Uterine fibroids are a common disease among women all over the world. This is a benign tumor that can cause great discomfort. The diagnosis of “intramural uterine fibroids” indicates that the tumor is located in the middle muscle layer.
In some cases, one or more nodules form in different parts of the muscle tissue of the uterus. Another option for the development of the disease is the formation of many seals in one place, connected to each other.
The more the tumors increase in size, the more seriously this affects the condition of the uterus and neighboring organs.
Accurate diagnosis, timely and appropriate treatment play an important role in a positive outcome.
Causes
Medical science has not yet determined exactly why in a woman’s body the muscle tissue of the uterus begins to degenerate, turning into nodules. So far, scientists have agreed that in each individual case the development of pathology occurs under the influence of various factors. The main causes of uterine fibroids are as follows:
- Excess estrogen. Hormonal disorders are usually placed first on such lists. While studying the disease, scientists noticed that during menopause, the nodular cells begin to gradually dissolve. In addition, hormonal drugs definitely influence the growth of uterine fibroids. If they are chosen correctly, the tumor will decrease in size.
- Mechanical damage. External interference in the structure of the muscle tissue of the uterus can provoke the degeneration of these cells. It has been noticed that intramural fibroids often form after various types of operations on the female reproductive organs, including abortions and curettage.
- Women's diseases. The formation of compactions in the uterus is sometimes associated with inflammatory processes. Tumor formation is also often explained by the presence of erosion, polyps and endometriosis.
- Unhealthy Lifestyle. It is generally accepted that nutrition, habitat and bad habits play an important role in the development of intramural fibroids.
- Chronic diseases. Scientists have noticed a connection between obesity and diabetes mellitus and the formation of uterine fibroids in women.
- Stress. It is believed that overexcitation of the nervous system can give impetus to the development of fibroids.
- Heredity. It has been established that a predisposition to the formation of the disease is often transmitted from mother to daughter.
Due to the last of these factors, a woman experiencing uterine fibroids should regularly check her daughter. It’s worth starting from adolescence.
General information
Uterine fibroids are a hormonally dependent benign neoplasm. Its formation is associated with increased levels of ovarian hormones (estrogen and progesterone), uterine injuries and metabolic disorders in the body.
Most often, the myomatous node is located on the anterior wall of the uterus. In relation to the myometrium, the tumor can grow:
- Interstitial - spreading within the muscle layer.
- Subserous - in the submucosal layer, located in the organ cavity.
- Submucosal - the node is localized in the upper, serous layer of the uterus.
Myoma on the anterior wall of the uterus in most cases is located in the body of the organ, but sometimes it can grow in the cervical and isthmus, uterine ligaments, and also grow into other organs.
The severity of symptoms of fibroids of the anterior wall of the uterus increases with its size.
The size of the node is usually described in centimeters and weeks of pregnancy, in which the uterus has a similar size. The following types of nodes are distinguished:
- Small – up to 4-6 weeks of pregnancy (less than 4 cm).
- Medium - no more than 10 weeks of pregnancy (4-6 cm).
- Large – from 12 weeks of pregnancy (6 cm or more).
- Giant – over 20 weeks of pregnancy (from 20 cm).
Symptoms
The formation of an intramural node in the uterus is not always accompanied by obvious signs. Much depends on the number and size of tumors. A woman needs to closely monitor her reproductive system, identifying changes in its functioning. Thus, the following symptoms may indicate the presence of benign lumps in the muscle tissue of the uterus:
- heavy and prolonged menstrual bleeding;
- bleeding in the middle of the cycle;
- feeling of tightness in the lower abdomen;
- pain in the uterine area, radiating to the lower back and sometimes to the legs;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- stagnation of fluid in the lower extremities due to impaired lymph flow;
- problems with bowel movements;
- intense pain during menstruation;
- inability to conceive a child.
The changes caused by intramural uterine fibroids are influenced by its location, size and growth rate.
If the disease is asymptomatic, examination using safe techniques will help identify the tumor.
