Almost half of the women on the planet have one or more ovarian cysts. Some representatives of the fairer sex are not even aware of their pathology. The tumor is detected only at the next gynecological examination or during an ultrasound examination. Today's article will provide you with information about how a burst ovarian cyst manifests itself. You will learn further about the symptoms of this complication and how to treat it.
What is an ovarian dermoid cyst?
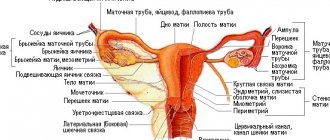
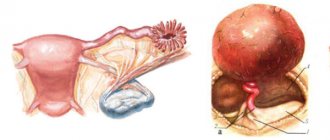
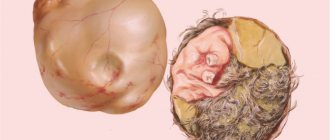
An ovarian dermoid cyst (mature teratoma, dermoid) is formed by ovarian cells and consists of a round or oval capsule with dense smooth walls, inside of which there is a jelly-like filling with fragments of hair, nervous, bone, adipose and other types of tissue, sweat glands, etc. , formed by ectoderm, endoderm and mesoderm - embryonic germ layers. Such a formation can reach large sizes - up to 15 cm in diameter.
The figure shows the contents of the dermoid - hair, teeth and other fragments formed by the embryonic layers
A dermoid cyst is sometimes present in parallel with pregnancy, in most cases behaving quite quietly and not threatening the health of the woman and the embryo. However, if the dermoid begins to increase in size during pregnancy, this can lead to negative consequences. The uterus, which has enlarged due to pregnancy, can displace the cyst from its occupied place, as a result of which the risk of pinching or torsion of the pedicle of the formation by organs located in the pelvic cavity increases, and this is already fraught with the development of inflammation and, as a rule, requires surgical intervention.
If the ovarian dermoid of the expectant mother does not exceed 5 cm in diameter, it is subject to constant monitoring throughout the entire period of pregnancy, followed by removal of the tumor - either after a natural birth or during a cesarean section.
Possible complications with such formations
Like other types of ovarian cysts, a mucinous cyst can provoke the following complications:
- development of a malignant process;
- infertility;
- leg torsion;
- spontaneous miscarriage;
- rupture of cystic formation.
The above complications can be caused by the following factors:
- late diagnosis of the disease;
- heavy physical activity;
- the onset of pregnancy;
- psycho-emotional overload.
Causes
There is a misconception that mature teratomas develop as a result of hormonal surges that occur in a woman’s body during puberty, pregnancy and premenopause. The basis for this point of view can be considered the fact that dermoids are most often diagnosed during such periods of a woman’s life cycle. However, a woman may not be aware of the presence of a cyst for years, so the time of diagnosis of the pathology cannot serve as confirmation of this point of view.
The dermoid develops from the tissues of the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm, in which differentiation has failed, and these embryonic layers remain for the time being in the ovary. Science has not yet given an exact answer about the circumstances under which such violations occur. Hormonal storms play only the role of a catalyst, contributing to the activation of a teratoma that already exists in microscopic form.
Such cysts, as a rule, grow extremely slowly and in most cases have a right-sided location - the left ovary remains unchanged.
Huge cysts during pregnancy
In cases where an actively growing cyst is detected in a pregnant woman, all additional studies are initially carried out, and then additional treatment is prescribed, which will be as safe as possible for the intrauterine development of the fetus. Large cysts are dangerous primarily because they put pressure on neighboring organs, as well as on the fetus itself, but it is much more important to prevent torsion of its legs and rupture in the abdominal cavity.
Only the attending physician can determine exactly what to do in a given situation. As a rule, surgical intervention and direct treatment of the tumor are not carried out until the birth of the child. But in case of serious danger, it is allowed to provoke premature birth with mandatory further excision of the hollow tumor. The presence of small formations cannot be treated during pregnancy in any way. Most of them can resolve on their own under the influence of hormonal changes in the body itself.
Symptoms and signs
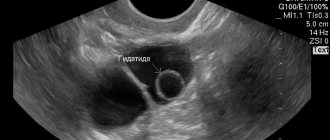
Dermoid may not remind you of itself for a long time, so the woman does not even know about the presence of pathology. During this period, the cyst may be accidentally diagnosed during a visit to the gynecologist or during an ultrasound scan.
