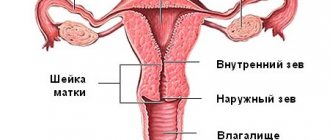
Uterine fibroids are a benign hormone-dependent tumor of the female reproductive system. Typically characterized by slow development. One muscle cell begins to divide, creating a knot in the uterus. The pathology is considered very common. Occurs in approximately 30% of women. Despite the rarity of malignant transformation, the disease can significantly reduce quality of life. Let us note that numerous medical studies of the last decade have radically changed the attitude towards this pathology. The Miracle Doctor clinic in Moscow provides all types of diagnosis and treatment of uterine fibroids and other diseases of the female reproductive system. The use of state-of-the-art equipment allows our specialists to identify even the smallest tumors and thereby provide timely assistance.
What is FUS ablation
Focused ultrasound is a method used to remove nodes formed in the uterus without making incisions or using anesthesia. Myoma is destroyed under the influence of waves that pass through the skin and muscles directly to the site of the disease, without affecting healthy tissue. This method is a good alternative to traditional operations.
A precisely directed ultrasound beam, for a short amount of time, seems to evaporate damaged cells, heating them to a temperature at which they begin to collapse. After this, the necessary fragment of the node dies. Thus, when the same action is repeated many times, all tumors are removed.
FUS ablation is performed under MRI guidance to maintain the required degree of heating and accuracy of execution.
The procedure is carried out when symptomatic fibroids develop, that is, when the course of the disease causes many complaints that significantly reduce the woman’s standard of living. Treatment is prescribed in the presence of the following pathologies:
- Heavy menstruation that lasts more than seven days. This condition can lead to the development of anemia, which means increased fatigue and inability to withstand even mild physical activity.
- Discharge that appears in the middle of the cycle and contains blood.
- Large knot. It puts pressure on internal organs, in particular on the bladder, which complicates the process of deurination. Sometimes this situation can lead to a delay in the outflow of fluid from the kidneys and the occurrence of pyelonephritis.
- Fibroids that develop in the posterior wall of the uterus. As the tumor increases in size, it will put pressure on the intestines, which can cause pain in the rectum or complicate the process of defecation, that is, cause constipation.
The onset of fibroid development is asymptomatic. It is discovered accidentally when an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs is performed.
Usually, when a single small tumor appears, it is treated with medications, but if the growth cannot be stopped, then FUS ablation is prescribed.
Types of surgery for uterine fibroids
There are several different surgical approaches to treating fibroids. The types of surgery will depend on the location of the fibroid. But first, the doctor will recommend conservative treatment methods. In cases where medications and other treatments do not help, surgical interventions are considered, such as:
Myomectomy
This is a surgical procedure in which fibroids are removed. Depending on its location, the surgeon may also remove other tissue. Surgeons offer various methods of myomectomy.
The traditional method is quite invasive as it uses a relatively large incision. This incision can go from the navel to the bikini line or run horizontally along the bikini line. Some surgeons perform laparoscopic surgeries, which use smaller incisions but require more skill. Although myomectomy preserves the uterus, women who want to become pregnant should talk to their doctor about possible complications. New fibroids can develop after a myomectomy, so this is not a permanent solution.
Radiofrequency ablation
Radiofrequency ablation destroys fibroids using electrical current, laser, cold therapy, or ultrasound. This requires a small incision. However, it can cause dangerous complications such as scarring and infection, so doctors do not recommend it for those planning future pregnancies.
Endometrial ablation
Endometrial ablation does not remove the fibroid itself, but it can help with severe bleeding. During an ablation, the surgeon uses a number of techniques that include heat, electric current, freezing, lasers, or wires to destroy the lining of the uterus. This procedure is less invasive than some other surgical options. Sometimes doctors can even perform it on an outpatient basis. Removing the endometrium may prevent women from becoming pregnant in the future, so it is not a good option for those who would still like to have children.
