Most women after 40 years begin to feel bad, their mood changes sharply, and sometimes they want to cry at the slightest reason. This may be accompanied by some changes in the body, fever and slight malaise are felt. Hormonal imbalance in women is to blame for everything. This is a normal phenomenon, but it does not make it pleasant. What to do about the problem and how to regain good health?
Causes and characteristics of hormonal imbalance in women
Hormonal imbalance is a pathological process of an endocrine nature caused by an imbalance in the amount of sex hormones. A woman's body contains:
- Estrogen is produced in the ovaries and is responsible for the reproductive system and the development of eggs. Excess of the hormone provokes the accumulation of fat in the lower abdomen and thighs, the appearance of tumors of various types. Deficiency causes premature aging, problems with nails, hair, and increased hairiness of the skin.
- Progesterone is a hormone that appears after the release of an egg and helps to conceive and carry a child to term. A decrease in its level in the blood causes premature birth, miscarriage, difficulty conceiving, and pathological growth of endometrioid tissue.
- Luteinizing hormone - stimulates the synthesis of estrogen, the formation of the corpus luteum, and is responsible for the menstrual cycle.
- FSH – regulates follicle formation.
- Prolactin is responsible for the growth of mammary glands and breastfeeding.
- Testosterone – stabilizes sexual desire. It makes a woman want to win the man she likes. Lack of the hormone leads to decreased libido. Excess promotes male-type weight gain and strong hair growth on the chest and limbs.
- Oxytocin – causes feelings of love and tenderness. It is actively produced in stressful situations, forcing a woman to care about preserving the life and health of children and loved ones after childbirth.
- Thyroxine regulates metabolism and is responsible for body structure and mental abilities. A deficiency leads to obesity, absent-mindedness, poor concentration, and forgetfulness. Increased content is manifested by severe thinness and irritability.
Normally, a woman’s blood contains equal amounts of hormones. A decrease or increase in one (several of them) can lead to hormonal imbalance, reproductive problems, manifested by menstrual irregularities, disappearance of the previous body figure, metabolic failure, and severe psychological disorders.
Lack of estrogen and progesterone can provoke the occurrence of hormone-dependent neoplasms.
In the process of life, women experience hormonal surges that do not require treatment. In this case, drug correction of the problem is carried out to relieve the severity of symptoms and more quickly restore the body.
Normally, hormonal imbalance occurs in:
- puberty;
- the very beginning of sexual activity (after losing virginity);
- the course of pregnancy;
- postpartum period;
- process of menopause.
Causes of pituitary dysfunction requiring therapeutic treatment:
- malfunction of the brain and central nervous system that occurs as a result of injuries, vasoconstriction, and insufficient blood supply;
- chronic endocrinological pathologies, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- inflammatory process of an infectious nature, benign and malignant neoplasms of the reproductive system (especially the ovaries);
- congenital pathological defects of internal organs;
- genetic predisposition;
- abortion, miscarriage;
- frequent respiratory infections;
- surgical operations of the female reproductive system;
- spontaneous refusal to feed a newborn with breast milk;
- instability in sexual life (long periods of abstinence);
- cauterization of uterine cervix erosion with a coagulator;
- excessive sunbathing on the beach or in the solarium.
Factors that provoke hormonal imbalance:
- pathological weight gain;
- fasting (strict diets) for rapid weight loss;
- strong physical activity;
- constant stress, emotional tension;
- taking oral contraceptives, hormone replacement therapy;
- bad habits: alcoholism, smoking, drug addiction.
Sex hormones and their role in psychology
Sex hormones are key to changing adolescent behavior. Their active production affects not only the body, but also emotions.
- Estrogens (female hormones) make the character softer; in particular, they are able to reduce the production of thyroxine, a hormone whose elevated level leads to nervousness and irritability. However, an essential feature of the functioning of a woman’s hormonal system is cyclicality with declines and sharp increases in estrogen production. And it is precisely in adolescence, when the menstrual cycle is not yet stable, that they can provoke the greatest mood swings.
