What are follicles in the ovaries in women? The ovaries are the paired organs of the female reproductive system. They produce an egg every month that is suitable for fertilization by sperm. However, you can often hear from a doctor about the maturation of the follicle in the ovaries. What does it mean?
The fact is that the number of eggs is limited and is individual for each woman. Immature forms are in a special protective shell, a kind of pouch. This is the follicle. It performs the following functions:
- Protecting the embryonic egg from the effects of negative factors.
- Hormone production. Participates in the synthesis of the female hormone estrogen.
- Ensuring the maturation of the egg. Inside the follicle, the egg matures monthly, and also ensures its release into the fallopian tubes during ovulation.
Note. It is impossible to say exactly how many follicles there should be in the ovary. It is generally accepted that their number is from 50 to 200 thousand.
What are follicles, their role in the body
Follicles are sacs containing immature eggs. Each woman has her own ovarian reserve of eggs, which is laid during the period of embryonic development, starting from the 6th week. The formation of follicles in the ovaries stops at birth. Their total number in the ovaries can be 500 thousand or more, but during the entire reproductive period (an average of 35 years), only 300-500 follicles fully mature, the rest die.
They have 2 main roles: protecting the maturing egg from external influences and producing estrogen.
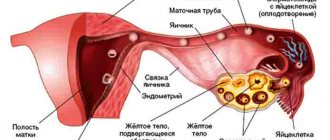
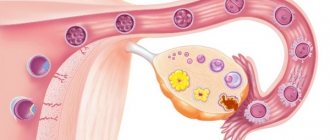
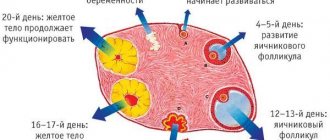
In the first phase of the cycle, under the influence of FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone of the pituitary gland), the growth of several follicles begins at once. A capsule with strong walls protects the egg until full maturity, which occurs in the middle of the cycle. The volume of liquid gradually increases, while the walls stretch. At the moment of ovulation, when the egg is ready for fertilization, the capsule bursts, giving it the opportunity to exit and move into the fallopian tube, where it meets the sperm.
In each cycle, only one follicle (dominant) usually reaches full maturity. The rest intensively produce estrogens, which are responsible for the development of the endometrium, the formation of female mammary glands and many other processes.
The follicles in the ovaries are filled with fluid containing proteins, salts and other elements necessary for the development of eggs.
Features of the maturation cycle
The number of female germ cells is formed at the stage of embryonic development. They are evenly distributed throughout the body of the ovary and, with the onset of puberty, the girl begins to mature.
The formation of follicles in the ovaries occurs during each menstrual cycle. Gradually, this sac increases in size, and by the middle of the cycle it ruptures, which is accompanied by the release of a mature egg and, possibly, its subsequent fertilization. If conception does not occur, menstrual bleeding is observed. This process is normally repeated every cycle.
When the follicles in the ovary mature, a woman may experience minor discomfort. This is due to an increase in the size of the organ and subsequent rupture of the sac. Initially, several follicles are formed in the ovaries. The quantity norm is up to 10 units per cycle.
By the middle of the cycle, single follicles remain in the ovary. Usually only 1 follicle reaches the end of the maturation cycle. It's called dominant. The remaining formations gradually resolve. If 2 follicles mature simultaneously in one or each ovary, the chance of conceiving twins increases.
Important! During artificial insemination or egg donation, artificial stimulation of multiple maturation of follicles in the amount of 6-30 pieces is performed.
Types of follicles
The following types of follicles are distinguished:
- dominant;
- persistent;
- antral.
Dominant
- This is the main follicle in the ovary that reaches maturity and ruptures during ovulation. Most often he is the only one. Much less often they appear on both sides at the same time. This happens, for example, when treating infertility by stimulating ovulation. In this case, the birth of twins is possible.
Persistent.
Its appearance is indicated when the capsule does not rupture, the egg in it dies. This cycle is called anovulatory. Conception in this case is impossible.
Antral.
This is the name given to those few follicles that begin to grow at the beginning of each cycle under the influence of FSH. After one of them becomes dominant, the rest stop growing and then die.
What is the significance of the number of antral follicles?
The number of antral follicles in the ovaries determines whether a woman can become pregnant.
Normally, there should be from 11 to 26. In this case, the probability that ovulation will occur is 100%. The chances of conception are maximum.
If their number is 6-10, then the probability of ovulation is 50%. In the case when there are less than 6, it is impossible for a woman to conceive naturally. In this case, only artificial insemination (IVF) can help.
If there are no follicles in the ovaries at all, they speak of the onset of early menopause and final infertility. However, a woman will be able to give birth if a fertilized donor egg is transplanted into her uterus.
The quantity is calculated using a transvaginal ultrasound sensor. The study is carried out on days 2-3 of the cycle. This indicator can be affected by changes in hormonal levels, the presence of diseases of the uterus and ovaries (polycystic disease, endometriosis).
If a woman has a deviation that indicates the impossibility of conception, this is not a death sentence. The situation may change next month even without any treatment if, for example, the cause of a hormonal imbalance is stress. In case of persistent infertility, a woman needs examination and, possibly, stimulation of ovulation with the help of special medications.
Additional examinations
Anovulatory cycles, when the dominant does not develop, occur several times a year in every healthy woman. This phenomenon is not pathological. During these periods, the ovaries “rest”.
In addition, after 30 years there is a slow but steady increase in anovulatory cycles. Early menopause, which occurs before the age of 45, also guarantees frequent anovulatory cycles. Despite the fact that women at this age rarely plan pregnancy, gynecologists believe that these deviations cannot be ignored and prescribe appropriate hormonal therapy.