Uterine artery embolization
The doctor can detect blood vessels that feed the fibroid. During surgery, the doctor inserts a tube into the blood vessels supplying the fibroid and then injects tiny particles that block the fibroid's blood supply. Lack of blood leads to fibroid shrinkage. This procedure is carried out both in the hospital and in the outpatient clinic, the recovery is quite fast. Fibroids usually do not grow back after embolization.
While pregnancy is sometimes possible after fibroid embolization, doctors don't know enough about the risks. Therefore, this procedure is not recommended for women wishing to become pregnant.
Focused ultrasound (FUS) ablation
With FUS ablation, the doctor uses ultrasound, which destroys the fibroids. This procedure targets only the fibroid and does not affect surrounding healthy tissue. The doctor does not recommend this surgery if the fibroids are too large or close to the bones or intestines. This technique may be a good option for women who are planning to become pregnant, since the uterus is not damaged.
Hysterectomy
A hysterectomy is an operation to remove the uterus and sometimes the ovaries. A hysterectomy permanently eliminates uterine fibroids. This procedure is not suitable for women who are planning a future pregnancy as it removes the uterus.
The surgeon may perform a laparoscopic hysterectomy, which uses several small incisions and a tiny camera to view the inside of the abdomen. An open hysterectomy requires a large incision between the belly button and the bikini line.
Another option is a vaginal hysterectomy, which is preferred by most people. In this procedure, the surgeon will remove the uterus through the vagina. A vaginal hysterectomy may not be possible if the uterus or fibroids are too large to pass through the vagina. Women who have an open hysterectomy may have a long recovery time. Doctors usually recommend a hysterectomy only for those whose fibroids are very large.
Morcellation
Morcellation is a procedure that reduces the size of fibroids so that a surgeon can remove them through a tiny incision in the abdomen. Your doctor may use morcellation during a myomectomy, hysterectomy, or other surgery. However, morcellation has significant risks.
pros
Since this method is not invasive, it does not have all the complications that are typical for surgical treatment, namely, intestinal obstruction, inflammation or adhesions will not develop, and there will be no blood loss. In addition, among the advantages of the procedure the following are noted:
- After this treatment method, the possibility of childbearing remains.
- There will be no scars left.
- Healthy muscle fibers will not be affected.
- There is no need to use anesthesia.
- You can influence several uterine nodes at the same time.
- The size of the fibroid does not affect the ultrasound treatment process.
- No severe side effects.
If a relapse develops, it is recommended to repeat the procedure, although the risk of fibroids after FUS ablation is only 10%.
Other Treatment Options
In most cases, your doctor may suggest other treatments before recommending surgery.
Treatment for fibroids includes:
Birth control pills
Hormonal contraceptives can slow the growth of fibroids and prevent heavy, painful periods.
Painkiller
Pain relievers can help with pain, especially occasional fibroid pain.
Iron supplements
Women with heavy bleeding that causes anemia may benefit from iron supplements.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists
These drugs can shrink fibroids. Some doctors recommend them before surgery to make fibroid removal easier.
Minuses
The use of focused ultrasound has the following disadvantages:
- The duration of the procedure is on average up to six hours.
- There is a risk of recurrence of nodes. This is due to the fact that undestroyed areas of damaged tissue may remain.
- High price.
- Insufficiently qualified specialists. Since this is a new technique for Russia, it takes time to master it.
- Dependence of the achieved result on the type of educational structure.
This method is innovative and very promising. Over time, it will be used in all clinics as an alternative to surgical interventions.
Who needs surgery?
Not all women with fibroids need treatment. In most cases, there is no reason to treat fibroids that do not cause any symptoms. Some women can successfully treat symptoms with hormonal birth control.
Before considering surgery, a woman should learn about other treatment options. Your doctor should provide information about the risks and benefits of each surgical procedure. Fibroids may shrink or disappear after menopause, so women approaching menopause and whose symptoms are not severe may want to delay treatment.
The benefits of surgery depend on the type of surgery. For example, there is no chance that fibroids will grow back after a hysterectomy. However, it may appear after other procedures.
