What pain is typical for uterine fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are diagnosed in 40% of patients who have crossed the age limit of 35 years. The risk of developing a neoplasm increases after menopause. The neoplasm often progresses during pregnancy if it was not detected before pregnancy. In this case, the woman is bothered by acute or nagging pain in the lower back and lower abdomen, which intensifies as the fibroids progress.
Attention! Girdle pain, covering the lower back and abdomen, is the first symptom that allows one to identify uterine fibroids in a woman at the stage of its formation. The peculiarity is that the pain syndrome is constantly present.
With uterine fibroids, the stomach often hurts due to the systematic growth of nodes. An accompanying symptom is the absence of menstruation. As the tumor progresses, the patient experiences intense pain. They become unbearable at the time of gynecological examination or sexual intercourse. Sometimes contacts provoke uterine bleeding.
Manifestations
Myoma symptoms may differ slightly depending on certain stages of the patient’s life.
With hormonal surges, the tumor begins to suddenly appear, causing pain or discomfort. Such changes are especially noticeable during pregnancy and menopause.
Myoma formation, although benign, can cause a lot of trouble for the patient, having a negative impact on her organic structures. In accordance with the nature and manifestations of fibroids, the specialist selects the necessary therapeutic method, conservative or surgical.
Symptoms during menopause
If uterine fibroids did not particularly bother you before the postmenopausal period, then during menopause it is quite capable of resolving. Such changes are caused by a sharp decrease in hormonal levels. But regression of fibroids is possible only with the normal onset of menopause.
The tumor can grow to a relatively large size, then it will be accompanied by heavy bleeding and severe pain. In such a situation, surgical treatment is necessary.
Only the tumor or formation along with the uterus must be removed. Large nodes can cause heavy intermenstrual bleeding, which is very dangerous during menopause.
If fibroids develop in parallel with the adenomyotic process, then women often suffer from severe forms of anemia. In addition, with such a combination, there is a high probability of malignancy of the myomatous formation.
During pregnancy
Quite often, fibroids begin to develop in pregnant women, which is also associated with hormonal changes.
Not all tumors can negatively affect the pregnancy process, however, if fibroids are detected, it is necessary to strictly follow medical recommendations.
Although fibroids are benign tumors, they can increase the risk of developing various complications such as:
- Inflammatory process and pain, which increase the tone of the uterus, and, therefore, the risk of miscarriage;
- Premature delivery or spontaneous miscarriage in the early stages;
- Placental abruption, which leads to abnormal fetal development;
- Hypoxic damage to the fetus.
Therefore, it is extremely important to strictly follow all the recommendations of the obstetrician-gynecologist if fibroids were detected during pregnancy.
Usually, when the nodes are localized far from the placental location, pregnancy disorders are not observed, but if the tumor forms next to the embryo, then there is a high probability of miscarriage or premature birth.
Causes of pain
The reason for the formation of fibroids is a mutation of genes in the myometrial cells; the tumor is formed from one deformed cell and over time the tumor reaches large sizes. If treatment is not carried out. Nearby organs suffer because the body of the tumor puts pressure on them as it grows.
While the neoplasm is small in size, it does not manifest itself and does not provoke the appearance of unpleasant sensations. The only change a woman notices is during menstruation and a few days before it begins. The volume of blood released increases, and changes in the cycle are observed. It can move by 5-7 days. The danger is that women rarely pay attention to such a minor change and ignore it.
As fibroids progress, periods become more painful and longer. When the tumor reaches a medium size, the discharge can continue for several weeks, and only at this point do women often turn to the doctor. It is impossible to ignore the first signs of the development of a pseudotumor, because it is possible to get rid of it in a conservative way only at the initial stage of development. If its parameters are large, surgical treatment is used.
If you ignore pain and changes in the menstrual cycle. The tumor continues to progress. In gynecological practice, there were cases when a woman with a large belly went for a consultation about pregnancy, and she was diagnosed with fibroids. It should be noted that hCG does not increase, which is why pregnancy tests give a negative result. The condition is dangerous because all organs with fibroids are shifted and pressed down; diseases of the liver, kidneys, stomach and lungs may develop against this background.
