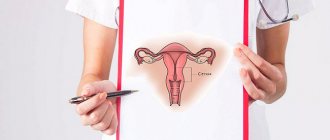
What is the cervix and where is it located?
The cervix is a kind of passage between the vagina and the uterus itself. It is quite thin and long, its location is responsible for the ejection of unnecessary cells of the uterine lining. Once in the vagina, these cells form such a complex and often painful process as menstruation.
What is this?
The cervix is the organ connecting the uterus and vagina. It has a trapezoidal shape. Among women planning a pregnancy, an abbreviation term has appeared - CMM. It is convenient to use when filling out the basal temperature chart.
The size of the neck varies for each individual woman. They depend on age, pregnancy experience and physiological characteristics. The position of the organ, as well as the structure, changes depending on the period of the menstrual cycle. It can be hard or soft.
, the external os is located on the cervix . Through this opening, secretions from the uterus enter the vagina. The pharynx takes on different states, depending on cyclical processes . It can be closed, semi-closed and open.
Determination of the position of the cervix is regularly carried out by touch with mandatory compliance with the conditions. The woman enters all the data in a separate notebook. The information helps to recognize ovulation or pregnancy. The most revealing studies will be in combination with measuring basal temperature and using ovulation tests.
Changes in the cervix during ovulation
Throughout the entire cycle, the cervix, its position and color may change. It can become dry, soften or narrow, practically blocking access inside. During ovulation, the cervix dilates. Viscous liquid from the opened cervical canal begins to move along it. This liquid resembles the consistency of egg white. During ovulation, the cervix becomes loose and very soft, like a sponge. During ovulation, the likelihood of pregnancy increases sharply, since the cervical canal is open. This contributes to:
- acceleration of sperm movement;
- maintaining their activity.
Position
The normal position of the uterus in a healthy woman is the center of the pelvis. The CMM analysis method is used when planning pregnancy. It helps to most reliably determine the fertile period.
This increases the chances of conception. At each stage of the menstrual cycle, the organ takes on a special position. Under the influence of hormones, it changes its structure.
A gynecologist can easily determine the position of the cervix most accurately. But some women are able to do this on their own. The main thing is to comply with the basic requirements and adhere to regularity. The rules for conducting the study include:
- The analysis should be carried out in the same position. The best position is lying on your back with your knees bent or squatting.
Before ovulation
At the beginning of the menstrual cycle of the study, the position of the cervix will be low. Its surface is dry and hard to the touch. The external os is tightly closed.
During ovulation
During days of increased fertility, significant changes occur in a woman’s body. The characteristic features of this period include:
Signs of ovulation appear under the influence of estrogen. The body begins to prepare for possible conception. This also affects the position of the ball. It gradually rises into the vagina. On the day the egg is released, it occupies its maximum point. Getting it becomes problematic.
The uterus becomes soft to the touch during ovulation. The external os is wide open. This is necessary so that sperm can easily penetrate the fallopian tubes. Their movement is helped by mucous secretions, which become more numerous than on other days of the cycle. They have a consistency similar to egg white .
After ovulation
After ovulation, the pharynx closes. This protects against infection. A woman's fertility gradually decreases. The cervix takes a mid-position, it is hard and dry. The further state of the organ depends on the presence of conception. If pregnancy has not occurred, the cervix descends into the vagina and later opens slightly, preparing for the release of menstrual flow.
Cervix before and after ovulation
Unlike the ovulation period, which lasts from 2 to 5 days, the cervix behaves differently during the period before and after ovulation. Here are the changes taking place:
- After the first days of menstruation (4-5 days of the cycle), the cervix narrows, becomes elastic and hard. On its walls there is either no cervical fluid or a very small amount of cervical fluid. The movement of sperm is slow, this period is not suitable for fertilization. In addition, the cervix is closed after menstruation to prevent germs and infection.
