03/19/2018 Category: Diseases and complications Author: Alena Lomakina
In an effort to have a child, many couples face numerous difficulties, and one of them is the anatomical features of the structure of the internal reproductive organs. Such a phenomenon as a saddle uterus occurs in approximately 0.5% of women of childbearing age, and may either have no effect on the ability to conceive or represent a serious obstacle in this matter.
- Causes of pathology
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
Video. Ultrasound image of the saddle uterus
- Correct positions for conception
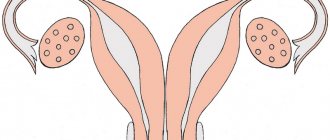
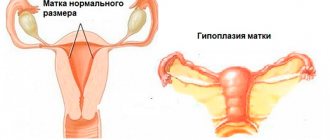
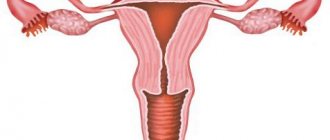
Saddle uterus - structural features compared to the norm
The female uterus is a hollow muscular organ designed to bear a fetus during pregnancy. Its average weight is 50 grams (for those who have given birth - up to 100 grams), and in shape it resembles a pear, flattened in front and behind. The organ consists of several parts:
- body - the main part of the uterus, resembling a triangle in shape, located with the wide part upward. The upper angles connect to the fallopian tubes;
- bottom - the upper wall of the organ, which is the line of entry of the fallopian tubes;
- The cervix is a continuation of the body that passes into the vagina (the narrow part located at the lower apex of the schematic triangle of the body of the uterus).
Normally, the fundus of the uterus is flat and is only part of the organ, without creating any obstacles to the performance of its functions. But there are a number of pathologies associated with the anatomical structure, in particular an arcuate or saddle-shaped uterus. In fact, this is one of the varieties or a mild form of the bicornuate structure of the organ; the diagnosis of saddle uterus implies deformation of the fundus in the shape of a saddle of varying degrees of severity. In this case, there is an expansion in the cross section, and although the splitting of the organ into 2 horns is practically not expressed, this can cause certain difficulties in the implementation of the main function.
The saddle uterus is the mildest form of anatomical pathology of the uterine structure
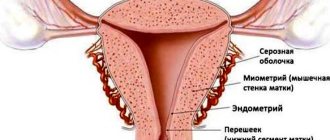
Location and shape of the uterus
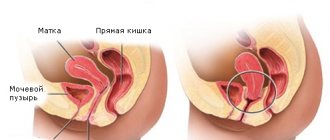
The uterus is located in the pelvic cavity between the bladder in front and the rectum in back. The shape of the uterus has been compared to a pear, flattened from front to back. Its length is about 8 cm, weight 50–70 g. The uterus is divided into a body, an upper convex part - the fundus, and a lower narrowed part - the cervix. The cervix protrudes into the upper part of the vagina. In a newborn girl, the cervix is longer than the body of the uterus, but during puberty the body of the uterus grows faster and reaches 6–7 cm, the cervix - 2.5 cm. In old age, the uterus atrophies and noticeably decreases.
The body of the uterus forms an angle with the cervix, open anteriorly (towards the bladder) - this is a normal physiological position. The uterus is held in place by several ligaments, the main of which, the broad ligaments of the uterus, are located on its sides and extend to the side walls of the pelvis. Depending on the filling of neighboring organs, the position of the uterus may change. So, when the bladder is full, the uterus deviates posteriorly and straightens. Constipation and intestinal fullness also affect the position and condition of the uterus. That is why it is important for a woman to empty both her bladder and rectum on time.
The uterine cavity is small compared to the size of the organ and has a triangular shape when cut. The openings of the fallopian tubes open into the corners of the base of the triangle (at the border between the fundus and the body of the uterus). Downwards, the uterine cavity passes into the cervical canal, which opens into the vaginal cavity through the opening of the uterus. In nulliparous women, this hole has a round or oval shape; in women who have given birth, it looks like a transverse slit with healed tears.
Causes of pathology
Doctors have not established specific reasons for the formation of the anomaly in question. It is known that the uterus begins its formation from 10–12 weeks of fetal development; initially it is connected to the vagina and looks like two cavities separated by a septum. Gradually, the wall resolves, forming a saddle-shaped organ, and by the time the girl is born, it acquires a normal pear-shaped outline, the bottom is leveled.
