Metrorrhagia in postmenopause is bloody discharge from the uterine cavity that is irregular and independent of the menstrual cycle. The reason for the appearance of such discharge may be a state of severe stress, physical or mental stress, the consequences of intoxication of the body or disruption of the endocrine system.
To make a diagnosis, an examination of the vagina, cervix, urinary tract and rectum is performed. During an external examination, pathological changes are detected or excluded, such as polyps, tumors, injuries, foreign bodies. The next step is to exclude causes associated with intrauterine and ovarian pathology. Such uterine bleeding can occur when hormonal and non-hormonal drugs are prescribed or taken incorrectly.
The laboratory takes clinical and biochemical blood tests, ultrasound of the pelvic organs, and takes blood to determine hormone levels. If the presence of tumors is suspected, a tumor marker test is performed.
Metrorrhagia, causes
Before prescribing treatment, it is necessary to accurately determine the cause of uterine bleeding. For this purpose, a number of laboratory tests are carried out to help identify the disease, the consequence of which is metrorrhagia. In some cases, this may be due to an overdose of drugs with high estrogen content.
In this case, it is recommended to stop using the drug, replacing it with another, or completely abandon such therapy. Sometimes the appearance of uterine bleeding during the postmenopausal period is caused by the occurrence of cancer of the body and cervix.
If anovulation is observed, then curettage is performed from the body of the uterus for diagnostic purposes and to achieve a therapeutic effect. Immediately after curettage, a hormone therapy complex is prescribed. If such treatment is not effective and bleeding occurs again, the doctor will prescribe surgical removal of the uterus.
Uterine bleeding during menopause can also be caused by the appearance of polyps, inflammation in the endometrium of the uterus, hormonally active neoplasms in the ovaries, hyperplasia, hyperthecosis, and tecomatosis.
Treatment
Treatment is prescribed depending on what disease caused the symptom.
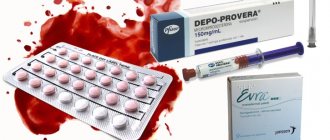
- In the presence of benign formations, hyperplasia, endometriosis, hormonal drugs are usually prescribed - combined oral contraceptives. They are used one tablet per day for a period of 3 to 6 months. Hormones help the tumor to dissolve. The cost of such drugs as Janine, Marvelon, Regulon ranges from 600 to 1500 rubles;
- Some types of cysts and polyps require surgical removal;
- Oncological processes also require specific treatment;
- Infectious and inflammatory processes require treatment depending on their characteristics. Often, antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.
Since metrorrhagia is accompanied by significant blood loss, iron supplements may be additionally prescribed to normalize hemoglobin.
B vitamins and magnesium in large quantities are also indicated. They will help relieve the unpleasant symptoms of significant blood loss.
Diagnostics
For timely diagnosis of metrorrhagia, the following is used:
- Collecting anamnesis of the patient’s lifestyle and previous diseases.
- Clinical examination on a gynecological chair.
- Blood tests for hemoglobin level, clinical, biochemistry, coagulation, hormones.
- Analysis of cervical smears and endometrial biopsy.
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
- Treatment of metrorrhagia
Treatment of metrorrhagia depends on the pathology. If glandular fibrous polyps are detected, they are removed under hysteroscopy control. If after this a relapse occurs and a suspicion of cancer arises, removal of the uterus and appendages is prescribed. But on an individual basis, it may be recommended to use a course of oxyprogesterone intramuscularly for a period of up to 4 years.
This treatment is carried out under strict control with regular collection of scrapings of the endometrium of the uterus. If it is not effective and relapses still occur, then the only solution to this problem is to remove the uterus and appendages.
If chronic inflammatory processes are detected, which are the cause of uterine bleeding, intrauterine administration of a mixture of dimexide, deoxyribonuclease, ribonuclease, chymotrypsin, lidase, hydrocortisone and isotonic sodium chloride solution is prescribed. The proportions are determined by the doctor.