- Before ovulation (7-13 days), the cervix begins to gradually open and rise, shortening. The cervical canal expands slightly, at the same time the follicle matures, which will soon enter the uterus in the form of an egg ready for fertilization. Before ovulation, the walls of the cervix are moistened and mucus is secreted. The female body prepares the conditions for conception.
- A short period favorable for conception lasts only 24-48 hours, after which the mature egg dies. Rejection of the empty membrane is accompanied by bleeding during menstruation.
- After ovulation, a woman may feel her period approaching. On days 15-17 of the cycle and before the onset of a new menstruation, the cervix begins to descend. It loses its elasticity and moisture and becomes harder. The cervical canal elongates and closes. The discharge from it decreases in volume every day and becomes thicker and more viscous. In this way, nature makes sure that the woman’s body is protected from infections and the entry of new sperm into the female organs, because there may already be an embryo in her. Therefore, after ovulation, the chance of getting pregnant is one of the smallest.
- Days before menstruation. Around day 25-26 of the cycle, the cervix drops completely, leaving a low passage for the membrane of the follicle of the mature egg. The cervix softens. The probability of getting pregnant at this time is close to zero. This is possible only in exceptional cases, when there are endocrine disorders or hormonal imbalance can be explained by a previous illness, medications taken, which affected the body as a whole.
About ovulation in simple words
Ovulation is the release of a developed, mature egg from a follicle in the ovary. Its release occurs halfway through the cycle, 14 days from the beginning of the previous menstruation (with a cycle of 28 calendar days).
Know! Innovative gynecology uses supersonic examination to determine ovulation.
How and when does ovulation occur?
From the birth of female babies, approximately 1 million eggs are present in their ovaries, located in the follicles. By the time of sexual maturation, not all eggs survive; the surviving, properly formed ones are ready to carry out the most important mission - the conception of a new healthy organism. From the time of the 1st menstruation, one egg matures and leaves the ovaries every month.
The menstrual cycle is accompanied by the maturation of twenty eggs in the follicle. Only one mature egg is released. After passing through the fallopian tubes and entering the uterine cavity, it meets sperm. If fertilization does not occur, the egg leaves the woman’s body with menstrual flow.
From this moment, a new follicle begins to develop. Few eggs are able to fulfill the required purpose. What is ovulation is asked by representatives of the fairer sex who want to get pregnant or women for whom pregnancy is undesirable.
Attention! In case of infertility, it is necessary to undergo an ultrasound to determine the dynamic growth of follicles.
Representation of the ovulation process is important for the purpose of speedy conception if a woman has seriously set out to become pregnant. The timing of ovulation varies noticeably among women. Even for one woman, the possible period may vary depending on different months.
Attention! Not so long ago, for the first time, science captured the ovulation process during an IVF procedure, filmed on video. Previously, it was a mystery; one could only guess about the action taking place in a woman’s body.
The process lasts approximately 15 minutes in total. An opening is formed in the wall of the follicle, similar to a wound, from which the egg emerges. It seems small and inconspicuous, but it is the largest cell in the human body.
Cervix after conception
We figured out what happens to the cervix if conception does not occur. But what will happen to her if the girl does get pregnant?
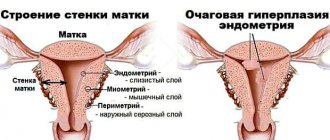
- In the early stages of conception (from 2 days to one week), the walls of the uterus become loose and very soft. By the appearance of the uterus, gynecologists and obstetricians can determine pregnancy no earlier than two weeks, because often the symptoms of early pregnancy are similar to the physical sensations of approaching menstruation. Then the cervix is involved in the process of lengthening, because it is necessary to provide maximum protection to the embryo located inside the uterus. Because of this, the walls of the cervix narrow after conception and the density increases. The cervical canal stretches, making it difficult for unnecessary and dangerous cells to enter for the unborn baby and the mother. In addition, the cervix changes color and becomes bluish due to active blood flow. At this time, by touching the cervix, you can determine whether the girl is in position or not.
