Dyspareunia
The vagina hurts during sex due to dyspareunia, as painful sexual intercourse is called in medicine.
Discomfort can occur both inside and outside the vagina. Many women face this problem, but men are no exception. True, the male sex has its own reasons for this.
Among the causes of dyspareunia in women are:
- Vaginitis;
- Endometriosis;
- Cystitis;
- Urethritis;
- All kinds of injuries;
- Long-term sexual abstinence;
- Stagnation of venous blood;
- Lack of the required amount of natural lubricant.
- Menopause period;
- Abnormal position of the uterus;
- Various neoplasms in the vagina;
- Oncological diseases;
- Allergies;
- Mental disorders.
Some compare dyspareunia to vaginismus, but this is a very erroneous opinion, since with dyspareunia, muscle spasms do not occur, causing the vaginal walls to contract.
The main symptom of dyspareunia is pain, which can occur at the beginning, middle, end, or after sexual intercourse. Each woman feels pain in her own way, some have colitis and tugging in the stomach, while others experience acute bursting pain.
You can easily get rid of these unpleasant sensations; you just need to find out the cause, which can only be done by a qualified specialist. Therefore, it is recommended that you never hide anything from your doctor.
Before prescribing treatment, the doctor must exclude all possible diseases that have similar symptoms. For this purpose, special diagnostics are carried out, which cannot be done without:
- Gynecological examination of the vagina and pelvis;
- Endocrinological examination, which helps check the concentration of sex hormones;
- Bacteriological analysis of a smear, which helps to find out whether there are inflammatory processes in the body;
- Psychological methods;
- Sexopathological, urological studies.
Women during the climatic period are prescribed estrogen creams or oral estrogen-based medications. They increase the amount of natural lubrication and prevent thinning of the vaginal walls.
If physical causes of pain are not found, the patient will require psychological treatment.
What else could it be?
Pain can also be caused by:
Bartholinitis is an inflammation of the large gland of the vestibule of the vagina. Bartholin's glands are paired formations up to 1 cm in size, which are located at the base of the labia majora. The function of the glands is to produce a mucus-like fluid to maintain moisture in the vagina. Bartholinitis can be caused by staphylococci, streptococci, E. coli, as well as gonococci and chlamydia. An acute inflammatory process is accompanied by low body temperature, mucous and purulent discharge, pain symptoms in the external genitalia, and changes in the menstrual cycle. Treatment of acute bartholinitis is carried out with the use of antibiotics. In case of an abscess, an autopsy is performed.
Salpingitis is inflammation of one or both fallopian tubes. The disease develops due to the penetration of pathogenic microflora into the fallopian tubes. Acute salpingitis can spread to the ovaries and abdominal cavity. Chronic salpingitis most often causes female infertility. The main signs of salpingitis are: impaired urination, excessive purulent discharge, cramps and pain during menstruation. Salpingitis is treated with anti-inflammatory drugs and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Pain in the vagina during menstruation can be present with all sexually transmitted diseases. Symptoms of sexually transmitted diseases include swelling and irritation of the vulva, painful and frequent urination. Unnatural discharge of various shades with an unpleasant odor irritates the vaginal mucosa and is accompanied by painful sensations.
The cause of pain during menstruation can also be a benign or malignant formation in the walls of the vagina. In such cases, the pain intensifies during menstruation, when the vaginal mucosa is slightly inflamed. The pain is nagging in nature, and the entire area of the lower abdomen will hurt. If you have any symptoms, you should immediately contact a gynecologist and undergo an appropriate examination.
In some cases, pain in the vagina during menstruation can be caused by diseases of neighboring organs. Stitching pain may be present against the background of cervical erosion or inflammation of the bladder.
On the eve of menopause, the pelvic floor muscles weaken, which contributes to the prolapse of the vaginal walls. The process may be accompanied by pain and discomfort.
What diseases can be
The presence of mild pain during menstruation is considered normal, taking into account natural physiological factors. In case of unpleasant sensations that cause torment and severe discomfort, it is necessary to determine the true cause of the pathology in order to carry out further treatment of the problem.