If such disorders are recorded in young women of childbearing age every month, this indicates pathological changes that require mandatory treatment.
Why the follicle does not grow or is not able to “release” a mature egg at the time of ovulation, only the attending physician can answer after a series of studies:
- Examination on a gynecological chair;
- Blood tests to detect levels of important hormones at different stages of the menstrual cycle;
- Folliculometry is an ultrasound diagnostic procedure during which the entire process of ovarian function during the menstrual cycle is monitored monthly.
The gynecologist also pays attention to the length of the menstrual cycle. A cycle that is too long or short is often evidence of ovulation disorders.
Most often, the absence of a dominant is associated with hormonal imbalance. The process of proper development of follicles is influenced by several hormones: luteotropic, follicle-stimulating, estrogen and progesterone. Each of these hormones is important at a certain stage of egg maturation. Their insufficient quantity or incorrect distribution leads to problems with the maturation of the dominant.
How do follicle sizes normally change during the cycle?
At the beginning of each menstrual cycle, if everything is normal, under the influence of FSH, the development of new follicles in the ovaries begins (folliculogenesis). The process develops as follows:
- From days 1 to 4 of the cycle (average duration 28 days), the size of the antral follicles increases to an average of 4 mm.
- From days 5 to 7 they grow at a rate of 1 mm/day.
- On day 8, one of them becomes the main one, continues to increase at a rate of 2 mm/day, and the rest regress and disappear.
- By day 14 (the moment of ovulation), the size of the dominant follicle is 24 mm.
What is folliculometry and why is it performed?
To determine the number and size of follicles and control their development, transvaginal ultrasound (using a vaginal sensor) is used. This method is called folliculometry. In the first half of the cycle, the state of the endometrium and eggs is studied, and in the second half, observations are made of how the follicles develop in the ovaries after ovulation.
The method is used to examine women suffering from various menstrual disorders or infertility. With its help, you can accurately determine the date of ovulation, determine on what day conception is most likely, monitor multiple pregnancies, determine the cause of cycle disorders and the nature of hormonal imbalance, and monitor the progress of treatment for ovarian diseases.
To get a complete picture, the study is carried out repeatedly, on different days of the cycle.
At the same time, other diagnostic methods are used, such as a blood test for hormone content (FSH, LH, estradiol, progesterone, anti-Mullerian hormone), ultrasound of the pelvic organs to determine the size of the ovaries and detect various diseases of the uterus and appendages. If necessary, a puncture is performed to select and examine the liquid contained in the capsule.
Note:
In the same way, the egg is retrieved before the IVF procedure. The ovaries are first stimulated to obtain several high-quality eggs.
Disorders due to improper development of the dominant follicle
The reason for a woman's infertility is often the lack of ovulation in the cycle, when the follicle grows to a certain size and then does not rupture. Subsequently, the following processes may occur:
- Atresia is a stunting of growth and subsequent reduction of the dominant follicle in the ovary. If this happens to a woman constantly, then she is infertile, and she may not have menstruation, but similar bleeding appears 2-3 times a year.
- Persistence. The follicle grows, but does not burst, remains unchanged in the ovary until the end of the cycle, and then dies.
- Formation of a follicular cyst. The unruptured follicle is filled with secretory fluid, its wall stretches, forms a bubble 8-25 cm in size. Over the course of several cycles, the cyst can resolve, as the follicle gradually decreases and dies.
- Luteinization is the formation of the corpus luteum in an unruptured ovarian follicle. This occurs when the pituitary gland produces too much LH. The cause is a disruption of the hypothalamic-pituitary system of the brain. With this condition, a woman who has a normal cycle and menstruation experiences infertility.
The causes of disorders may be diseases of the thyroid gland and other organs of the endocrine system, or the use of hormonal contraceptives. Anovulatory cycles are often observed in adolescents at the beginning of puberty, as well as in premenopausal women with sharp fluctuations in hormonal levels.
Warning:
To eliminate such a pathology, folk remedies should never be used. You should not try to cause rupture of the follicle artificially through gymnastics or increased physical activity. All these measures are not only useless, but can also cause great harm to the body, cause complete cycle disruption, and contribute to the formation of cysts.
Video: Causes of anovulatory cycles, how treatment is carried out
When there is no dominant follicle: why and what to do
If there is no dominant follicle, then there will be no conception.
If conception does not occur for more than a year of regular attempts, it is time to talk about infertility. Infertility is the absence, over several cycles, of a leading follicle within which the egg should mature.
Why is the “dominant” not developing, how should the female body work correctly, and how to get rid of this problem? There are many questions. But first things first.
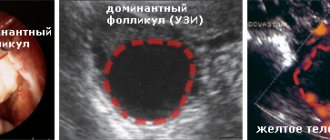
The photo shows the dominant follicle. It happens that it simply does not exist, and it is not produced from cycle to cycle.
Stages of follicle development
A girl who is still in the womb has a certain number of eggs. They are inactive until menstruation begins. The follicles then begin to grow and die each month. Their development occurs in stages.
Stages of follicle maturation:
- First phase (beginning of the cycle). At this point, several equally sized follicles develop.
- The second phase is the emergence of a “leader”. This happens around day 8-10 of the cycle. One of the structural components of the ovary becomes larger than the others. He is the leader. The remaining follicles become smaller and begin to die.
- The onset of ovulation (12-14 days). The “dominant” becomes the maximum size. A rupture occurs and a mature egg emerges. Instead of the leading follicle, a corpus luteum is formed, which supplies the female body with the hormone progesterone, which is important for maintaining pregnancy.