- Until about 23 weeks, the cervix remains closed, preventing infections from entering the uterine cavity. But after 23 weeks her condition changes dramatically. It is greatly shortened due to the weight of the baby inside, because at 5-6 months almost all of the child’s organs are already developed, and he only continues to grow in size. The cervix shrinks to support the weight of the fetus and amniotic fluid.
- Until childbirth, the cervix only shortens and no longer changes its position. Sometimes the cervix becomes “stubby” due to the fact that the density level is high to avoid pathogenic substances from entering the uterus. This process does not affect pregnancy in any way, only protecting the woman and the unborn baby from premature birth.
Methods for determining ovulation
Let's look at methods to determine ovulation:
- tests;
- calendar;
- according to the state of mucus;
- by basal temperature;
- according to the condition of the cervix;
- by saliva;
- according to your health, without a doctor.
How to determine ovulation by urine
The urine test is based on luteinizing hormone. The hormone is always present in urine. A sharp increase in its concentration indicates that the egg will be released in 24–36 hours.
When should the test start? It all depends on the length of the cycle. If the cycle remains unchanged, testing begins seventeen days before the start of the future menstruation. With a 28-day cycle, tests should begin on the 11th day, with a 35-day cycle, on the 18th.
The urine test is quite simple. The package contains 5 paper test strips. Each strip is divided into 2 halves. One strip is a control strip with a colored line. The other, with an applied reagent, is diagnostic. This stripe is colorless until it comes into contact with urine. With the 28th cycle, testing begins on the 11th day.
Attention! Women with unstable cycles select the shortest cycle from the last six months and calculate the test time.
It is recommended to drink more fluid during the testing period and carry out tests daily, at the same time. The test works like this: dip the strip into the urine for 3 seconds and look at the result. A strip that becomes the color of the control or slightly darker indicates a positive result. If the strip is lighter, the tests are repeated on the following days.
Know! If there are delays of more than a month and cycles are inconsistent, it is not advisable to use a urine test due to the ineffectiveness of the results and the high cost of the tests. Only with joint monitoring with ultrasound, it will be obvious that the follicle has reached 18–20 cm, and the test will give a positive result.
Determining the ovulation period using a calendar
The calendar method is one of the most popular. With a systematic menstrual cycle, a woman can easily calculate the time of ovulation. Typically, egg maturation occurs in the middle of the cycle. The increased possibility of fertilization is 4 days before ovulation and 4 days after ovulation. That makes nine days.
Why do they add 4 days? This happens because the sperm in the uterus are functional for two to three days; a fourth day is added for safety reasons.
If the cycle is 28, conception is possible on days 10–17. Here, day 1 is considered to be the 1st day of the onset of menstruation. The last day is considered to be the 1st day of future menstruation. If you do not want pregnancy at this time, you should abstain from sexual intercourse or resort to contraception.
Attention! With the calendar method, the ovulation period is calculated - a cycle of 28 days: subtract 18 from the last day of the cycle to get the tenth day. This day opens the period of probable conception. The last day will be day 17 (28–11=17).
From a scientific point of view, the calendar method is considered ineffective. Women during the ovulation period closely monitor their health. It is also necessary to monitor your well-being, uterine secretions, and the condition of the mammary glands.
Ovulation time based on basal temperature
The procedure is performed using a thermometer. For safety reasons, it is advisable to use an electronic thermometer rather than a mercury thermometer. Every day, waking up in the morning and without getting up, measurements are taken in the vagina, rectum for seven minutes, in the oral cavity for five minutes. The results are recorded. The basal temperature before the release of the egg does not rise above 37ºC. When the temperature rises above 37ºС, this will be evidence that ovulation has occurred.
Know! For the purpose of family planning and the birth of offspring, it should be remembered that the life of an egg lasts 24–28 hours. This is the period for the undeniable and effective conception of a new life.
