Hyperplasia - how soon will pregnancy occur?
Different diagnoses during a gynecological examination make a woman wonder whether she can give birth with such a disease? What caused the disease and how to get rid of it as quickly as possible. Hyperplasia is a common disease that occurs more often in women over 40, but there are cases where younger girls are faced with this disease.
Causes
Pathological tissue proliferation can be caused by several factors.
- Hormonal imbalance can occur for various reasons. One of them is the misuse of oral contraceptives.
- If there is a deviation in fat and carbohydrate metabolism, obesity occurs. Adipose tissue produces estrogens, which cause endometrial hyperplasia.
- The presence of chronic diseases, including diabetes, hypertension and liver problems.
- Diseases of the endocrine glands. These include the thyroid, pancreas, and adrenal glands.
- Inflammatory processes in the genital organs. Inflammation can occur in the uterus and other organs due to sexually transmitted infections, as well as due to the use of contraceptive devices.
- Improper functioning of the immune system. Due to the erroneous protection of immune cells in relation to the tissues of the uterus, endometrial hyperplasia occurs.
- Many representatives of the fairer sex experience endometrial hyperplasia during menopause and after it. Changes in uterine tissue can occur in teenage girls during adolescence.
- Frequent abortions and curettages. The endometrial layer is disrupted, which reduces the sensitivity of its cells.
- Congenital defects of the uterus, as well as genetics.
Is it possible to get pregnant
Conception with this disease is possible, but this happens very rarely. It is worth noting that after the diagnosis is made, it is necessary to identify why the tissue began to grow and stop the source of irritation as soon as possible. It is not possible to conceive a child due to lack of ovulation.
For endometrial hyperplasia
For girls with this diagnosis, conception is contraindicated until the disease is cured. It is extremely difficult to get pregnant with hyperplasia, but if conception occurs, there are negative consequences:
- miscarriages;
- incorrect placement of the embryo;
- embryo development stops;
- malignant neoplasms.
Once diagnosed, doctors recommend an abortion to avoid negative consequences in the mother’s body.
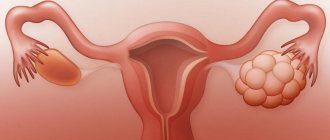
If you have ovarian disease: is it possible to get pregnant?
Hyperplasia provokes tissue proliferation, and subsequently adhesions appear in the pelvis. This manifestation has a bad effect on conception. Pregnancy in this case rarely occurs. In the early stages, the disease can be cured quickly by taking hormonal medications. Only the doctor can tell you what medications to take.
Hyperplasia of the right ovary is most often observed. Growths on the left ovary are very rare.
Endometrial hyperplasia during breastfeeding
Does the disease affect the baby if the mother is breastfeeding? No. However, there is no need to delay treatment.
The main reason for the development of endometrial hyperplasia during lactation is hormonal changes during childbirth. In addition, concomitant diseases appear:
- ovarian cyst;
- endometriosis;
- myoma;
- mastopathy.
Another important reason is the absence of menstruation after childbirth (amenorrhea).
Features of pathology during breastfeeding
- spotting during the period when menstruation has not yet occurred;
- after delays, heavy bleeding;
- cycle failure;
- chronic weakness and fatigue;
- decreased immune functions of the body.
If such symptoms occur, you should consult a doctor. Otherwise, you can get complications such as the transition of hyperplasia to an atypical form, the development of malignant tumors, and infertility.
Pregnancy after
If you have successfully completed the course of treatment, then you can safely try to conceive a child.
After therapy, the functioning of the reproductive system returns to normal, and the desired pregnancy will occur quickly.
When is it possible
After a complete examination, you should refrain from trying to conceive for 3 months. This needs to be done so that the expectant mother’s body returns to normal. Therefore, 3 months after treatment you can plan a pregnancy.
Contraindications
There are a number of contraindications in which a woman will not be able to get pregnant on her own:
- After treatment, the endometrium began to grow again. This suggests that not all problems have been resolved. In this case, the girl will undergo treatment again, since pregnancy is contraindicated.
- After treatment, the girl’s hormonal levels did not return to normal.
- Liver and heart diseases.
Special Moments
A common cause of ovarian hyperplasia is reduced immunity, use of contraceptives for more than 5 years, hypothermia, infections, and inflammation. The presence of pathology is indicated by the following symptoms:
- nagging, sharp pain in the lower abdomen, lower back;
- Irregular menstruation or its complete absence;
- acyclic uterine bleeding;
- increased tone of the abdominal muscles;
- abdominal spasm;
- high body temperature;
- pain during sexual intercourse.
If a woman has at least several of these symptoms before pregnancy, additional research is necessary. During the period of bearing a child, methods of influence are limited and not so effective.
