≡ Home → Tumor diseases of the uterus → Myoma →
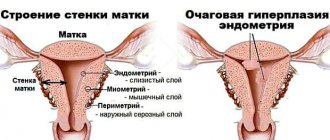
Subserous uterine fibroids are a benign tumor of the myometrium that grows towards the abdominal cavity or extends beyond the organ. The subperitoneal node may be connected to the uterus by a thin stalk or have a wide base, located near the bladder or rectum. Such a tumor is asymptomatic for a long time and makes itself felt only when it reaches significant sizes and compresses the pelvic organs.
Subserous uterine fibroids and pregnancy are quite compatible. Practitioners indicate that the subperitoneal node is the best option for a woman who dreams of motherhood. A tumor of small and medium size does not interfere with conception and bearing a child and practically does not interfere with natural childbirth. Problems arise only with large nodes, but even in this case the patient has every chance of becoming a mother. Modern medical technologies make it possible to carefully remove a subserous tumor without affecting intact tissues and without posing a threat to a woman’s reproductive health.
Symptoms
Signs that can be used to determine whether fibroids are forming in the body appear long before pregnancy. Some patients do not attach due importance to them and prefer to attribute everything to a banal ailment. The general picture of symptoms is indeed similar to the typical manifestations of non-dangerous inflammatory diseases or premenstrual syndrome. Among them are:
- pressure and nagging pain in the pelvic area, often radiating to the lower back;
- discomfort during sex;
- increased urge to urinate ;
- intestinal dysfunction: constipation or diarrhea ;
- painful and heavy menstruation.
With fibroids, just like during pregnancy, the abdomen begins to enlarge (the size of the formation is calculated in the same way - by week). In addition, there is a deterioration in general condition, weakness, lethargy and decreased ability to work.
If you notice one of the above symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor for diagnostic measures.
Rapid growth of fibroids
The rapid increase in the size of the pathological formation is due to the proliferation of muscle tissue as a result of cell division. This process is also called proliferation. Uterine fibroids can be either fast-growing or slow-growing.
Typically, the tumor reaches significant size without treatment within five years. However, under the influence of external and internal factors, its growth accelerates. Without treatment, the tumor can lead to infertility, miscarriage, and provoke premature birth. The norm of growth per year is its minimal increase or lack of development.
The volume of uterine tumors is measured in weeks, as in pregnancy. Until recently, the indication for radical organ removal was the size of the fibroid at 14 weeks. Methods of modern gynecology are aimed at preserving the organ and reducing the size of the formation through medication or through myomectomy. The peculiarity of the latter is that after it is carried out, the functions of the reproductive system are not impaired.
Risk factors
The main reason for the formation of fibroids is an endocrine disruption in a woman’s body, namely a sharp jump in estrogen levels . Under their influence, uterine cells begin to rapidly divide, which leads to the formation of multiple nodes of various shapes.
There are a number of etiological factors that increase the level of hormones in the blood:
- burdened hereditary history (uterine fibroids are a genetically determined disease, and if one of the patient’s relatives had similar formations, there is a high risk that she will suffer from the same pathology);
- infectious inflammatory processes in the genital organs;
- long-term and uncontrolled use of oral contraceptives ;
- abortions (surgical and medical);
- cyst-like neoplasms in the ovaries;
- excess or lack of body weight;
- irradiation of the whole body , in particular the genitals;
- long-term wearing of hormonal intrauterine devices without timely replacement.
Several years ago, the fact that if a woman has fibroids cannot become a mother, it was considered indisputable and the only true one. There is some truth in this: many patients with benign tumors suffer from infertility, but there are a number of cases in which pregnancy is quite possible .
Treatment
To treat small fibroids, conservative treatment methods are often used, combining symptomatic agents and hormonal compounds.
Symptomatic treatment consists of using the following groups of compounds:
- anticoagulants;
- antiplatelet agents;
- hemostatics;
- painkillers;
- antispasmodics.
Attention! If the cause of the disease is emotional disturbances, antidepressants are indicated.
If the tumor does not reach a size of 1.5 cm, progestin-based drugs are used. More often, the composition is used in the form of tablets (COCs), which are enough to be taken once a day. The action of the drug is aimed at normalizing the process of hormone production by implementing the function of the ovaries, which actively produce progesterone, which suppresses the growth of neoplasm cells. The duration of the course is about six months. After this time, the tumor decreases to 0.6-1.0 cm. Further, the condition of the tumor is constantly monitored. The patient should undergo a transvaginal ultrasound once every six months.
The optimal treatment method for hormone-dependent fibroids in women of reproductive age is the Maren spiral. A product that prevents unwanted pregnancy helps eliminate fibroids that have existed in the uterus for 5 years or more. The device blocks the production of estrogen. During treatment, the IUD releases levonorgestrel into the blood in small quantities. This method is considered the most convenient and safe. When drug therapy does not produce a noticeable result, surgical intervention is necessary.
