One day, while performing routine hygiene procedures, a woman discovers that she has a lump near her vagina. Of course, such a find will cause fear, because a variety of thoughts will immediately pop into your head. Some will even try to remove the growth themselves, picking it out with a fingernail or something else that their imagination allows. This must not be done under any circumstances!
To begin with, it is important to understand what a lump at the entrance to the vagina is, and only a doctor can help you with this. Either he will immediately reassure the patient, or after the examination he will propose a treatment regimen. In any case, you should visit your gynecologist so as not to torment yourself with dark thoughts. In this article we will tell you what types of seals there are and what symptoms accompany them, as well as how a specialist makes a diagnosis.
Causes
A neoplasm that arises on the external organs of the reproductive system often has a different origin. In order to get rid of a lump, it is necessary to identify the factor that caused its occurrence.
When seeking help from a doctor, women call the new growth in the vaginal area a lump. A lump in the vagina may be the result of previously suffered inflammatory and hyperplastic changes and processes.
The sources that provoke the growth of the tumor can also be the glands of the vulva, various membranes of the vaginal wall and tissues close to the pelvic organs.
The most common factors causing this formation are the following gynecological diseases:
- Bartholinitis;
- Cyst;
- Fibroids;
- Lipoma.
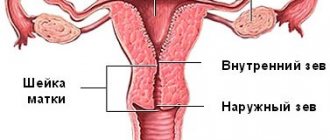
In medical practice, cases have been recorded when a woman mistakes the cervix for a lump. This phenomenon occurs due to severe weakening of the pelvic ligaments and as a result of this, the cervix drops very low down to the vestibule of the vagina.
Such pathological changes most often occur in older or older women who have previously experienced more than one childbirth and also engaged in heavy physical work. In addition, at this age women also experience menopause, which is characterized by a huge number of changes and processes, including hormonal imbalance.
Definition and classification of vaginal cancer
The content of the article
Vaginal cancer develops as a result of malignant degeneration of the vaginal mucosa. This is a rare pathology. It accounts for about 1-3% of all malignant neoplasms of the female genital organs. This pathology can develop both in young and old age, however, the peak incidence occurs in the 60-70 years of life. Histological types of vaginal cancer:
- squamous cell carcinoma (almost 90% of all types of malignant tumors of the vagina);
- adenocarcinoma (2-3.5%);
- glandular squamous cell carcinoma (1-2%).
There are also more rare types of adenocarcinoma of vaginal cancer: mesonephroid or clear cell, endometrioid, adenoid cystic.
There are primary vaginal cancer and secondary (develops as a result of metastasis). Primary vaginal cancer develops directly from vaginal cells and accounts for about 1% of the total disease. Metastatic vaginal cancer develops as a result of the spread of the following malignant tumors:
- cervical cancer – 33%;
- kidney and bladder cancer – 5%;
- endometrium and choriocarcinoma – 24-55%;
- rectum – 2%;
- breast – 1%;
- ovaries – 1%.
Tumor in the vagina
Symptoms
A visit to a doctor begins with collecting anamnesis and all complaints that worry the woman. In this case, the main problem troubling her will be the formation of a lump in the vagina. After this, the women's doctor will ask the woman to undress and go to the gynecological chair for a follow-up examination.
The gynecologist, conducting an examination on the chair, uses special medical equipment and also conducts a bimanual examination. During the examination, the specialist pays attention to all local and general signs that may be associated with the occurrence of a neoplasm of unknown etiology.
Bartholinitis
Picture taken from zhenskay-pilulya.info
Very often, the appearance of a lump in the intimate area is associated with bartholinitis. This pathological condition is very common and is characterized by inflammation of the Bartholin glands located at the base of the female labia.
The Bartholin gland is a paired organ responsible for the production of a special lubricant that helps soften the friction that occurs during sexual intercourse. The production of this substance occurs directly during the period of sexual desire. In teenage girls, bumps associated with bartholinitis do not occur, since the gland is not fully developed.