The appearance of a leading follicle is possible on any or even both ovaries at the same time. However, it usually ripens on the right.
The appearance of a “dominant” on both ovaries is a common occurrence when ovulation is additionally stimulated, as well as during IVF or artificial insemination.
By the way, if a dominant follicle has formed in both ovaries, the girl has a chance to get pregnant and give birth to twins or even triplets. But if a woman does not develop a “dominant”, then ovulation and conception do not occur.
The problem with the appearance of a dominant follicle can be identified using ultrasound diagnostics.
What examination is prescribed?
The absence of a “dominant” is not always a sign of illness. Any healthy representative of the fairer sex experiences periods when the follicle does not form. Anovulatory cycles 3-4 times annually are considered the norm. The ovaries seem to “go on vacation.”
In women after 30 years of age, such periods become more frequent every year. With early menopause, which occurs before the age of 45, the eggs “fall asleep” more often. Although most women of this age do not plan to conceive, experts recommend not ignoring changes in the body. Gynecologists often suggest that patients get rid of the problem with the help of hormonal therapy.
If a woman of childbearing age has these abnormalities, this indicates pathology. In this case, treatment is mandatory. The attending physician will be able to tell about the reasons for the non-developing dominant follicle only after conducting research.
The examination consists of:
- examination by a gynecologist;
- hormonal blood tests. It will help you find out the level of hormones necessary for the proper functioning of the female body at different stages of the cycle;
- Ultrasound diagnostics. The procedure for tracking the functioning of follicles is called folliculometry. The diagnostician monitors the functioning of the ovaries throughout the menstrual cycle. The procedure is repeated for a number of cycles.
It is important for a gynecologist to know the length of the cycle. If it is too long or, conversely, too short, this may indicate a malfunction of the ovaries. The absence of a “dominant” is often associated with changes in the level of hormones in a woman’s body. For proper development of follicles, certain levels of several hormones are required.
Namely:
- Luteotropic.
- Follicle-stimulating.
- Estrogen.
- Progesterone.
All of them are important at certain stages of egg maturation. When these hormones are not enough in the body, or they are distributed incorrectly, the “dominant” does not develop.
To identify the reasons for the absence of a dominant follicle, it is necessary to donate blood to determine the amount of hormones.
Behavior of the follicle during disturbances in the body
There are several reasons for the absence or improper development of the “dominant”. However, there is only one outcome - ovulation does not occur. A pathological change in the body can cause the follicle to behave “wrongly”. Read more about what can happen if his behavior is abnormal.
The appearance of a persistent follicle
A lack of luteinizing hormone or progesterone can lead to the development of a persistent follicle rather than a dominant one. Its growth is observed.
However, having reached its maximum size, the “dominant” does not break at the right moment. The egg remains inside the follicle.
One of the signs of persistence - “dominant” is visible on diagnosis throughout the entire period of menstruation, and sometimes even after it.
Other characteristic features of persistence:
- no corpus luteum;
- increased levels of estrogen in the body;
- Progesterone levels, on the contrary, are reduced;
- absence of fluid behind the uterine cavity.
There is also another option for the behavior of follicles - the absence of their growth at all. This period for the ovaries is called “sleeping”.
Follicular growth regression
Another type of deviation from the norm is slow maturation and stopping of follicle growth at a certain point in development. Then they begin to “deteriorate”. Another type of abnormal behavior is when the dominant follicle develops, but does not grow to the required size for ovulation. In this case, a hormonal blood test will not show any deviations from the norm.
Follicular cyst formation
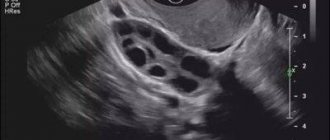
The picture shows a follicular cyst of the left ovary.
A follicular cyst occurs if the “dominant” continues to grow, does not release an egg, and accordingly, ovulation does not occur. The cause of the appearance of a benign formation is most often a change in the amount of hormones in the female body.
But there are other factors that influence the appearance of a cyst.
Here are some of them:
- Presence of chronic diseases;
- Lack of regular sex life;
- Frequent abortions or miscarriages;
- Mental disorders in women.
Surgery performed on the organs of the genitourinary system could also influence the appearance of pathological changes. The presence of a follicular cyst affects the regularity and duration of the menstrual cycle.
A cyst can form on the corpus luteum. This happens if, after the rupture of the follicle, too much fluid has formed (it is always formed, but not in large quantities) or it contains blood.
If you detect a follicular cyst, do not worry - no special treatment is required. The formation disappears on its own after several cycles, and if pregnancy occurs, after the first trimester.
Treatment in the absence of a dominant follicle
A non-growing dominant follicle is observed in patients with inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system.
Constant stress, depression, abortions - all this can also cause improper development or the absence of a “dominant” at all.
The doctor prescribes medications to restore normal ovarian function only after a comprehensive diagnosis. Often the problem is solved with the help of hormonal therapy.
Clostilbegit is a drug often prescribed by gynecologists to women who are planning to have a baby. The product is very popular in Russia, but it should be taken strictly as directed by your doctor.
Clostilbegit has many contraindications and is not suitable for all girls. However, any hormonal drug taken uncontrollably can harm the female body rather than strengthen it.
Under no circumstances should you take any hormonal medications without a prescription!
To improve the functioning of the reproductive system, they also take folic acid and multivitamins. The drugs are selected individually, as is their dosage. The doctor takes into account the patient’s age and general health.
Questions for a specialist
Practicing obstetrician-gynecologist Natalya Yuryevna answers the questions.
