≡ Home → Endometrium → Endometriosis →
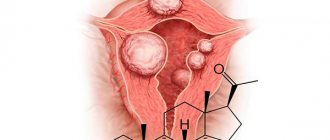
Endometriosis is a disease in which cells from the lining of the uterus are found outside the uterus. This is an esterogen-dependent pathology that occurs during reproductive age and persists until menopause. Progressive endometriosis manifests itself as pelvic pain, dyspareunia, menstrual irregularities and leads to infertility.
Endometriosis of the abdominal cavity and pelvic peritoneum is one of the common localizations of the pathological process. With this form of the disease, pain comes to the fore. Surgical treatment – removal of heterotopias, dissection of adhesions, restoration of fertility. Drug therapy is ineffective.
In this article we will tell you how abdominal endometriosis manifests itself and what treatment regimens exist.
Is it possible to cure uterine endometriosis?
Today's development of medicine makes it possible not only to relieve a woman of pathological symptoms, but also to completely cure the disease.
The chances are especially high if she sought help when the first signs of the disease appeared - discomfort during sexual intercourse, painful, heavy periods with blood clots, difficulty conceiving, and others.
Endometriosis is curable at the initial stage, and in most cases, women do not need to resort to surgical methods to eliminate the pathology. The exception is a running form.
Treatment of the disease is carried out using hormonal drugs. But if the conservative method does not produce results, then the patient will be recommended to undergo surgery.
Surgical intervention guarantees complete cure of endometriosis, but can be complicated by the development of infertility.
In modern practice, laparoscopic techniques are most often used, which preserves a woman’s fertile abilities: she will be able to conceive and bear a child.
Possible complications
If a woman categorically ignores visiting a doctor if she has symptoms and does not undergo treatment for endometriosis, severe complications develop, and ascites is one of them.
Ascites is dropsy in the abdominal cavity that occurs due to inflammation of tissues damaged by endometriosis cells.
Ascites is manifested by an increase in abdominal volume, severe pain, and signs of intoxication of the body. The disease can only be treated through surgery. If the operation is not performed in a timely manner, the fluid-filled dropsy will burst, leading to peritonitis.
Despite the fact that during surgical treatment of abdominal endometriosis the foci of the disease are removed, there is still a risk of relapse of the disease. Recurrence of lesions occurs if the cause of endometriosis has not been treated.
Another complication after surgery is endometriosis of the postoperative scar. The pathology develops gradually and may manifest itself after a few years. With the development of this disease, endometrial cells begin to rapidly grow outside the uterine cavity and grow into the postoperative scar. Symptoms and treatment are identical to the general clinic of endometriosis.
A woman experiences severe abdominal pain and the cyclicity of menstruation is disrupted. Therapy is conservative if the disease was diagnosed early, or surgery is prescribed when medications do not help, the pathology is advanced and there are complications.
What is the treatment for endometriosis?
Treatment of the disease requires an integrated approach. And the earlier a woman consults a doctor, the higher the chance of success of the selected conservative treatment regimen.
If left untreated, a woman will develop new lesions during each period. Later, cystic formations appear, healthy tissues are replaced by scar tissue, which leads to the development of adhesive disease. The result is a violation of the patency of the fallopian tubes and infertility.
Pathology therapy is carried out in several directions. This is medical, surgical practice and a combination of these methods.
Characteristic signs
It is quite difficult to detect the development of the disease in a timely manner, because symptoms at an early stage are often not traced. Even if ovarian endometriosis occurs together with a cystic process, there is a possibility that pronounced signs will not appear until the last stage of development or rupture of the cyst.
The most characteristic symptoms inherent in the lesion:
- infertility;
- severe premenstrual syndrome, a woman complains of pain in the lower abdomen, apathetic mood, nausea and dizziness;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- pain in the lower back, which is constant or periodic;
- changes in the menstrual cycle - most often it shortens, but periods become heavy;
- When the process spreads to nearby organs, urinary retention is observed and pain occurs during defecation.