The culprits of a condition that brings suffering to a woman, in which, among other symptoms, the vagina still hurts during menstruation, are:
- inflammatory process in the bladder;
- disruption of intestinal function;
- abnormalities in the formation of the genital organs during the first menstruation;
- genital endometriosis;
- tumor formations;
The cause of pain may also be inflammation of the ovaries
- cysts, inflammation of the ovaries;
- damage to the uterus during labor and surgery;
- endocrine diseases;
- vaginismus;
- using large tampons;
- age-related changes associated with prolapse of the genital organs;
- venereal diseases.
Preventive measures
In order to avoid the occurrence of pathologies, representatives of the fairer sex need to be regularly examined by a gynecologist and check the condition of their genitourinary system.
Timely diagnosis of the disease speeds up the healing process.
You can prevent many problems of the female reproductive system by following simple recommendations:
- It is necessary to use contraception and maintain an intimate relationship with one partner. A considerable percentage of genital pathologies occur after unprotected sexual intercourse.
- Hygiene during menstrual periods must be strictly observed, since discharge during menstruation is a favorable environment in which pathogenic bacteria multiply. For the same reason, it is recommended to abstain from sex during menstruation. You should wash yourself at least twice a day. Douching the vagina at this time is prohibited. Taking a bath and swimming in ponds should also be limited.
- Hygiene products should be changed at least every 5 hours.
- Instead of toilet paper, you can use special wet wipes designed for feminine hygiene.
- It is better to replace soap that contains fragrances with baby or laundry soap.
The use of painkillers helps relieve cramps during menstruation. Before using them, you should definitely consult a specialist to make sure the drug is safe.
Periodic visits to a gynecologist (at least every six months) prevent the development of serious complications and help avoid many problems with women's health.
Representatives of the fair sex during menstruation, in addition to bleeding, often feel discomfort in the lower abdomen, pain in the chest and lumbar region. As a rule, such symptoms are considered normal. Sometimes women have vaginal pain during menstruation, which indicates abnormalities in the genitourinary system that require medical intervention.
In order to avoid the occurrence of pathologies, representatives of the fairer sex need to be regularly examined by a gynecologist and check the condition of their genitourinary system.
Timely diagnosis of the disease speeds up the healing process.
You can prevent many problems of the female reproductive system by following simple recommendations:
The use of painkillers helps relieve cramps during menstruation. Before using them, you should definitely consult a specialist to make sure the drug is safe.
Periodic visits to a gynecologist (at least every six months) prevent the development of serious complications and help avoid many problems with women's health.
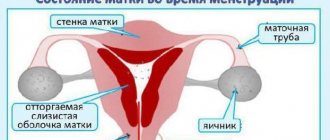
Discomfort in the lower abdomen, bleeding, pain in the lumbar region and chest accompany many females during menstruation. Most women experience these symptoms every month. And this, in principle, is considered the norm. For each of them, however, all this happens differently. Others take it easier. There are women whose vagina hurts during menstruation. There should not be such a symptom, since the vagina is not a direct participant in the menstrual cycle, it only facilitates the removal of blood and endometrium to the outside.
Many women, having felt pain in the vagina during menstruation, think that this should be in the order of things. They take a painkiller pill and forget about this trouble until the next menstruation. In fact, these pains may indicate many abnormalities in the genitourinary area. An inflammatory process in the vagina may occur, which is fraught with various complications and requires immediate medical or even surgical intervention. Therefore, every woman should listen to herself and not ignore the SOS signals coming from her body.
Disorders in the cardiovascular system
At those moments when there is a load on the blood vessels during menstrual bleeding, the female body is busy eliminating toxins.
In most cases, waste products enter the blood, which, for natural reasons, can lead to an increase in ESR levels and the development of inflammatory processes, as well as severe headaches during menstruation.
It is noteworthy that after the end of menstruation, the composition of the blood becomes the same, and headaches most often cease to bother you almost immediately after the last day of bleeding.
Also, this symptom can develop with loss of vascular elasticity. The fact is that during menstruation, blood actively moves through the vessels. If they lack elastic properties, they will not respond correctly to increased blood flow, which will lead to headaches during menstruation.
The reasons may also be related to the phenomenon of spasm of the walls of blood vessels, which provokes oxygen starvation of the brain and, as a result, headaches. Some experts believe that you can drink a small cup of coffee to dilate blood vessels and eliminate the spasmodic phenomenon.
Internal intoxication
If you have a headache during menstruation, this can also be caused by internal intoxication, when the body begins to get rid of toxins, throwing them into the blood. At the same time, there is an acceleration of blood flow, which means that the body is in a hurry to remove harmful substances as quickly as possible into the intestinal environment. But even here some difficulties may arise.