- I took a course of Cyclodinone to regulate my too short menstrual cycle. It has become longer, but now after menstruation I feel very unwell. Diagnostics did not show the growth of a dominant follicle. What should be done? Answer : An in-depth examination is necessary, including hormonal blood tests on certain days of the cycle. Consultation with an endocrinologist is also necessary.
- After four years of taking Regulon, I cannot get pregnant, although I stopped taking the drug more than 6 months ago. The dominant follicle does not develop, the cycle is too long. What should I do? Answer : You need to contact a gynecologist-endocrinologist and get tested for hormones. After the examination, the doctor will prescribe treatment to restore ovarian function.
- Is pregnancy possible if the follicle grows and decreases in size closer to ovulation? Answer : This is a sign of ovarian dysfunction. You and your partner need to be tested. For you - the amount of hormones in the blood (prolactin, insulin, reproductive and thyroid glands), for your partner - a spermogram. Based on the results, the doctor will prescribe treatment.
- Can taking Utrozhestan during the period from 16 to 25 days of the cycle cause the formation of a follicular cyst? A similar problem has arisen before, and without treatment the formation did not disappear. Answer : While taking the drug in phase 2 of the cycle, an ovarian cyst should not form. If cysts are present, any ovarian stimulation is prohibited. Contact your doctor to prescribe treatment. Monitoring for pathological changes is necessary.
Prescribing potent drugs in the absence of a dominant follicle is not always justified. It should be remembered that the more effective the product, the higher the risk of side effects.
Therefore, first of all, a woman with such a problem needs to find a qualified doctor who can justify the prescription of certain medications. The key to success will be an adequate determination of the cause of ovulation disorders.
Most patients noted positive dynamics after taking vitamins and folic acid.
Brief summary
Source: https://ekobesplodie.ru/besplodie/kogda-dominantnogo-follikula-net-pochemu-i-chto-delat
Regulating the process of follicle maturation
The goal of treatment is to restore the menstrual cycle and get rid of infertility. This is achieved by stimulating ovulation and regulating the process of maturation of follicles in the ovaries.
Stimulation of ovulation
It is carried out to reduce the number of anovulatory cycles and increase the likelihood of pregnancy. Contraindications are complete depletion of the ovarian reserve (the onset of early menopause), as well as obstruction of the fallopian tubes.
Drugs (for example, clomiphene) are used, which are taken according to a strictly defined regimen. In the initial phase of the cycle, the production of estradiol and follicle growth are stimulated, and then the drug is abruptly discontinued, which increases the production of LH and rupture of the follicular capsule.
In order to prevent the formation of cysts, an injection is given of the drugs pregnin or gonacor, containing the hormone hCG, which inhibits the growth of the follicle membrane.
Decreased number of antral follicles
If the content of antral follicles in the ovaries is increased, therapy is carried out to normalize hormonal levels (regulate the production of FSH, LH, estrogens, prolactin and progesterone).
Treatment is carried out using combined oral contraceptives (COCs). Depending on the nature of the deviations, drugs containing estrogens (estradiol), progesterone (Duphaston) or a mixture of them (Anzhelik, Klimonorm) are used.
Clostilbegit is also used. It regulates estrogen levels by acting on the estrogen receptors of the ovaries. Depending on the dose, the drug may also weaken or enhance the production of pituitary hormones.
Is it possible to increase the number of antral follicles?
The number of follicles depends only on the content of anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) in the body, which is produced by ovarian cells regardless of the general hormonal background. It is impossible to enhance the production of the hormone with medications or other means. It depends only on the genetic characteristics of the body and the age of the woman.
If her health and conception problems arise due to a lack of antral follicles in the ovaries (and, accordingly, eggs), then you can only increase the chances of their successful maturation by stimulating the work of the ovaries. For this purpose, drugs containing biologically active substances are used, as well as vitamins, agents that have an anti-inflammatory effect and improve blood circulation.
Video: Polycystic disease, its consequences and treatment in the “Live Healthy” program
The female body has many unique features, which include the mechanism of functioning of the reproductive system.
Even in the mother's womb, a certain number of follicles are formed in the girl's body, which is approximately five hundred thousand. By the time you reach puberty, only about forty thousand follicles remain in the ovaries, but not all of them are destined to mature and release an egg at the time of ovulation. Over the course of a woman’s entire life, about five hundred follicles fully mature, while the rest undergo a process of atresia (fade in development).
Diagnosis and treatment
To diagnose in such cases, it is necessary to undergo a complex of laboratory and hardware tests. With their help, it is possible to identify follicles suitable for development in the ovaries or the causes of deviations in these processes. Diagnostics include:
- blood tests (general and biochemical);
- tests for thyroid hormones;
- tests for sex hormones;
- gynecological examination;
- Ultrasound of the ovaries.
The normal size of follicles in the ovaries is about 6-8 mm at the beginning of the cycle. Gradually their number decreases and their size increases, and a large dominant formation can be seen.
Only a doctor can explain the situation, why there are no follicles in the ovaries, and give recommendations on how to eliminate this problem. Treatment is selected individually and is generally aimed at achieving the following goals:
- normalization of hormone levels;
- elimination of cystic formations;
- stimulation of ovulation;
- restoration of the menstrual cycle;
- elimination of diseases of the endocrine system;
- improvement of metabolic processes.
Most often, treatment is limited to the use of hormonal drugs. In severe cases, surgical intervention may be required, in particular, puncture if cysts form that threaten a woman’s ability to conceive and bear a child. When there is an accumulation of immature follicles, cauterization of the ovary is performed.