Signs of the cervix
Most women do not resort to this method, although the genitals are the best weather forecasters. The fear of vaginal penetration frightens the female sex. If you have an irresistible desire to have a child, it is easy to learn to understand the degree of dilation of the uterus, its density and position. It is recommended to master this method for breastfeeding mothers, women in their 40s and 50s during premenopause, when the body changes as it approaches menopause.
Before ovulation, the cervix feels dry to the touch, quite hard, like the tip of the nose. It is lowered into the vagina and closed. By the time the egg is released, the cervix becomes covered with mucus, becoming wet. Then the cervix opens and rises, occupying a position in the upper area of the vagina that is convenient for the passage of sperm. At this time, the cervix is soft, like an earlobe.
At the end of ovulation, the cervix occupies the lower part of the vagina, that is, it descends, closing and becoming hard again.
By vaginal mucus or “Pupil Effect”
The pupil effect is a specific secretion called cervical and located in the cervix. The existence of mucus is determined during examination by a gynecologist. The presence of mucus is considered an indicator of ovulation. The path to the cervix is filled with mucus, which prevents microorganisms from penetrating from the vagina into the uterus.
During the monthly cycle, the secretion is very viscous and prevents microorganisms and sperm from entering the uterus. During the period of ovulation, the secretion becomes less viscous, and sperm freely rush to the uterus. The pupil effect is explained by the appearance of mucus, similar to a droplet (pupil).
Attention! The “pupil effect” is an archaic technique not used in the present period.
Despite the antiquity of the technique, women use it at home. Regular mucus testing helps determine when an egg is about to be released.
How to determine ovulation by saliva
This method is called the “fern symptom” or saliva crystallization method. During ovulation, a woman's body maintains a certain hormonal balance. Saliva applied to a microscope glass forms crystals similar to a fern leaf.
Signs of ovulation determined without a doctor:
- nagging, aching pain in the lower abdomen, which can radiate to the lower back;
- increased discharge from the uterus: viscous, cloudy or transparent;
- breast sensitivity increases;
- the “wet panties” sign is evidence that ovulation has occurred;
- increased sexual desire;
- increased rectal temperature.
Attention! Urine or blood tests can help determine the time of ovulation.
Feel the cervix during your cycle
The condition of the cervix can be determined by palpation. What should it feel like during a full cycle?
Let's start with ovulation. During this period, the cervix should look like a mound, the cervical canal opens slightly. The neck is high and shortened.
Before menstruation, the passage narrows, protecting the uterine cavity; it expands again during menstruation, and the cervix itself lengthens and decreases.
After menstruation, the uterine os narrows and begins to rise, preparing for the period of ovulation.
Attention! When pregnancy occurs, the cervix tends to close the cervical canal. If conception has occurred, the cervix becomes soft to the touch!
If your cervix is hard during ovulation
This is a complex case in which a number of factors need to be taken into account. Only doctors can determine the first sign of any pathology associated with the hardness of the uterus after ovulation. One of the most common causes of a hard cervix is fertilization. This is a sign of pregnancy in the early stages; in later stages it can be a sign of uterine hypertonicity. In any case, if you have a hard cervix, consult a doctor! Timely registration of pregnancy will improve the situation of the mother, who will begin to monitor her lifestyle more carefully. And timely diagnosis of a number of diseases will speed up the process of their cure and complete restoration of the body.
Mucus in the cervix after ovulation
Normally, mucus in the cervix continues to be released after ovulation, but not as abundantly as in the pre-ovulation period. The discharge becomes more viscous, but less abundant due to the increase in density. They may turn brownish or dark yellow before the first day of the cycle.
Attention! If you have green or green-gray mucus, you should immediately consult a doctor! This color indicates the process of inflammation, which can occur both in the vagina (thrush or other fungal diseases) and in the cervix. Only a specialized doctor can prescribe the correct solution to this problem. No need to self-medicate! This leads to irreversible processes that directly affect a woman’s reproductive function!