When the formation reaches ten or more centimeters in diameter, the following symptomatic picture develops:
- feeling of heaviness and fullness in the lower abdomen;
- soreness in the ovarian area;
- frequent urination;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- enlargement of the abdomen (with large tumor sizes).
In some cases, patients complain of pain when dense stool passes through the segment of the large intestine, which is under pressure from the dermoid cyst. Dermoid does not affect menstrual function in any way.
In the case of inflammation of a mature teratoma due to strangulation of the cyst or torsion of its leg, the following symptoms are present:
- a sharp increase in temperature;
- feeling of weakness;
- acute abdominal pain radiating to the rectum and groin.
This condition is dangerous due to the development of peritonitis and therefore requires immediate medical attention.
Acute pain in the abdomen may indicate torsion of the leg or inflammation of the dermoid
Consequences
You already know how to understand that an ovarian cyst has burst. The sooner you seek medical help, the less likely it is that unpleasant consequences will occur. What threatens the situation when a cyst on the ovary bursts? Consequences (after surgery) may be as follows:
- formation of adhesions in the pelvis;
- menstrual irregularities and hormonal imbalance;
- psychological disorders;
- allergic reactions to the drugs used (during surgery);
- not aesthetically pleasing (scar after laparotomy);
- infertility (with removal of the ovaries).
After surgery, a woman needs conservative therapy aimed at recovery and prevention of complications. If the body temperature rises sharply, this indicates an inflammatory process. The patient needs antibiotics to help cope with the complication. It is important to choose the right drug.
Diagnosis of the disease
During a gynecological examination, a mature teratoma is defined as a mobile elastic round tumor, painless to the touch and localized in the area of the uterine appendage. To make a differentiated diagnosis, the following examinations are usually performed:
- vaginal ultrasound is the most informative method in this case, since it allows you to determine the size and nature of the tumor - the thickness of the capsule walls, the density of the contents, the state of the blood supply, the presence of inclusions and thus differentiate the dermoid from other types of cysts;
- MRI - if necessary, is used to clarify data obtained using ultrasound;
- pregnancy test - to exclude ectopic pregnancy;
- tumor marker CA-125 - to exclude the malignant nature of the tumor;
- laparoscopy - to clarify the diagnosis and take material for a biopsy.
Ultrasound is the most informative examination method in this case.
Health care
If you experience the symptoms described, you should urgently call for help. Remember that you cannot take medications before the doctors arrive. Painkillers and antispasmodics may show a blurred clinical picture. Take a horizontal position and apply cold to your stomach. Gynecology in Moscow, as in other cities of Russia, involves hospitalization of the patient for the described complaints. In a hospital setting, doctors will be able to conduct an examination, which includes:
- gynecological examination;
- ultrasonic monitoring;
- blood and urine tests;
- puncture.
Depending on the results obtained, further tactics of action are chosen. Here are some addresses of clinics in the capital of the Russian Federation: st. Lobachevsky, 42; lane Samotechny, 21; st. Pokrovka, 22 and so on.
Treatment
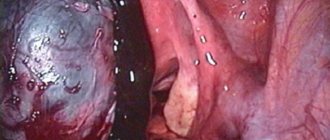
The only treatment option for mature teratoma is surgery, which can be performed either by a more gentle laparoscopic method or by a traditional laparotomy using a surgical incision. The choice of surgical procedure will depend on the patient’s age, size and condition of the tumor.
Methods for removing formation
In patients of fertile (childbearing) age, the main task of the surgeon is to preserve the integrity of the ovary as much as possible. In such cases, a cystectomy or resection of the ovary is performed, in which the formation is removed and damaged tissue is excised. Typically such operations are performed by laparoscopy.
In most cases, cystectomy is performed laparoscopically.
In women of menopausal age, in most cases, the entire ovary, on which the dermoid cyst is located, and sometimes the entire uterine appendage is removed. These operations are usually also performed laparoscopically.
During the operation, a rapid analysis of the tissues taken is performed. If no signs of malignancy are found, treatment of the cyst can be considered completely completed. Otherwise, the surgeon expands the degree of intervention and continues the operation according to a different scenario.
In emergency cases - in case of inflammation of the dermoid or torsion of its legs - an urgent operation is performed using a laparotomy method in order to be able to thoroughly examine the patient’s abdominal cavity.