Features of the process of follicle maturation
The process of follicle maturation is very complex from a biological point of view. A whole host of factors can influence it. The beginning of this process occurs in the first phase of your menstrual cycle under the influence of special hormones. About ten follicles undergo simultaneous maturation, but subsequently only one is released, which is called dominant. It is from this that the mature egg will be released.
If your menstrual cycle is regular, you can track the process of follicle maturation yourself. Around the seventh day of the cycle, using ultrasound, you can visualize follicles, the size of which will be several millimeters. If you continue to carry out regular monitoring, you can clearly track the growth trend of follicles and identify which one is dominant.
The follicle grows by 2 mm per day and when it reaches 20 mm it bursts and the egg is released (ovulation occurs).
When fully mature, the follicle measures about twenty-one millimeters in size. This suggests that ovulation should soon occur, during which the follicle will burst, and a mature egg, ready for fertilization, will come out of it. Normally, ovulation occurs around the thirteenth to fifteenth day.
You can also try to track the process of follicle maturation using characteristic signs of ovulation:
- often the process of follicle maturation is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen;
- the volume of mucous discharge from the genital tract also increases;
- directly on the day of ovulation, the rectal temperature decreases, after which it rises again;
- The level of the hormone LH in the blood increases.
What treatment is prescribed if there is no dominant
Problems of missing dominant follicles most often affect women who have been diagnosed with inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary area. Prolonged stress and depression, abortions also lead to impaired maturation of the dominant follicle.
A gynecologist will tell you what to do to restore proper functioning of the ovaries after a comprehensive diagnosis, which we discussed above. Hormone therapy is most often prescribed.
Gynecologists often prescribe. This drug is popular in Russia, but it must be used with great caution and only under the supervision of the attending physician: the drug has many contraindications. In addition, some patients are strictly prohibited from using it.
It should be remembered that any potent hormonal drugs, if taken uncontrolled, can harm health rather than help. Therefore, self-medication in this case is unacceptable.
To maintain the reproductive system, folic acid and multivitamins are also prescribed. In this case, the selection of drugs and dosage are selected individually, depending on the age and general health of the woman.
Why don't follicles mature?
Unfortunately, today a very common problem, the cause of which is often a violation of the maturation process of the follicle. If you encounter a similar problem, it is very important to contact a specialist to accurately identify its cause. The follicle may not ripen, provoking it, under the following circumstances:
- with ovarian dysfunction;
- for various dysfunctions;
- in the presence of tumor formations in the pituitary gland or hypothalamus;
- in the presence of inflammatory and infectious diseases of the pelvic organs;
- with frequent stress, emotional instability, depression;
- with early menopause.
If you have one or more of the above disorders, the consequence may be a complete absence of follicles in the ovaries, a violation of their development, in which the follicle stops at one of the stages of its development or begins to regress. Also, the follicle may not reach the required size or simply not rupture, preventing the egg from being released.
One of the features of the female body is a unique mechanism of the reproductive system. Nature arranges it this way that while in the womb, the number of follicles in a girl’s body reaches half a million. Upon reaching sexual maturity, their number decreases significantly - to 40,000. Only 400-500 follicles reach full maturity, and the rest undergo the process of atresia.
Maturation of the follicle in the ovary
Follicle maturation is a complex biological process that is influenced by many factors. It begins in the first phase of the menstrual cycle. Under the influence of follicle-stimulating hormone, approximately 10 follicles begin to mature simultaneously, but later one is formed, from which the egg will be released. The remaining follicles stop developing and dissolve over time.
For many women, it is fundamentally important to know on what day the follicle matures, since this information can be used as a method of contraception, as well as to determine the most favorable days for conceiving a child. Follicle maturation day by day is much easier to track with a regular menstrual cycle.
If everything is in order in the body, then most often there should be no delays in the maturation of follicles. For example, on the 7th day of the menstrual cycle, follicles measuring 5-6 mm are visualized using ultrasound. With further monitoring of follicle maturation, their growth can be noted and the dominant one can be clearly determined.
After the follicle has fully matured, its size reaches 21 mm in diameter - this indicates the imminent onset of ovulation. Normally, the release of the egg occurs on days 13-15. If a woman’s menstrual cycle is irregular or there are any hormonal imbalances or diseases of the genital area, then it is impossible to give an unambiguous answer as to how many days the follicle will mature.
You can try to track the maturation of the follicle by characteristic symptoms. Objective and subjective signs of ovulation include:
- pain in the lower abdomen during follicle maturation;
- a characteristic symptom of follicle maturation is an increase in mucous membranes;
- a decrease in rectal temperature on the day of ovulation with its subsequent increase;
- increase in the amount of progesterone.
Why don't follicles mature?
Often women, having a desire to conceive a child, are faced with the problem of impaired follicle maturation. In such cases, it is important to determine the reason why the follicles do not mature and ovulation does not occur. Deviations may be due to:
- dysfunction of the ovaries and parts of the brain;
- endocrine system disorders;
- neoplasms of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus.
- inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- stressful situations and depression.
Consequently:
How many follicles should mature?
Basically, nature provides that one follicle can mature in one menstrual cycle. However, if two follicles mature, this is not considered a pathology. On the contrary, it increases the chances of conceiving, and perhaps more than one baby at once.
An ultrasound examination of infertile women is done to determine whether the egg is maturing and whether ovulation occurs. The main sign is a dominant follicle before ovulation and its absence after it.
Even in the fetal body, during the formation of organs in the ovaries, about 500 thousand follicles are formed, some of them regress and by the time women reach puberty, about 200 thousand remain. Of these, only a small proportion matures and can participate in fertilization. Therefore, data obtained from an ultrasound examination can help to find out the cause of infertility and begin treatment on time.