Olvik
Hyperplasia is an increase in the number of cells in any tissue (except tumor) or organ, resulting in an increase in the volume of this anatomical formation or organ.
Histologically (according to cellular composition), several types are distinguished:
1) glandular endometrial hyperplasia;
2) glandular cystic hyperplasia;
3) atypical endometrial hyperplasia (synonym - adenomatosis, adenomatous hyperplasia);
4) endometrial polyps.
The first two forms of endometrial hyperplasia differ in the presence of cyst-like dilated glands and the ratio of glands to stroma.
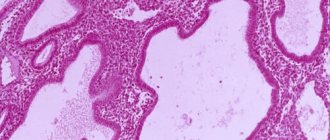
Atypical endometrial hyperplasia is histologically characterized by profusely overgrown glands, an increase in the size and polymorphism of nuclei, an abundance of mitoses, and a decrease in stromal elements.
According to most authors, the first two types of hyperplasia are not a precancerous disease. The third type, atypical hyperplasia, is a precancerous disease. If present, the risk of degeneration into a malignant tumor (endometrial cancer) in the absence of therapy ranges from 1 to 14% and is most often observed during menopause (cessation of menstrual function due to age).
Precancerous hyperplastic processes develop into endometrial cancer in approximately 10% of patients (according to various authors, from 2 to 50%), they often persist for a long time, and sometimes undergo reverse development. However, taking into account the real threat of the process progressing to endometrial cancer, a doctor’s attentive attitude towards patients with endometrial adenomatosis and adenomatous polyps is necessary.
There are opinions about the possibility of considering glandular hyperplasia and hyperplastic processes that arise again (recur) after endometrial curettage or are not amenable to hormone therapy as precancer of the endometrium.
The risk of malignancy (malignancy) of hyperplastic processes increases with metabolic disorders caused by extragenital disease (obesity, impaired carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, dysfunction of the hepatobiliary system and gastrointestinal tract), concomitant with the development of endometrial pathology.
A localized, localized form of endometrial hyperplasia is called an endometrial polyp. Histologically, they are also divided into several types depending on the cells that predominate in their structure.
Forms of endometrial polyps:
- glandular;
- glandular fibrous polyps;
- fibrous polyps.
Cause and mechanism of development of the disease
Risk factors for the occurrence of this pathology are:
— The occurrence of hyperplastic processes in the endometrium is facilitated by hereditary burden (uterine fibroids, genital and breast cancer, hypertension and other diseases), damaging effects during intrauterine life, diseases during puberty and associated disorders of menstrual and subsequently reproductive function. In mature women, the appearance of hyperplastic processes is often preceded by gynecological diseases and surgical interventions on the genital organs.
— Hyperplastic processes of the endometrium are often accompanied by obesity, hypertension, hyperglycemia (this triad of symptoms is especially often combined with atypical and hyperplastic processes recognized as precancer of the endometrium), uterine fibroids, mastopathy, endometriosis, which are largely hormonal-dependent diseases, as well as disorders functions of the liver responsible for the metabolism of hormones.
The leading factor in the cause of occurrence and further development belongs to hyperestogenia - an increase in the level of the hormone estrogen.
Clinical picture
In the clinical picture of the pathology, the following symptoms are most often noted:
- Uterine bleeding that occurs after a delay in the next menstruation. They can be either long in duration with moderate blood loss, or short in time but abundant;
— Bloody intermenstrual discharge;
— Primary or secondary infertility, which is based on the process of lack of formation of a normal egg;
— In some patients, symptoms are mild or completely absent.
— The most common, almost constant symptom of endometrial polyps is menstrual irregularities. With polyps against the background of a normal functioning endometrium, women of reproductive age experience scant intermenstrual and premenstrual blood discharge with a preserved menstrual cycle, as well as an increase in menstrual blood loss.
— In women of reproductive age, glandular fibrous and fibrous polyps can cause menorrhagia. Menorrhagia [from Greek. men - month and rhegnymi - breakthrough], heavy and prolonged menstruation, in which the periodicity of the menstrual cycle is preserved, but the amount of blood lost during each menstruation is increased. M. is based on processes that reduce the contractility of the uterine muscles. It is observed in chronic inflammation of the uterus (metritis), acute inflammation of the uterine appendages, uterine fibroids and other gynecological diseases. It may also be a consequence of blood diseases characterized by decreased blood clotting. Treatment: elimination of the cause that caused M.