At an early stage, a myomatous node causes nagging pain in the lower abdomen and lower back. Such pain can radiate to the kidneys. Since the neoplasm puts pressure on the rectum and bladder, the woman experiences difficulty defecating, the frequency of urination increases, and the development of chronic cystitis is possible.
With fibroids, pain of the following nature can be observed:
- pulling;
- cutting;
- aching;
- cramping;
- spicy.
Acute pain syndrome in women is extremely rare. This is explained by the slow increase in tumor size.
Pain covers the following areas:
- underbelly;
- small of the back;
- sacrum;
- stomach area.
The intensity and nature of the pain syndrome varies depending on the shape of the fibroid; if there is no torsion or is located in the thickness of the myometrium, the pain intensity will be low.
Submucosal fibroid
A submucous myomatous node is a rather dense neoplasm that forms in the inner part of the myometrium. The pseudotumor partially protrudes into the uterine cavity or is attached to a stalk. The node increases the activity of menstrual bleeding and increases the intensity of pain. Pain with submucous fibroids is often cramping in nature. It has medium intensity.
Sometimes this type of fibroid can be complicated by its exit through the vagina. The woman's uterus contracts as during childbirth. The woman feels periodic cramping pain. If the tumor protrudes into the vaginal cavity, the pain is bursting in nature and is localized in the pubic part. In case of complicated fibroids with the birth of a neoplasm, the woman needs surgical help. The stalk of the fibroid is cut off and the uterine cavity is curetted.
Subserous fibroid
Subserous fibroids are located in the outer layer of the endometrium. The formation is localized along the anterior or posterior wall of the uterine organ or located closer to the cervix. The clinical picture significantly depends on the position of the tumor. If the tumor is located on the front wall, it compresses the bladder, which provokes a frequent urge to urinate. Against this background, cystitis often develops. The pain is dull in nature and intensifies during emptying of the bladder or with a sudden change in body position, especially when bending forward.
Symptoms accompanying the lesion include:
- discomfort in the urethra;
- burning;
- sharp pain or cramping in the lower abdomen that appears during urination.
If the node is located on the left side of the back, the pain is localized in the lower back. The knot presses on the rectum and disrupts the process of bowel movement. Women often experience false urges to defecate and constipation occurs. The nature of the pain is dull. The pain syndrome may spread to the legs, and cramps may occur.
The serous node is often fixed on the stalk, a complication is torsion. Against this background, the vessels are compressed, and the myomatous node itself begins to necrotize. Torsion can be triggered by sexual intercourse or heavy physical activity. Immediately after the torsion, the woman feels piercing pain. When this symptom appears, the woman is advised to undergo urgent hospitalization; assistance measures are limited to radical removal of the node. The lack of timely surgical intervention results in the spread of toxins throughout the body and provokes the development of sepsis and peritonitis.
Pain with uncomplicated fibroids
With uncomplicated fibroids, pain may be constant. However, most often they appear immediately before menstrual bleeding, as well as during its period. Nagging, aching pain radiates to the lower back, sacrum, coccyx, left or right hypochondrium (depending on the location of the node). The woman feels constant weakness, the pain is of moderate intensity. A change in the intensity of pain indicates the development of complications and is a reason for an unscheduled visit to the gynecologist. If the pain is considered unbearable, it is better to call an ambulance; sudden movements are contraindicated for the patient.
How to identify complications of fibroids
Many patients believe that if the fibroid is small in size, the likelihood of dangerous complications occurring is minimized. Even a small tumor of the uterus can press on the blood vessels and provoke a malnutrition of the node. You need to understand that the larger the diameter of the fibroids, the higher the likelihood of developing necrosis. Statistics show that about 7% of patients experience impaired blood supply to the tumor and the development of ischemia.
Ischemia of fibroids is more common with rapid growth of the tumor. Leg torsion is a complication of subserous fibroids. The risk of necrosis increases during pregnancy due to decreased blood flow to the neoplasm. Impaired blood supply leads to acute pain in the lower abdomen. The pain appears suddenly against the background of normal health and is unbearable. Other symptoms also appear:
- nausea and vomiting;
- disturbance of urination and defecation;
- increased body temperature;
- excessive tension in the abdominal wall.