There is no dominant follicle in the ovaries: why it does not grow and mature
Conception occurs due to ovulation. It is provided by one leading follicle, in the depths of which the egg matures. If there is no dominant follicle for several cycles, this indicates infertility.
How the “dominant” develops, why in some cases it does not exist, read our article.
Follicle maturation: how it should be
A certain number of eggs are laid in the ovaries of each girl during the period of intrauterine development. Before puberty, they are in a “dormant” state, and with the onset of the menstrual cycle they begin to function.
The growth and death of the follicles in which the egg develops occurs monthly. In this case, follicular development goes through several stages.
At the beginning of the cycle, the growth of several follicles begins, which are of the same size.
However, around the 9th day of the cycle, a leader begins to clearly stand out among them: a follicle that is significantly larger than the others in size (it is also called the Graafian vesicle). Its diameter can reach 15 mm.
From the moment the dominant is isolated, the remaining follicles begin to regress, that is, decrease in size and gradually die.
Ovulation
Approximately on the 14th day of the cycle, the dominant reaches its maximum size (from 18 to 24 mm) and ruptures, “releasing” a mature egg. Ovulation occurs.
In place of the bursting dominant follicle, a corpus luteum begins to form. Its task is, in case of successful conception, to supply the woman’s body with the hormone progesterone necessary for pregnancy.
A dominant can develop on any ovary. Although most often it is observed on the right. There are frequent cases of the development of a dominant follicle on both ovaries.
This mainly occurs after stimulation of ovulation or during artificial insemination. In this case, the chances of conceiving twins or triplets are high.
If an ultrasound reveals that there is no dominant follicle in a woman’s ovaries, ovulation, and therefore conception, cannot occur.
Additional examinations
Anovulatory cycles, when the dominant does not develop, occur several times a year in every healthy woman. This phenomenon is not pathological. During these periods, the ovaries “rest”.
In addition, after 30 years there is a slow but steady increase in anovulatory cycles. Early menopause, which occurs before the age of 45, also guarantees frequent anovulatory cycles. Despite the fact that women at this age rarely plan pregnancy, gynecologists believe that these deviations cannot be ignored and prescribe appropriate hormonal therapy.
If such disorders are recorded in young women of childbearing age every month, this indicates pathological changes that require mandatory treatment.
Why the follicle does not grow or is not able to “release” a mature egg at the time of ovulation, only the attending physician can answer after a series of studies:
- Examination on a gynecological chair;
- Blood tests to detect levels of important hormones at different stages of the menstrual cycle;
- Folliculometry is an ultrasound diagnostic procedure during which the entire process of ovarian function during the menstrual cycle is monitored monthly.
The gynecologist also pays attention to the length of the menstrual cycle. A cycle that is too long or short is often evidence of ovulation disorders.
Most often, the absence of a dominant is associated with hormonal imbalance. The process of proper development of follicles is influenced by several hormones: luteotropic, follicle-stimulating, estrogen and progesterone. Each of these hormones is important at a certain stage of egg maturation. Their insufficient quantity or incorrect distribution leads to problems with the maturation of the dominant.
How does the follicle behave?
There are several reasons why there is no dominant follicle or its development is pathologically altered. But in any case, with these disorders, ovulation does not occur. Let's look at exactly how a “wrong” follicle can behave.
Follicular growth disorder
In this case, they mature poorly, and stopping at a certain phase of development, they begin to regress. Or the dominant develops successfully, but does not reach the required size by the ovulation phase. A blood test for hormones will be normal.
Ovarian cyst
If the dominant follicle continues to grow without releasing an egg, it will give rise to a follicular cyst. This benign formation appears if there is no ovulation. The cause of this pathological change is hormonal imbalance, which most often occurs due to dysfunction of the cerebral cortex. The appearance of a follicular cyst is also influenced by the following factors:
- Poor nutrition;
- Chronic diseases;
- Irregular intimate relationships;
- Mental disorders;
- Frequent abortions;
- Surgical intervention for diseases of the genitourinary area.
A follicular cyst can affect the regularity and duration of the menstrual cycle.
A cyst-like change may also appear at the site of formation of the corpus luteum. After a follicle bursts, liquid always remains. If its amount exceeds the norm or contains blood, a cyst appears on the corpus luteum.
In most cases, such cystic changes do not require special treatment. They disappear on their own after 2-3 cycles, and if conception occurs, by the beginning of the second trimester.
What treatment is prescribed if there is no dominant
Problems of missing dominant follicles most often affect women who have been diagnosed with inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary area. Prolonged stress and depression, abortions also lead to impaired maturation of the dominant follicle.
A gynecologist will tell you what to do to restore proper functioning of the ovaries after a comprehensive diagnosis, which we discussed above. Hormone therapy is most often prescribed.
Gynecologists often prescribe clostilbegit when planning pregnancy. This drug is popular in Russia, but it must be used with great caution and only under the supervision of the attending physician: the drug has many contraindications. In addition, some patients are strictly prohibited from using it.
It should be remembered that any potent hormonal drugs, if taken uncontrolled, can harm health rather than help. Therefore, self-medication in this case is unacceptable.
To maintain the reproductive system, folic acid and multivitamins are also prescribed. In this case, the selection of drugs and dosage are selected individually, depending on the age and general health of the woman.
At a consultation with a gynecologist
Obstetrician-gynecologist Elena Artemyeva answers patients’ questions.