With irregular bowel movements and weakened peristalsis, a woman may have deposits in the intestines, so waste is only partially eliminated, which is why harmful toxins begin to be absorbed into the blood and enter the brain, causing severe headaches during menstruation.
The causes of pain can be prevented by taking laxative herbs and special drugs to empty the intestines.
Cervical osteochondrosis
If osteophytes (saline shoots) appear in the vertebrae during menstruation, they can compress the vessels that are responsible for transmitting blood to the brain, as well as the nerve fibers that connect the brain and other organs. If on other days of the menstrual cycle the body is able to adapt to these phenomena, during menstruation this is not possible, so the head often hurts.
In order for the body to receive a sufficient amount of oxygen, it is important to regularly massage the shoulder area and neck, and perform special useful exercises for the cervical spine
Anemia
If a woman has signs of red blood cell deficiency, which often becomes one of the key symptoms of anemia, a woman has a headache during her period. This is because during menstruation the brain needs more oxygen than usual, but if you are anemic, it will be impossible to replenish the oxygen supply.
Anemia is treated with the help of special preparations based on plant components, green chlorophyll, which is considered to be an analogue of the red blood cell molecule.
Disturbances in the hormonal system
When hormonal imbalance occurs during menstruation and there is a loss of tissue elasticity, symptoms of hypertension and swelling may appear. With swelling, the brain experiences significant compression, which is why headaches begin during menstruation, localized in the back of the head or crown.
Most often, if this problem exists, the doctor prescribes special diuretics.
The nature of pain in the vagina and labia: causes
If a woman has pain in her labia during menstruation, it is important to pay attention to the following problems:
- disturbances in the functioning of the ovaries;
- pelvic organ injuries;
- vaginismus;
- adenomyosis;
- endometriosis;
- violation of hygiene rules;
- prolapse of the uterus and vaginal walls;
- congenital malformations of the genital organs;
- presence of tumor processes.
Also, the vagina can hurt if a woman chooses the wrong tampon size. If you experience discomfort in the area of the labia and cervix, you should visit a gynecologist.
The nature of vaginal pain during menstruation can accurately indicate the presence of a particular problem. For example, nagging discomfort that occurs before menstruation indicates vaginal endometriosis. The walls of the vagina are sensitive to changes in hormonal balance: this disrupts the microflora and increases the risk of developing an infectious process. Pain can be felt even after severe stress during menstruation. Sometimes the lesion is located in the ovaries. In this case, pain may be felt in the labia. Sources of discomfort are divided depending on their origin and are caused by inflammatory processes and non-inflammatory processes.
Pain due to inflammatory processes
During the period, the natural protection of the vagina is weakened, which increases the risk of infection. In this case, a nagging pain is felt in the vagina, accompanied by purulent discharge.
Possible pathologies:
- gardenerellosis;
- vaginitis;
- candidiasis, etc.
The following can cause discomfort and inflammation:
- violation of hygiene rules;
- wearing uncomfortable underwear;
- unprotected sexual intercourse.
If you suspect inflammation, you must visit a gynecologist and undergo a series of examinations.
Non-inflammatory pain
Non-inflammatory pain can be felt for a long time after menstruation. In this case, not only the perineum hurts, but also the lower abdomen. Just as in the case of an infectious lesion, some pathologies are accompanied by discharge with an unpleasant odor
To make an accurate diagnosis, it is important to contact a gynecologist and undergo an examination. Non-inflammatory processes include tumor processes of the pelvic organs, congenital pathologies and erosions of the cervix and mucous membranes
Adhesive process
Pain in the vagina during menstruation often indicates an adhesive process. In this case, “fusion” of the tissues of some organs occurs, accompanied by inflammation. Most often, the problem develops against the background of mechanical injuries.
Presence of a pessary on the cervix
A pessary is placed on a woman during pregnancy. This is a soft ring that reduces the risk of premature birth. Sometimes the ring causes discomfort that radiates to the labia.
Colpitis
Colpitis is an inflammatory disease that affects the vaginal mucosa. It is provoked by staphylococci, streptococci, chlamydia, trichomonas and other microorganisms. The symptoms of the disease are similar to those of cystitis. A common cause of the problem is failure to comply with personal hygiene rules during menstruation.
consultation with a gynecologist
Diseases that cause pain in the side
Unnatural pain in the side during menstruation is a clear sign of gynecological problems. The fact is that before menstruation, all chronic diseases worsen, so their symptoms are felt more clearly. Pain in the right or left lower abdomen most often indicates problems with the ovaries, as well as structural changes in the organs of the reproductive system.
