The causative agents of infection are staphylococcus, E. coli, fungi of the genus Candida, chlamydia, gonococcus, trichomonas. A pregnant woman must undergo treatment so that microorganisms do not penetrate the fetus and cause various complications.
In some cases, discharge is a sign of leakage of amniotic fluid. The appearance of minor wet spots on underwear, which over time turn into large ones and have a specific odor, should alert a woman. If this phenomenon is observed in the second trimester at 25-26 weeks, it threatens complications for the health and well-being of the baby.
At week 37, the appearance of copious yellow, watery discharge indicates rupture of amniotic fluid and the onset of labor.
Green
This color of mucus indicates the presence of an active phase of inflammation caused by bacterial microflora. In this condition, the genitals become hyperemic and there is severe discomfort with itching and irritation.
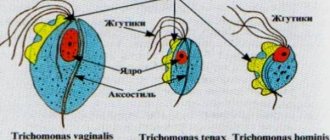
If the consistency of the mucus resembles foam, it is most likely that the expectant mother has sexually transmitted diseases - gonorrhea, trichomoniasis. Along with leucorrhoea, itching in the genitals and painful urination occurs.
Another reason for the appearance of green discharge is considered to be vaginal dysbiosis, in which it smells like fish, and when it dries, it remains on the underwear in the form of crusts.
Brown
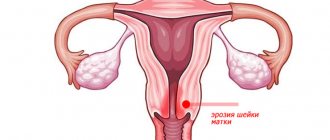
The safest reason for the formation of beige secretion is the implantation of the embryo into the uterine wall, which damages the capillaries. This occurs after recent ovulation, and the discharge resembles discharge before menstruation. In the first and second trimester, a brownish tint indicates clotted blood, so experts regard them as a threat of spontaneous abortion. Sometimes, due to increased uterine tone, mucus with this color appears at 18 weeks. In addition, the secretion can be a manifestation of an ectopic or non-developing pregnancy, as well as cervical erosion.
In reviews in pregnancy forums, questions often arise: can brown mucus appear in late gestation. Yes, it can, but you need to worry: it is a harbinger of an imminent birth.
Pink
This color indicates the appearance of blood in the organs of the reproductive system. In the early stages, pathology occurs due to microcracks in the vaginal mucosa, traumatic effects during smear collection or sex.
During pregnancy, snotty discharge may have pink, barely visible streaks, accompanied by nagging pain in the lower abdomen and lumbar region. This is a dangerous condition, regarded as a threat of termination of pregnancy.
At the 8th month of gestation at a period of 35-36 weeks, a mucous secretion appears mixed with pinkish drops. This is not considered a pathology: the body is preparing for labor.
Peculiarities
What does discharge like egg white mean? This interests many. Almost colorless, whitish or slightly yellowish, liquid or slightly viscous, odorless - such discharge may be normal.
But only if they are not accompanied by other symptoms such as itching, burning during urination or even at rest, swelling of the mucous membrane or redness of the skin. The appearance of any of these signs indicates that pathology is occurring.
When to see a doctor
During pregnancy, the secreted fluid should be clear, colorless and not have a foul odor. If you notice changes in the nature of vaginal discharge (unhealthy color, unpleasant odor, excessively watery consistency, impurities of pus or blood), you should definitely consult a qualified specialist. This will avoid threats to the health of the expectant mother and child.
If you experience nagging pain in the lower abdomen, followed by bloody discharge, call an ambulance immediately: such symptoms may indicate a threat of miscarriage!
Treatment of infections that cause mucus discharge
Therapeutic measures depend on the reason why the mucus has become pathological. Any leucorrhoea during pregnancy caused by infection should not be ignored. Do not doubt that the drugs will harm the baby. Currently, doctors prescribe medications that are approved for different periods of gestation and are safe for the child.
If the inflammatory process is caused by a nonspecific bacterial microflora, the use of antibiotics will be required - Cefazolin, Amoxiclav. They are prescribed only by a doctor, and he does not recommend using them until the 12th week, when the formation of fetal organs occurs. It is strictly forbidden to change the dosage or duration of therapy on your own. Vaginal suppositories with an anti-inflammatory effect are prescribed - Hexicon, Terzhinan.