- I am 24 years old. I have never been pregnant. Menstruation is scanty, cycle is 20 days. I took Cyclodinone for four months (prescribed by a doctor), my cycle became longer. But now at the end of the cycle I feel very unwell. An ultrasound scan of the ovaries did not show dominant follicles. How to cure it? Is it necessary to take hormones? I'm afraid of gaining weight due to hormonal treatment.
– You need to undergo an in-depth examination. You will have to donate blood for hormones twice: on the fifth-seventh and twentieth-twenty-third days of the cycle. Your gynecologist will tell you which specific hormones to test for. Be sure to visit an endocrinologist and undergo an examination to rule out pathologies of the thyroid gland and pituitary gland. You may need to do an MRI of the brain.
Depending on the results, treatment will be prescribed. You may need stimulation with hormonal drugs for the growth of dominant follicles and ovulation. In most cases, they do not cause sudden weight gain, don't worry.
– I took Regulon for four years, I stopped taking it six months ago. Pregnancy does not occur. The cycle is 34-36 days. The ultrasound did not show a dominant follicle or corpus luteum. Can I get pregnant?
– Normally, after oral contraceptives, ovulation is restored within 2-4 months. Your case is not the norm.
You need to contact an endocrinologist or, better yet, a gynecologist-endocrinologist and examine your hormonal profile, in particular, you need tests for insulin, prolactin, TSH, as well as “female” hormones. After the examination, you will be prescribed treatment.
Will you be able to get pregnant? Why not, if ovulation and normal cycle are restored? In most cases, hormonal imbalances can be corrected.
“I haven’t been able to get pregnant for two years.” Could it be that the follicle first grew to 8 mm (on the 7th day of the cycle), and then, on the 11th day of the cycle, became smaller - 6 mm. This is the result of my folliculometry...
– This is a sign of ovarian dysfunction. Get tested for hormones (sex, thyroid, insulin, prolactin). Depending on the results, you will be prescribed treatment. It is also important for the husband to be examined (in general, examination of a couple always begins with confirmation of the man’s fertility). Let him do a spermogram.
Source: https://MyZachatie.ru/zhenskie-zabolevaniya/dominantnogo-follikula-net.html
Why is it needed?
Every month in a woman’s body, 7–8 follicles begin to increase in size, then their development stops and only one, rarely two, continue to grow - this is the dominant follicle, the rest regress and undergo atresia. During the day its size increases by 2–3 millimeters. Before ovulation, it reaches 18–20 mm, and an egg is released from it, capable of fertilization.
If a dominant follicle is not formed, or its pathological development is observed, then the egg does not mature and cannot be fertilized. Therefore, when examining women with infertility, a gynecologist prescribes an ultrasound examination to see if there is any developmental pathology.
Stages of development
In the fetus, premordial follicles are formed in the ovaries; these are immature eggs surrounded by connective tissue. During the menstrual cycle, they become covered with a connective tissue membrane and begin to produce estrogens. They are called preantral. On days 8–9 from the beginning of the cycle, they are filled with fluid and their size is 10–15 mm; these are antral follicles. One of them continues to grow and becomes dominant or dominant. The rest undergo atresia.
When the follicle bursts and the mature egg begins to move through the tubes to the uterus, a corpus luteum forms in its place. The hormones produced in it prepare the uterine lining for pregnancy. If pregnancy does not occur, menstruation begins.
What can an ultrasound show?
The dominant follicle can normally be seen on ultrasound from days 5–8 of the cycle. Already at this time it is ahead of its fellows in size. Growth is due to the action of follicle-stimulating hormone. A decrease in it in the blood can cause a situation where it does not reach its normal size and reverse development occurs. Ovulation may not occur if the ovarian membrane is sclerotic, then it continues to develop and can turn into a cyst. After ovulation, it disappears and in its place a corpus luteum can be seen in the ovary. Sometimes overripe follicles are found, their size is 21–23 mm, that is, ovulation has not occurred.
This is interesting!
It has been noted that the dominant follicle is more often found in the right ovary. This is evidenced by the frequent detection of the corpus luteum in the right ovary and ectopic pregnancy with rupture of the tube on the right. What this is connected with is still unknown, although there is a hypothesis that on the right they are formed more often in right-handed people due to increased nervous stimulation from the nervous system.
Ultrasound helps to detect the cause of infertility. This method is called folliculometry. The patient undergoes an ultrasound examination over several days, during expected ovulation. You can detect the absence of a dominant follicle or pathology of its development.
How does the follicle behave?
There are several reasons why there is no dominant follicle or its development is pathologically altered. But in any case, with these disorders, ovulation does not occur. Let's consider exactly how the “wrong” follicle can behave.
Persistence
If a woman has a lack of LH or progesterone, it develops instead of the dominant one.
The development of the follicle reaches the size required for ovulation, but it cannot rupture, releasing the egg. Therefore, she remains in his body.
A characteristic feature of persistence is the ability of the dominant to remain on the ovary throughout the entire period of the menstrual cycle. Moreover, it is often recorded even after the end of menstruation.
Signs of the development of a persistent follicle:
- The corpus luteum is absent;
- The amount of estrogen is increased;
- The amount of progesterone is reduced;
- Lack of fluid behind the uterine cavity.
"Sleeping" ovaries
The follicles do not mature, they do not grow at all, so ovulation cannot occur.
Follicular growth disorder
In this case, they mature poorly, and stopping at a certain phase of development, they begin to regress. Or the dominant develops successfully, but does not reach the required size by the ovulation phase. A blood test for hormones will be normal.
