After childbirth, almost every second woman experiences cervical pathology. And many people are asking the question: where does this come from and what is it connected with? Let's figure out what happens to a woman's body during pregnancy, childbirth and after, namely what the cervix is like after childbirth and before.
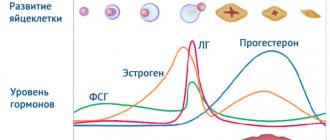
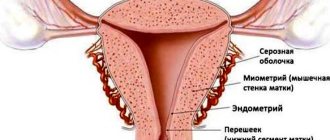
Many changes occur in a woman's body during pregnancy. All systems are rebuilt for full childbearing, subsequent birth and feeding. But the greatest changes are observed in the genital organs, especially in the uterus, which changes dramatically from conception to birth. Its weight instead of 50-100 grams is 1000-1500 without a fetus, and its height from 7 cm grows to 35 by the end of pregnancy. These changes in the uterus occur due to the stretching of muscle fibers under the influence of hormones produced by the placenta. Changes also occur in the cervix, because it is it that ensures the protection and safety of the fetus.
By looking at the cervix, a gynecologist can judge the presence of pregnancy in the early stages. The color of the mucous membrane changes: in a non-pregnant woman it is pink, and in a pregnant woman it becomes bluish. There is also asymmetry in relation to the uterus, and upon palpation the tissues change their structure and become soft. The cervix plays a vital role during pregnancy, special attention is paid to its length, because shortening in the early stages is an indication for hospitalization, as this is a huge risk of premature labor.
What is the uterus and cervix?
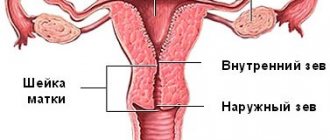
The uterus is a smooth muscle unpaired hollow organ that can expand many times during pregnancy for favorable gestation. The cervix is the lower segmental part of the uterus, one side opens into the uterus, the other into the vagina. Thus, we can say that this is a kind of “gate”. Normally, the uterus is smooth, hard, and pale pink in color. Before the onset of menstruation, it loosens, softens and opens slightly, which means the body is ready for fertilization and implantation of the embryo. If pregnancy does not occur, menstruation occurs and the uterus returns to its previous state.
Looseness of the cervix normally occurs during pregnancy, in the early stages and in the last weeks, closer to childbirth. This is a physiologically normal phenomenon. But if the cervix softens mid-pregnancy, it can lead to miscarriage or premature birth. Why is this happening?
There are several main factors leading to loosening of the cervix:
- Many mechanical injuries resulting from cleansing, abortion, diagnostic procedures, as well as frequent, including difficult, childbirth;
- Weak uterine muscles, loss of tone;
- Weakening of general and local immunity;
- Hormonal disorders of the reproductive/endocrine systems;
- Congenital abnormalities (underdevelopment of the organ, infantilism of the uterus, deficiency of connective fibers, etc.).
The most common cause is cervical insufficiency of the cervix (decreased muscle tone). Actually, this pathology provokes spontaneous miscarriages and premature births. This deficiency is determined by several types:
Functional type:
- an excessive amount of male sex hormones - the uterine cervix loosens and becomes shorter, and with excessive stress it may open;
- insufficient production of progesterone (ovarian dysfunction) - sharply increases the risk of miscarriage.
Organic type:
- the presence of abortions, curettage - as a result of trauma or infection, the walls of the uterus become thinner and become unsuitable for bearing subsequent pregnancies;
- difficult birth - tissues become scarred after ruptures in the walls of the cervix, and in subsequent pregnancies it does not close completely.
The main indicators of cervical insufficiency are looseness of the cervix and its premature dilatation during pregnancy. But in nulliparous women, its diagnosis is very difficult, because it is asymptomatic. Other signs include:
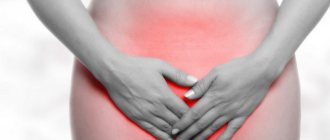
- a feeling of discomfort, a bursting feeling in the lower abdomen, heaviness;
- tingling, shooting pains radiating to the vagina;
- a large amount of discharge, sometimes bloody;
- bleeding outside of menstruation.
Childbirth with a loose cervix
During pregnancy, the uterus undergoes significant changes. In the first days after conception, thanks to hormones, the uterus softens to better secure the embryo in the uterine cavity and provide adequate nutrition. Then, during the first month, the uterus returns to its normal structure. It will continue to change throughout pregnancy, but looseness should normally appear in the last days before delivery.
At the same time, the cervix expands slightly, the tone goes away, and it shortens. This is considered normal and prepares the body for childbirth and facilitates the birth itself. Such phenomena do not require treatment.