Some benefits include:
- reduction of bleeding
- reduction of pain or pressure
- fibroid removal
Most women who have fibroid surgery have no serious complications, but they may experience pain or bleeding after surgery and will need time to recover. However, a small number of people do experience serious complications. Certain complications and their likelihood depend on the type of surgery and may include:
- risks associated with anesthesia
- infections
- heavy bleeding
- unsuccessful operation
- fibroid growth
- damage to the uterus or other surrounding organs
- in case of morcellation, spread of cancer
Contraindications for FUS ablation
The procedure is not recommended for women who are protected with an intrauterine device, who have a large number of scars on the anterior wall of the peritoneum that appear after the liposuction procedure in the abdominal area. If the fibroma is located close to the sacrum, there is a risk of injury to the sciatic nerve. Other contraindications include the following:
- Weight more than 100 kg.
- Presence of a pacemaker or metal implants.
- Malignant tumors located on the genitals.
- An inflammatory process occurring in the uterus, complicated by elevated temperature.
- Severe form of claustrophobia.
- Exacerbation of chronic liver and kidney diseases.
- Pregnancy.
- The presence of disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
- Individual intolerance to contrast agents.
- Age under 18 years.
- More than five neoplasms.
Indications and contraindications for non-surgical treatment of fibroids
Sometimes even surgical intervention cannot guarantee a successful outcome: according to statistics, tumor recurrence is observed in 15% of cases. The main goal of non-surgical treatment of uterine fibroids is to restore blood supply to the ovaries and hormonal balance.
Indications
- Pregnancy planning. Information about the location of the fibroids is a decisive factor in making a decision. If the tumor leads to deformation of the uterus, then conception is undesirable, since the development of nodes can lead to expulsion of the fetus and heavy bleeding. Drug therapy can make it possible to reduce the node, which is considered sufficient when planning pregnancy.
- Moderate symptoms. The primary goal is to preserve reproductive function for young women. If obvious discomfort occurs and anemia develops, then the patient may experience chronic fatigue, drowsiness, dizziness, loss of strength and increased irritability. Taking medications + iron supplements helps restore hemoglobin, reduce the myomatous node and normalize the amount of bleeding.
Among alternative methods of treating uterine fibroids, hirudotherapy, osteopathy, and acupuncture are also considered. Mainly all measures are aimed at eliminating unfavorable factors that contribute to the development of the disease. However, in most cases they are ineffective. If you have questions or doubts about the prescribed therapy, our clinic specialists are ready to advise you at a convenient time.
Contraindications
- Precancerous conditions are a combination of fibroids with adenomyosis, hyperplastic processes in the uterus (proliferation of mucous tissue).
- Recurrences of hyperplasia, polyps, severe pain, heavy bleeding.
Which doctor performs FUS ablation and where?
Such a procedure is carried out only in a specialized clinic located in large cities of Russia, where there is all the necessary equipment and a doctor - an endovascular surgeon or an FUS-MRI specialist with sufficient knowledge.
In addition, FUS ablation is performed in foreign medical institutions, for example, Turkey, the USA or Israel, where this method has been used for a long time, and doctors have experience in performing such operations. In the CIS countries, the use of focused ultrasound treatment is not popular.
Benefits of the procedure
Today there are several effective ways to combat uterine fibroids. FUS-MRI ablation is a relatively new, but fairly well-known treatment method. Has the following advantages:
- does not require incisions or other violations of the integrity of soft tissues;
- not accompanied by bleeding;
- allows you to delete several nodes at the same time;
- does not leave scars or other damage to the uterus;
- performed without anesthesia;
- painless;
- reduces the risk of relapse.
FUS ablation is suitable for patients intolerant to anesthesia. In exceptional cases, with severe fear, local anesthesia is used. The absence of damage to the reproductive organs allows you to avoid problems with pregnancy and childbirth in the future.
Unlike abdominal operations, FUS ablation does not have a long rehabilitation period. If no complications are observed, then the woman is allowed to leave the hospital a few hours after the procedure.
When a woman is diagnosed with several myomatous nodes, the duration of therapy will not increase. FUS ablation is well tolerated and rarely causes complications. During the procedure, the patient is conscious, controls her well-being and informs the doctor about negative symptoms. When the latter are identified, any manipulations are stopped.