The only way to save the patient's life is surgery. The woman is indicated for hospitalization in a hospital. Doctors remove the necrotic node or the entire uterus. The volume of intervention is determined depending on the severity of the process and the affected area.
Forms of formations and their symptoms
Some clinical features depend on the specific type of formation.
There are 5 different types of fibroids:
- Subserous tumor - such a fibroid is localized on the external uterine layer, often has a stalk and grows into the pelvic and retroperitoneal space. Such a tumor does not cause an enlargement of the abdomen, but may manifest itself as urinary disorders, constipation, discomfort in the lower half of the abdomen or pain in the suprapubic and lumbar region, hemorrhoids and cramping pain;
- Interstitial myomatous form - forms in the uterine muscle layer, but can grow inside or outside the uterus. Accompanied by traditional pain above the pubis, urinary disorders and constipation, heavy menstrual and intermenstrual bleeding;
- Submucosal form of the tumor, or submucosal. Such a tumor grows in the uterine cavity, is characterized by rapid development and is characterized by heavy prolonged bleeding between and during menstruation, weakness, infertility, lumbar and abdominal pain;
- Cervical form of fibroid tumor - this formation forms in the uterine cervix and is relatively rare. Such a tumor does not cause menstrual disruptions or irregularities, and the main signs of a tumor are traditional pain, problems with reproduction, and compression of nearby structures;
- Intraligamentary fibroid tumor - forms in the interligamentous space and develops asymptomatically. When progressing to large parameters, fibroids begin to put pressure on neighboring tissues, causing constipation and frequent urination.
How to remove pain
If a woman experiences pain, antispasmodics and sedatives can be used to eliminate discomfort. Lifestyle and sexual activity play a major role in the process of pain relief.
Safe and effective pain relievers
To eliminate pain, you can purchase painkillers. A group of such medications includes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Most often, women use Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, Indomethacin, Nise.
Paracetamol and Ibuprofen in the case of fibroids have low effectiveness. The drugs will not help relieve severe pain and inflammation. If the pain is moderate, it is advisable to take them. If severe pain occurs, it is better to give preference to the drug Nise or Nimesulide. Such products can also be purchased at a pharmacy without a prescription, but it is not recommended to use them on an ongoing basis. Before using the product, you should consult a doctor and undergo a full examination.
Attention! Women should take into account that independent and long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can provoke the development of gastritis. Such drugs irritate the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract and are therefore contraindicated in patients with gastric ulcers.
Antispasmodics
Antispasmodic drugs are often used in gynecological practice. Doctors recommend these medications to their patients for painful menstruation. Drugs such as Papaverine and No-shpa are often prescribed for pain due to fibroids.
Papaverine is best used in the form of suppositories, and No-shpa is taken in tablet form. The medicine is indicated for menstrual bleeding or acute uterine spasms that occur outside of menstruation. They help relieve pain in the lower abdomen caused by contractions of the uterus. On the recommendation of a doctor, the products can be used on an ongoing basis. The duration of the course, frequency of administration per day and dose are determined individually.
Sedatives
Sedatives are also used to eliminate fibroids. Psychologists say that any gynecological diseases significantly worsen a woman’s general well-being. When the reproductive organ is damaged, stress occurs in the body, general health worsens and the quality of sleep decreases. Such drugs affect the functioning of the brain. During treatment, the patient's condition significantly improves, resistance to stress increases and the frequency of neuroses decreases.
Attention! To provide pain relief, some sources recommend using the dry heat method, but gynecologists do not recommend this method. Under the influence of heat, the blood supply to the tumor improves and the tumor can grow.
Lifestyle and nutrition
Changing your diet in some cases helps prevent constipation and reduce the likelihood of vitamin deficiency and anemia. Nutrition should be complete; this will increase the body’s immune defense. A woman also needs physical therapy or gymnastics. Light physical activity will help restore blood flow and improve nutrition of all organs and tissues of the body. If a woman is obese, the intensity of the exercise can be increased.