Today, two stages of the disease are known, which differ in the nature of their course, namely:
- acute stage of bartholinitis - pain in the labia area, redness and swelling, hyperthermia;
- chronic stage - in the presence of this stage, the pain can periodically worsen and bother the woman for a long time.
With the onset of the chronic stage, compaction and blockage of the Bartholin glands occurs. As a result, the lubricant stops coming out, forming lumps (Bartholin gland cysts).
At first, these tumors do not bother the woman and do not cause pain or other extremely unpleasant symptoms. If harmful microorganisms get inside, an inflammatory process begins.
If a woman does not consult a gynecologist in a timely manner, she may develop an abscess of the Bartholin gland. It is important to undergo special diagnostics and therapy aimed at eliminating the tumor.
The main symptoms indicating the occurrence of an abscess are the following changes:
- swelling and severe redness of the skin;
- the occurrence of painful sensations when pressing;
- blocking the entrance to the vagina;
- pain begins to appear at the slightest movement;
- increase in body temperature.
In the event of true purulent inflammation, tissue melting begins, very often accompanied by more pronounced symptoms, bringing enormous discomfort. The most common symptoms for this condition are considered to be:
- enlargement of regional lymph nodes;
- severe swelling of the labia;
- deterioration of the woman’s general condition;
- increased weakness and fatigue;
- headache.
When a purulent neoplasm is opened, it is not completely emptied and, as a result, the risk of relapse increases, followed by a very protracted course.
An exacerbation of the chronic process often occurs during the onset of menstruation, as well as in the case of a sharp decrease in immunity and the occurrence of various diseases. At this moment, a small compaction begins to appear in the area where the gland is located, causing discomfort to the woman during movements. If no measures are taken, a cyst will form at this site.
To summarize, we can say that bartholinitis is a disease that occurs as a result of the ingress of bacteria and other microbes that provoke the development of the inflammatory process of the Bartholin gland, located at the vestibule of the vagina. This phenomenon is accompanied by the appearance of a lump, which brings pain and other unpleasant sensations.
Cyst
A factor that can result in a lump in the vagina is a cyst. This disease is much less common than bartholinitis, but you should not forget about it.
A cyst is a neoplasm filled with fluid or epithelial tissue inside and is formed from the walls of internal organs. This pathology can be congenital or occur after various types of injuries.
The disease is practically asymptomatic; therefore, it is detected during a preventive examination. There are exceptions when a cyst that is quite large in size contributes to the appearance of the following symptoms:
- a woman feels a foreign body;
- during sexual intercourse unpleasant sensations appear;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- problems with bowel movements.
During a gynecological examination, this neoplasm does not cause pain, and its smooth shell is practically no different from the mucous membrane of the reproductive system.
A huge cyst creates great obstacles to the birth of a baby. If inflammation occurs, a woman experiences discharge that is uncharacteristic of the normal state, accompanied by pain. In this case, not only expression, but also independent opening of the cyst may occur.
Symptoms of vaginal cancer
The clinical picture of the disease depends on its stage. The development cycle of vaginal cancer consists of the following stages: dysplasia, preinvasive form and invasive form of the disease. According to the histological structure, the preinvasive form of cancer does not differ significantly from severe dysplasia. The invasive form of cancer develops from non-invasive cancer in approximately 12-15 years.
At the early stage of vaginal cancer, there are no obvious symptoms of the disease. During the formation of an ulcer, bloody or bloody discharge appears; it can be spontaneous or occur after sexual intercourse. The growth of the tumor leads to pain in the pubic area, groin, and sacrum. The act of defecation is disrupted, and frequent urination is typical.
Symptoms of vaginal cancer:
- bleeding during and after sexual intercourse;
- abnormal vaginal bleeding;
- painful urination;
- pain in the pelvic area, pubic area;
- feeling of pressure in the bladder area;
- painful act of defecation.
Abnormal bleeding
Painful urination
In percentage terms, the most commonly observed are:
- bloody discharge – 58-67%;
- pathological leukorrhea (excessive pathological leucorrhoea with an unpleasant odor and uncharacteristic color) – 14-28%;
- urinary disorders – 16%;
- pain in the sacrum, lower back, lower abdomen - 15-28%.