Main reasons for development
Any disease does not arise on its own; there are always certain provocateurs. Metrorrhagia in postmenopause is no exception. So that the doctor can choose the right treatment tactics, the causes of the disease must be correctly identified.
- Diseases, including chronic ones, in the female genital area can be considered the leading causes of the development of this pathology. Most often, the cause of bleeding is a violation of the integrity of the endometrium, for example, the appearance of polyps, ulcers, erosions, fibroids, as well as the presence of oncological processes.
- Very often, in order to maintain hormonal levels during menopause, women take medications with estrogen. If their concentration exceeds the needs of the body of this particular woman, then unexpected bleeding of varying degrees of intensity may occur.
- In the premenopausal stage, anovulation can often be the cause of uterine blood loss. This is a dishormonal disorder, which consists in the fact that for some reason the egg matures again in the ovaries, but it cannot leave it.
- Another cause of the disease may be pathologies of other organs and systems. In particular, blood clotting disorders, problems with the thyroid gland during menopause (hypothyroidism), liver cirrhosis and others.
- One of the factors causing the disease may also be severe overwork, prolonged stress and general emotional distress. It is not without reason that they say that all diseases arise from nerves. Stress is the strongest provocateur. Disorders of the central nervous system can also intensify this problem.
- Insufficient intake of vitamins and minerals, in particular vitamin C, can also lead to adverse changes in the functioning of the reproductive system.
- Intoxication of the body can also provoke the disease.
What else to do
If staphylococcus joins the inflammatory process, an alcohol solution of chlorophyllipt is added to this mixture. This is a long-term therapy, the course of which lasts more than 1 thousand procedures. The prognosis of treatment depends on the nature of the inflammatory process. Metrorrhagia in postmenopause is treated by eliminating anovulatory dysfunction, eliminating metabolic and endocrine disorders, and using hormonal contraception.
In addition to treating the cause of uterine bleeding, the patient is prescribed complete rest, bed rest, cold is applied to the lower abdomen, preferably an elevated position of the pelvis 25-30 cm above the level of the body position. Thus, you can alleviate the condition and reduce blood loss.
Uterine bleeding during menopause can be significantly reduced by using herbal remedies that can reduce or stop bleeding, but it should be remembered that these are only auxiliary methods of control and cannot be used as the main treatment. Improvement in the condition after herbal medicine is observed after 2-3 weeks. Before use, you must carefully study the composition, contraindications and side effects.
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding in the premenopausal period
The climacteric period is the time of extinction of all reproductive functions. Menopause is a condition characterized by the absence of menstruation for a year or more after the age of 45.
The appearance of any bleeding from the genital tract (menometrorrhagia) in premenopause is a sign of obvious trouble in a woman’s body. You should not be negligent about this threatening symptom.
Metrorrhagia in premenopause: causes
- Hormonal imbalances due to dysfunction of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland;
- The presence of hormonally active ovarian tumors;
- The presence of malignant neoplasms of the uterus. This pathology can be represented by both endometrial cancer and cervical cancer, which can bleed during sexual intercourse.
- Coagulopathic conditions;
- Hyperplastic processes of the endometrium.
DUB in premenopause: diagnosis
When bleeding occurs during menopause, fractional diagnostic curettage is mandatory, both to stop bleeding and for diagnostic purposes. This allows not only to stop the bleeding, but also to examine the resulting material for oncological pathology.
If necessary, hysteroscopy and colposcopy with biopsy of areas suspicious for cancer can be performed.
An ultrasound examination of the pelvic and abdominal organs, fibrogastroscopy, and, if necessary, magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography are also performed.
Therapy of DUB in menopause
As mentioned above, the preferred management strategy for such patients is surgical hemostasis in the form of curettage of the uterine cavity and cervical canal.
When cancer pathology is detected, the woman is referred to a gynecological oncologist, who, based on the stage of the process, offers possible treatment options.