Sex life
Often, after diagnosis of pseudotumor, women refuse sexual intercourse for fear of pain and complications of the disease process. If there is no risk of complications, then you can have sex. With regular sexual intercourse, a woman’s hormonal levels are normalized and libido is maintained. Such conditions can reduce the risk of developing concomitant gynecological diseases. During sexual intercourse, prostaglandins enter the woman’s vagina along with sperm, which prevent inflammation and normalize the natural secretion of estrogen. If pain is present, it is better to avoid sexual intercourse. Firstly, the woman will not receive the necessary satisfaction, and secondly, complications may arise.
Hormonal treatment
Hormonal treatment is the basis of drug therapy indicated for patients with uterine fibroids. The drugs help stop the growth and subsequent development of the tumor, and in some cases reduce its size. Treatment is carried out with GnRH analogues. Long-term use of drugs with this spectrum of action is not recommended. The duration of the course of therapy is determined by the gynecologist. While taking these compounds, the intensity of pain decreases.
During pregnancy
The small size of fibroids rarely interferes with conception and development of pregnancy. The only obstacle can be its location in the area of the opening of the fallopian tubes and in the cervix, which does not allow the free movement of sperm. An increase in sumbucous fibroids during pregnancy can cause some problems for the growth of the embryo, since the tumor is located and grows towards the uterine cavity and occupies a certain place in it. A special threat to pregnancy in the form of late miscarriage in this case occurs at 11 weeks. The location of fibroids in the cervix makes natural childbirth impossible, as it is an obstacle to movement along the birth canal. Such changes in the condition of the reproductive organs necessitate a cesarean section.
During pregnancy, the hormonal levels in a woman’s body change significantly, which can provoke fibroid activity. Therefore, the course of pregnancy in such situations requires careful monitoring.
Prevention of development
Regular sex life and avoidance of abortions help prevent the likelihood of developing fibroids. Women who have a genetic predisposition to the disease should regularly visit a doctor once every six months. If there are no prerequisites for the development of the disease, the frequency of visits can be reduced to once a year. There is an opinion that the likelihood of developing the disease increases in women who refuse lactation after the birth of a child. To minimize the risk, the baby should be breastfed for the first 6 months. An ultrasound examination helps to identify the disease, which every woman should undergo once a year. Only the right approach to prevention will help reduce the likelihood of gynecological diseases in the body.
Pain manifested in the lower abdomen and lumbar region is often the main and only marker indicating the development of uterine fibroids in a woman. You should not pay special attention to the appearance of such a symptom; it is this that allows you to identify a tumor at an early stage of its development. If detected early, the formation is harmless and can be successfully treated with medication. In advanced cases, when the disease is accompanied by anemia, massive bleeding and acute pain, the woman needs to undergo surgery.
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice. Always trust your doctor first!
How to determine the disease
It is not difficult for an experienced and qualified specialist to identify uterine fibroids at the first gynecological examination.
To confirm the diagnosis, additional diagnostics are prescribed such as:
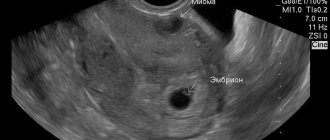
- Ultrasound examination;
- Laparoscopic diagnostics;
- Hysteroscopy;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- Hysterosalpingography, etc.
Chronic pain syndrome and related problems
The likelihood of developing this complication is directly related to the size of the myomatous node. In the initial stages of its existence, the tumor exists asymptomatically. Small fibroids (up to 2.5 cm) do not hurt or bother. Problems begin when the tumor reaches 3 cm or more. Pain occurs in the lower abdomen, radiating to the lumbar region, perineum and groin, extending down to the thigh or radiating up to the chest. The localization and distribution of pain is determined by the location of the fibroid. Read more about the nature of pain with fibroids and methods of pain relief.
On a note
Pain syndrome with subserous formation occurs later, which is associated with the special localization of the node. On the contrary, submucosal tumors make themselves known earlier with nagging pain during menstruation and shortly before it. Cervical fibroids are a concern already when they reach a size of 2-3 cm.
Variants of localization of myomatous nodes.
Large leiomyomas (from 6 cm) cause maximum discomfort. Such a knot is dangerous not only because of constant debilitating pain, but also because it disguises unpleasant sensations as other diseases. Often a woman is forced to visit more than one doctor before the cause of the pain is found and the correct diagnosis is made.