— With anovulatory cycles and the presence of polyps of the glandular structure against the background of hyperplastic processes of the endometrium, metrorrhagia is observed, the cause of which is not polyps, but dystrophic, necrotic changes in the endometrium and hormonal disorders. Such clinical manifestations are more typical for premenopausal women (after 45 years). Metrorrhagia [from Greek. metra - uterus and rhegnymi - breaking through (breaking through)], uterine bleeding occurring randomly, i.e. with disruption of the menstrual cycle. It is observed in many types of obstetric (abortion, hydatidiform mole, ectopic pregnancy, etc.) and gynecological (polyposis of the uterine mucosa, cervical erosion, submucous fibroids, sarcomas, genital cancer, etc.) pathologies. In some cases, M. is the most pronounced sign of pathology of the menstrual cycle; the cause of these bleedings is a disorder of blood circulation in the uterine wall due to a violation of regulatory mechanisms in the central nervous system, leading to disruption of the endocrine function of the ovaries. Treatment: elimination of the cause that caused M.
Diagnostics
— Ultrasound diagnosis of endometrial hyperplasia. It should be considered a screening test since ultrasound only records endometrial thickness.
| Endometrial structure | Endometrial thickness, mm |
| Unmodified | 9,8 ± 2,1 |
| Hyperplasia | 15,4 ± 0,4 |
| Adenocarcinoma | 20,12 + 2,04 |
— For diagnostic purposes, diagnostic curettage of the mucous membrane of the uterine body is widely used. The diagnosis is established on the basis of histological examination of the endometrium obtained by curettage under hysteroscopy control. Endometrial biopsy with a curette or a specially designed aspiration biopsy instrument may give a false negative result in the presence of focal atypia. It is recommended to scrape the endometrium on the eve of the expected menstruation or at the very beginning of the appearance of bleeding. In this case, it is necessary to remove the entire mucous membrane, including the area of the uterine fundus and fallopian tube angles, where foci of adenomatosis and polyps are often located. For this purpose, endometrial curettage is performed under hysteroscopy control. The removed mucous membrane is sent for histological examination
The picture of hyperplastic endometrium is considered highly specific - the informative value of hysteroscopy for endometrial hyperplasia is estimated at 94.5%, transvaginal echography - at 68.6%.
Histological examination is the most reliable method for diagnosing hyperplastic processes and determining the nature of this pathology (glandular cystic hyperplasia, atypical hyperplasia - diffuse, focal adenomatosis, polyps - glandular, adenomatous, fibrous).
Is curettage always done for endometrial hyperplasia?
Always. This is the first stage. It allows you to obtain a sample of endometrial tissue and make an accurate diagnosis: what kind of hyperplasia, and whether there are any precancerous changes. Further treatment depends on this. Even if these are hormones (the most favorable situation), they will only help prevent the development of hyperplasia again, but not cure it. The changed endometrium can only be removed mechanically.
Treatment
Treatment of endometrial hyperplastic processes is carried out taking into account numerous factors - the patient’s age, the causes of hyperplasia and the nature of this pathology, clinical manifestations, contraindications to a particular treatment method, tolerability of medications, concomitant extragenital and gynecological diseases.
The main treatment is hormonal (selected individually).
When prescribing hormone therapy, certain conditions and strict consideration of contraindications are required.
After 3 and 6 months, a control ultrasound is indicated.
For hyperplasia associated with polycystic ovary syndrome, the first stage of treatment is wedge resection of the gonads. This operation is especially indicated for recurrent hyperplasia, which is alarming for endometrial precancer. If the clinical effect of ovarian resection is insufficient (control - biopsy and histological examination of the endometrium), hormone therapy is carried out according to the guidelines adopted for various types of endometrial hyperplastic processes.
Surgical methods are preferable for recurrent glandular cystic hyperplasia that has developed against the background of diseases of the endocrine glands (diabetes, prediabetes, etc.), obesity, hypertension, liver and vein diseases. Surgical treatment is indicated for precancer (adenomatosis, adenomatous polyps) of the endometrium, especially when this endometrial pathology is combined with adenomyosis and uterine fibroids, and pathological processes in the ovaries.
Patients with fibrous polyps are not subject to hormonal therapy.
Women of reproductive and especially premenopausal age who have glandular and glandular-fibrous polyps against the background of endometrial hyperplastic processes are advised to remove the polyp followed by hormonal therapy. For adenomatous polyps in premenopausal women with metabolic and endocrine disorders, an alternative is removal of the uterus with a thorough revision of the ovaries (hyperplasia of the tissue body, the presence of hormonally active tumors). Adenomatous polyps in postmenopausal women are an indication for removal of the uterus and appendages.
How does hyperplasia affect pregnancy?