Price
The cost of the procedure will depend on the clinic in which the treatment is carried out, as well as on the characteristics of the disease. Approximate prices must be clarified with the institution’s specialists, since the cost can vary between 55-100 thousand rubles . In order to reduce costs, all preliminary examinations can be done free of charge at the antenatal clinic at your place of residence.
Treatment in European clinics will cost much more, but it involves patient management at all stages of examination and therapy, as well as an increased level of service. If the patient does not speak a foreign language, an interpreter will be provided.
Venue and cost
FUS ablation is an expensive medical procedure and is therefore most often performed in private clinics. Budgetary medical institutions are rarely equipped with MRI machines and other instruments. The procedure is performed by a gynecologist and a specialist working with a tomograph.
The cost of FUS ablation largely depends on the location and qualifications of the doctors. It is influenced by the prestige of the clinic, the region in which it is located, the quality of the equipment and medications used. The price varies from 50 to 120 thousand rubles. Diagnostic procedures, accommodation and meals in the hospital are paid separately.
A non-invasive way to combat uterine fibroids is a good replacement for surgery. The absence of a long rehabilitation period allows a woman to quickly recover and return to an active life.
Preparation
FUS ablation requires a thorough examination by specialists, as well as:
- Undergoing a general examination by a gynecologist. To confirm the diagnosis and exclude errors, the doctor must first collect all the information about the course of the disease and conduct an examination on the chair. If necessary, an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs will be prescribed.
- Clarification of the size of fibroids and its location in relation to other organs. To do this, it is recommended to do a tomography, and the type of node and how amenable to treatment it is will also be assessed.
The effect of the impact depends on the structure of the node and its ability to absorb energy. Based on this, all neoplasms are divided into several types:
- Dark areas are areas of tissue that have the most intense color in MRI images. This color corresponds to a simple formation that does not have edema and is well amenable to FUS ablation. To remove them, a small number of impacts and a low level of wave power are used.
- Grays are islands that are characterized by stromal edema and are less responsive to treatment. It will be carried out in several stages: first drying, then evaporation.
- White areas are hyperintense areas that cannot be treated at all due to their low ability to absorb energy.
After a thorough examination has been carried out, doctors will have to choose which option of ultrasound ablation should be used in each specific case.
Advantages and disadvantages
FUS ablation allows:
- preserve reproductive functions intact;
- treat large fibroids without resorting to surgery;
- prevent relapse of the disease;
- remove myomatous formations without scars;
- remove fibroids without traumatizing healthy areas of the mucosa;
- delete several nodes at once;
- remove fibroids without consequences or side effects;
- carry out the removal procedure without the use of anesthesia;
- recover after the procedure as soon as possible.
Despite the fact that FUS ablation is a safe and affordable method of treatment, there are still contraindications to the procedure.
As for the disadvantages, these include the fact that the procedure is difficult for formations that have a heterogeneous structure, partitions, as well as calcifications that contribute to the reflection of ultrasonic waves.
In addition, the following complications may develop:
- slight increase in general body temperature (short-term);
- redness of the skin at the site of exposure to rays;
- dyspeptic disorders;
- discomfort in the lumbosacral region.
Disadvantages also include the duration of the procedure and its price.
How to properly perform FUS ablation, duration of the procedure
The process of ultrasonic exposure does not require careful preparation and occurs as follows:
- On the day of the procedure, you may eat and drink liquids.
- Before the procedure begins, a catheter is placed in the vein to administer medicinal solutions.
- You need to wear special compression stockings on your legs.
- The patient is placed in the MRI chamber and placed stomach down on a gel-filled pillow.
- They give you a button in your hand, with which you can inform the clinic staff about inconveniences or stop the process to adjust the power of exposure.
The duration of the procedure depends on the volume of formation and the number of nodes.
Price
The average price of FUS ablation of uterine fibroids is about 46-117,000 rubles. The final cost depends on the degree of damage to the uterus, the area of treatment, the status of the clinic and the doctor performing the procedure.
