Breast fibroadenoma, without a doubt, is considered a controversial, ambiguous disease and, most unpleasantly, almost unpredictable.
On the one hand, breast fibroadenoma may seem like a harmless benign tumor that may not particularly bother a woman. But, on the other hand, this is precisely the tumor-like process whose unpredictability is frankly frightening.
For example, a fibroadenoma of the mammary gland, once formed, can remain the same size throughout the patient’s life, without presenting the slightest problem.
And in some cases, the same tumor can, under certain circumstances, begin to actively increase in size, injuring the tissues surrounding it, and even (extremely rarely, but it still happens) degenerate into breast cancer.
Naturally, the treatment of such neoplasms in different situations can involve radically different techniques, and now let’s talk a little more about this.
What is breast fibroadenoma
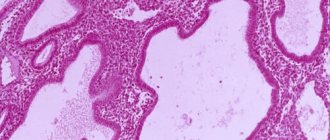
For many women, the diagnosis of breast fibroadenoma sounds like a death sentence. However, you should not panic. Fibroadenoma is a benign formation that is formed from glandular tissue under the influence of pathological processes.
Unambiguous causes of the disease have not been established, but the growth of a hormone-dependent tumor can be triggered by disturbances in natural processes in the body (late pregnancy, lack of conception, refusal of breastfeeding, early menstruation and sexual activity, taking hormones, etc.).
Fibroadenoma is detected mainly in girls in the age group from 15 to 30 years. Despite the fact that the formation is benign, it often requires radical treatment. If no measures are taken, the size of the tumor from the usual 2–3 cm can increase to 6 cm or more. In 20% of cases, multiple neoplasms are diagnosed. Leaf-shaped and intracanalicular tumors have the property of malignancy into a malignant form.
Symptoms of fibroadenoma
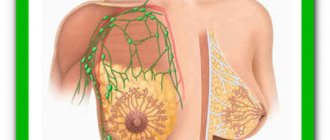
The main and main symptom of the disease is the detection of a dense elastic ball in the mammary gland. Often women are able to identify the signs themselves during self-examination. Tumors are often localized in the outer upper quadrant of the breast, but other locations are possible.
Most often there is only one tumor, but there may be more.
In addition, women experience the following complaints:
- pain with slight pressure on the chest in the area where the tumor is detected, intensifying before menstruation;
- inflammation of the mammary gland - mastopathy. May be accompanied by various discharge from the nipples and requires immediate medical attention;
- a feeling of discomfort in the chest, accompanied by its hardening and engorgement;
- breast enlargement if the tumor is large.
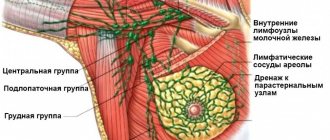
The disease is not characterized by changes and damage to the skin and areolar zone. The tumor rarely occurs in the areolar area (near the nipple). Also, it is not typical for fibroadenoma to involve axillary lymph nodes in the pathological process.
Regular self-examination allows you to identify fibroadenoma at the very beginning of its development, before pain, discomfort, inflammation and other symptoms occur.
Indications for surgery
When diagnosing breast fibroadenoma, surgery is performed in advanced cases or in the absence of positive results from conservative therapy.
Indications for fibroadenoma removal:
- leaf-shaped tumor;
- the diameter of the neoplasm is more than 2 cm;
- multiple formations;
- rapid growth of fibroadenoma;
- signs of malignancy (malignant)
- pregnancy or planned conception.
Fibroadenoma, like most hormone-dependent tumors, often forms and begins to actively grow during pregnancy. Removal of the formation during pregnancy is recommended only for a period of 12 weeks or more.
Fibroadenoma and pregnancy
During pregnancy, hormonal changes occur in a woman's body, which can trigger the development of fibroadenoma. Often the development of the disease occurs during this period. If the pathology appeared before pregnancy, it can begin to grow rapidly. Therefore, the examination plan for all pregnant women includes a consultation with a mammologist and an ultrasound of the breast. Treatment depends on the type and course of the disease. Only in the case of a severe form of the disease with rapid growth of the tumor is it removed during pregnancy. It is often recommended to remove the tumor after childbirth and after breastfeeding has ended.