The severity of symptoms depends on the size of the vaginal tumor and its infiltration into adjacent tissues. In the severe stage of the disease (III-IV), when the tumor spreads, swelling of the lower extremities develops, and vaginal and genitourinary fistulas form.
Types of tumors
All tumor neoplasms are divided into two large groups:
- benign;
- malignant.
Benign tumors
This group of tumors, which are benign in nature and most often occur in the vagina, include:
Fibroma is a neoplasm that has a benign etiology and is localized in the connective tissue of the labia majora, and extremely rarely in the fascia of the parametrial tissue. To eliminate this tumor, a surgical method is used.
Figure taken from medknsltant.com
Fibroids are a benign tumor formation that does not contribute to tissue destruction and the appearance of metastases. Fibroids arise from muscle fibers and most often appear in the form of a lump on the labia majora. The problem can only be eliminated by excision of the tumor.
Lipoma is a more severe form of tumor neoplasm, which, like the previous two, has a benign etiology. Lipoma arises from adipose tissue located in the vicinity of the vulva and takes the form of a small nodule or several small bumps that have a dense and stable stalk.
Often the lipoma is very small in size, but over time it can grow significantly. A neoplasm can be diagnosed during hygiene procedures of an intimate organ. If the necessary therapy is not applied, various complications and pathological processes may occur.
Most often this manifests itself in the form of swelling, hemorrhage, infectious and inflammatory process, as well as possible necrosis. To remove a lipoma, it is excised, and then maintenance therapy is used to prevent the disease from reoccurring.
All of the above-described neoplasms arise from the layers of the vaginal wall and do not have the characteristic features of atypical growth. Basically, tumors belonging to this group do not cause symptoms and most often appear on the surface of the vagina. It is extremely rare for a woman to experience the following changes:
- minor pain of a pulling or aching nature;
- discomfort during intimacy;
- disruption of vital processes such as urination and defecation.
The changes described above mainly occur in the presence of a fairly large tumor.
Malignant tumors
Tumors that have a malignant etiology are characterized by the following processes:
- the cells of this neoplasm have a medium and low degree of maturity, and are significantly different from ordinary cells;
- malignant cells grow into nearby tissues, nerves and blood vessels;
- neoplasms contribute to the occurrence of metastases;
- Malignant tumors are characterized by the phenomenon of relapse.
One of the most common malignant neoplasms, which is extremely dangerous, is carcinoma or vaginal cancer. Often, oncology occurs secondary, or more precisely, in the case of the spread of infected cells from other sources. Mostly, carcinoma is asymptomatic, but there are cases where the disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- the appearance of scanty bloody and other pathological discharge in the period between menstruation;
- the occurrence of pain during intimacy.
When a tumor grows close to tissues, dysuric disorders, as well as defecation disorders, may occur. In extremely advanced cases, a decrease in the woman’s general condition occurs.
Forecast
The success of treatment depends on the stage of the disease, the location of the tumor and its size, the age and general health of the woman. One of the most important criteria for assessing the effectiveness of treatment is relapse-free overall survival of patients. In comprehensive annual terms, regardless of the stage of the disease, the average survival rate is five years in 45% of patients (from the moment of diagnosis). This indicator is pure statistics. The prognosis of the disease is influenced by a large number of factors. In each specific clinical case, the prognosis may be different.
Relapses can develop in regional lymph nodes (in most cases) or at the site of the tumor, when its large size did not allow for sufficient radiation dosage.
Prevention of vaginal cancer consists of periodic visits to specialists (gynecologist, mammologist) with all the necessary examinations.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Diagnostics
In order to establish the cause of a lump in the vagina, as well as its belonging to a specific etiology, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- examination on a gynecological chair;
- taking a general blood and urine test;
- blood chemistry;
- analysis of discharge from the vaginal cavity;
- smear for oncocytology;
- colposcopy;
- biopsy.
Based on the results of a complex of clinical and laboratory tests, the gynecologist can make a conclusion and prescribe appropriate therapy to eliminate the tumor.