A woman who does not undergo regular examination by a specialist runs the risk of encountering an advanced form of the disease and its complications.
Features of subserous fibroids
Photo - subserous fibroid
This type of hormone-dependent tumor forms in the muscle layer of the uterus. It grows and develops from the outside towards the abdominal cavity. The number of nodes and their sizes may vary. The knot is usually attached to the tissue with a wide base. Sometimes located on a thin stalk.
Women of reproductive age are susceptible to the disease. It develops slowly and without any special clinical manifestations. Danger arises when the leg is twisted. Necrosis of the myomatous node develops. In the dead tumor tissues, swelling, degeneration, inflammation and hemorrhage appear.
In this case, symptoms occur suddenly. The woman is worried about acute pain in the abdomen, reminiscent of cramps, nausea, vomiting, fever and fever.
CAREFULLY! Without appropriate treatment, progressive necrosis will lead to peritonitis.
Reasons for the formation of subserous formations
Subserous uterine fibroids appear in the presence of the following factors:
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- hereditary predisposition;
- multiple abortions;
- hormone imbalance and menstrual cycle disruption (menopause);
- traumatic disorders of the myometrium (childbirth, pregnancy, heavy menstruation);
- inflammation of the reproductive system;
- stress, nervous breakdowns, excess weight, smoking.
When several causes combine, the likelihood of the disease increasing.
Symptoms of the disease
The growth and enlargement of the subserous node is accompanied by pain in the patient. They appear above the pubis, in the lower abdomen with a pulling, aching character. They worsen after active physical exertion, overwork, hypothermia, or being in an uncomfortable position for a long time.
The development of the disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- bleeding between menstrual cycles;
- prolonged and heavy discharge during menstruation;
- periodic pain in the lower abdomen, which increases with the growth of fibroids;
- dizziness and loss of consciousness.
Complications
Intramural uterine fibroids are not a malignant tumor, but treatment should not be delayed. As a rule, women do not rush into this if they do not experience unpleasant symptoms. But they must understand that uterine fibroids often progress without proper intervention. The signs described above gradually appear, and serious complications may develop.
Lack of timely treatment threatens the beginning of the process of tumor cell death. In this case, severe poisoning of the body with toxins occurs and immediate hospitalization is required. In addition, due to heavy bleeding, which is a symptom of the disease, a woman may develop anemia.
Neighboring organs suffer from compactions in the uterus, so the formation of thrombosis in the veins of the lower extremities and infertility cannot be ruled out.
How is the disease expressed?
Signs of intramural leiomyoma can appear only in advanced stages of the disease. At first, the woman will not experience any problems.
Only over time will disruptions in menstruation begin to appear, characterized by an increase in the duration of the cycle, and the volume of hemorrhages will also increase.
Due to the appearance of leiomyoma, even a certain stage and signs of anemia can form:
- hair will become dull and brittle;
- weakness, fainting will appear, the patient will begin to get sick, attention will wander;
- the skin will become pale and take on a white tint;
- tachycardia will appear with minimal exertion;
- constant nausea, lack of appetite.
Depending on the rate of growth of the node, the patient may show signs of a violation of the location of the internal organs. There will be a frequent desire to urinate due to the pressure of the tumor on the bladder.
Diagnosis
The initial detection of a tumor in the muscle tissue of the uterus usually occurs during a standard gynecological examination. Using a mirror, a specialist can see fibroids almost anywhere. In some cases, the lump is not visible in this simple way, even when there are symptoms indicating it. In any case, to clarify the diagnosis, additional research is prescribed using effective methods.
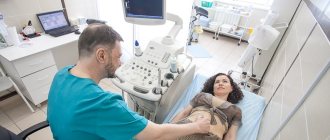
Transvaginal examination
This type of diagnosis is performed using ultrasound radiation. During the procedure, the patient sits in a gynecological chair and a device sensor is inserted through her vagina. This technique is more effective in examining fibroids than an examination that involves moving a probe across the abdomen. As a result, the exact location, size and density of the tumor is determined.
