What is fibroid
Uterine fibroids are a pathology of the reproductive system, which is characterized by the formation and growth of a benign tumor in the muscular lining of the uterus. Most often, the disease is detected in women aged 30-40 years with a history of childbirth, abortion or surgical interventions. Now the disease is also detected in younger age groups; fibroids are diagnosed in girls 20-25 years old.
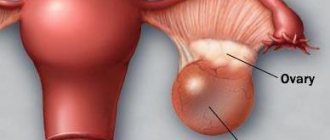
The term fibroid refers to a neoplasm localized in the body of the uterus (95% of cases), the remaining 5% are ectopic (cervical) localization. A tumor can form not only from muscle tissue, but also from connective tissue under the excessive influence of estrogen hormones.
In gynecological practice, it is customary to distinguish the size of a benign neoplasm in centimeters or in obstetric weeks of pregnancy. The conclusion “uterine fibroids at 12 weeks” is not associated with pregnancy, but it confirms that the tumor has reached a size similar to the size of the fetus at this stage.
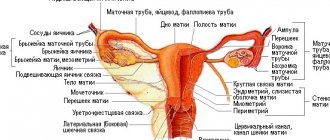
The following classification of fibroids is accepted depending on the muscle layer:
| Localization | Description |
| Muscular (interstitial) | The node is located in the thickness of the myometrium. |
| Subserosal | The neoplasm is located under the mucous membrane of the uterus near the peritoneum. |
| Submucosal (submucosal) | The node is located under the inner mucous membrane, in the uterus. |
| Interligamentous | The node is located between the wide uterine ligaments. |
Attention! Myoma may be pedunculated, and the same classification of location is applicable.
Diffuse forms of the tumor are diagnosed quite rarely. In this case, there is no pronounced node. Pointed growth of the myometrium is characteristic.
Diagnosis of small tumors is complicated by the fact that in the early stages of development there are no characteristic symptoms at all. As the tumor progresses, signs of menorrhagia appear - the woman notes an increase in the volume of menstrual bleeding, but such an alarming symptom rarely becomes a reason for an unscheduled gynecological examination and ultrasound.
Against the background of heavy periods, signs of anemia appear. A woman experiences excessive weakness, increased fatigue, and pale skin. As iron is removed from the body, tissue hypoxia develops, wrinkles appear on the face, nails and hair become dry, lifeless and brittle.
The reason for the appearance of these symptoms is that the pseudotumor has radically affected all layers of the uterus, and contractility changes. The risk of non-menstrual bleeding increases.
Diagnostics of education
The detection of a benign neoplasm often occurs in the gynecologist’s chair. An experienced doctor is able to use palpation to determine whether a problem is developing on the right or left side of the ovary and to detect uterine fibroids. In addition, there are other ways to identify this pathology:
- Ultrasound This technique uses ultrasound waves to track the progression of the disease. In addition, this type of diagnosis allows you to accurately determine the size of uterine fibroids and its shape.
- Computed tomography is also very popular for diseases of the uterus. The essence of this examination is an X-ray scan of the affected areas. All results are then subjected to good digital processing to obtain high-quality images. This diagnosis is used when it is necessary to determine the nature of the tumor and location.
Medical studies have proven that in women who have given birth to at least one child, the risk of developing fibroids of the right ovary is reduced several times. However, it has not been established whether childbearing protects girls from fibroids.
In order for the disease to develop, the patient’s body must have various unfavorable factors such as: abortion, improper use of contraception, chronic diseases of the appendages, stressful and conflict situations, excessive exposure to sunlight and much more.
Reasons for development
The list of main reasons that can trigger the development of a tumor includes:
- hereditary predisposition;
- the consequences of abortions and IUDs;
- injuries received during operations on the female genital organs;
- constant stress;
- infectious lesions of the reproductive system;
- pathologies of the endocrine system, in particular diabetes;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- absence or irregularity of sexual activity.