There are a number of factors that can affect the natural process of organ development and cause its irregular shape:
- lack of vitamin and mineral components in the mother’s body;
- severe stress;
- use of drugs, alcohol, smoking during pregnancy;
- infectious diseases suffered during pregnancy;
- state of chronic hypoxia in a child;
- pathologies in the development of the maternal cardiovascular system;
- congenital diseases of an endocrine nature.
Symptoms
Detection of the saddle uterus usually occurs by chance, most often during ultrasound examinations during pregnancy, since there are no specific symptoms of the pathology. During an examination in a gynecological chair, the doctor also cannot determine the presence of an abnormal form. Manifestations of the disease occur only when it is significantly severe as part of attempts to become pregnant and give birth to a baby. The risks of placental pathologies, spontaneous miscarriage, premature birth and weak labor activity increase. With significant curvature of the fundus, primary infertility can be diagnosed, that is, the inability to conceive from the very beginning.
What causes a bicornuate uterus during pregnancy?
Basically, various abnormalities and pathologies in the structure of the female genital organs are diagnosed completely by accident, when a routine or unscheduled preventive examination is performed by a gynecologist for another reason.
But sometimes women turn to a gynecologist due to the inability to get pregnant or due to spontaneous abortions in the early stages of pregnancy. Then a thorough diagnosis of the woman’s genital area is carried out and, as a rule, various anomalies are identified.
The bicornuate uterus is just a striking example of this.
What is a bicornuate uterus?
In general, congenital anomalies of the uterus, fortunately, are not often encountered in gynecological practice (research data indicate a figure from 1 to 5 per thousand women). A bicornuate uterus (sometimes called a bicornuate uterus) is the most common uterine defect.
Metrosalpingogram for a bicornuate uterus
A normal healthy uterus is a single pear-shaped cavity, with the narrow part located at the bottom, and a significant expansion towards the top of the uterus.
And in the case of a bicornuate uterus, one cavity is split in the upper (wide) part into two independent ones, which are connected in the lower part. Often, both parts of the cavity are located symmetrically with respect to the septum in the uterus, and are also fully developed. If you look at the photo, the bicornuate uterus is similar in general appearance to hare ears or a heart, but not anatomically correct, but drawn.
Types of disease
This splitting is not always the same; the separated upper parts merge at different levels of the lower part of the uterus, depending on this, three variants of a bicornuate uterus are distinguished:
- incomplete bicornuate uterus;
- complete bicornuate uterus;
- saddle-shaped bicornuate uterus.
With an incomplete bicornuate uterus, the division of the cavity occurs in the upper part (approximately a third), and both horns are exactly the same in both shape and size. The opening between the horns is usually shallow.
In the second option, the division of the common uterine cavity, and, accordingly, the divergence of the horns on the sides, comes from the uterosacral ligaments.
In this case, the angle of the branch of the horn-like cavities may be different in relation to the solid lower part of the uterus. The horns are like separate niches, or rather two separate uteruses, located close to each other.
If a woman has a full bicornuate uterus, there is a chance of normal fetal development in one of the cavities.
With a saddle-shaped bicornuate uterus, the expansion begins from the cross section, and the name comes from the similarity of a small depression in the area of the uterine base with the saddle. Doctors do not exclude the possibility of conception, but the further normal course of pregnancy is quite problematic.
Reasons for education
Why does a bicornuate uterus form, the reasons for its occurrence - this is the question women ask the doctor when making a diagnosis. What is the main reason for this anomaly?
It turns out that this pathology occurs due to embryonic disorders (fusion of the paramesonephric ducts, as a result - splitting of the uterine body into two communicating cavities), and it begins in the first trimester. This happens due to:
- abuse of nicotine, alcohol, drugs, medications and chemicals;
- poisoning with toxins;
- various infectious diseases (influenza, toxoplasmosis, syphilis, measles, rubella);
- endocrine diseases (thyrotoxicosis, diabetes mellitus);
- heart defect in the potential mother;
- lack of vitamins, minerals and nutrients in the body;
- mental trauma of the expectant mother.
Some doctors note the adverse effects of chronic fetal hypoxia and severe toxicosis during pregnancy on ontogeny.