Ovarian cyst
If the dominant follicle continues to grow without releasing an egg, it will give rise to a follicular cyst. This benign formation appears if there is no ovulation. The cause of this pathological change is hormonal imbalance, which most often occurs due to dysfunction of the cerebral cortex. The appearance of a follicular cyst is also influenced by the following factors:
- Poor nutrition;
- Chronic diseases;
- Irregular intimate relationships;
- Mental disorders;
- Frequent abortions;
- Surgical intervention for diseases of the genitourinary area.
A follicular cyst can affect the regularity and duration of the menstrual cycle.
A cyst-like change may also appear at the site of formation of the corpus luteum. After a follicle bursts, liquid always remains. If its amount exceeds the norm or contains blood, a cyst appears on the corpus luteum.
In most cases, such cystic changes do not require special treatment. They disappear on their own after 2-3 cycles, and if conception occurs, by the beginning of the second trimester.
Developmental pathologies
Egg release in women is impossible in the absence of a dominant follicle. This happens due to hormonal imbalance and various diseases:
- it is not formed when follicle-stimulating hormone decreases or luteinizing hormone increases in the blood;
- regression or atresia occurs due to hormonal disorders, including an increase in insulin in the blood;
- observed on does not occur. It does not undergo regression, is of normal size or slightly enlarged (overripe). Sometimes women have dominant and persistent follicles in different ovaries;
- A follicular cyst is formed from a dominant follicle that continues to grow. Fluid accumulates inside, the size of the cyst on ultrasound is more than 25 mm, if there are many of them, then this condition is called polycystic;
- luteinization. In place of the dominant follicle without.
Important!
If the follicle persists, its membrane may rupture and the egg will be released into the abdominal cavity. In this case, pregnancy cannot occur due to the inferiority of the egg.
All these pathologies require study and additional examination. It is necessary to check the hormonal level in a woman’s blood and find the reason for its change. These may be endocrine diseases, pathology of the pituitary gland, anomalies of ovarian development.
Reasons for violations
To eliminate deviations, it is important to find out what exactly triggered their occurrence. The reason why follicles in the ovaries do not mature may be the following factors:
- Gynecological diseases. Most often we are talking about ovarian pathologies, for example, polycystic disease. Various inflammatory processes and oncology can also have an impact.
- Hormonal fluctuations. A disruption in any hormone can have an effect. But the greatest influence is exerted by prolactin, which is involved in the process of stimulating lactation.
- Taking hormonal contraceptives. Especially if the means were chosen incorrectly, or the order of taking birth control pills was violated.
- Thyroid diseases. Such pathologies of the endocrine system negatively affect the activity of the whole organism.
A sign of disturbances can be not only an increased menstrual cycle, but also its shortening. There may be pain and discharge at different periods of the cycle.
What to do?
Ultrasound examination is carried out as a preventative measure for diseases of the reproductive system. It can assess not only the condition of the ovaries, but also the uterus. So, there is the presence of free fluid in the abdominal cavity. Depending on the ultrasound picture, the doctor decides what to do:
- during a routine examination, the detection of a dominant follicle is normal; it depends on the time of the ultrasound. If there are complaints about the inability to get pregnant, you need to repeat it in the middle of the menstrual cycle;
- when there is no dominant follicle, then it is necessary. It will help you figure out what is happening, especially since its absence also occurs during normal development after ovulation. It is also necessary to examine the level of blood hormones at different stages of the menstrual cycle, it will be different in different phases;
- if there are two or more dominant follicles, the cause may be stimulation of the ovaries by drugs, heredity (twins are often born in a family), or diseases with which differential diagnosis needs to be carried out (polycystic disease);
- if developmental pathologies are detected (luteinization, persistence), then further examination is necessary to find out the cause. Such pathologies can be observed simultaneously with the normal development of the dominant follicle. For example, a developing follicle is found in one ovary, and a persistent follicle in the other.
Stopping oral contraceptives can also lead to multiple pregnancies. This is due to sudden changes in a woman’s hormonal balance that occur after discontinuation of the drug.
This is important to know!
Oral contraceptives can affect the level of hormones in a woman’s blood. They not only prevent pregnancy, but also normalize the cyclicity of menstruation, therefore they are often prescribed in the first period of treatment for infertility associated with irregular menstruation.
If a woman has 2-3 dominant follicles visible on ultrasound, and this is often observed during ovarian stimulation, in preparation for in vitro fertilization (IVF), it can be hereditary, then under favorable conditions, both of them can be fertilized and lead to multiple pregnancies. In such cases, fraternal twins or twins are born.
If an ultrasound reveals a dominant follicle in the first phase of the cycle, this may not necessarily be a pathology, but its absence during this period may indicate the impossibility of getting pregnant. In this case, you need to do folliculometry and other additional examinations.
What could go wrong
The process of egg development does not always occur normally. A situation may occur when in a particular menstrual cycle there are no follicles in the ovaries. What does it mean? In this case, the egg does not mature, which means conception naturally becomes impossible. In addition, the menstrual cycle fails, and there is a lack of menstruation on time.
The absence of follicles can be either a temporary phenomenon or a sign of infertility. This is also one of the symptoms of the onset of menopause, when the resource of germ cells laid down in the prenatal period is depleted, or their maturation fails.
Disorders associated with the maturation of an empty follicle are also often observed. In this case, pregnancy is also impossible.
A slightly different situation is that the growing follicle in the ovary does not burst or does not open completely, that is, it becomes persistent. Such a violation also provokes cycle disorders, and the accumulated fluid in the sac can transform into a follicular cyst. Over time, when the process normalizes, the cyst resolves on its own, but with frequent failures of this kind, polycystic ovary disease develops.