But if this happens in the middle of pregnancy, then it requires treatment, otherwise the risk of labor starting prematurely increases.
In a normal pregnancy, the cervix will be firm, long and well closed. If the cervix is insufficient, it loosens and the pharynx opens. If, during examination, the membranes of the amniotic sac are visible in the mirrors, the cervix is shortened to two centimeters, then the diagnosis is confirmed.
Initially, hormonal therapy is prescribed for two weeks. If after this, upon re-examination, improvements are noticeable, the threat of miscarriage is significantly reduced, then treatment is continued. Additional medical supervision is required throughout pregnancy.
There are other treatment methods if hormonal therapy is ineffective.
A pessary (ring) is an additional measure; it is placed on the cervix. Thus, it performs a bandage function - it supports the neck and does not allow it to open. Requires constant monitoring by a doctor; while wearing a pessary, it is necessary to regularly undergo ultrasound and undergo flora tests. It is removed towards the end of pregnancy, but if bleeding occurs or premature labor begins, it is removed earlier.
If the pessary is ineffective, a surgical measure comes to the aid of the loose cervix - suturing. The operation is performed in a hospital under local anesthesia. Indications for suturing are:
- previous pregnancies ended in miscarriages;
- the external os or canal of the entire cervix is enlarged;
- the neck is loose and short.
It is important to select anesthesia as accurately and carefully as possible, because it should not harm the baby. Sutures are removed a couple of weeks before the expected date of birth, but in some cases this is done earlier: premature contractions, the onset or complete breaking of waters (with a long absence of labor there is a risk of hypoxia and infection of the fetus), bleeding.
The surgical treatment method has virtually no complications, but still has contraindications:
- Severe cardiovascular abnormalities;
- The presence of infectious, genetic diseases, liver or kidney dysfunction;
- Fetal malformations;
- Pathogenic flora of the cervix or vagina.
Before pregnancy occurs, pathology can be seen in the presence of scar changes or other defects on the cervix. In other cases, diagnosis is possible only after the first miscarriage.
Women with cervical insufficiency have a high risk of miscarriage. For this reason, infertility is often diagnosed, so after discovering such a diagnosis, it is necessary to immediately begin treatment.
Balanced diet
After the birth of the baby, the mother must be very careful about her nutrition. Diet, as a goal of losing weight, is strictly contraindicated at this time, especially during breastfeeding.
Mother's milk should contain all the nutrients valuable to the baby. To restore a slim figure and good lactation, nursing mothers are recommended to:
- Eat at least six times a day. Between meals, it is advisable to have small snacks of fruit and dairy products.
- Drink at least one and a half liters of liquid daily. Taking the required amount of water, compotes, freshly squeezed and diluted juices helps speed up metabolism.
- Forget about fried, smoked, salted foods. Eliminate baked goods, soda and processed foods from your diet.
- Eat boiled lean meat, fish, vegetables, fruits, cereals, dairy and fermented milk products.
- Take a natural and high-quality vitamin and mineral complex.
Why is there a loose uterus after childbirth?
The postpartum recovery procedure may not always be without complications. Looseness of the uterus after childbirth is one such phenomenon, which may be a symptom of subinvolution.
The first months of the postpartum period are the most important, it is at this time that involution occurs - restoration of organ functions, normalization of hormonal levels. However, it happens that the cervix is blocked by particles of membranes, placental debris or blood clots, or is bent due to weakening of the ligaments; Due to mechanical or viral damage, the uterus cannot shrink to its natural size. This condition is called subinvolution.
Symptoms of the disease are an enlarged, loose uterus and heavy brown bleeding that does not stop.
Sometimes the disease is accompanied by elevated body temperature.
Causes and treatment
There are two types of subinvolution: infectious and true. Infectious occurs due to inflammatory processes after childbirth (against the background of pyelonephritis and anemia of pregnant women), as a result of retention of the remnants of the placenta or membranes in the uterine cavity, as well as due to infection during childbirth. True subinvolution occurs due to excessive stretching of the uterus due to polyhydramnios, a large fetus or carrying twins, with too fast or very long delivery. It can also occur after a cesarean section, against the background of cervical fibroids or adenomyosis.
Possible complications
Changes in the acidity of the environment increase the susceptibility of the tissues of the internal genital organs to infections. Cicatricial deformation of the cervix increases the likelihood of developing endometritis, cervicitis and endocervicitis.
In turn, these inflammatory diseases can lead to keratinization and atrophy of the epithelial tissues of the endocervix. Against the background of such a pathology, cervical erosion often develops. The presence of deformities negatively affects the reproductive functions of the body. Violation of tissue trophism leads to improper cell development - there is a possibility of malignant degeneration and the development of cancer.