Ultrasound is a highly informative diagnostic method, often used in gynecology. It is available to every patient, as it is inexpensive and is carried out in many hospitals. Ultrasound radiation is absolutely harmless to humans, so examinations with its participation can be carried out at any frequency. There are no contraindications to the technique. In addition to initial diagnosis, ultrasound is used to monitor changes during treatment.
Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is an additional diagnostic method. This is an invasive procedure that has a number of contraindications. It is carried out using a hysteroscope equipped with a camera, which is inserted into the uterus through the vagina. The method determines submucosal uterine fibroids with 100% accuracy.
An anesthetic drug is injected into the cervix before the examination. The image from the camera is immediately transferred to the monitor. Having noticed a suspicious area, the doctor can perform a biopsy, that is, take a piece of tissue using a hysteroscope for a detailed examination. Thus, diagnosis and treatment of uterine fibroids in some cases can be carried out simultaneously.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
MRI often plays an irreplaceable role in the study of intramural uterine fibroids. This diagnostic method is prescribed at the final stage of the examination, when previous methods did not provide a clear description of the disease. MRI allows you to determine the exact location, size and type of formed nodes. Even compactions several millimeters in size are detected.
To check the health of the uterus using magnetic resonance imaging, an MRI of the pelvis is prescribed. Additionally, it becomes possible to assess the condition of the urinary, lymphatic and circulatory systems, intestines, ovaries and vagina.
This examination method is highly informative, as it shows organs in layer-by-layer sections. A computer program stitches the individual frames together into a single image, creating a three-dimensional model. The disadvantage of magnetic resonance imaging is the use of x-rays. This limits the frequency of diagnosis and the number of those for whom it can be indicated. Thus, MRI is not prescribed to pregnant women and children unless absolutely necessary.
Diagnostic methods
You should consult a doctor if typical symptoms appear. The gynecologist performs the following examination:
- inspection with mirrors
- two-manual examination
Using palpation, the gynecologist can immediately detect nodular formations. After this, an ultrasound is prescribed to confirm the diagnosis. Additional diagnostic method: transvaginal sensor. It allows you to determine the location of nodes, their sizes, and condition.
Hardware diagnostics
Ultrasound alone is not used to diagnose fibroids, since a node in the muscle layer may not be displayed on the screen. An ultrasound will show endometriosis, which simultaneously develops with fibroids.
The next research method is hysteroscopy. It is reliable even in the initial stages, allows you to determine the size and condition of the node, and prevent necrosis.
What is myometrium: concept, structure and features of recognition in medical research
MRI and CT also give good results. A photo of all nodes, their sizes and location is taken. The method makes it possible to determine which layers are affected by fibroids and whether there is an impact on neighboring organs.
If there is a suspicion of an ovarian tumor, then it can be differentiated from fibroids using laparoscopy. This is necessary because fibroids and ovarian tumors have similar symptoms.
Treatment of intramural fibroids
A woman with intramural uterine fibroids should rely entirely on the experience of her doctor. When creating a treatment strategy, he will definitely take into account the following features of the disease:
- size, localization and intensity of compaction development;
- symptoms of pathology;
- accompanying illnesses;
- woman's age.
The patient’s age is of interest to the doctor due to the fact that some treatment methods do not make it possible to preserve reproductive function. The woman’s own view on this issue is also important.
Hormone therapy
Having carefully studied the patient’s hormonal background, the doctor can prescribe medications to correct it. This treatment is considered classic; it can stop the growth of intramural uterine fibroids and even begin the process of reducing it. The method is effective in cases of small tumors.
Hormonal therapy must be carried out very carefully, since additional disruptions in this system can lead to aggravation of the problem or the occurrence of other disorders in the body. The main goal in most cases of treatment for uterine fibroids is to suppress the production of the hormone estrogen.
How to treat leiomyoma?