- Androgens (male hormones), on the contrary, can contribute to aggressive behavior, and not least of all, leadership qualities and the desire to win depend on them. The most active of all androgens, testosterone, is responsible for libido (sex drive). And its increase at the age of 12-13 also affects the behavior of a teenager.
Puberty in girls begins earlier than in boys by about a year or two, at the age of 11-12 years. During this period, the difference in the emotional sphere of adolescents is clearly visible: while boys still have childish behavior patterns, interests and hobbies, girls begin to be interested in more adult topics. Activation of sex hormones in boys begins at 12-14 years of age.
Negative consequences
Hormonal imbalance is characterized by dysfunction of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and adrenal glands.
Lack of stabilization of the amount of estrogen with progesterone provokes the occurrence of:
- Leiomyomas of the uterus.
- Formations with liquid content (cysts) on the ovaries.
- Hormone-dependent benign (or malignant) tumors of the genital organs. Pathology develops with a sharp increase in the amount of estrogen.
- Mastopathy.
- Fibroadenomas of the mammary glands.
- Breast cancer.
- Abnormal sexual development in teenage girls. It is characterized by the appearance of underdeveloped genitals, changes in the shape or asymmetrical growth of the breasts, and the absence of secondary sexual characteristics.
- Failure to carry a pregnancy to term. Depends on the absence of the hormone prolactin. High levels of estrogen prevent the fertilized egg from implanting in the reproductive organ, causing spontaneous miscarriage.
- Early menopause.
- Infertility caused by a decrease in the amount of estrogen. In the absence of the hormone, the eggs cannot fully develop and leave the ovary.
- Diabetes mellitus. Pathology occurs when the thyroid gland malfunctions and insulin production stops.
- Obesity. The appearance of excess weight occurs spontaneously and cannot be reduced through dietary adjustments and exercise.
- Sclerosis of cerebral vessels.
- Bronchial asthma.
- Cardiac pathologies.
- Heart attack, stroke.
- Sexual disorders, accompanied by decreased desire, dry genitals, microtrauma during sexual intercourse.
- Osteoporosis caused by calcium leaching from the body.
What are the dangers of hormonal imbalance?
A decrease or increase in the production of sex hormones causes changes in well-being and disrupts the menstrual cycle. It affects a woman's appearance. Hormonal imbalance can cause a number of serious complications. Among them:
- infertility.
- osteoporosis.
- obesity.
- various gynecological diseases.
- type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- endometriosis.
- uterine fibroids.
- early menopause
- atherosclerosis with subsequent occurrence of stroke or heart attack.
- hormone-dependent malignant tumors.
Symptoms in teenage girls
Symptoms of hormonal imbalance in girls over 15 years of age are manifested by the absence of external sexual characteristics and menstruation.
Before this age, the norm is:
- irregular first menstrual cycles;
- early or late onset of monthly bleeding (depending on DNA predisposition);
- different duration of critical days.
Hormonal imbalance most often occurs in teenage girls:
- having small stature;
- those suffering from excessive thinness;
- those who are fond of starvation diets (patients with anorexia);
- subject to severe physiological and emotional overload;
- taking hormonal medications (including spontaneous use of contraceptives);
- those who started sexual activity early;
- having a DNA predisposition to hormonal problems;
- patients with endocrinological pathologies;
- with congenital problems of the reproductive system.
In addition to the absence of menstrual bleeding, disruption of the activity of progesterone and estrogen receptors is indicated by:
- blockage of the sebaceous glands, manifested by the appearance of acne, acne;
- obesity;
- the appearance of stretch marks caused by sudden weight gain;
- constant sweating, accompanied by an unpleasant odor;
- causeless irritability;
- growth arrest (deviation from the norm to a greater or lesser extent);
- disproportionate development (complete absence) of the mammary glands.