Scar on the cervix after childbirth
Scars are formations of connective cells on the damaged mucous membrane of the cervix, or scars. After childbirth or as a result of surgery, they can occur on the cervix. One of the main provoking factors is difficult childbirth. Their danger lies in the possibility of infection as a result of retention of the remains of the placenta or fetal membranes separated after childbirth on them. In this case, curettage of the uterine cavity will be required; lack of treatment can lead to blood poisoning.
Alarming symptoms that are a reason to consult a doctor are:
- Pain in the pelvic region, radiating to the lower back;
- Discomfort, heaviness, unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen;
- Numerous whitish viscous discharge;
- Pain during sexual intercourse;
- Failure of the menstrual cycle;
- Pain during menstruation.
Treatment of the disease can be therapeutic (restoring hormonal levels, relieving inflammation, boosting immunity) and surgical.
Surgical intervention: features of the procedure
In some cases, complete surgical intervention is necessary. If the patient is a woman past reproductive age, the doctor may recommend trachelectomy. During the procedure, the cervix is completely excised, and the uterus itself is sutured - this helps prevent it from descending into the vagina.
Young patients are prescribed surgery during which only scar tissue is removed. Excision using a laser beam is considered safer, since the risk of complications (infection, the appearance of new scars) in this case is much lower.
When removing a large amount of affected tissue, patients need another operation - cervical plastic surgery. The procedure is aimed at restoring the normal shape of organs.
Cervical inversion after childbirth
Eversion of the cervical mucosa is called ectropion. It occurs when the uterus receives severe trauma due to the birth of a large fetus, malpresentation of the fetus, hardness of the cervical tissue as a result of incorrect sutures after ruptures or after a cesarean section.
If severe trauma to the uterus occurs, and all layers are affected, including the muscular layer of the cervix, scarring subsequently occurs, as a result of which the tissue is not sufficiently supplied with nutrition. The cervical mucosa, as a result of a gap in the vagina, is damaged by the acidic vaginal environment, which can result in infections and reproductive dysfunction.
There are no specific manifestations of the disease; it is diagnosed during examination by a gynecologist (open cervical mucosa, cloudy mucus discharge, scar changes on the cervix causing deformation). To confirm the diagnosis, colposcopy and cell examination (cytology) are prescribed to confirm the benignity of the process.
Inversion of the cervix can provoke a disturbance in the physiological state of the cervical canal, the development of an inflammatory process, reproductive dysfunction and some other pathologies.
The essence of treatment is to correct the structure of the cervix by such methods as diathermocoagulation and diathermopuncture, plastic surgery and reconstruction, and conization of the cervix.
Whatever questions about the state of your reproductive system bother you, a consultation with a gynecologist is always necessary. By following all the recommendations, you can maintain your health and prevent the development of many diseases.
Video: cervical maturity. Preparing for childbirth
Cervical maturity, what is it? (Part 2) Preparing the cervix for childbirth
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine is very popular in the treatment of cervical prolapse. Women managed to overcome pathology with the help of unconventional treatment methods. Before starting to use traditional methods, you need to cleanse the intestines, and then the liver and kidneys. Only in this case will it be effective.
Steam bath. Collect about 10 pebbles and wash them well. Wrap the edges of a metal bucket with cotton cloth or a towel so that you can then sit on it. Next, hot pebbles and a few cloves of garlic are dropped into the bucket, and tar is added. You need to cover yourself with a blanket and sit on a bucket. Pour about half a glass of vodka onto the stones. Take a steam bath for about half an hour.
Banks. Lubricate the area around the navel with Vaseline. Place a warm liter jar on the navel area and hold for about ten minutes. Then remove and lie there for about another half hour. Repeat this procedure for a week.
Tarawa. Method No1. Take the following herbs: mint - 2 tbsp. l.; St. John's wort - 2 tbsp. l.; yarrow - 2 tbsp. l., mix in one bowl. Pour 1 liter of boiling water and leave for about 2 hours. Then strain. Use throughout the day in three approaches. Drink during the week.
Method No. 2. Take herbs 1 tbsp. l.: inflorescences of nettle, yarrow, mint. Brew 1 liter of boiling water and drink a glass during the day in 3 approaches for 2 weeks.
Traditional methods are quite good if they are combined with special exercises. Exercise is the main and most effective way to strengthen your pelvic floor muscles. Physical exercise improves blood circulation and metabolism in the muscles, tones them. Proper physical activity corrects pathologies of the female reproductive system.