The pain that accompanies endometriosis manifests itself with varying intensity, but the peritoneal area is considered the most painful. The pain can radiate to the lower back, lower back, and legs. The nature of the menstrual cycle changes: periods become scanty or heavy, therefore a change in the quality of discharge is always a reason for an unscheduled visit to the gynecologist. There may be bleeding from the genital tract that is not associated with menstruation. A woman develops anemia due to blood loss, and her libido decreases. Against the background of the constant presence of pain, mental disorders develop, and general health deteriorates sharply.
Treatment
Treatment of the disease involves several approaches. The technique depends on the current clinical picture and the extent of the pathological process. The treatment protocol is drawn up individually for each patient.
Conservative methods are practiced in women of reproductive age.
If pathology is detected during premenopause and with the onset of menopause, it is possible to combine medication with surgery, since endometriosis cured without surgery can cause relapses. As a rule, as the pathology progresses, radical surgical interventions are implemented.
Conservative
The conservative treatment method for endometriosis is used at all stages and includes:
- taking hormonal, anti-inflammatory, desensitizing agents;
- increasing immune defense;
- carrying out symptomatic therapy;
- physiotherapy.
The basis of conservative treatment is taking hormonal medications, which helps reduce the number and size of endometrial lesions and relieve pathological symptoms.
Medication
If the patient does not have the opportunity to take hormonal drugs, and surgical methods are also unavailable, then the disease is treated using non-hormonal agents.
The following medications are used during therapy:
- "Wobenzym";
- "Endoferin";
- "Ovariamin";
- "Indomethacin";
- "Cyclodinone".
Surgical
Surgical treatment is practiced when there is no effect from previous therapy. Conventionally divided into 2 groups:
- Endoscopic operations. The doctor gains access to the uterus through the cervical canal using a hysteroscope. The destruction of the endometriotic lesion is carried out in several ways - liquid nitrogen, a coagulator or a laser beam.
- Traditional intracavitary interventions. During the procedure, the body of the uterus is removed. The appendages are preserved.
Endoscopy is implemented in the focal form of the disease, when the doctor is able to distinguish between healthy and diseased tissues.
In case of a diffuse course and no result from taking hormonal drugs, complete removal of the uterus is the only way to eliminate the pathology.
Causes
It is very difficult to answer the question of why abdominal endometriosis occurs. There are numerous theories that try to explain how endometrial cells travel from the uterus to other organs and tissues:
- The implantation theory suggests that endometrial cells are introduced into the peritoneum during menstruation (retrograde movement) or during gynecological operations, but endometriosis can occur before the first menstruation and during menopause.
- Embryonic theory - from the same cells from which the genital organs are formed in the womb, endometriosis lesions subsequently form. This theory is confirmed by the occurrence of endometriosis in girls before menarche and its frequent co-occurrence with abnormal development of the genital organs.
- Genetic, environmental, hormonal, and immunological factors have recently been considered as having a cumulative effect on the development of this disease.
Currently, most doctors adhere to the implantation theory, which states that endometrial cells are brought into the pelvic area through retrograde (reverse, through the fallopian tubes) menstruation. It is important to note that retrograde blood flow is a physiological phenomenon and occurs in 70-80% of women , but the disease develops only in 10% of cases.
It is worth noting that the implantation theory is confirmed by the occurrence of endometriosis of the anterior abdominal wall after cesarean section; it belongs to the extragenital form and is quite rare in practice.
In order for endometrial cells to “successfully take root” in the pelvic area, the following changes occur in the body:
- The level of hormonal receptors for estrogen and progesterone changes dramatically in endometriotic lesions.
- The level of estrogen also increases significantly in the formations, but under the influence of medications that suppress the production of estrogen, the lesions decrease.
- Resistance to progesterone occurs, the balance of enzymes producing estrogens and progesterones is disrupted.