How to understand that problems with hormones have begun?
Symptoms may vary, depending on two factors: age and the cause of the imbalance. Most often, women note the following signs:
- hirsutism (excessive hair growth on the face (mustache and beard), body, arms and legs);
- hair loss;
- decreased libido;
- cycle disruption;
- mood swings;
- excessive irritability;
- aggression and pronounced anger;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- constant rashes and acne;
- headaches during menstruation;
- nail plates become brittle;
- increased premenstrual syndrome;
- sleep disturbance and constant headaches.
A woman may associate these signs with constant fatigue or workload, both at work and while housekeeping or raising children. Do not forget that this can cause the development of severe pathologies. Therefore, it is recommended to immediately make an appointment with a doctor.
Signs in women after 30 years
The causes of hormonal imbalance in women over 30 years of age are based on dysfunction of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus caused by:
- pregnancy;
- childbirth;
- production of prolactin, responsible for breastfeeding;
- taking birth control pills;
- passion for diets;
- sports activities;
- nervous overload;
- chronic fatigue, constant lack of sleep.
Manifestations of hormone imbalance are characterized by:
- absence (irregularity) of menstruation;
- increase in body weight, characteristic of men (accumulation of adipose tissue occurs in the chest, abdomen, and face);
- increased PMS symptoms;
- constant irritability;
- reluctance to engage in sexual contacts;
- constant feeling of fatigue;
- skin problems (acne, gray complexion, early wrinkles);
- violation of the condition of the hairline;
- the appearance of stretch marks;
- tachycardia;
- severe migraines;
- osteoporosis;
- the appearance of stretch marks on the chest, abdomen, thighs;
- frequent surges in blood pressure.
At this age, hormonal imbalance can be caused by pregnancy, accompanied by:
- depression;
- constant headache;
- the appearance of tumors on the genital organs.
These symptoms arise due to the lack of rapid restructuring of the body. After an abortion, the pituitary gland continues to sense pregnancy for several days. Removing the fetus leads to a failure of processes aimed at preserving the embryo.
Expecting a child, childbirth, and breastfeeding also provoke a sharp surge in hormones. In the period after the birth of a baby, a young mother may feel a depressive state provoked by a violation of the production of oxytocin. Apathy goes away on its own after completion of the lactation process and restoration of the menstrual cycle.
Hormone activity in adolescents
Puberty - the period of puberty, when sex hormones are activated in the body and under their influence the entire endocrine system is reconstructed - begins at approximately 11-12 years. At this age, there is a sharp jump in hormone levels. The synthesis of some gradually decreases and returns to the normal level of an adult. Such, for example, are thyroid hormones, in particular thyroxine, which, from 11 years to 60, is produced at the same level - 60-155 nmol/l. For comparison: the normal level of the hormone in a newborn is 100-250 nmol/l.
However, most hormones are activated. The hypothalamus begins to actively synthesize gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), which stimulates the production of luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones. Namely, they are responsible for the amount of sex hormones produced.
After 40 years
The causes of hormonal imbalance in women over 40 years of age are characterized by a decrease in the body's production of progesterone.
Symptoms suggesting hormonal imbalance:
- changes in the duration and nature of the menstrual cycle;
- complete absence, severe delay of monthly bleeding;
- sudden weight gain that cannot be normalized with diets or exercise;
- constant insomnia, frequent periods of wakefulness during the night, contributing to chronic fatigue;
- decreased sexual desire;
- fragility and hair loss;
- the appearance of black fuzz on the face;
- increased hairiness of the limbs, chest, pubic area;
- reduction or deformation of the mammary glands, spontaneous displacement of the nipple;
- memory impairment.
At menopausal age
The causes of hormonal imbalance in women during menopause are associated with the completion of the body's reproductive abilities. By the age of 50, the pituitary gland and hypothalamus stop producing estrogen and progesterone, and endometriotic tissue becomes thinner.