If hormonally active tumors are detected, they are removed
The main thing in the prevention of this process is constant preventive examinations for early detection of the pathological process with the aim of timely treatment of identified conditions.
And if bloody discharge appears, immediately seek medical help.
Physiology and pathology of the postmenopausal period
Postmenopause is the period of a woman’s life after the cessation of menstruation. The status of menopause can be diagnosed based on tests of estradiol levels (less than 30 pg/l) and an increase in FSH of more than 40 IU/l in the blood serum. The average age of menopause is 51 years. Due to a decrease in estrogen levels, this age period accounts for the largest number of cancers of the genital organs.
Changes in the functioning of the ovaries and adrenal glands begin even before menopause. A decrease in the level of progesterone, estrogen and estrone leads to many disorders in the body. On the one hand, this is a normal physiological process, and on the other, it can cause significant damage to a woman’s health. About 70% of women are susceptible to such diseases associated with disruption of normal ovarian activity.
Metrorrhagia during premenopause
Perimenopause is a period of decreased estrogen due to low ovarian activity. The process is typical for women aged 40-50 years, but can also affect earlier years. Perimenopause is a completely normal process in the female body; it ends after the ovaries stop producing eggs.
Metrorrhagia in premenopause indicates that polyps have formed in the uterine cavity. These benign tumors often cause miscarriage and premature birth.
Due to polyps, the fertilized egg cannot implant in the uterus. During such periods, menstrual bleeding is either absent altogether or lasts more than 7 days, and in profuse form. In premenopause, these phenomena can mean pathologies in the uterus and other inflammations in the reproductive system.
Menopause symptoms and their treatment
Elderly women are more often susceptible to urogenital disorders 2-5 years from the beginning of the postmenopausal period. Under the influence of a decrease in estrogen levels, symptoms of diseases such as atrophic vaginitis, dyspareunia, decreased lubrication function and pistourethritis, pollakiuria, and urinary incontinence occur. During this period, genital prolapse may also appear.
Due to the occurrence of estrogen deficiency, the number of cardiovascular diseases caused by atherosclerosis increases. Preventative measures such as exercise and a healthy, nutritious diet can help combat such symptoms. Diseases of this nature are treated as prescribed and under the close supervision of a doctor.
Older women face problems with unwanted facial hair. The solution may be depilation and hormone replacement therapy.
Loss of skin elasticity leads to sagging breasts, facial contours and body contours. Massage courses, sports, healthy eating, skin care products and hormonal therapy courses will come to the rescue.
Another of the most serious consequences of postmenopause is osteoporosis, which makes bones brittle and thins the skeletal structure. In addition to hormone replacement therapy, a diet high in calcium and magnesium, sunbathing and exercise are prescribed.
What it is
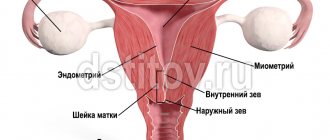
Metrorrhagia is the appearance of blood secretion that is not associated with menstruation. The pathology occurs between menstruation, is layered on them, or is a continuation. Bleeding can last a long time, be scanty, or, on the contrary, profuse. In any case, the disease cannot be ignored, since prolonged bleeding leads to anemia, weakness and other symptoms of iron deficiency.
The menstrual cycle consists of several phases that replace each other.
The first phase is follicular. During this period, the follicle matures, containing an egg inside. The production of various hormones, including estrogen, increases. When the follicular phase ends, ovulation occurs, the egg begins to move into the uterus, getting rid of the follicle.
The second phase is called the luteal phase. In place of the egg, the corpus luteum develops, which produces the pregnancy hormone. During the luteal phase, the female body actively prepares for possible fertilization within 13 days. If pregnancy does not occur, the egg dies, the corpus luteum dies, the inner uterine layer is rejected, after which secretion occurs. Together with the secretions, the corpus luteum is removed from the body.
Hormonal imbalance provokes disturbances in the follicular phase, and an increase in estrogen levels leads to problems in the endometrium, which causes bleeding. The amount of blood released depends on how damaged the endometrial functions are. This entire process is called dysfunctional uterine bleeding. Pathology most often occurs during puberty.