Traditional methods of treating anovulation
Anovulation is the absence of ovulation, which sometimes women are not aware of. Symptoms:
- Increased and heavy periods.
- Violation of the regular cycle.
- Always low basal temperature.
To restore the correct, effective functioning of the ovaries using folk remedies, they must first conduct research on the patency of the fallopian tubes. They periodically take hormone tests to determine the condition of the whole body.
Hormone levels may fluctuate: in one cycle the hormonal levels will be positive, another increased or decreased. Take ovulation-stimulating infusions only when the imbalance is restored.
Doctors recommend taking hormonal medications to treat anovulation. There is a more gentle method - folk recipes using various herbs.
Recipe with sage
- 1 tbsp. l. sage;
- 250 gr. boiling water
Steam and leave for twenty minutes. Drink: from the seventh day of the cycle, 4 times a day, 60 grams. Duration ten days. Repeat the infusion for 2 months.
They won't accept it for three months. Then they start drinking sage tincture from the fourth day of the menstrual cycle.
Linden and sage
- 1 tbsp. l. linden;
- 1 tbsp. l. sage;
- 300 gr. Hot water.
Pour in the herbs and infuse. Drink 1 tablespoon three times a day (from the fifth day of the cycle).
Adam's root
Take 2 tsp. Adam's root is brewed with 1 glass of hot water. Leave for 120 minutes. Strain. Drink one tablespoon 4 times a day.
Plantain seeds
- 1 tbsp. l. seeds;
- 250 gr. water;
Pour water over the seeds and bring to a boil. Cook for five minutes over low heat. Leave for 60 minutes. Take two tablespoons 4 times a day for 1–2 months half an hour before meals.
knotweed
- 4 tbsp. l. herbs;
- 0.5 liters of water.
Brew, leave for 4-5 hours, filter. Drink three times a day: 15–20 minutes before meals, 200 grams.
Ramisha is one-sided
In a thermos, steam 3 tbsp with 0.5 liters of boiling water. l. herbs. Leave for 12 hours. Drink 4 times a day after meals (every hour) 150 grams.
Tingling in the cervix during ovulation
Tingling in the cervix is often observed during menstruation, but during ovulation this unpleasant symptom can be a sign of illness.
What diseases accompany tingling in the cervix during ovulation?
- Endometriosis. This is the accumulation of endometrial cells in various organs of the reproductive system. When complicated, this disease affects ovulation and the uterine cycle; in the future, this can develop into primary or secondary infertility, greatly affecting the life of a woman and her family.
- Pyelonephritis and inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system.
- Cystitis is the most common disease in girls and women of different ages; this disease can be treated at home. But it's better to see a doctor.
- Cervical cancer (growth). One of the terrible, but, thanks to modern medicine, treatable diseases of gynecology. Usually, with cervical cancer, colic is not as severe as, for example, during menstruation or endometriosis, but one of the main factors diagnosing oncology is small bleeding throughout the cycle and even during ovulation.
The health of the reproductive organs is very important, regardless of gender. After all, how we can conceive, bear and give birth to our offspring depends on reproductive function.
Video: signs of ovulation
Video: how to determine ovulation by cervical mucus secretions, basal body temperature and cervix?
How to determine the time of ovulation with an irregular menstrual cycle
Many women have irregular cycles: shorter, longer than the average - fourteen days. In a woman with a short cycle, ovulation occurs at the end of her period.
How to calculate ovulation:
- Determine the shortest cycle in a year and subtract 18.
- Take the longest cycle and subtract 11.
- The results obtained will determine the time of ovulation.
Know! Healthy women can independently conduct tests at home to determine the date of ovulation using saliva analyzers and urinary tests.
If you have an irregular cycle, you need to know exactly the duration of your menstruation per year. Effective methods include saliva crystallization and temperature measurement.