Hormonal imbalance during menopause is a normal physiological phenomenon, manifested by:
- hot flashes to the upper parts of the body (most often to the face) caused by the cessation of estrogen production;
- long-term absence of monthly bleeding;
- sudden changes in blood pressure;
- increased anxiety, restlessness, provoked by a large amount of thyroxine in the blood;
- fragility of bone tissue, which appears due to the leaching of calcium from the body;
Menopause is the reason why hormonal changes occur in the body and therefore disruptions occur
- decreased concentration, predominance of long-term memory over short-term memory;
- deterioration of the central nervous system, unscheduled outbursts of anger and irritation.
- a sharp increase in body weight of 20 kg or more;
- the appearance of genital warts on the face and body.
Timely use of hormonal therapy will minimize the unpleasant symptoms of menopause.
Is it dangerous to delay menstruation?
For personal convenience and comfort (competitions, trips, sea holidays), women use the method of shifting menstruation with the help of hormonal contraceptives. This is often done independently, without consulting a gynecologist.
If such interference in the natural cycle is repeated repeatedly, then the rhythm of hormone secretion may change in the pituitary-hypothalamic region. First of all, this applies to follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones, as well as prolactin. Against this background, ovarian dysfunction and infertility may occur, requiring further long-term treatment.
And here is more information about obesity due to hormonal imbalance.
The menstrual cycle is characterized by changes in the formation of pituitary hormones, estrogens and progesterone. In healthy women, such fluctuations cause a stable rhythm of menstruation. If scanty or heavy menstruation appears, a delay of 7 days, or absence, a full gynecological examination is required. Inducing menstruation or artificial delay on your own is extremely dangerous.
Therapeutic treatment
Hormonal imbalance in women is corrected depending on the cause of the pathology.
To diagnose the disease, the following is carried out:
- Gynecological examination on a chair and questioning of the patient regarding complaints and the nature of the symptoms that have arisen.
- Consultation with an endocrinologist, during which the presence of thyroid pathologies is determined.
- Ultrasound diagnostics of the pelvic organs and thyroid gland.
- Laparoscopy to study the patency of the tubes and the condition of the ovaries.
- Hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive method that allows you to examine the uterine cavity using a hysteroscope.
- Blood test for the amount of hormones.
After receiving the research results, treatment is prescribed. In case of hormonal imbalance, complex drug therapy is used, aimed at stabilizing the amount of hormones, eliminating the excess or deficiency of one of them, and normalizing the menstrual cycle. If a hormone-dependent tumor or fibroma is detected, surgical intervention is performed.
Complex therapeutic treatment includes:
| Characteristics of drugs | Name | Pharmacology | Dosage |
| Oral contraceptives. Used to stabilize the menstrual cycle, normalize hormonal levels |
| Low-dose, monophasic, oral combined estrogen-antiandrogen contraceptives | 1 tab. daily for 21 days. This is followed by a 7-day period for withdrawal bleeding to occur. At least 6 months |
| Drugs that compensate for the lack of estrogen |
| Contains estradiol. Promote the development of the uterus, ovaries, and secondary sexual characteristics. Relieves negative symptoms caused by hormone deficiency | 1 drop according to the regimen depending on the doctor’s recommendation |
| Medicines that relieve increased estrogen production |
| Antiestrogens. Block the estrogen receptor. They enhance the production of LH and prolactin, and stabilize ovulation. Prevents the development of estrogen-dependent tumors | 50-150 mg from the 5th day from the beginning of the menstrual period. Treatment time is strictly individual |
| Tablets that activate progesterone production |