Planning to conceive a child with uterine fibroids
First of all, it is necessary to pay attention to the fact that this process with myomatous nodes in the body is very difficult. They affect ovulation (a large number of anovulatory cycles are noted), compress the fallopian tubes, deform the uterus, and impede the movement of sperm. In this case, the existing nodes should be removed through surgery.
If there are few formations and they do not exceed the permissible size (thus not causing deformities), then the likelihood of pregnancy increases sharply. But such patients may have problems with bearing a fetus. It is necessary to pay attention to the tumor’s predisposition to growth and the presence of legs. If such factors are present, planning a pregnancy is prohibited. First you need to remove the formations, and only then start conceiving a baby.
How does fibroid growth occur?
With each ovulation, receptors for progesterone and growth factors accumulate on the surface of cells. Under the influence of the hormone, hyperplasia and hypertrophy of the myometrium occurs in equal proportions.
If conception does not occur, the uterus returns to its previous state, however, the constantly repeated process leads to an excess number of smooth muscle cells. The decisive role is played by damaging factors: spasm of the arteries during menstrual bleeding, uterine injuries, chronic foci of infection (endometriosis).
Cells damaged as a result of these processes are partially removed from the body, while another part becomes the basis for the formation of myomatous nodes.
The growth potential of cells is different; after passing through the stage of active growth at the beginning of formation, development occurs due to the formation of estrogens and connective tissue. Tissue proliferation occurs clonally, while the cells of healthy areas of the myometrium remain intact.
Due to the autonomous method of growth, complete regression of fibroids cannot be achieved; the main task is to stop its development and growth.
Therapeutic measures are aimed at stopping the blood supply to part of the node with its subsequent reduction, while the core of the fibroid remains stable.
Childbirth with fibroids
Pathology affects not only the course of pregnancy, but also the process of delivery itself. Childbirth in such patients is less easy and most often is protracted. If the myomatous nodes are large, this can cause abnormalities in the position and presentation of the fetus. In this case, the birth of a child naturally is not possible, and doctors perform a caesarean section. In some situations, simultaneous removal of fibroids is permitted (if a tumor is diagnosed in the incision area).
In patients with this disease, placental abruption often occurs. This must be taken into account throughout pregnancy and during childbirth.
Classification of fibroids by size
The size of fibroids is determined using ultrasound. It is described in weeks and centimeters. As the tumor grows, the uterus enlarges in the same way as during pregnancy. That is, in the case of an enlarged uterus at the 10th week of pregnancy, a woman is diagnosed with “fibroids at 10 weeks.” The sizes in weeks and cm are:
Fibroids in the uterus
- Small – up to 2 cm or 20 mm. This usually corresponds to 4 or 5 weeks of pregnancy;
- Average - up to 6 cm or 60 mm. This indicator is considered normal for 6-11 weeks of pregnancy;
- Large - from 60 in mm or 6 in cm or more. Usually relevant at 12 weeks of pregnancy and beyond.
When the formation corresponds to 20 weeks of pregnancy, it can significantly affect the functioning of neighboring organs. Myoma is also dangerous because it can disrupt the functioning of neighboring organs without causing pronounced symptoms. But most often, minor symptoms are still present.
You can see photos of fibroids by size below.
In what cases are surgeries performed to remove a tumor?
Most doctors prefer to practice conservative treatment in the first stages of antitumor therapy. It is as follows:
- taking iron-containing medications , vitamin complexes (A, E, B, folic and ascorbic acids);
- balanced diet with a predominance of protein foods;
- sufficient physical activity with a special set of exercises, alternating with rest and bed rest.
If conservative therapy is ineffective, the woman has the tumor removed in one of the following ways:
- laparoscopy (minimally invasive surgery using a video camera), which reduces the likelihood of adhesions and tubal obstruction, is ideal for small (up to 5-6 cm) formations;
- laparotomy (abdominal surgery), which is used to remove large myomatous nodes.
After the procedure, pregnancy planning is possible no earlier than a year later.
One of the newest and most progressive methods of surgical intervention is uterine artery embolization . Its essence lies in the introduction of special polymer balls of the same diameter. They close the lumen of the vessels that saturate the myomatous node without affecting the degree of blood supply to the uterus. Education is deprived of nutrition and access to necessary substances. Cell death occurs in it (they are replaced by connective tissue). This process usually lasts for a year. During this time, the fibroid decreases in size without causing discomfort to the patient. Strictly speaking, after embolization of the arteries, the nodes cease to represent fibroids: they turn into ordinary fibrous structures.
At the end of this type of operation, the rehabilitation period is easier than after standard interventions. In addition, the likelihood of complications and the length of time during which you cannot become pregnant are significantly reduced.