Diagnosis and symptoms
As mentioned above, it is possible to identify such a uterus only with a detailed gynecological examination. At the first suspicion, clarifying probing of the uterus is carried out. However, this will not immediately give a complete picture; to confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct several special studies:
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs - both abdominal and transvaginal methods are suitable, the pathology is easily visible;
- hysterosalpingography - a specialized X-ray examination of the uterus using a contrast agent;
- endoscopic research methods - hysteroscopy, laparoscopy.
Such procedures make it possible to clarify and confirm the diagnosis of “bicornuate uterus”, as well as establish the degree of pathology. If one of these studies turns out to be positive, then the information is considered completely reliable and does not require additional confirmation.
You can suspect this anomaly in yourself using relative symptoms, since there are no specific symptoms associated with this abnormality. In rare cases, a bicornuate uterus may present with the following symptoms:
- abnormal uterine bleeding (repeated several times);
- inability to get pregnant or spontaneous abortion (miscarriage);
- in some cases - vomiting, nausea, general weakness of the body, algomenorrhea (aching, pulling or cramping pain in the lower abdomen, reminiscent of menstrual pain in nature).
Bicornuate uterus and pregnancy
As studies and examples from gynecological practice show, a bicornuate uterus and pregnancy are completely compatible concepts.
If a woman manages to become pregnant with such a uterus, then there is a chance of fully bearing a healthy child, of course, provided that the embryo can take hold in the uterus and a miscarriage does not occur in the first trimester of pregnancy. But even when a diagnosis of infertility is made, there is an option - artificial insemination.
To bear a child, at least one cavity of the bicornuate uterus must be of sufficient volume and fully functioning. Possible complications during pregnancy with a bicornuate uterus:
- risk of spontaneous, unexpected self-abortion;
- premature birth;
- lack of space for the developing fetus;
- disruption of intrauterine blood supply;
- early aging of the placenta;
- isthmic-cervical insufficiency.
Of course, such a pregnancy will require special close monitoring by doctors throughout the entire period. If there is a threat of termination of pregnancy in the later stages (at least 28 full weeks), a caesarean section is performed immediately to save the baby’s life.
If the patient managed to carry the fetus to full term, the issue of delivery should be determined taking into account all factors: what type of bicornuate uterus does the woman in labor have, how the fetus is presented and in what position, whether there are concomitant pathologies in the mother.
For example, the combination of a saddle-shaped bicornuate uterus and a narrow pelvis eliminates the possibility of an independent birth process.
Natural childbirth is quite possible, but in case of complications, it is necessary to prepare for an emergency caesarean section in order to avoid birth injuries to both the child and the woman in labor.
There are various options for fertilization and the course of pregnancy with a bicornuate uterus. If the fertilized egg is implanted in one of the horns, which is rudimentary and underdeveloped, then the pregnancy proceeds as an ectopic one, and this threatens rupture of the horn and bleeding. In very rare cases, it is possible for fertilized eggs to implant in both horns at the same time.
Current treatment for bicornuate uterus
It should be noted that treatment of a bicornuate uterus is necessary only if the patient cannot become pregnant or bear a child two or three times in a row. In this case, surgical intervention (uterine plastic surgery) is used to restore a single normal uterine cavity (Strassman, Thompson operation). The standard operation goes like this:
- the bottom of the uterus is dissected with a transverse incision;
- the median septum is removed;
- two branched uterine cavities are sutured into one single one.
At the end of the operation, it is especially recommended to install an intrauterine device for contraception for six months or a year. The gynecologist surgeon will also prescribe concomitant treatment.
As can be seen from the above, a bicornuate uterus is not a final verdict; if the necessary requirements are met, there is a great chance of becoming pregnant and giving birth to a healthy child.
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/healthmatka/iz-za-chego-voznikaet-dvurogaia-matka-pri-beremennosti-5b8fd7e4f7c61400ad22372c
Diagnostics
It is possible to determine whether a woman has a pathological form of the uterus only during pregnancy or in the second phase of the cycle using the following diagnostic methods:
- Ultrasound through the abdominal wall or intravaginal;
- hysteroscopy (introduction of an optical system into the uterine cavity);
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
When detected, differential diagnosis is carried out with a normal and completely bicornuate uterus.