Unfortunately, drug therapy will not help cure a teratodermoid cyst. Under no circumstances will a dermoid cyst resolve on its own! Moreover, the use of drugs and dubious folk recipes, including, for example, the Neumyvakin method, which involves treatment with hydrogen peroxide and soda, can seriously harm a woman, depriving her of the ability to bear children, and cause serious damage to her health, since in 2–3% of cases dermoid capable of becoming malignant.
Recovery after surgery
After laparoscopic removal of the cyst, you are allowed to get out of bed after 5–7 hours, postoperative rehabilitation takes place very quickly—3–5 days, and complete recovery—within a month. There are practically no seams left.
Recovery prognosis
If pseudomucinous cystoma is detected, the prognosis is favorable. The likelihood of its degeneration into a malignant formation is minimal, as is the risk of its reoccurrence. When it reaches a large size, it is necessary to remove the ovary, but pregnancy is possible if the other appendage and uterus are preserved.
The prognosis of papillary mucinous ovarian cyst is much worse. It has a high degree of malignancy and quickly grows into other organs and tissues. This complicates the operation and sometimes makes it impossible to completely remove the tumor. Chemotherapy is used to improve the prognosis.
Forecast and prevention of the disease
With timely treatment of mature teratoma, all sexual functions of a woman, namely menstrual, sexual and childbearing, are preserved. Planning a pregnancy is allowed 6 months or a year after surgery.
Recurrence of dermoid occurs extremely rarely and only in cases where hidden rudiments of pathology were already present in the ovary. To prevent recurrence of the disease, after a cystectomy it is necessary to see your doctor twice a year and undergo an ultrasound scan.
For timely detection of pathology, it is necessary to regularly visit a gynecologist, especially in cases where the symptoms discussed above appear. A mature teratoma that is not removed in time carries a certain danger to a woman’s health - it can fester or become inflamed at any moment, not to mention its ability to undergo malignant degeneration, and then the operation will have to be carried out not as planned, but as an emergency.
Reviews from patients who underwent cystectomy
I had an operation (abdominal) to remove a dermoid cyst from an ovary about 7 cm in diameter. After 2 days, my period began, the doctor said that this was a normal reaction of the body. They traveled as usual - 4-5 days. After the operation, Lindenet 20 was prescribed through the cycle to allow the ovaries to rest and recover.
Olka
https://www.woman.ru/health/woman-health/thread/4089370/
I had a laparoscopy to remove a dermoid 5 days ago. The doctor warned that my period might come (although I did it on the 3rd day after the end). On the third day I was discharged. They didn't prescribe ANYTHING. In general, there was not even any talk about any appointment. There is no discharge or menstruation. I'm sitting at home, waiting for everything to heal. They said that pregnancy can be planned in six months.
Natalia
https://www.woman.ru/health/woman-health/thread/4089370/
I had surgery to remove a dermoid cyst, laparoscopy. After 4 days I was home. Everyone who had the same operation also went well. The doctor said that a dermoid cyst is not scary. After the operation nothing was prescribed. She said everything was as usual. Good luck.
Guest
https://www.woman.ru/health/woman-health/thread/4089370/
Don't delay treatment. I had a dermoid cyst. They themselves are very light and mobile - as a result, the cyst twists with the ovary, resulting in an emergency operation. The right ovary was removed. Don't delay the operation. Do laparoscopy. This is better than abdominal surgery and long thoughts later - “can I get pregnant with one ovary?”
Anaitka
https://sovet.passion.ru/l.php/kista-yaichnika—povod-dlya-bespokoistva_2.htm
Main Difference
The difference between a cyst and any cystoma is that it very rarely becomes the cause of an oncological process. Cystoma, having gone through several stages of its development, can transform into cancer. That is why such a tumor is subject to mandatory surgical removal.
Cysts have a thin shell that is easily damaged, as well as an almost ideal spherical shape and usually small in size (except for teratomas). They do not have an internal epithelial lining. They do not affect nearby tissues, because they grow due to an increase in the amount of internal contents.
The inside of the ovarian cyst is lined with epithelium. Having become a malignant tumor, it often grows into neighboring tissues and organs. Over time, it most often acquires impressive dimensions.
The cyst can transform into a cystoma. If this happens, the woman is recommended to undergo surgery to excise the tumor. In most cases, a true epithelial tumor is formed from a simple cyst of any ovary. Sometimes it is multi-chamber.