Therapy
Once the cause that provokes the appearance of a lump in the vagina has been established, as well as whether it belongs to the group of benign or malignant neoplasms, the doctor chooses appropriate therapy that will help get rid of the problem as quickly as possible.
Basically, all benign neoplasms occur without the occurrence of any symptoms, so they are constantly monitored. If growth prospects appear, surgical therapy is used and the tumor is excised. If the lump is located directly on the mucous layer of the vagina, it is simply removed from it.
In the presence of a malignant tumor formation, the main methods of treatment are surgery followed by radiation.
In addition, a woman may be prescribed drugs belonging to the group of antibiotics, which will help eliminate infectious and inflammatory processes, as well as prevent the development of complications. In combination with medicinal drugs, the use of antibacterial baths is recommended.
Bartholinitis
Very often, bumps on the labia appear due to inflammation of the Bartholin glands. They are localized at the entrance to the vagina and are located in the subcutaneous fatty tissue of the labia majora. The Bartholin gland synthesizes a mucous secretion that forms in the vagina on the eve of sexual intercourse. Blockage of the excretory ducts of these glands leads to an inflammatory process in the organ, resulting in neoplasms in the form of small bumps. This disease often occurs in women who do not pay due attention to personal hygiene.
How do symptoms develop?
- The specificity of the disease is such that symptoms do not appear immediately;
- 1-2 weeks after the onset of the inflammatory process, a seal forms on the inside of the labia majora;
- The ball begins to hurt and cause discomfort, especially when wearing tight underwear;
- The large lips swell, there is a burning sensation and pain in the perineum;
- Suppuration and effusion of exudate are possible, but more often this does not happen.
Bartholinitis does not require specific treatment, however, in its complete absence, women experience frequent relapses of the inflammatory process. At the same time, a new disease begins - a Bartholin gland cyst. In this case, surgical treatment is used, since alternative therapeutic methods become powerless. If the lump begins to suppurate during bartholinitis, there is a sharp deterioration in general well-being, pain during sexual intercourse, and an increase in body temperature up to 40 degrees. It should be emphasized that bartholinitis during pregnancy can provoke spontaneous abortion.
If you have been diagnosed with bartholinitis, our experienced specialists will select a course of gentle antibiotic treatment for you or use surgical tactics to excise the cyst. Do not forget to maintain your health after treatment, maintain good personal hygiene and use contraceptives when changing partners. Know that bartholinitis can also develop due to parasitism of pathogenic microorganisms in your individual microflora. Often the disease is a consequence of trichomoniasis, gonorrhea and chlamydia.
Prevention
After completing a course of therapy, a woman must follow the following recommendations:
- strict adherence to personal hygiene rules;
- use of individually selected intimate hygiene products;
- use contraception during sexual intercourse;
- avoid severe hypothermia and control body heat balance;
- undergo regular gynecological examinations;
- give up bad habits;
- lead a healthy lifestyle.
Following the recommendations described above will help to significantly reduce the risk of relapse of the disease, as well as maintain intimate health for as long as possible. If you discover any neoplasm in your vagina, it is recommended to make an appointment with a gynecologist as soon as possible and be sure to undergo an examination in a chair. Early detection of a tumor significantly reduces the risk of developing various complications and prevents the disease from becoming chronic.
Treatment
Treatment of benign vaginal tumors, if they do not grow and do not lead to disruption of the functionality of the genitourinary organs, consists of observation. In other cases, conservative therapy or surgical intervention is performed:
- for papillomas, Solkovagin is used;
- the doctor can also excise or remove the tumor from the submucosal layer;
- ligation or intersection of the tumor pedicle, if present, can be performed;
- if there is a threat of damage to surrounding tissues, then the cyst wall can be partially excised, after which the edges of the remaining part are ligated, and the resulting cavity is drained;
- the use of cryodestruction helps destroy the tumor using liquid nitrogen;
- using electrocoagulation or plasma coagulation, the tumor and its vessels are cauterized or desoldered;
- Sclerotherapy is carried out in order to stop the vessels feeding the tumor with special drugs.