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a gynecological condition in which the tissue that forms the lining of the uterus is found on other structures throughout the pelvis, including the ovaries, fallopian tubes, bladder, and pelvic floor. In more severe cases, the tissue grows into the intestines, diaphragm, liver, lungs and even the brain.
A displaced endometrium can cause adhesions, chronic inflammation, blood-filled cysts, and internal bleeding. All this can cause excruciating pain in the pelvic area on the right, left, and lower abdomen.
Adenomyosis
Adenomyosis is similar to endometriosis, except that the endometrium, which implants outside the uterus, is found deep within the uterine muscle. In women with adenomyosis, the uterus looks like a bruised muscle. Symptoms of adenomyosis include cramps and painful sexual intercourse, and the right side may hurt during menstruation. Adenomyosis usually occurs in women over 30 who have already had children. However, this has also been seen in adolescents.
Uterine fibroids
Three out of four women will develop fibroids, but most do not experience any symptoms. Fibroids range in size from microscopic to large enough to distort the shape of the uterus.
Before your period, your left or right side often hurts because the uterus must contract during this period to expel large blood clots, which often result from heavy bleeding. Fortunately, fibroids do not increase a woman's risk of cancer and very rarely become cancerous.
Inflammation
Pelvic inflammatory disease is an infection of the female reproductive tract that is most often caused by sexually transmitted infections. Without treatment, scarring, painful menstrual cramps and infertility occur.
Inflammation is manifested by various pains, including soreness in the side and lower abdomen.
If detected early, the inflammation can be treated with antibiotics, but they will not correct the structural damage caused by the infection. Practice safe sex and get tested frequently for any sexually transmitted infections, especially if you have severe pain on your right side before your period.
Uterine defects
When a female baby is still in the mother's womb, her own uterus develops from two structures known as the Müllerian ducts. In some cases, the uterus does not form properly, which can lead to infertility, periodic side pain during menstruation, and painful sex. In women with structural abnormalities such as:
- bicuspid - two uteruses that lead to one cervix;
- separated uterus with fibrous tissue bisecting it;
- unicorn, which develops from only one Müllerian duct;
- didelphys - two cervical septa or a septum separating the vaginal canal.
Menstrual cramps stem from blockages and septa that separate the uterus and vagina.
Treatment
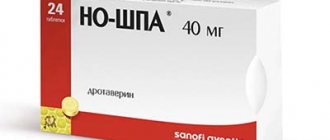
During painful periods, it is recommended to take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Voltaren). Rectal administration of any of the listed drugs in the form of a suppository relieves pain and relieves tension inside the genital canals.
The following prescriptions help eliminate the main pathologies that cause dysmenorrhea:
- Antibiotic therapy. Stops inflammatory and infectious processes.
- Hormonal drugs. Corticosteroids are administered; substances produced by the pituitary gland.
- Vitamin therapy. Whole complexes or individual vitamins are prescribed.
- Analgesics. They relieve pain and normalize general well-being.
- Drugs are administered aimed at normalizing blood pressure levels (if their levels decrease).
- Dyspeptic disorders are treated with antiemetic medications.
Additionally, the patient is prescribed a course of physiotherapeutic treatment (enterofuresis, magnetic therapy, UHF). To eliminate pathological discharge from the surface of the genitals, it is necessary to treat the tissues with antiseptic solutions. If a woman is diagnosed with anemia (caused by massive blood loss), injection of iron supplements is indicated. When sexually transmitted diseases are detected, not only the woman, but also her sexual partner undergoes treatment.
Folk remedies that can reduce pain
Very severe pain during menstruation, the causes of which lie in diseases of a number of organs, can be eliminated by traditional medicine.
The painful symptom will help remove horsetail. To prepare the infusion, pour a tablespoon of the herb into a mug (300 ml) of boiling water. Let it brew for an hour. Take 50 mg every hour and reduce the dose as the pain subsides.
Severe pain before menstruation, the causes of which are individual for each woman, can be relieved by water pepper. Two tablespoons of the plant are poured with half a liter of boiling water, after which the mixture is boiled over fire for another 10 minutes. Before use, the herbal infusion must be cooled and strained. Take 100 grams three times a day.