To prevent the development of uterine fibroids, women of childbearing age who are at risk should visit a gynecologist at least once every 6 months. If detected early, a hormone-dependent neoplasm responds well to drug correction and regresses.
Prevention
To avoid the development of dangerous complications and prevent the need for surgical intervention, every woman should be examined by a gynecologist at least once a year (optimally every 6 months). In addition, to reduce the risk of subserous myomatosis, it is important to adhere to the following rules:
- have regular sex life;
- provide the body with physical activity;
- balance the diet, include a large amount of fresh fruits in the menu;
- take vitamins that support hormonal balance;
- use combined oral contraceptives selected by your doctor.
Factors that provoke tumor growth
Uterine fibroids are formed from a cluster of cells of the same type. The neoplasm is sensitive to hormones and consists of smooth muscle cells. Education is manifested under the influence of certain factors, but subsequent growth is often due to the influence of such reasons:
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- non-use of barrier contraception;
- infection with sexually transmitted infections;
- consumption of certain foods;
- excessive physical activity activates blood supply in the pelvic area;
- weight gain.
Attention! The neoplasm shows a tendency to rapid growth against the background of the progress of diseases of the endocrine system, arterial hypertension and psycho-emotional disorders.
Patients often believe that the risk of malignancy of tumor cells increases against the background of the active development of the tumor, but this is incorrect. This fact has been refuted in various studies and confirmed clinically. The only limitation is the need for surgical intervention to ensure embolization of the uterine arteries. When carried out in the early stages of development, the uterus can be saved; in the case of diffuse damage, the prognosis worsens.
Nutrition
By eliminating several foods from your daily diet, you can prevent the progression of a uterine tumor:
- Soy products. Consumption in moderation can benefit the female body, but daily consumption of soy for fibroids is unacceptable. The composition contains a lot of phytoestrogens - plant hormones can also cause fibroids to grow quickly.
- Products that have undergone radical heat treatment. Flavorings, preservatives, dyes, artificial additives always have a detrimental effect on the state of the reproductive system - not only female, but also male.
- Pesticides and herbicides. Often have an effect on the process of hormone production by organs.
- Soy milk. The popularization of this product has led to an increase in the incidence of breast and reproductive organ cancer in women.
Since the cause of the development of fibroids is the radical effect of estrogen hormones, the patient should minimize the consumption of foods containing such substances.
Physical exercise
Sport in general has a beneficial effect on the condition of the female reproductive system, but when diagnosing fibroids, it is worth excluding any radical effects. The growth of the tumor can be provoked by cardio training and strength training, so a woman needs to be careful during physical activity. Such a restriction is not a reason to refuse training, they are necessary for the normal functioning of the body, but it is better to give preference to light exercises, classes in the pool, gymnastics, and yoga.
Pelvic organ dysfunction
A similar complication occurs when the uterus reaches 12 weeks of age and occurs mainly with subserous formations growing into the pelvic cavity. The following dangerous conditions arise against the background of large fibroids:
Bladder compression
In the initial stages of the disease, the pressure of the enlarged uterus on the bladder is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Lower abdominal pain;
- Frequent urination, feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- Urinary incontinence;
- Discomfort when emptying the bladder - heaviness and pain in the lower abdomen.
A large nodular tumor compresses not only the bladder, but also the ureters. The outflow of urine is disrupted, which leads to enlargement of the kidneys and the development of hydronephrosis. The process can be one- or two-way. Symptoms increase slowly over many years. Over time, swelling, increased blood pressure, and pain in the lumbar region are noted. Without treatment, prolonged clamping of the ureters threatens the development of renal failure.
Compression of the ureters by large fibroids.
Intestinal compression
A tumor growing towards the pelvis and abdominal cavity puts pressure on the organs of the digestive tract. First of all, the rectum suffers, then the rest of the gastrointestinal tract. Constipation occurs, accompanied by a feeling of incomplete bowel movement, pain in the lower abdomen, and flatulence. If the fibroid is not operated on, the growing tumor can completely block the lumen and lead to intestinal obstruction. In the future, this threatens intestinal necrosis and may become a reason for its resection. Such complications rarely occur, since at this stage the fibroid makes itself known through uterine bleeding, and the woman somehow ends up on the operating table.