It is important to know
If you experience chronic pain in the pelvic area, you should make an appointment with a gynecologist and have an ultrasound scan. The recommendation is relevant for women of any age. Increasingly, myomatous nodes are detected before the age of 30, and when conducting a diagnostic search for pain in the lower abdomen, it is first necessary to exclude tumors of the uterus and appendages.
Growing uterine fibroids threaten not only constant pain, but also the development of other unpleasant conditions:
- Shortness of breath and difficulty breathing. Similar complications arise with giant nodes that reach the level of the lower ribs and prop up the diaphragm;
- Rapid heartbeat, dizziness and fainting are associated with compression of the inferior vena cava by nodular fibroids;
- An increase in the size of the abdomen creates not only aesthetic discomfort. This symptom indicates that the uterus has moved beyond the pelvis, and the fibroids continue to grow, squeezing the abdominal organs: intestines, liver, spleen, etc.
Serious problems arise with large nodes when the uterus reaches the size of a 12-week pregnancy or more. Below you can see a cross-sectional photo of a large fibroid. Such a tumor does not go unnoticed and causes considerable discomfort. Large nodes are not amenable to drug therapy, and the only treatment option is myomectomy.
Large fibroids in cross-section.
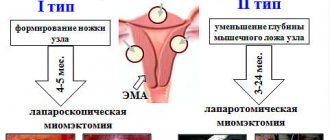
What will happen to a woman if a large fibroid is not removed? The tumor will continue to grow uncontrollably, deforming the uterus and nearby organs. Pain will become a woman’s constant companion. Living with such a disease is difficult, and sooner or later the problem that arises brings the patient to the operating table. But, if in the early stages the fibroid can be removed within healthy tissue, then in advanced cases it is necessary to remove the uterus along with the tumor. Find out more about the consequences of hysterectomy for fibroids.
Methods for pain relief
To reduce the discomfort of uterine fibroids, the following drugs are prescribed:
Antispasmodics
Relieve muscle spasms, relax the uterus, eliminate discomfort. A good effect was noticed when prescribed during menstruation and a few days before it. They can be used during early pregnancy as drugs that are safe for the growing fetus. Examples: drotaverine (No-shpa), papaverine.
Directions for use: 1 tablet orally for pain 2-3 times a day. Can be prescribed intramuscularly (in a hospital setting). The course of therapy is up to 7 days.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
They block the production of prostaglandins, substances that cause pain and inflammation. They act quickly, work for 4-12 hours, allowing you to reduce pain from fibroids both during menstruation and on other days of the cycle. Pregnant women are prescribed only for strict indications and mainly in the second trimester.
Examples: ibuprofen (Nurofen), paracetamol, diclofenac.
Directions for use: orally or intramuscularly strictly according to the instructions, without exceeding the indicated dosage. Self-administration course – up to 3 days. If pain persists, further use of NSAIDs is possible only with the consent of your doctor.
On a note
Analgin-based products cause a large number of side effects, so they are prescribed only for special indications and under the supervision of a specialist.
Hormonal medications also help relieve pain due to fibroids. Medicines selected by the doctor reduce the diameter of the tumor, eliminate pain and associated symptoms. Young women with small fibroids are prescribed combined oral contraceptives. These drugs reduce the amount of blood loss during menstruation, stabilize the level of progesterone and estrogen, which also helps reduce pain.
It is important to understand that all painkillers can only temporarily relieve a woman from the unpleasant manifestations of the disease. The absence of pain does not mean that the problem is solved. To fully treat fibroids, hormonal drugs are used or the question of surgery is raised.
Interesting video about the development of fibroids and how to treat them
Uterine bleeding, life-threatening!
Full uterine bleeding, dangerous to a woman’s health, is preceded by menstrual irregularities. In the initial stages of the disease, heavy and prolonged periods are observed. Menstruation can last 7 days or more, accompanied by nagging pain in the lower back and above the womb. Such cycle disorders lead to the development of chronic anemia with all the symptoms of the disease:
- Unmotivated weakness, decreased performance, fatigue;
- Headaches and dizziness;
- Paleness of the skin;
- Tendency to faint.