The causes of cycle disorders can be stressful situations, diseases of the thyroid and adrenal glands, injuries, hypovitaminosis, and poor quality of life. During reproductive age, the diagnosis is made only in 4-5% of cases. Bleeding occurs at any time in life. They indicate a failure of the hormonal system or the presence of some disease. Metrorrhagia refers to bleeding due to menstrual irregularities caused by external factors.
Discharge
Vaginal discharge during postmenopause does not change its consistency, color or smell - this is the norm. Postmenopause does not affect these indicators. The only exception is the quantity, which is significantly reduced. But if the discharge has changed after menopause, this may be the first symptom of the development of pathologies. The cause may be either an infection or a hormonal imbalance.
During menopause, urogenital disorders may develop. Depending on the rate of progression of hormonal deficiency, complaints of vaginal dryness, itching, burning sensation and extreme discomfort appear. Against the background of such symptoms, a secondary infection may occur. The discharge acquires an unpleasant, specific odor, changes color, and increases in volume.
Against the background of all the changes that characterize postmenopause, discharge is one of the first sources of information for a woman that a malfunction has occurred in the body that requires immediate treatment.
The hormonal imbalance that occurs during this period can also lead to bloody discharge, which should be the reason for an urgent visit to the gynecologist. Problems of this nature can be solved using both medical and surgical methods.
Forms of the disease
Metrorrhagia can occur in girls and women. The source of the disease is always damage to the inner layer of the uterus. The main causes of metrorrhagia are as follows:
- ulcer;
- cervical erosion;
- stress, depression;
- uterine fibroids;
- physical stress;
- mental fatigue;
- tumor in the uterine cavity and ovaries (uterine myomatous node);
- hormonal disorders;
- prolonged exposure to a negative environment (for example, increased hazards at work).
Minor pain may be present in the abdomen
To correctly determine the presence of a disease, it is necessary to focus not only on the symptoms. If you notice bloody discharge from the vagina, which should not be present at the moment, you should immediately consult a doctor. Already in the hospital additional actions will be taken:
- Determination of hemoglobin and platelet levels in the blood.
- Measuring the thickness of the endometrium and examining the size of the uterus.
Identification of NMC by type of metrorrhagia (menstrual irregularities) occurs at the stage of collecting anamnesis. In this case, the patient will have the following characteristics:
- the duration of menstruation is less than 3 or more than 7 days;
- scanty or heavy periods that do not appear in the menstrual cycle;
- sharp pain in the lower abdomen.
NMC in the reproductive period (from 20 to 35 years) is a common and normal phenomenon. However, if the deviations are caused by metrorrhagia, the disease can cause a decrease in a woman’s ability to conceive.
Anovulatory metrorrhagia is very often detected. It develops more often than ovulatory. In this situation, the release of an egg does not occur in women, and the cycle proceeds in phase 1. This condition is possible with atresia of the follicle or with difficulty in releasing the egg. Functional bleeding from the genital organs is not associated with organic diseases.
If uterine bleeding occurs during premenopause, this may indicate the presence of a polyp. Bleeding also occurs in older women. We are talking about metrorrhagia during menopause. The main causes are hormonal changes and tumors of the genital organs. The most common cause is tumors in the ovaries.
Postmenopausal pain syndromes
Most women experience pain during menopause. The nature and locations of localization may vary.
Chest pain occurs due to the replacement of glandular tissue with fibrous and fatty tissue. If diseases of the mammary glands are not detected, the cause of such pain may be severe psycho-emotional stress.
Painful sensations in the abdominal area indicate the presence of problems in the genitourinary system or intestines, the cause of which may be a decrease in estrogen levels.
Headaches are constant companions of menopause. They are a normal reaction of the body to stress and depression. Treatment will be to eliminate the causes and take analgesics.