How to stop the development of fibroids
Conservative treatment methods can stop the growth of the tumor if it is mild. It is not always possible to achieve positive dynamics through the use of medications, which is why doctors recommend that women pay attention to the need to correct their lifestyle, namely:
- a complete and balanced diet, excluding the consumption of foods rich in phytoestrogens;
- regular physical activity (at least 3 times a week), excluding periods of poor health;
- healthy 8 hours of rest at night;
- taking special vitamin complexes for women;
- cessation of nicotine addiction and alcohol consumption.
Compliance with these rules will reduce the risk of further development of fibroids. If proper hormonal correction is ensured, complete regression of the tumor is possible. It should be borne in mind that achieving such a goal often requires a sufficient amount of time, so changing your lifestyle will take more than one year.
Medications
Surgery is an additional risk for a woman’s reproductive health, so in the early stages of tumor development, doctors try to use the most gentle tactics possible. The main goal of drug treatment is to stop the growth of fibroids, reduce their size, and prevent relapses and complications.
The following medications are used:
- Logest belongs to the group of combined oral contraceptives. The drug suppresses ovulation. The drug stops the growth of the tumor, but does not lead to regression. The drug relieves symptoms in the form of periodic heavy uterine bleeding.
- Decapetil is an active hormonal agent. Suppresses the production of gonadotropin. The drug suppresses growth and provides regression; within six months of use, the neoplasm decreases by 2 times its original size.
- Mifepristone – has an antiprogestogen effect. Used for tumor regression and during the recovery period.
- Duphaston. Leads to degeneration of abnormally growing cells, stopping the growth of pseudotumor.
Attention! Uterine fibroids are called fast-growing if they increase by more than 1 cm within a year. Regression is also assessed using this marker, the only criterion being a reduction in size.
Traditional methods
Is it possible to stop the growth of fibroids by using decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs? It is quite difficult to answer this question accurately. Adherents of traditional medicine argue that such techniques can only be used as a complement to a medication course to increase its effectiveness. Doctors do not recommend taking such formulations orally due to the risk of cross-reaction with medications. They should be used locally. The list of popular formulations intended for home use includes:
- Treatment of fibroids with honey and propolis. A water-honey solution is used for douching and vaginal irrigation, and special suppositories are made from propolis.
- Hellebore infusion. It should be borne in mind that the drug from this plant is used orally. Hellebore is poisonous in high dosages, so when preparing infusions, proportions must be observed.
- Sea buckthorn oil. Used for applications to the cervix.
The duration of use of such methods is always determined privately by the attending physician. Uncontrolled use of traditional medicine can cause a woman’s well-being to deteriorate, so you should not risk your own health. Under the influence of certain components, fibroids can grow and become quite large. Dramatic progress can make non-surgical treatment impossible.
Physiotherapy
The following physiotherapy techniques can also contribute to the regression of the tumor:
- electrophoresis;
- radon baths;
- iodine-bromine baths;
- ozone therapy;
- magnetotherapy.
Hirudotherapy or treatment with leeches is an unconventional method of treating fibroids, but some patients confirm the effectiveness of this method.
Treatment and recommendations
The main goal of treatment is the possibility of preserving the patient’s uterine organ to continue reproductive function:
- Normalization of hormonal levels. Therapy uses drugs that include progesterone and testosterone derivatives. Their action is aimed at reducing the size of nodes and stabilizing the menstrual cycle. Mineral and vitamin complexes increase immunity in the fight against disease. Women of childbearing age are prescribed the drug "Norkolut", while "Buserelin" is effective for the menopausal period.
- Surgical methods:
- abdominal surgery to remove subserous nodes. It is performed when fibroids grow to large sizes or if they become malignant. Excised through an incision in the lower abdomen;
- laparoscopic method of fibroid removal. Using a special device (laparascope) the growths are removed from the uterine cavity.