In the early stages, it is necessary to focus efforts on stopping the growth of the pathology. Often, leiomyoma simply resolves and disappears without any surgical intervention.
Observation is necessary before initiating drug treatment. Indications for conservative treatment of uterine pathology are:
- manifestation of a number of characteristic signs of leiomyoma;
- increase in pathology;
- existing risk of complications during surgery;
- reducing the size of fibroids immediately before surgery.
Treatment with medications is possible only when the tumor has not yet reached the size corresponding to 12 weeks of pregnancy.
Non-hormonal remedies for getting rid of uterine leiomyoma
- hemostatics to prevent hemorrhages;
- antispasmodics (used as a pain reliever);
- medications for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia;
- drugs that provoke frequent contractions of the uterus;
- antioxidants, vitamins;
- herbal medicine for accelerated tissue regeneration.
Hormone therapy
If the size of the pathology is small, you can get rid of leiomyoma using hormonal therapy:
- young girls use Duphaston and Utrozhesan;
- Gestrinone and Danazol are taken by women who are in a premenopausal state;
- Zoladex, Buserelin - agents that suppress estrogen production;
- hormonal contraceptives that inhibit the development of the disease.
Prevention
Preventive measures against intramural uterine fibroids are closely related to the causes of its development. A woman should avoid abortions, which negatively affect hormonal levels. Experts advise giving birth between the ages of 20 and 30. If possible, reduce the negative influence of the environment and stress.
In addition, every woman should be careful about her health - undergo regular examinations and promptly treat inflammation in the genitourinary system. Women over 30 need to listen especially carefully to themselves.
Fibroids and pregnancy
Multiple small nodes do not affect the possibility of conception and the course of pregnancy. If the cause of the disease is a lack of hormones, then their levels normalize during pregnancy and the problem goes away.
Large nodes have a negative impact on the course of pregnancy. Possible complications: miscarriages, premature birth, bleeding, placental abruption, weak fetus.
Ultrasound alone does not give a reliable result if the node is located in the muscle layer. During pregnancy, the node stretches and its borders become stretched and invisible. This is the reason why the nodes come back after pregnancy.
The course of pregnancy is influenced by the size and location of the intramural node. The node located near the placenta has a negative effect. A tumor can lead to infection of the fetus, block the supply of nutrients and oxygen, and provoke a miscarriage.
Reviews
A huge number of women encounter intramural uterine fibroids in their lives. Some of them willingly share their experiences, features of the prescribed treatment and results.
According to the results of the ultrasound, they discovered a nodule in my uterus measuring 12 mm. At the consultation, the doctor said that this is a benign formation that will not interfere with conception and childbirth. In addition, he added that after childbirth it can resolve on its own. No treatment was prescribed.
Olga
Not long ago, menopause began, and the fibroids immediately began to gradually decrease. I hope it will disappear completely soon.
Natalia
More than a year ago, I had several nodules removed from my uterus. The largest had a diameter of 6.5 cm. After using the laparoscopic method, three tiny holes remained on the stomach. 6 months later I became pregnant, everything is going as it should.
Oksana
I was diagnosed with uterine fibroids 3.5 cm in diameter after a miscarriage. The doctor said it was a small tumor. I received recommendations from him to do an ultrasound every 6 months to monitor the situation, not to bask in the sun, and not to go to the bathhouse. Pregnancy was prescribed as a “treatment”.
Lily
Why is uterine fibroid dangerous for a woman?
Any neoplasm can lead to serious consequences if the pathology is not detected in time and treatment is not started. The main danger is twisting of the leg; this symptom leads to necrosis and cell death, which without proper treatment very quickly leads to death.
If a tumor in a woman’s abdominal cavity begins to collapse, then there is no way to cope with such a symptom without surgery. In addition, the rupture of the tumor itself is very dangerous for the patient. In such a situation, a woman not only feels severe pain, but also uterine bleeding appears, which is very difficult to stop. What diagnostic methods will help to accurately determine the location of intramural-subserous fibroids of the body of the reproductive organ?