Video. Ultrasound image of the saddle uterus
Saddle uterus and conception
Many women with this pathology are interested in the question: is it possible to get pregnant with a saddle-shaped uterus? Experts identify several positions for conception with a saddle-shaped uterus, which increase the chances of fertilization naturally. The first position is knee-elbow. In this position, the male genital organ enters deeply into the vaginal cavity. After completing sexual contact, a woman is recommended to lie on her stomach, placing a cushion or pillow under her pelvis, and lie there for 15-20 minutes.
“General” is another position that experts recommend for effective fertilization. During intimate relations, a woman needs to lie on her back, bend her knees or raise them. After the end of sexual intercourse, you should slowly pull your legs to your chest, clasp them with your arms and lie down for a while.
Trying unusual positions or experimenting during sexual intercourse is not recommended. The above positions are the most optimal for conception, since they do not allow sperm to leak out of the vagina and, thanks to deep penetration, ensure full interaction of the uterine cervix with sperm.
Treatment
In most cases, no therapy is carried out when a deformity is detected, since it does not affect the woman’s reproductive function. The only method to correct the shape of the fundus is surgical intervention, and it is indicated only in a situation where it is impossible to get pregnant and bear a child precisely because of severe deformation. Reconstruction can be done in different ways:
- hysteroscopic method - allows you to correct deformation without incisions, through natural pathways;
- metroplastic surgery (performed through several punctures in the abdominal wall).
After treatment, the chances of getting pregnant and successfully bearing a child increase significantly.
Effect on conception, pregnancy and childbirth
Minor deformation of the uterine fundus does not in any way affect the onset of pregnancy and the process of successful gestation. However, a pronounced curvature in the form of a saddle can prevent the attachment of the fertilized egg to the wall of the organ, which makes implantation and further gestation impossible. A saddle uterus with a significant change in the shape of the fundus may continue to create problems:
- disruption of the placental attachment process, high probability of low or lateral attachment, which threatens early abruption;
- the likelihood of a transverse or oblique position of the fetus increases, since there is less space in the altered uterus and it is more expanded to the sides;
Due to the specific shape of the saddle uterus, there is a high probability of a transverse position of the fetus during pregnancy
- the incorrect shape causes incorrect contractile activity of the uterine muscles, which can cause weak contractions during the delivery process;
- in the postpartum period there is a risk of bleeding, since the deformed organ cannot contract normally.
Every woman who has been diagnosed with a saddle uterus must constantly monitor the course of her pregnancy and be under the close attention of specialists.
A woman should not worry about the baby - the specific form does not cause any inconvenience to the fetus and does not have a negative impact on its development (neither physical nor mental).
What does a bicornuate uterus look like?
The saddle uterus differs from the standard one by the presence of a concave depression at the bottom. This leads to the fact that the organ in cross section begins to resemble a saddle or a heart. If the anomaly is pronounced, even a person who does not have a specific education can notice its presence. In normal condition, the uterus should be pear-shaped.
A uterus with a bicornuate anomaly has pronounced physical signs; the organ cavity is divided into two parts. This rudimentary process can fuse at different levels of the lower section. In gynecology, the size of the cleft is used in the following classification of bicornuate anomaly:
- full;
- incomplete;
- saddle-shaped
Full
A bicornuate anomaly of this type is characterized by the separation of the cavities in different directions, starting with the uterosacral ligaments. The angle between the horn “pockets” may differ from case to case. The separation is pronounced; two separate niches are formed, which are located in close proximity to each other. Pregnancy can proceed normally in one part of the uterus.
Incomplete
The separation may be partial. Incomplete duplication of the uterus is externally distinguished by the splitting of the internal space by only a third with a shallow opening between the two horns. The horny anomaly on both sides is the same size. Pregnancy can proceed normally in one of the “pockets”; there have been cases of conceiving twins. Both fetuses are located in a separate uterine horn.
Saddle
A bicornuate uterus of this type has a slight depression in the bottom (upper part) that visually resembles a saddle. If there are accompanying defects, there is a possibility of miscarriage, but conception with this type of anomaly is possible. If a girl has a narrow pelvis with this pathology, the possibility of abnormal fetal position cannot be ruled out. In such cases, it is necessary to perform surgery during childbirth (caesarean section).