Collecting the following herbs will help relieve pain: knotweed, centaury, horsetail, cinquefoil in a ratio of 1:3:1:5. Here a tablespoon of the mixture is steamed with a glass of boiled water. They insist for an hour. Drink one sip during the first day of menstruation.
Elecampane root helps cope with pain. Pour a teaspoon of boiled water into a glass, wait an hour, and filter. Take a tablespoon in the morning, lunch and evening.
These and other folk recipes can overcome menstrual pain, so they cannot be discounted.
Before menstruation, itching and burning appear. Why and how to treat
Many women are familiar with the problem of itching before menstruation. Discomfort occurs in the vagina, the nature of the discharge changes, and the labia become slightly swollen.
An irritated intimate area disturbs peace and undermines self-confidence. The causes of discomfort in the groin are numerous, and in most cases, itching signals the development of the disease.
What to do when you are worried about itching before your period
Treatment of vaginal itching before menstruation is not the same for all patients. Gynecologists select the method of therapy taking into account the cause of discomfort.
If a woman is worried about thrush, she will be prescribed antifungal agents (Mycozon quickly relieves itching). When herpes worsens, the problem is eliminated with the help of antiviral drugs Gerpevir, Acyclovir, Liposome.
Vaginal itching associated with hormonal disorders is treated with Ovestin and Kolpotrofin. To combat bacterial infections, Terbizil, Actovegin and Pimafucin are used. Allergic itching in the groin is effectively eliminated by the pharmaceutical product Vagisil.
External agents are applied to the genitals 2 times a day. Burning sensation due to stress is eliminated by using a sedative (Maprotiline, Fluoxetine, Clomipramine).
For colpitis, wash the vagina with solutions of Citeal, Rotokan, Rivanol. Grains of potassium permanganate are dissolved in water and used for douching.
Knowing why the patient’s intimate area itches before menstruation, the doctor can prescribe medications such as:
- Acylact – 1 suppository is recommended to be placed at night for a course of 10 days.
- Terzhinan - vaginal suppositories are used 1 pc. per day (10 times in a row).
- Clotrimazole - 1 tablet is inserted into the vagina for 6 days.
- Polygynax - vaginal capsules are placed in the morning and evening (course 12 days).
- Metronidazole – tablets taken orally, 2 pieces. for one and a half weeks.
:
Folk recipes
Baking soda will help a woman relieve severe itching in the intimate area. 1 teaspoon of the product is mixed with the same amount of table salt and thrown into boiling water.
After a couple of minutes, remove the dishes from the oven and cool the contents so that they are warm. Next, 10 drops of iodine are added to the solution. The prepared preparation is used in the morning and evening for douching. Relief comes quickly. The duration of therapy is 1 week.
You can also use an aqueous infusion of medicinal herbs for douching:
- Nettle.
- Calendula.
- Chamomile.
Take 1 tsp of all ingredients. and leave in boiling water for 20 minutes. For procedures, the product is used warm. The frequency of manipulations is 2 times a day. During menstruation, douching is not done, even if the itching continues to bother you.
When the vagina is attacked by a fungus, aloe pulp can be used to restore the mucous membrane. The phytomass is wrapped in gauze and inserted like a tampon.
A decoction of basil helps with itching that bothers you before menstruation:
- Place 5 leaves in an enamel bowl and pour water.
- Place the container on the stove and prepare the decoction at a moderate boil.
- After 20 minutes, remove the product from the oven and cool.
Take a decoction of basil orally, drinking half a glass of the drug 3-4 times a day.
The use of folk remedies for the treatment of itching and burning in the intimate area is allowed only as an auxiliary measure. Herbal medicines cannot completely replace drug therapy.
Prevention
Preventative measures will help women prevent itching before menstruation:
- Increased stress resistance.
- Using condoms to protect against STDs.
- Having a trusted sexual partner.
- Strengthening general immunity.
- Visit a gynecologist once every six months. Scheduled and unscheduled examinations by a doctor reveal diseases in the early stages. They are much easier to treat than advanced forms of pathologies.
Personal hygiene deserves special attention in solving the problem of severe itching in the intimate area. But excessive cleanliness is no less harmful to the vaginal microflora than infrequent washing of the genitals (water washes away beneficial bacteria). In the absence of sexual contact, it is enough to wash yourself once a day, directing a stream of warm water from the pubis to the anus.