Pain in the back, lower back, and joints should not simply be relieved with painkillers, as they are a manifestation of existing diseases, such as arthritis and arthrosis, osteoporosis. Comprehensive treatment under the supervision of specialists is necessary.
If during menopause your nipples hurt or strange discharge appears from them, this may be a symptom of serious diseases, such as: ductal papilloma, mastopathy, mastitis, galactorrhea, ductal ectasia of the mammary gland, cancer. A consultation and examination by a mammologist is simply necessary.
Chest pain during menopause is often confused with pain in the heart. Cardialgia is one of the companions of the menopause. Manifested by the appearance of chills, increased sweating, and a rush of blood to the head. These symptoms worsen at night. The appearance of such signs should be a reason to visit a cardiologist and rheumatologist.
Difficult period in a woman's life
The weakening of reproductive function gradually increases and leads to menopause, the complete cessation of the menstrual cycle. As a rule, the period of adjustment, premenopause, lasts several years. During this time, the body produces less and less estrogen.
As a result, disruptions begin in the usual onset of ovulation. The process involves not only the reproductive organs, but almost all life support systems.
The period, from the first signs to menopause, is accompanied by pronounced symptoms, taking into account which a woman is able to recognize the initial stage of menopause and try to normalize the basic processes with the help of drug therapy or common folk methods.
Characteristic signs of premenopause
Since the process progresses smoothly and takes several years, pronounced signs are not immediately noticeable. You may not notice any abnormalities without associating increased fragility and dryness of hair, decreased skin elasticity and the appearance of facial wrinkles with the approach of menopause.
In fact, it is these symptoms that become the first signs of age-related changes affecting the sexual sphere.
Over time, the process becomes more pronounced and is often accompanied by the following symptoms:
- systematic decrease or increase in blood pressure;
- blood clotting disorder;
- diseases of the heart muscle;
- atherosclerosis;
- increased sweating;
- depressed mood;
- hot flashes;
- insomnia;
- emotional swings;
- urinary incontinence of varying degrees of intensity;
- sagging and tenderness of the mammary glands;
- infectious processes in the vagina associated with changes in microflora;
- increased fragility of bone tissue;
- obesity.
However, the main sign that women pay attention to is the duration of menstruation in premenopause and the irregularity of their arrival. By the way, a violation of the cyclicity of the menstrual cycle does not mean the absence of the possibility of conception. However, at this time it is quite difficult to bear a fully developed child. Therefore, it is recommended to use contraception to avoid unwanted pregnancy.
It is also worth not ignoring the symptoms and starting treatment for premenopause without waiting for disruptions in the body to lead to significant complications and the development of serious pathologies.
Herbal medicine for postmenopause
Herbal medicine for the treatment of postmenopausal symptoms has a very effective effect on the general condition of the patient. However, it cannot be a substitute for hormonal therapy prescribed by the attending physician.
In nature, there are plants that are organic substitutes for estrogen. These include:
- St. John's wort. Used to treat climatic neuroses, reduces the frequency and severity of hot flashes.
- Ginseng. Reduces fatigue and reduces stress levels.
- Licorice. Causes estrogenic activity in the body, improves the condition of bone tissue.
- Angelica Sinensis. Improves sleep quality, relieves anxiety and irritability
- Sage. Significantly reduces sweating and is also used for insomnia, nervous exhaustion, and rapid heartbeat. Jujube and astragalus have the same properties.
Characteristic symptoms of metrorrhagia during menopause
The main thing that should make you think is the appearance of abnormal bleeding. If we are talking about the premenopausal period, then any bleeding between menstruation, especially heavy and prolonged, should be alarming. Traces of blood after sexual intercourse are also not normal.
Important! If menopause has already stabilized, then any bleeding is dangerous and requires urgent treatment at the clinic. Any delay can lead to irreversible consequences and the development of dangerous conditions.
Concomitant signs of abnormal bleeding caused by internal changes and blood loss may include the following manifestations:
- weakness and increased fatigue;
- pale skin;
- emotional instability, irritability, tearfulness;
- sudden spontaneous weight loss;
- painful sensations localized in the lower abdomen;
- pain during intercourse.