If pathological leucorrhoea occurs due to sexually transmitted diseases, antibacterial drugs are prescribed taking into account the causative agent of the disease. For chlamydial, mycoplasma or ureaplasma infections, the antibiotic Josamine is used, for trichomonas or gonococcus - Metronidazole. At the same time, local antiseptic therapy with Miramistin and Chlorhexidine is carried out.
For thrush you will need antifungal drugs - Pimafucin, Nystatin. To restore normal vaginal flora, a specialist prescribes suppositories with bifidobacteria and lactobacilli - Bifidumbacterin, Vaginorm.
Pathological secretion
You should definitely go to the hospital if the discharge has the following characteristics:
- cheesy consistency (candidiasis);
- yellow, green, gray tint (infection);
- dark brown color (clotted blood);
- sharp pain (pathologies of the genital organs).
It is important not to confuse a normal condition with a pathological one. Yellowish discharge without pus or lumps is considered normal, but rich yellow secretion, which is accompanied by itching, burning and other unpleasant sensations, may indicate thrush or infection.
Regarding diagnosis, the examination is selected based on the patient’s symptoms and complaints. Most often, the doctor prescribes a test for protein in the urine, a smear for flora, a blood test, and an ultrasound.
The described discharge can have a wide variety of reasons. It is important to take into account the day of the month in which they occurred, as well as the accompanying sensations. Independent observation of the nature of secretion, taking into account reviews on the forum, is not the most accurate diagnostic method, but with its help you can understand that something is wrong in the body and it’s time to go to the hospital.
Preventive measures
When carrying a child, a pregnant woman must carry out a set of measures to prevent pathological processes in the body with the appearance of leucorrhoea:
- Watch your diet: food must contain essential nutrients.
- Do not overexert yourself: physical activity should be rational and alternate with proper rest.
- Regularly observe the rules of personal hygiene of the external genitalia. After each visit to the toilet, you need to wash yourself in the direction from the pubis to the anus.
- Choose underwear made from natural material, as synthetic fabric promotes the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
- Take probiotics: they are designed to restore normal vaginal microflora.
- Wash your hands exclusively with soap, without using sponges or washcloths, as germs multiply in them.
- Treat all diseases in a timely manner, preventing them from becoming chronic.
- Have sex with only one trusted partner to avoid acquiring sexually transmitted diseases.
- Avoid prolonged use of panty liners.
Changes throughout the cycle
The appearance of discharge like egg white before or after ovulation is a natural signal of physiological processes in the body. It is necessary to take into account that each woman has her own concept of the thickness and consistency of cervical mucus, but there are certain conditions in the reproductive cycle that are characteristic of everyone.
After menstruation
At the beginning of the cycle there should be no secretion, with the exception of postmenstrual discharge, which may have a slightly pink or brown tint. At this time, a new egg matures, and to protect it, a very thick cervical fluid is produced, which prevents the entry of germs, infections and sperm.
But just before ovulation, the discharge becomes abundant, transparent and liquid, it is white or colorless, slides and stretches up to 1 centimeter between the fingers (see photo).
In this way, the body prepares for possible fertilization, creating favorable conditions for sperm penetration.
In some women, discharge similar to egg white appears shortly before the ovulatory period, while in others it occurs only during the release of a mature egg.
In the middle of the cycle
When a couple plans to have a child, the question begins to worry about how many days before ovulation mucous discharge appears, because it is they who act as one of the signals of the right time for conception.
A few days before ovulation, the very thick plug of the cervix liquefies, so clear, viscous mucus comes out. This is the first sign that the egg will soon be released from the follicle and will begin to move through the fallopian tubes. The time between mucus liquefaction and the onset of ovulation varies for each woman. It may take 24 hours or three days until the egg is released and ovulation occurs. Therefore, calculating favorable days for conception based on discharge is not a reliable method.
Sometimes slight brown mucous discharge or pink discharge like egg white appears in the middle of the cycle, which is acceptable (see photo).
They are caused by damage to the follicular sac. Bloody discharge appears several hours before actual ovulation and lasts no more than two days. Using this sign, it is easier to calculate ovulation, but it is characteristic of only a small percentage of women and not in every cycle.
Discharge during ovulation has the following characteristics:
- cloudy white tint;
- medium viscosity;
- stretches well between fingers.
As soon as the third phase of the cycle begins, the secretion will again become thick and creamy. The entire ovulation period lasts from 3 to 7 days. Its duration depends on the individual characteristics of the woman. The released egg is ready for fertilization within about 48 hours, that is, ovulation itself lasts only two days.