Source: https://MenCikl.ru/zud-pered-mesyachnymi.html
Causes of pain
If the pain syndrome lasts a month or more, then this may be a sign of a serious pathology and requires timely treatment:
- One of the causes of vaginal pain during menstruation can be injury to the genital organ. The mucous membrane can be damaged by improper douching or during gynecological manipulations, such as abortion, diagnostic curettage.
- If pain during menstruation occurs after childbirth, then the causes are improperly sutured birth ruptures. The resulting scars will be bothersome and painful. In addition, many women experience pain in the genitals after childbirth.
- If your vagina hurts during your period, then perhaps the tampons you use are too large.
- Vaginal endometriosis is the process of tissue growth (endometrium) outside the uterine cavity. The disease develops as a result of complicated childbirth, abortion and other gynecological manipulations. During surgery, endometrial cells penetrate the wound surface, and endometriotic proliferation occurs. Dense painful scars, nodes and thickenings form in the thickness of the vaginal walls. Symptoms of endometriosis include: heavy and prolonged periods, pain in the vagina during menstruation, spotting before and after menstruation, pain during sexual intercourse, and frequent urination. Vaginal endometriosis is diagnosed using laparoscopy, which determines the extent and location of endometriosis. Therapeutic measures include excision of the endometriosis lesion and taking hormonal medications in the postoperative period.
- Vaginitis is a gynecological pathology characterized by an inflammatory process in the vaginal mucosa. The disease can be caused by sexually transmitted diseases, hormonal disorders, diabetes, and obesity. Damage to the mucous membrane often occurs due to improper medical procedures. In some cases, vaginitis develops due to an allergy to the latex of the condom or to medications inserted into the vagina.
- Symptoms of vaginitis include: swelling and redness of the external genitalia, itching and pain in the vagina, intensifying during menstruation, vaginal discharge of a mucous and purulent nature. To confirm the diagnosis, a gynecological examination with speculum is performed and a smear is taken for analysis.
If necessary, PCR diagnostics are performed to determine urogenital infection. Treatment of vaginitis is carried out using complex therapy, taking into account the causative agent of the disease. Medicines that suppress bacterial infection are prescribed, douching is done to restore the vaginal microflora, vaginal suppositories and tablets are administered. If necessary, additional hormonal therapy is prescribed.
Diagnostics
If pain in the vagina during menstruation is severe, causes severe discomfort, or is accompanied by discharge with an unpleasant odor, then you should definitely consult a gynecologist. An external examination of the vagina will help make assumptions about the causes of pain, and other analysis methods will help clarify the diagnosis.
Tests for infection
Urine and blood tests, bacterial culture of a vaginal smear will help determine the presence of pathogenic microorganisms and establish their nature, because this is necessary for further treatment.
During an infection, the blood contains antibodies to it; the urine may also contain these substances, as well as the pathogenic microorganisms themselves if they have entered the urethra. Sowing a smear from the vagina on a nutrient medium allows you to accurately see the picture of the “inhabitants” of the vagina.
Tests for neoplasms
Cytological analysis and colcoscopy will help determine the presence of neoplasms on the mucous membrane. In the first case, a small number of cells are taken from the vaginal tissue, and in the second, the vaginal walls and cervix are examined using a special device - a colcoscope.
If previous diagnostic methods do not produce results, then it is necessary to do an ultrasound of the pelvic organs, because pain in the vagina sometimes occurs due to abnormalities in its structure:
- severe curvature of the vagina;
- position too close to the bladder;
- curvature of the cervix;
- disruption of the mucous layer and friction between the walls of the vagina.
Ways to feel better
Non-drug methods during dysmenorrhea can partially normalize well-being. They are based on the use of heat sources, performing massage and changing the attitude towards the condition. In addition to the psychological aspect, the remaining 2 factors require prior approval by a gynecologist.
Warming treatments
A warm shower is not only allowed during dysmenorrhea, but also useful. It provides a full level of hygiene, relieves pain, relaxes and warms. The use of hot water is contraindicated. During the procedure, it is advisable to massage the abdominal area.