Long-term anemia depletes a woman, contributes to a decrease in immunity and exacerbation of chronic pathology. To correct this condition, iron supplements are prescribed - orally or by injection, but this is not enough to solve the problem. Medicines only remove the symptom, while the fibroid remains, continues to grow and leads to uterine bleeding. Such complications can develop in one of the following scenarios:
- Heavy menstruation lasts up to 7 days, does not stop and turns into full-fledged bleeding;
- Bloody discharge occurs in the middle of the cycle. Heavy discharge should be considered as uterine bleeding.
If you have heavy periods lasting more than 7 days, you should consult a doctor to find out the cause, otherwise the lack of timely treatment can lead to the development of iron deficiency anemia.
Women with large and/or multiple nodes bleed almost constantly. Heavy menstruation after a few days is replaced by spotting in the middle of the cycle. Acyclic bleeding lasts from one day to a week, then there is a break - and the next menstruation. Iron deficiency anemia becomes an inevitable complication. A woman’s quality of life suffers and problems arise in the sexual sphere. The likelihood of developing bleeding is high at any age.
It is also useful to read: Large uterine fibroids - is it necessary to remove them?
To learn how to distinguish dangerous uterine bleeding from normal menstruation, see the following video:
It is important to know
Uterine bleeding is a condition that threatens the health and life of a woman. If there is excessive blood loss, the patient may die. To stop it, therapeutic and diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity is performed. During the procedure, the doctor removes the endometrial layer and the bleeding stops. The resulting material is sent to the laboratory for cytological and histological examination to confirm the diagnosis.
Uterine bleeding is especially dangerous in old age, and there are several reasons for this:
- A similar symptom occurs not only with fibroids, but also with other diseases of the uterus, including malignant tumors. The simultaneous development of several diseases is possible;
- Curettage of the uterine cavity is performed under anesthesia. The use of anesthetics after the age of 50 is dangerous and can lead to disruption of the functioning of internal organs.
With fibroids, you can safely enter menopause and live to old age, but everything depends on the rate of tumor growth. A small nodule is not dangerous and usually resolves on its own during menopause. But if the formation actively proliferates and leads to the development of complications, you should not delay treatment. Uterine bleeding during menopause is an indication for fibroid removal. Find out: is it possible to stop bleeding at home?
Pelvic organ dysfunction
A similar complication occurs when the uterus reaches 12 weeks of age and occurs mainly with subserous formations growing into the pelvic cavity. The following dangerous conditions arise against the background of large fibroids:
Bladder compression
In the initial stages of the disease, the pressure of the enlarged uterus on the bladder is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Lower abdominal pain;
- Frequent urination, feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- Urinary incontinence;
- Discomfort when emptying the bladder - heaviness and pain in the lower abdomen.
A large nodular tumor compresses not only the bladder, but also the ureters. The outflow of urine is disrupted, which leads to enlargement of the kidneys and the development of hydronephrosis. The process can be one- or two-way. Symptoms increase slowly over many years. Over time, swelling, increased blood pressure, and pain in the lumbar region are noted. Without treatment, prolonged clamping of the ureters threatens the development of renal failure.
Compression of the ureters by large fibroids.
Intestinal compression
A tumor growing towards the pelvis and abdominal cavity puts pressure on the organs of the digestive tract. First of all, the rectum suffers, then the rest of the gastrointestinal tract. Constipation occurs, accompanied by a feeling of incomplete bowel movement, pain in the lower abdomen, and flatulence. If the fibroid is not operated on, the growing tumor can completely block the lumen and lead to intestinal obstruction. In the future, this threatens intestinal necrosis and may become a reason for its resection. Such complications rarely occur, since at this stage the fibroid makes itself known through uterine bleeding, and the woman somehow ends up on the operating table.
Associated symptoms of the disease
Large tumors lead to a significant enlargement of the uterus, which inevitably affects the woman’s health. The uterus puts pressure on the abdominal organs, props up the diaphragm, which provokes the appearance of various unpleasant symptoms:
- Pain under the right rib with compression of the bile ducts and dysfunction of the gallbladder;
- Shortness of breath and difficulty breathing due to pressure on the diaphragm;
- Heartburn and belching when the stomach is not working properly;
- Pain around the navel, in the left or right side due to compression of the intestines, disruption of its patency, chronic constipation;
- Interruptions in the functioning of the heart due to increased stress on the body.