How to stop the growth of fibroids
Doctors use therapeutic and radical surgical measures to normalize the patient’s health condition. After conducting a thorough diagnosis and determining the stage of the disease, the doctor selects an individual treatment regimen.
If the myomatous node is small in size from 2-4 weeks of pregnancy, therapy will be aimed at correcting the woman’s hormonal levels, normalizing the body’s metabolism and eliminating clinical symptoms. As a result of treatment, the tumor will slow down or stop growing altogether. In the future, periodic monitoring by a gynecologist will be required. Treatment is carried out with hormonal drugs, immunomodulators, and homeopathic remedies. In combination therapy, physiotherapeutic methods are used: electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, therapeutic baths.
Treatment of fibroids with combined oral contraceptives
Third-generation oral contraceptives are capable of affecting the tumor, regardless of the cause of its occurrence. The stage of its development is fixed at the initial level, not determined even with the help of an ultrasound machine. An important definition is the ability of drugs to protect a woman from the formation of fibroids even at the prevention stage.
Logest is an effective drug for reducing fibroids with an initial size of up to 1.5 cm. Therapy with a combined contraceptive drug has a positive effect on the woman’s reproductive system. However, side effects may occur in the form of general weakness and weight gain. The contraceptive effect persists for several months after discontinuation of Logest.
Novinet, Ovidon, Mercilon are similar in effect, which is explained by the same pharmacological composition.
Duphaston - the active ingredient in it is dydrogesterone. It selectively acts on the endometrium, preventing the increased risk of developing endometrial hyperplasia and uterine malignancy in conditions of excess estrogen. Duphaston does not protect against pregnancy, it does not affect the menstrual cycle. As a result, conception is possible when using the drug. There is no need to terminate pregnancy during therapy.
The peculiarity of taking hormonal contraceptives is that they do not protect against sexually transmitted infections. Under the influence of an infectious agent, fibroids often begin to actively grow rather than shrink. In this case, it is necessary to undergo a course of antibiotic therapy to stabilize the size of the tumor.
The course of treatment ranges from several weeks to six months. It all depends on the state of the tumor and the rate at which it decreases.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists
Their action is based on stimulating the pituitary gland. The hormones produced in it have an inhibitory effect on fibroids, stopping the growth of connective tissue. The size of the tumor may be reduced by half after several months of taking the drug. In addition, drugs in this group relieve pain. If there are multiple nodes, treatment will take longer. Medicines in this group include: Zoladex, Decapeptyl, Buserelin. Side effects include irritability, depression, and lack of menstruation.
The Mirena release system can only be used by mature patients if there has been at least one birth in the anamnesis. Its difference from hormonal oral contraceptives is the absence of a preventive effect on the female body. The spiral is effective for fibroid sizes not exceeding 2 cm.
Additionally, during the treatment process, symptomatic drugs are prescribed: anti-inflammatory, vascular-strengthening and sedative drugs.
Detection of fibroids during pregnancy
The decision to terminate the pregnancy is made by the doctor, taking into account the patient’s medical history, her age, and diagnostic data of the tumor.
Pregnancy continues according to the following indications:
- young age of the woman in labor
- localization of nodes under the peritoneum
- small size of fibroids
- late detection of pathology
- inability to conceive again
In other cases, termination of pregnancy is indicated.
Surgical treatment for fibroids 15 weeks
If there is no effect of conservative treatment and the tumor is large, myomectomy is performed. The procedure allows you to subsequently carry and give birth to a child, the function of hormone production by the ovaries is not impaired. Amputation of the uterus is performed only in severe cases.
Types of surgical resolution of the disease:
- laparoscopy – elimination of the tumor through an incision on the anterior wall of the abdomen
- hysteroscopy – removal of a tumor through the vagina
- abdominal surgery
- hysterectomy – complete amputation of the uterus, performed for emergency reasons
Before a myomectomy, drug treatment is prescribed to reduce the size of the tumor before it is removed, as well as to reduce the risk of complications. Such drugs are progesterone-containing drugs: Danazol, Duphaston. The mechanism of their action is to inhibit the work of the ovaries, as a result of which the tumor stops increasing in size.
Traditional medicine recipes
When you decide to use traditional medicine, do not forget about basic therapy. The beneficial properties of medicinal plants can only be used as auxiliary methods and after consultation with a doctor. Some of them:
- Aloe leaves are known for their anti-inflammatory and regenerative properties. A tampon moistened with plant juice is placed inside the vagina for a month.
- A decoction of walnut partitions after boiling and infusion is recommended to be taken three times a day, one tablespoon for seven days.
- Burdock juice has a decongestant effect and stops cell proliferation. It is taken according to the scheme, always freshly squeezed.
Homeopathic remedies normalize hormonal levels and metabolism in the body, therefore they are used as a combination therapy.