- complete removal of the uterus. Hysterectomy. It is prescribed in cases where the fibroid cannot be removed due to its large size. Considering the negative psychological stress for a woman, this procedure is carried out when there is a threat to the patient’s life.
- Sound wave method. A distinctive feature of this treatment is the minimal risk of infection entering the wound.
After the course of treatment, the woman is registered at a dispensary for the disease. The medical examination procedure and examination must be carried out at intervals established by the attending physician.
Features of the course of the tumor process during pregnancy
A neoplasm is a foreign body in the uterus that complicates the natural process of pregnancy. The tumor can cause spontaneous abortion at different times due to disruption of the placental maturation processes; the fetus at this time will face a lack of oxygen and nutritional components.
The prospect of pregnancy with fibroids is not rosy, but the disease does not prohibit the possibility of conception and successful pregnancy. Medicine knows cases of the birth of healthy children with normal weight in women with the diagnosis, but statistics cannot be ignored: 60% of pregnancies with fibroids occur with complications:
- uterine bleeding;
- premature birth;
- placental abruption.
If the size of the neoplasm exceeds 8 cm in diameter, doctors recommend immediately terminating the pregnancy, because during fetal development the hormonal levels change and the defect receives additional nutrition. As it develops, the fibroids will also increase in size. If a woman refuses to have an abortion, the birth is ensured by a caesarean section, which is performed after 35 weeks.
Complications
Each pathology can cause complications. When these tumors are combined, the risk of worsening the patient's condition is much higher.
Fibroids and ovarian cysts can cause:
- malignancy of neoplasms;
- cyst rupture;
- development of endometriosis or adnexitis;
- infertility;
- development of infectious diseases.
Despite the fact that both diseases progress on the reproductive organs, there is still a possibility of getting pregnant (if infertility is not diagnosed). When two tumors occur together, this probability is significantly lower than when there is only one tumor.
A woman who has been diagnosed with fibroids or a cyst can not only carry, but also calmly give birth to a healthy child. However, risks still exist (premature birth, abnormal fetal position, etc.). Childbirth usually ends with a caesarean section. In some women, after childbirth the tumors went away on their own, without any medical intervention, so pregnancy is a kind of treatment method (in the absence of contraindications).
Diseases can be detected at an early stage if you regularly visit a gynecologist. A timely fight against pathological tumors can save you from dire consequences.
How dangerous is a submucosal tumor and how does it progress?
Submucous fibroids are considered the most dangerous and unfavorable in terms of prognosis. It is she who has a predisposition to rapid and uncontrolled growth; for example, a medium-sized pseudotumor can reach 12 weeks in just 3-4 weeks. That is why, when such a disease is detected, wait-and-see tactics are used extremely rarely. There is a risk of rapid germination into all layers of the uterus, then recovery is possible with complete removal of the reproductive organ.
Attention! If, when a submucous fibroid is detected, the doctor insists on its immediate removal, you should not refuse the operation. Drug treatment does not always ensure good results and tumor regression.
Diagnostics
Cervical cysts are most often detected using a speculum by a gynecologist. If the node is small in size, then it can be recognized in the following ways:
- Ultrasound with a vaginal probe.
- Hysteroscopy with simultaneous biopsy to exclude cancer.
- Laparoscopy is a bloodless operation and treatment at the same time. Using a laparoscope, through a puncture in the peritoneum, the intra-abdominal cavity and external walls of the uterus are examined, and, if necessary, adhesions between organs are removed.
Symptoms of submucosal leiomyoma of the uterus
The clinical picture of the disease depends on the type and size of the formation. The submucosal node is characterized by:
- changing the duration of the cycle towards its lengthening;
- copious discharge during menstruation;
- the presence of clots in bloody discharge during menstruation;
- cramping pain;
- infertility;
- spontaneous termination of pregnancy.
Uterine leiomyoma is characterized by a benign course. However, with the submucosal variant of the disease, there is a fairly high risk of cellular degeneration into a malignant tumor.