Physical activity
With dysmenorrhea, many exercises are contraindicated. Especially if they involve impact on the abdominal muscles. Fiber tension contributes to increased discomfort and increased blood loss. It is recommended to limit physical activity aimed at the uterus and genitals to massage. It can be done with or without special oil. Stroking circular movements in the lower abdomen (in the umbilical area) relieve pain, tension, and help reduce spasms. The duration of the procedure is up to half an hour.
Diet during menstruation
To reduce pain, you should avoid foods that irritate the walls of the urogenital tract. It is recommended to refrain from eating sour, spicy, salty foods. Drinking alcohol is strictly contraindicated (alcohol increases bleeding and spasms). Although caffeine is a substance that irritates organ tissue, its use during menstruation is acceptable. The reason is that due to blood loss, the woman’s blood pressure level decreases. Coffee supports its indicators, preventing weakening of the body, dizziness and other symptoms.
Psychological attitude
Concentrating on a problematic health condition, it is difficult for a woman to relax and thereby reduce uterine spasms. In order not to regard dysmenorrhea as a stress factor, it is recommended:
- do outdoor training
- listen to soothing music
- use aromatherapy
Due to pain in the lower abdomen and back, the woman becomes irritable. At the peak of discomfort, it is advisable to limit communication with others so as not to cause conflict situations. Rethinking the situation comes down to understanding that pain during menstruation is not a condition that simply needs to be experienced, but a signal from the body about the disturbances that exist in it.
Symptoms
The clinical picture that complements perineal pain in men and women will differ depending on what disease caused the main symptom. It follows that the symptoms will be individual in nature.
However, it is worth highlighting the most common symptoms:
- spread of pain to the lumbar area, lower abdomen and pelvic area;
- frequent and painful urge to urinate, including at night;
- a feeling of cutting and burning during emptying of the bladder;
- periodic or constant pathological discharge from the vagina or urethra, which may have a specific color and smell;
- the presence of impurities of pus or blood in urine or semen;
- false urge to defecate;
- feeling of a foreign object in the rectum;
- increase in body temperature;
- enlargement of the affected testicle;
- increased intensity of pain during sex or physical activity;
- significant redness of the penis or labia;
- feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
Useful video
General information
The appearance of menstruation (periods) in women is the result of complex interactions of reproductive hormones, the levels of which in the body rise and fall at different periods of the menstrual cycle, which lasts approximately one lunar month (28 days).
Many women do not notice any significant changes in their body during the entire menstrual cycle, with the exception of bleeding for a few days. However, about a third of women in the world suffer from unpleasant menstrual symptoms associated with fluctuations in hormone levels, with negative menstrual sensations especially noticeable during the last 7-14 days of the cycle.
Pain in the lower abdomen during menstruation occurs in 30-50% of women, but only in 5-10% of cases the pain is too severe (dysmenorrhea) and leads to decreased ability to work.
Causes of pain in the lower abdomen during menstruation
Causes of abdominal pain during menstruation may indicate the following:
insufficient level of endogenous opiates (endorphins, enkephalins);
luteal phase deficiency;
functional failure of endometrial tissue enzymes and impaired fragmentation of the rejected uterine mucosa;
excess prostaglandins;
increased pain sensitivity.
Volitional effort and switching attention to intellectual activity can ease the pain in the lower abdomen during menstruation or even completely suppress it. Algodysmenorrhea is manifested by severe pain in the lower abdomen during menstruation, weakness, loss of consciousness, and low blood pressure.
Symptoms of pain during menstruation:
cramping pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the lumbar region, less often to the area of the external genitalia, groin and thighs.
general weakness, nausea, vomiting;
spastic headaches, dizziness;
temperature rise to 37°C;
dry mouth;
mental disorders (anxiety, irritability, insomnia, depression, memory impairment, absent-mindedness and apathy);
cravings for sweets, increased appetite, reaction to sugar (cardiac arrhythmia, fainting);
weight gain, swelling of the arms and legs, swelling and painful sensitivity of the mammary glands;
fainting and other disorders.
Sometimes the leading symptom becomes more disturbing than pain in the lower abdomen. The pain is not accompanied by dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract.
Pain during menstruation in girls
Severe pain in the lower abdomen during menstruation in adolescence (primary algodismenorrhea) usually occurs in thin, emotional girls, 1-1.5 years after the first menstruation, with the onset of ovulation. Severe pain in the lower abdomen during menstruation in teenage girls, as a rule, is not associated with anatomical changes in the internal genital organs.