FUS ablation of a myomatous tumor is considered a very effective alternative to surgical removal of fibroids; however, such a procedure remains minimally traumatic for body tissues, because there are no incisions, no pain, no anesthesia is needed, and recovery lasts a couple of days. Therefore, the technique is becoming increasingly popular, especially among young patients.
Video about FUS ablation of uterine fibroids:
How does a woman feel during FUS ablation?
Usually the manipulations are painless. The patient is monitored by an anesthesiologist who monitors all vital signs.
Sometimes the following symptoms may appear:
- Intense heat to the point of burning.
- Nagging pain in the abdominal area.
- Unpleasant sensations in the sacrum, radiating to the leg.
The occurrence of such signs should be reported to the nurse.
After the end of ultrasound therapy, a follow-up examination using MRI is required. Then the woman is sent to the ward, where she remains for several more hours until the effect of the sedatives administered to her wears off.
Recovery
Since this examination method is painless, it does not require long-term rehabilitation.
After the manipulation, MRI monitoring is necessary , which is recommended to be done after three, six, and then a year.
Women should remember that within 60 days there is a high probability of pregnancy, which is extremely dangerous in such a situation. In this case, you should carefully protect yourself .
Once and for all?
Important
Doctors do not accept for FUS therapy women with malignant tumors of the uterus and ovaries, those who have cardiac pacemakers (the strong magnetic field of ultrasonic magnetic resonance can disrupt this device), as well as patients who have undergone abdominoplasty: the scar left after it on the abdominal wall may cause burns when interacting with ultrasound. The effect of the procedure is assessed immediately upon completion. For doctors, the main thing is not just to burn out the fibroid, but to deprive it of nutrition and not give it a chance for further growth. Experts say: even if 40 to 50 percent of the myomatous node is coagulated, we can say with confidence that fibroids (except for complex, advanced cases) will not grow.
Some time after the procedure, the tissue that has died from thermal exposure is resorbed, and the destroyed cells are utilized through the blood. No rehabilitation is required after ultrasonic evaporation of the myomatous node. The patient goes home the same day after the procedure. On the second or third day, however, the temperature may rise (as a reaction to coagulation), but, as a rule, it quickly normalizes.
A woman who has gotten rid of fibroids should see a doctor in a month, then three, six months and a year after the procedure. For control.
Those who have undergone remote ablation of fibroids note that their pain has disappeared, their menstrual cycle has normalized, heavy, debilitating bleeding has stopped, and patients who complained of frequent and painful urination have noted a significant improvement in their condition.
Reviews from women about FUS ablation of uterine fibroids
She was treated with hormonal pills prescribed by a gynecologist. The effect was zero, since the nodes continued to grow anyway. I was terribly afraid to do a regular operation, and I can’t tolerate anesthesia very well. When I learned about what was done without incisions or anesthesia, I decided to undergo the procedure. It turned out to be lengthy, but as a result everything was successfully removed.
Marina, 28 years old
I had FUS ablation and regretted it. A few months later the tumor reappeared. Of course, I was warned that this could happen, but it’s still offensive. So much money was spent, and now we have to start all over again.
Oksana, 44 years old
When my fibroid was discovered, it had already grown to a huge size. There was no choice - they were removed by evaporation. I was satisfied. I came home that same day. It's okay for now.
Larisa, 35 years old
Indications for passing
FUS ablation is recommended in cases where the disease has a pronounced clinical picture. Typically the patient complains of:
- heavy menstruation;
- malfunctions of the pelvic organs;
- spotting on “dry” days of the cycle.
FUS ablation is not only an effective but also a safe procedure, but it has contraindications
, namely:
- installed intrauterine contraceptives;
- malignant tumors in the uterine cavity;
- ovarian cysts;
- subserous on a thin stalk, as well as fibroids less than 2 cm, localized less than 10 cm from the anterior abdominal wall and 4 cm from the sacrum;
- diagnosed infertility;
- adhesions;
- claustrophobia;
- overweight (II-III degree);
- strong posterior bend of the uterus;
- pathologies of the heart, liver, kidneys during exacerbation;
- installed metal prostheses, pacemakers.