| Analogues of natural progesterone. Suppress endometrial hyperplasia, cause the 2nd phase of the menstrual cycle, make it possible to conceive and preserve the fetus by reducing the contractile activity of the uterus | 1 drop. 2 days a day, starting from the 14th day of the last menstrual cycle |
| Drugs that reduce excess testosterone |
| Block receptors that produce testosterone. Prevents increased growth of body hair, improves the condition of the skin and bone tissue, and prevents the development of osteoporosis | 1-2 drops per day (2-3 times) |
| Homeopathy prescribed to stabilize the menstrual cycle |
| They normalize hormonal imbalance, relieve hyperprolactinism and active estrogen production. Prevents the development of hormone-dependent tumors in the reproductive system and mammary glands | 1 tab. (20 drops) 1 time per day. At least 3 months |
| During menopause | Klimadinon (dry extract of black cohosh rhizomes) | Has an estrogen-like effect. Relieves symptoms of hormonal imbalance during menopause | 1 tab. (2-3 times a day). No more than 90 days |
| Vitamin complexes containing tocopherol, retinol, calcium, minerals |
| Activate the immune system, normalize hormonal levels, improve the condition of hair, skin, bone tissue | 1 drop. once a day |
| Antidepressants |
| The drugs have antidepressant and anxiolytic qualities. Block the activity of serotonin in the central nervous system. Have a sedative effect | 1 tab. 3 days a day |
Folk remedies for restoring hormonal imbalance
The causes of hormonal imbalance in women of any age can be easily eliminated with the help of herbal medicine, including:
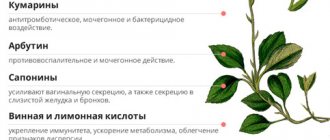
- flaxseed is a phytoestrogen that relieves symptoms of hormonal imbalance during menopause;
- sage – increases estrogen levels;
- Potentilla anseri – increasing the activity of progesterone receptors;
- oregano – normalizing the monthly cycle;
- fenugreek - stimulates the appearance of prolactin, promoting rapid rehabilitation of the body after natural childbirth;
- mint – regulating hormonal balance, relieving severe symptoms.
Recipes:
- 2 tbsp. l. flaxseeds are poured into 250 ml of hot water. Leave for 15 minutes. Take 20 ml per day (2 times)
- Goose cinquefoil, oregano (taken 20 g each) are brewed in 500 ml of boiling water. Strain, infuse, and administer 20 ml before each meal.
- 30 g of fenugreek is mixed with warm liquid. The mixture is placed on the fire and heated to a boil (15 minutes). The finished suspension is removed from the stove, cooled, filtered, and consumed 1 tbsp. l. 2 per day.
- Mint (30 g) is crushed and added to hot tea taken before going to bed.
Monotherapy for hormonal imbalance with medicinal herbs:
- From 1-5 days from the beginning of the menstrual period. 20 g of wormwood is mixed with warm liquid. Infuse for 30-40 minutes, drink 1 tbsp. l. before meals.
- From 7-14 days. 30 g of sage must be steamed with 300 ml of water heated to 90⁰C, left for 15 minutes, filtered. On an empty stomach you need to take 1⁄4 cup at least 3 times a day.
- In the 2nd phase of the cycle before bleeding occurs. 50 g of a mixture of ortilia unilateral and radiola quadruple are poured into 400 ml of boiled liquid. Strain, drink 20 ml 2 times a day.
If you have problems with hormone levels, you need to increase your daily iodine intake. Your diet should include fresh cucumbers and seaweed. Before meals, you can drink a tincture made from 2 drops. iodine and 1 drop. apple cider vinegar. 3 days a week (at night) you should do an iodine grid on the buttocks.
Changes in hormone levels during, before and after menstruation
A normal menstrual cycle corresponds to the following characteristics:
- menstruation begins at 11-14 years of age;
- over the course of a year or 1.5 years, a stable cyclicity is established;
- from the first day of the previous one to the beginning of the next menstruation, it takes from 21 to 33 days (on average 28);
- stop at 45-50 years of age.
Although each organism is individual, and sexual function is influenced by both external and internal factors, when deviations from these standards occur, diseases are detected more often.