Lifestyle during postmenopause
The well-known “three pillars” of a healthy life will help to significantly alleviate the symptoms of postmenopause.
- Change your diet to be healthier. It is absolutely necessary to switch to proper nutrition, taking into account the age-related needs of the body for vitamins and microelements.
- Playing sports and physical activity does not harm anyone, and during the postmenopausal period it will also help reduce the risk of joint diseases and also give you energy.
- Stressful and depressive conditions can be overcome by proper, healthy sleep and consultations with a psychologist.
- You definitely need to give up bad habits such as smoking and overeating. Excess weight leads to a decrease in the production of estrogen, which is already insufficient at this time. Therefore, getting rid of these habits will help the body feel better.
Uterine bleeding during menopause
Metrorrhagia during menopause occurs due to hormonal imbalance or the presence of cancer in the body. The provoking factor can be various tumors or formations in the pelvic area.
Bleeding during menopause is accompanied by sharp, sharp pains in the lower abdomen. The presence of such a sign indicates serious disorders in the body, so the woman should immediately consult a doctor.
During this same period, women often experience a whole bunch of different diseases. Ovarian tumors are not uncommon in women over 50 years of age. If an ovarian cyst is detected during menopause, the doctor prescribes surgery. This is the only way to eliminate the tumor.
Any cyst during menopause is removed surgically. This is necessary to prevent the risk of developing cancer.
Signs
Metrorrhagia, the symptoms of which can appear suddenly, is always accompanied by a cycle disorder. In addition to the main symptoms, manifestations of the disease that caused the bleeding are often noticeable. If blood is released profusely, the patient feels nausea, severe fatigue, dizziness and general weakness. In some cases, there is a rapid heartbeat and a decrease in blood pressure (blood pressure).
The main symptom of the pathology is a change in the rhythm of menstruation.
In addition, severe pain and increased body temperature may occur when blood loss is caused by an ectopic pregnancy or the development of a submucosal node. Since metrorrhagia is directly related to menstruation, they can be delayed, start early, take too long, or end quickly.
Other signs of metrorrhagia:
- palpitations, tachycardia;
- pale skin;
- weakness and drowsiness;
- dizziness;
- intense bleeding with clots;
- delay of menstruation by 1.5-3 months.
With tumors in the uterus, cervical or tubal pregnancy, abnormal bleeding is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen and hyperthermia. Menstrual irregularities such as metrorrhagia have individual symptoms, that is, each patient characterizes her sensations differently.
The main signs of pathology are:
- the period between menstruation is 2-3 months;
- bleeding is heavy and prolonged;
- severe pain appears at the very beginning of bleeding and discomfort during the remaining periods.
If a woman notices at least one symptom, she urgently needs to see a gynecologist.
Prevention and recovery
After successfully getting rid of metrorrhagia, the female body needs to be supported with restorative medications, good nutrition and timely rest. Thanks to this, biochemical blood parameters and overall health are restored. For some patients, it is useful to take vitamins and minerals, including iron, rutin, ascorbic acid and calcium.
To prevent relapse, it is advisable to undergo examinations 1-2 times a year. If gynecological pathologies are detected, it is imperative to undergo appropriate treatment. It is important to give up all bad habits and monitor your psycho-emotional state. Often, oral contraceptives are taken for prevention. Reception regimen:
- first 3 cycles – 5-25 days;
- 3 more cycles – 16-25 days;
- for 5-6 months, 16-25 days take gestagenic drugs.
Oral contraceptives will help avoid hormonal imbalances, as well as unwanted pregnancy, breast cancer, infertility and other diseases. During the recovery period, you should not overload yourself with too much hard work and be under constant stress.
It is advisable to exclude all negative factors, then recovery will come much earlier. Bleeding cannot be ignored, because it may indicate the development of a serious disease that will not be easy to cure.