Severe pain during menstruation, which occurs due to anatomical changes in the uterus (impaired contractile activity of the myometrium, hyperanteflexia, hyperretroflexia, adenomyosis, fibroids).
Pain during menstruation in women
The causes of severe pain in the lower abdomen during menstruation in women over 30 years of age are as follows:
consequences of childbirth, abortion, inflammatory gynecological diseases;
endometriosis (with endometriosis, aching pain in the lower abdomen extending to the rectum can bother you throughout the entire menstrual cycle);
use of intrauterine contraceptives;
submucous uterine fibroids;
varicose veins of the pelvic veins;
malformations of the genitals (obstruct the outflow of menstrual blood).
In case of painful periods, it is better to consult a gynecologist to make sure there are no serious health problems. If there are no complications, a properly selected diet and vitamins will help get rid of pain during menstruation.
Causes of abdominal pain as during menstruation in their absence
Shortly before menstruation, the uterus prepares to shed the extra layer of endometrium that has formed while preparing the body for fertilization. It spasms, blood flow to the pelvic organs is disrupted, and unpleasant sensations arise. There is no period when discomfort occurs due to natural or pathological processes.
Natural causes
The menstrual cycle is regulated by hormones. Under the influence of various factors, the rate of production of progesterone and estrogen changes, so there may be a cycle shift. In this case, premenstrual symptoms begin, but the symptoms are not present in the due time. The stomach hurts like during menstruation, but it does not exist for the following reasons:
- Excessive physical activity. Due to severe tension in the body, the speed of transmission of commands from the brain to other organs is disrupted. If a woman worked hard physically shortly before the start of the cycle, pain in the lower abdomen appears, but the regulation does not improve. Discomfort may increase if the abdominal area is subject to tension.
- Stress and anxiety. A stressful situation also forces the brain to slow down the rate of reproductive processes. The uterus is preparing for the rejection of the endometrium, but the processes that facilitate the release of secretions are not activated.
- Pregnancy. After fertilization of the egg, discomfort in the abdomen appears for some time, but menstruation does not come. Unpleasant sensations arise due to the fact that the embryo, when implanted into the uterus, slightly damages the uterine layer.
- Lack of ovulation. Sometimes the ovaries do not produce an egg, so ovulation does not occur. This phenomenon is called the anovulatory cycle. This condition is normal for every woman. The number of anovulatory cycles increases with age. Despite the absence of a mature egg, menstruation occurs, but with a delay of about a week. However, all premenstrual symptoms persist.
- Poor nutrition. The lack of vitamins and microelements in the diet negatively affects the formation of hormones and the contractility of the uterus. The stomach may hurt, but the discharge does not begin.
- Change of climate, rhythm of life, moving. The body perceives new conditions as a threat. During the adaptation period, periods are delayed. However, when preparing for them, my lower abdomen still ache.
- Age-related changes. After 45 years, the production of estrogen in the female body decreases. The following symptoms appear: pain in the lower abdomen, dizziness, no menstruation.
Pathological processes
As a rule, if the lower abdomen hurts, but there is no regulation for natural reasons, the process returns to normal in the next cycle. However, when the pain is severe and the cycle does not return to normal, diseases of the reproductive system may develop.
The absence of menstruation with abdominal pain indicates the following pathologies:
- Ectopic pregnancy. Disturbances in the functioning of the reproductive system lead to the fact that the fertilized egg attaches itself outside the uterine cavity. There is no menstruation, but unpleasant symptoms appear. The pain during ectopic implantation is very severe.
- Risk of miscarriage. If a pregnancy test shows a positive result, but your stomach hurts and feels tight, there is a risk of fetal rejection.
- Hormonal imbalance. With a lack or excess of female sex hormones, menstruation is delayed or does not occur at all. In this case, discomfort manifests itself both at the beginning and in the middle of the cycle.
- Inflammatory processes of the urinary tract (cystitis, pyelonephritis, urolithiasis). At the same time, unpleasant sensations accompany a woman on different days of the cycle - both before and after menstruation.
- Inflammation of the genital organs. Pain and delayed menstruation are caused by endometritis, adnexitis, salpingitis, and infectious processes in the cervix and vagina. Discomfort is present regardless of cyclicity.
- Appendicitis, gastrointestinal diseases.
- Hernia in the lower part of the spine, inflammation or pinched nerve.
- Benign and malignant tumors.