Throughout the course of therapy, the doctor can change medications to achieve long-term remission or complete recovery of patients. To prevent the appearance of fibroids, you need to take care of your health throughout your life, and also do not forget about preventive measures.
Is it possible to conceive a child after removal of uterine fibroids?
The answer to the question of whether it is possible to become pregnant after its removal directly depends on how the disease was treated. Statistics on this matter are disappointing: the chances of successful conception and pregnancy are approximately 50%. They depend on many factors of various etiologies:
- if the patient becomes pregnant during the postoperative recovery period (sooner than 12 months after surgery), the risk of spontaneous abortion increases sharply;
- If, upon completion of the operation, complications such as the appearance of adhesions in the pelvis, intrauterine synechiae and obstruction of the fallopian tubes arise, the likelihood of infertility becomes very high.
If there is a postoperative scar on the uterus, pregnancy management should be especially careful and attentive. Delivery in this case is carried out only by caesarean section.
You can avoid the appearance of myomatous nodes by following some recommendations:
- visit a gynecologist regularly ;
- avoid abortions (medical and surgical);
- take oral hormonal contraceptives (only after consultation with a specialist); properly selected drugs can serve as an excellent means of preventing fibroids, but they are not able to cure an already existing formation;
- lead a healthy lifestyle (follow the basics of proper nutrition, exercise regularly, give up bad habits);
- avoid stressful situations and prolonged depression.
How to determine the size of a tumor in weeks
What to do when making an appropriate diagnosis? How do you know if you are being treated correctly? There is a table that shows the size of fibroids by week and what treatment method is used (table of correspondence between the height of the uterine fundus and the period):
| Size in weeks | Fundal height of the uterus | What type of treatment is used |
| 1-4 | 1-2 cm or 10-12 mm | Hormonal and drug therapy |
| Up to 7 | 3-7 cm or 30-70 mm | |
| Up to 9 | 8-9 cm or 80-90 mm | |
| Until 11 | 10-11 cm or 100-110 mm | |
| Up to 13 | 10-11 cm or 100-110 mm | Surgical (operational) intervention |
| Up to 15 | 12-13 cm or 120-130 mm | |
| Up to 17 | 14-19 cm or 140-190 mm | |
| Up to 19 | 16-21 cm or 160-210 mm | |
| Until 21 | 18-24 cm or 180-240 mm | |
| Up to 23 | 21-25 cm or 210-250 mm | |
| Up to 25 | 23-27 cm or 230-270 mm | |
| Up to 27 | 25-28 cm or 250-280 mm | |
| Up to 29 | 26-31 cm or 260-310 mm | |
| Up to 31 | 29-32 cm or 290-320 mm | |
| Up to 33 | 31-33 cm or 310-330 mm | |
| Up to 35 | 32-33 cm or 320-330 mm | |
| Up to 37 | 32-37 cm or 320-370 mm | |
| Up to 39 | 35-38 cm or 350-380 mm | |
| Up to 41 | 38-39 cm or 380-390 mm |
Depending on the stage of development of the pathology, its inherent symptoms make themselves felt.
Myomectomy and conception
The fact that myomectomy rarely leaves no consequences for the body is known to every woman who has at least once tried to conceive a child after a successful operation. After the intervention is completed, the patient needs to take a course of hormonal therapy for some time to prevent relapse of the disease and restore ovarian function. At the same time, it is very important not to forget that conception is successful only if the woman strictly followed the doctor’s recommendations and used contraception for a year after the end of myomectomy.
Natural childbirth after completion of the operation is permitted in the following situations:
- the placenta is located outside the uterine scar;
- coincidence in the size of the fetal head and pelvic region;
- the rehabilitation period after the intervention passed without complications;
- the lower uterine segment retained its usefulness (which was repeatedly confirmed instrumentally and in the laboratory).
In case of breech presentation of the fetus, pregnancy that lasts more than 40 weeks, as well as women over 30 years of age, a caesarean section is mandatory.
Throughout pregnancy, a patient with a history of myomectomy should be under the supervision of the attending physician. This is necessary to prevent complications and situations that threaten the lives of the mother and her baby. The occurrence of alarming symptoms and conditions is considered a reason to visit a specialist.
Submucosal fibroids and pregnancy after 35 years: how is pathology detected?
If conception occurs with submucous fibroids, the forum will tell you how to diagnose in this case.
To detect a uterine tumor, the following clinical tests are required:
- Examination by a gynecologist;
- Taking tests to identify genetic predisposition;
- Echography using a special vaginal sensor. To obtain information about the pathology, an ultrasound is prescribed;
- Blood and urine tests to detect the occurrence of inflammatory processes, as well as to determine the level of hemoglobin;
- Doppler measurements to assess blood flow in the tumor and the prospects for its growth;
- Hysteroscopy.