Contraindications for surgery
Apart from the first trimester of pregnancy, surgery is contraindicated in patients with severe pathologies of the heart, lungs, liver and kidneys.
Other contraindications:
- diabetes mellitus in the decompensated stage;
- blood clotting disorder;
- development of acute infections.
If there are indications for surgery and contraindications, the doctor assesses the risks of tumor persistence. If the restrictions are temporary, the surgical intervention is postponed.
Possible complications
Despite all the safety and proven treatment technology, surgical intervention can lead to certain complications caused by disturbances during the operation and hypersensitivity of the body.
The most common problems are pain for several days, hematoma, swelling, inflammation at the site of the suture . These manifestations disappear during the recovery period.
The following complications are more dangerous: recurrence of tumors (in almost 15 percent of cases), changes in the shape and size of the breast, suppuration due to infection.
A rather unpleasant phenomenon is seroma, i.e. discharge of serous fluid at the incision site mixed with blood plasma. In this case, it is necessary to provide drainage.
NOTE!
In general, more than 95 percent of all operations, according to statistics, take place without serious complications, which is confirmed by numerous positive reviews.
How is the operation performed?
Removal of breast fibroadenoma in Moscow at the Yusupov Hospital is carried out in a surgery clinic by a qualified oncologist surgeon. The method of surgery is determined depending on the clinical picture and indications. With a significant size of the tumor and its spread, it is practically impossible to avoid traumatic surgical procedures. If the tumor is small in size, then a minimally invasive surgical technique is selected to avoid cosmetic defects.
Methods for removing fibroadenoma.
- Enucleation. A minimally invasive method of surgery with excision of tumor tissue. It is performed only if there is no risk of malignancy of the formation. Enucleation is performed under local anesthesia. The surgeon gains access to the internal tissues through a small incision, which is closed with a cosmetic suture.
- Sectoral resection. A more traumatic operation consisting of resection of part of the internal tissue of the mammary gland along with the tumor. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. Sectoral resection of the mammary gland is performed if there are signs of breast tumor transition.
- Total resection of the gland. The operation is also called a mastectomy. Radical surgical intervention for complete removal of the mammary gland is indicated when diagnosing a malignant form of fibroadenoma. Postoperative defects cannot be avoided.
After sectoral resection, the tumor and breast tissue are sent for histological examination to determine the likelihood of the presence of cancer cells. If the diagnosis of cancer is confirmed, the patient undergoes further treatment. The Yusupov Hospital has a modern oncology department that treats cancer patients.
Need for treatment
Is it necessary to remove fibroadenoma? The answer to this question depends on many factors.
The need for removal can only be determined by a doctor after conducting appropriate examinations..
One thing is important: if signs of pathology appear, you must contact a specialist who should take control of the situation. First of all, the woman herself will not be able to differentiate fibroadenoma from a malignant tumor. This requires histological studies.
If fibroadenoma is identified, then the question of treatment method is determined based on the type of pathology, the size of the formation and its progression.
Expert opinion
Dmitrieva Elena Yurievna
Gynecologist-endocrinologist, 40 years of experience
“Fibroadenoma extremely rarely leads to complications that are dangerous to the health, and even more so, the life of a woman. At the same time, self-resorption of formations is observed only in 7-8 percent of cases, and their growth occurs 5-6 times more often. Surgical removal of fibroadenoma is definitely necessary in cases of suspected cancer, the presence of a phyllodes tumor, active growth of the tumor, or the appearance of cancerophobia. You should also think about surgery when planning a pregnancy.”
The following factors should be considered as indications for surgical removal of fibroadenoma::
- The size of the seal is more than 2 cm.