- Inflammatory processes develop - a huge amount of prostaglandins, cytokines and other elements are formed. They contribute to increased pain and the development of infertility.
All these factors in patients with endometriosis interact with each other, and they all “work” for the engraftment and functioning of endometriosis cells in the peritoneum.
What medications should you take?
Treatment of endometriosis is carried out through a course of hormonal medications. Includes:
- oral contraceptives;
- gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonists;
- progesterone and its analogues;
- drugs that block the production of follicle-stimulating hormone.
Birth control pills Janine and Yarina
Combined OCs from the group of estrogen-progestogen agents are prescribed, in particular, “Zhanin” and “Yarina”. Helps in eliminating heavy, painful menstruation. Duration of treatment – up to 9 months.
Utrozhestan, Duphaston
"Utrozhetan" and "Duphaston" belong to the drugs from the group of gestagens. Prescribed for 6 months at any stage of the disease.
Treatment may be accompanied by the development of depressive states, the appearance of unscheduled bleeding, and soreness of the mammary glands.
Danazol
Danazol belongs to the group of antigonadotropic drugs. Designed to suppress the production of follicle-stimulating hormone.
Duration of treatment is 6–8 months. High levels of androgens and hirsutism are contraindications for use. During treatment, hair growth may increase and the activity of the sebaceous and sweat glands may increase.
Buserelin, Goserelin (Zoladex)
"Buserelin" and "Goserelin" belong to the GnRH agonists. Used to suppress the menstrual cycle. They are effective, reduce the frequency of relapses, and eliminate pathological symptoms. Not prescribed for young women.
Prevention
The following rules will help prevent or promptly detect the disease:
- Women over the age of 20 need to visit a gynecologist 2 times a year.
- As prescribed by your doctor, undergo an ultrasound of the pelvic organs at least once a year.
- Treat diseases of the female reproductive system.
- Avoid having sex during menstrual periods.
- Do not use tampons during menstrual bleeding.
- Follow the rules of healthy eating.
Important! The main reason for the development of ovarian endometriosis is when a woman takes combined oral contraceptives. These drugs have a significant effect on female hormonal levels, therefore they should not be taken uncontrollably.
What organs does the disease affect and forms of endometriosis?
Depending on the location, two forms of pathology are distinguished. This:
- genital;
- extragenital.
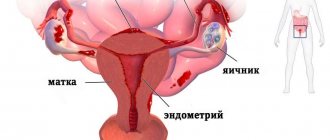
The genital variety is characterized by the formation of pathological foci on the tissues of the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes. In the extragenital form, endometrial cells are detected outside the reproductive system: in the intestinal tract, in the tissues of the lungs and kidneys, in the navel, etc.
Endometriosis is a serious disease that requires adequate treatment. Otherwise, serious consequences cannot be avoided. That is why, when the first signs of pathology appear, it is necessary to obtain medical advice.
Occurrence
The first stage is the degree of development of endometriosis. Accordingly, in fact, it occurs as often as endometriosis itself. And according to various sources, from 14 to 38% of all women in the world currently suffer from it. Moreover, the absolute majority are patients of reproductive age, which is due to the nature of the disease. With menopause, on the contrary, in most cases it goes away even without treatment.
Another question is how often the disease is diagnosed at this stage. This happens extremely rarely. There are several reasons for this:
- Extremely mild symptoms, and most often completely absent, so the patient does not see a doctor;
- It is difficult to diagnose this condition by visual examination, hysteroscopy or colposcopy - if the doctor does not look for them “specifically”, then isolated small lesions may not be noticed;
- There are no symptoms on ultrasound at this stage.
The only diagnostic method that will show with absolute accuracy the presence of endometriosis at this stage is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). But patients rarely perform such procedures, which is why the disease is most often diagnosed at the third or fourth stage, when there are severe symptoms. And it is precisely these symptoms that force patients to see a doctor.
However, the simplest and most effective treatment for this disease is possible at the first stage. In addition, therapy at this stage takes much less time.