The first phase includes menstruation itself and the period of maturation of the follicle in which the egg is located. This period depends on the content of estrogen and follicle-stimulating hormone, which regulates their production. The inner layer of the uterus (endometrium) is first shed, bleeding occurs (in the absence of pregnancy), and then the uterine cavity is restored by cell growth (proliferation).
Once the follicle is fully mature, it ruptures and the egg travels through the fallopian tubes into the uterus. This process is called ovulation. It is accompanied by a surge of hormones - estradiol and luteinizing hormone. Immediately after this peak, the second phase begins - the luteal phase. It is characterized by increasing formation of progesterone.
The endometrium moves from growth to secretion (release) of substances that will help attach the fertilized egg during conception. If it does not happen, then another menstruation occurs.
And here is more information about vitamins for a woman’s hormonal levels.
Impact of diet and lifestyle
During the treatment of hormonal imbalance, a balanced diet, sufficient physical activity, and normalization of mental health are important.
Your daily menu should include foods rich in phytoestrogens:
- roots;
- fruits;
- berries;
- mushrooms;
- legumes;
- onion;
- eggs.
It is obligatory to consume food enriched with zinc and selenium:
- lean meats (especially veal);
- unsalted lard;
- cereals;
- dairy products;
- leafy root vegetables (spinach, dill, green salad, white cabbage, celery);
- nuts (hazelnuts, almonds);
- pumpkin seeds;
- garlic.
Should be limited:
- chocolate candies;
- honey;
- granulated sugar;
- marshmallow;
- marmalade;
- cakes;
- cakes;
- ice cream;
- pies and buns;
- potato;
- condensed milk;
- fatty meat products;
- fast food;
- lemonade;
- canned food;
- sausages;
- smoked meats
In case of severe weight gain due to a malfunction of the pituitary gland, special dietary nutrition is used, aimed at increasing the synthesis of hormones that help effectively burn subcutaneous fat.
Diet features:
- one-time consumption of no more than 300-350 g of food;
- you need to eat up to 5 times a day with a break of up to 3 hours;
- dinner should be no later than 3.5 hours from the planned time of falling asleep.
- the amount of liquid you drink daily is 2 liters or more.
The diet is divided into 3 stages:
1. 1st is used for quick and emergency weight loss. Lasts no more than 14 days. During the process, you are only allowed to eat foods with a “0” rating.
2. The 2nd is aimed at stabilizing body weight (you should stick to it for as long as possible).
5 meals a day are used according to the following scheme:
- breakfast – “4”;
- 2nd breakfast "2";
- lunch – “2”;
- afternoon snack – “1”;
- dinner – “0”.
3. The 3rd stage aims to maintain the achieved figure. After establishing normal weight indicators, you should move to the final stage, adding 1 point to any one meal. Gain should be continued until the weight loss is completed.
Table of foods according to energy points:
| «0» | «1» | «2» | «3» | «4» |
|
|
|
| Any products |
Approximate power calculation:
Indicator “4” means that you can choose:
- 1 product with index “4” and any amount of “0” food;
- 2 products with a score of “2” or “1” + “3” and food with a score of “0”.
In addition to proper nutrition, you need:
- Play sports, giving preference to cardio equipment, running, dancing, swimming (exercise should be done at least 3 times a week).
- Take walks daily.
- Try to avoid conflict situations. If necessary, seek psychological help.
- Mark the days of the beginning and end of menstruation.
- Visit a gynecologist at least once a year.
- Monitor your well-being.
- Give up alcohol and cigarettes.
- Develop a sleep and wakefulness routine. Leave to rest overnight for at least 8 hours.
The occurrence of hormonal imbalance in women of different ages is associated with dysfunction of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and adrenal glands. Properly selected hormonal therapy, normalization of nutrition, and rest regimen will help eliminate unpleasant symptoms and return to a normal lifestyle.
Article design: Mila Friedan