- Increase in the size of the formation by 2-2.5 times in 2-3 months.
- Increased risk of tumor malignancy.
- The presence of a pronounced cosmetic defect (significant breast tuberosity, deformation of the gland, the appearance of asymmetry, etc.).
What types of pathology require surgical treatment? It is necessary when identifying fibroadenoma of the leaf-shaped (phylloid) type due to its rapid growth and risk of oncology.
You should not rush into surgery for pericanalicular formation (especially in adolescents) . In this case, it is enough to carry out a course of therapy and provide control.
The problem should be discussed with a specialist when planning pregnancy. Small, stable lumps do not require intervention and can be lived with for life.
However, during pregnancy the hormonal balance changes dramatically, and this leads to an increased risk of rapid growth of fibroadenomas..
They do not affect the development of the fetus, but breastfeeding may become difficult in the future.
Consequences
After surgery to remove breast fibroadenoma, the patient requires a hospital stay from several hours to 2 days. When surgery is performed under local anesthesia, discharge is possible on the same day. Anesthesia and radical manipulations are indications for longer-term monitoring of a woman’s condition.
The consequences of the operation depend on the methods of its implementation. After enucleation, recovery occurs quickly and no significant aesthetic defects remain. Sectoral resection will lead to a change in the shape of the breast. In a total resection, the breast gland is removed.
At the Yusupov Hospital, methods are available to remove fibroadenoma with simultaneous breast surgery, which will avoid repeated surgery for correction and psychological trauma due to a pronounced breast defect. Modern equipment, qualified surgeons, experience in using modern techniques - the opportunity to provide comprehensive assistance to patients in maintaining not only health, but also beauty.
Prevention
Since the cause of fibroadenoma has not yet been studied, effective methods for preventing the disease have not been identified. But you can significantly reduce the risk of developing the disease. To do this, you must follow the following recommendations:
- Perform regular breast self-examinations;
- visit a gynecologist and mammologist if symptoms of the disease are detected;
- undergo a medical examination in accordance with age recommendations;
- lead an active healthy lifestyle;
- take oral contraceptives only as prescribed by a gynecologist;
- fight excess weight.
These methods will help not only to identify the disease in the early stages of its development, but also to stop its growth and development.
What are we talking about?
According to statistical data, fibroadenoma in very rare cases can degenerate into a malignant tumor. This happens not only rarely, but also when a significant number of specific factors coincide. For example, there must be a tendency to cancer.
Endocrine disorders in this case turn out to last for many years. The state of the immune system plays a significant role. Tumor diseases appear only when there are serious problems with the immune system. But if at least one risk factor is present, doctors prescribe surgery.
Such measures are not necessary for small fibroadenomas. For example, if the latter appeared for the first time, in a single copy and measuring less than 2 centimeters, the mammologist may suggest not taking any steps. This will avoid stress on the body (meaning anesthesia and related things).
Signs
Laser removal
Laser ablation is an extremely effective technique that does not require either anesthesia or hospitalization of the patient.
Under the control of an ultrasound navigator, a laser beam is directed at the tumor and destroys its tissue through intense thermal exposure. Healthy tissues are not harmed. The procedure leaves only a barely noticeable mark on the skin.
Cryodestruction
This is a modern, fast and effective method of removing fibroadenoma by freezing it with liquid nitrogen. Thanks to high-tech equipment with ultrasound navigation, the procedure takes no more than a quarter of an hour and is carried out in an outpatient setting.
Radio frequencies
This type of ablation is performed using radiofrequency equipment. Having made a tiny (no more than eight millimeters) incision over the tumor, the tip of a surgical knife is inserted into it, separating healthy tissue from the affected tissue. After this, a robotic installation removes the tumor tissue.
Postoperative period
Postoperative recovery for patients with fibroadenoma is usually quick and completely painless.
Reputable clinics practice counseling patients who have undergone surgery by telephone.
During such a conversation, the attending physician will definitely give his ward a number of useful recommendations.