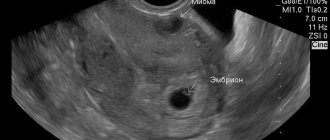
Pregnancy once diagnosed is practically impossible, but in the early stages of the disease, embryo implantation can occur. Therefore, in this case, a medical abortion is performed. This disease disrupts the natural process of embryo development, which will subsequently provoke a miscarriage, and if not, the child will be born with abnormalities. Also, there is a high probability of malignant tumors. Depending on how quickly they grow, death can occur.
Layer norm on different days and weeks of the cycle in the 1st trimester
To increase the chances of successful conception and safe pregnancy, it is necessary to plan your pregnancy correctly. One of the procedures that needs to be completed in advance is calculating the size of the epithelial layer at ovulation. This can be done with an ultrasound.
Ultrasound diagnostics is necessary to confirm an important condition for pregnancy, such as a three-layer endometrium. It is observed in the first phase of the cycle. Even if this mucous membrane is thin, but three-layered, conception occurs in most cases.
When the endometrium is of normal thickness, but homogeneous, fertilization will not occur. Therefore, it is important to know at what endometrium pregnancy is possible throughout the entire cycle, and at what endometrium you can not hope for it.
| Cycle day | MIN thickness in cm | MAX thickness in cm |
| 1 and 2 | 0.4 | 0.8 |
| 3 and 4 | 0.2 | 0.5 |
| from 5 to 7 | 0.5 | 0.9 |
| from 8 to 10 | 0.6 | 1.1 |
| from 11 to 14 | 1 | 1.3 |
| from 15 to 18 | 1 | 1.6 |
| from 19 to 23 | 1.1 | 1.8 |
| from 24 to 28 | 1.2 | 1.9 |
Women carrying a baby for the second time should not worry if doctors find out “what kind of endometrium you had in the first trimester,” since they need this data for comparison with the indicators of the new pregnancy.
The optimal thickness of the endometrium by week in the first three months is 9-14 mm, which is typical for the very first days after confirmation of successful conception and no more than 21 mm at 21-30 days of pregnancy.
It is important to know that the transformation of the mucosa during an ectopic pregnancy occurs in a similar way, since the body does not immediately understand that the embryo is not where it is needed. Bloody discharge and abdominal pain are the main signs of pathology.
What do the doctor's say
With such a disease, it is worth starting treatment as soon as possible. If left untreated, it will lead to infertility in the future. After a course of therapy, natural pregnancy occurs in 80% of cases.
It is almost impossible to bear a healthy child with such a disease.
If you have been diagnosed with this, do not delay treatment until later. In the early stages, you can still get rid of the disease without consequences. Otherwise, the reproductive system will stop working, leading to infertility.
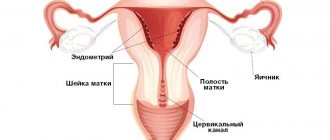
Endometrium: what is it and why is it needed?
The endometrium is the inner mucous layer of the uterus, which consists of glandular, integumentary epithelial membranes and a whole system of blood vessels.
It thickens with each regular menstrual cycle. This is influenced by sex hormones. In this way, the body prepares favorable soil for the possible implantation of an embryo. To better understand the purpose of the endometrium, it is worth visiting a women’s forum about pregnancy and reading reviews from patients who experienced its transformation in the first trimester.
So, after successful fertilization, the mucous layer of the uterus begins to work hard, performing the following functions:
- creates a favorable environment for the placement of the zygote;
- until the placenta is formed, it nourishes the embryo and supplies it with oxygen;
- helps form the placental layer;
- prevents the fusion of the walls of the uterus.
The size of the endometrium depends on hormones and their levels in a woman’s body, as well as the age of the expectant mother, and its growth is especially affected by infectious diseases, hormonal imbalances and a number of other pathologies of the reproductive system.
Every woman needs to have at least basic knowledge about internal ailments, especially the reproductive system. The lecture “Hyperplastic diseases of the internal genital organs” will help you better study and understand your body.
The concept of hyperplasia
First of all, endometrial hyperplasia is a gynecological diagnosis, during which endometrial tissue in the uterine cavity begins the process of intensive growth in the wrong places. This pathology develops due to an imbalance of hormones in a woman’s body. The amount of estrogen (sex hormone) is in excess.
Supposed causes of hyperplasia, according to doctors:
- estrogen levels increase in a woman’s body;
- the presence of chronic inflammatory processes;
- violation of the metabolic process (metabolism);
- diabetes mellitus;
- many abortions;
- fibroids in the uterine cavity;
- problems with the endocrine system;
- curettage performed in the past;
- presence of endometriosis;
- liver pathologies;
- presence of polycystic disease;
- tumors of the genital organs, as well as tumors of the mammary glands;
- hereditary predisposition;
- gynecological operations;
- presence of ovarian dysfunction.