Gynecologists recommend that all women of childbearing age keep not only a menstrual calendar, but also record basal temperature. This is necessary in order to monitor how the ovaries work, monitor hormonal levels and the functioning of the reproductive system.
So what does it mean if the basal temperature is more than 37? It all depends on the phase of the cycle: this procedure will help determine that the girl is “in an interesting position” or identify serious pathologies in her body. After all, a basal temperature of 37, even with a negative test, is a sign of pregnancy. And a basal temperature of 37 and a positive test before menstruation 100% indicate the presence of pregnancy.
In what cases is temperature measurement necessary?
Measuring body temperature rectally allows you to obtain the most accurate data, since in the rectum, closed by the sphincter, body temperature does not change under the influence of external factors. Moreover, the rectum, being part of the human internal system, allows you to transmit the exact temperature of the organs located next to it, which also helps determine the presence of inflammatory processes.
What is the normal temperature in the rectum? It is slightly higher than in the armpit. And it should be within 37-37.7 degrees Celsius.
Temperature measurement using this method is carried out in the following situations:
- Inability to measure armpit temperature due to severe exhaustion of the patient.
- Age less than 2 years.
- In case of severe external hypothermia, if the patient’s skin has been frostbitten.
- For injuries and other damage to the skin in the armpits.
- When the patient is unconscious.
- When planning pregnancy and monitoring its progress.
It is strictly not recommended to use the rectal temperature measurement method for inflammation of the rectum, hemorrhoids, and stool disorders.
Thermometry in children
Children's body temperature is slightly higher than that of adults. Newborn babies are very sensitive to both hypothermia and overheating. At this age, thermometry is one of the most objective ways to assess health status.
Because The axillary and oral measurement method does not allow achieving accurate results in patients of this age; the method of measuring body temperature in the ear canal is quite popular. But measuring a child's rectal temperature provides the most accurate data.
Taking rectal temperature measurements in children with a mercury thermometer without certain skills carries a certain danger. Therefore, digital thermometers have become especially popular lately.
The normal rectal temperature in infants is within 38° C. During the procedure, the child should be reassured, because The slightest movements can cause an increase in indicators.
Especially in the first months of a child’s life, the temperature curve is just being established.
Up to two or three months, its changes can be provoked by the slightest factors: crying, breastfeeding, swaddling. The air parameters of the room in which the child is located also have an impact. Stable humidity and temperature of 20 - 22° C are considered optimal for a child.
It should be remembered that for children under 1 year of age, body temperature above 38 - 39 ° C can be dangerous - in such a situation the child runs the risk of fibril seizures. Therefore, if the high temperature does not subside for a long time, you should contact your pediatrician.
What does an increase in temperature indicate?
An increase in temperature in the rectum indicates the patient's condition. First of all, this means the development of an inflammatory process in the body, often accompanied by the release of pus. Any viral infectious disease also affects it.
The normal temperature in the rectum in women is generally the same as in men, but in some cases it changes. This helps to track the ovulation process and, accordingly, plan pregnancy.
Often high temperature in the rectum accompanies the formation of tumors of various types.
Measuring rectal temperature in a child
First of all, you need to know what temperature should be in the rectum of a child under 2 years old in normal condition - 38 degrees Celsius. Moreover, the child should be in a calm state. After all, if it is active, then the body temperature in the rectum rises. Moreover, it also increases when screaming, crying, during feeding, or massage.
In this case, a slight increase, for example, 38.5 degrees, requires the attention of a specialist. Knowing the normal temperature in the baby’s rectum, if it increases slightly in a calm state, you should immediately call a doctor.
Changes in BT during pregnancy
An increase in basal temperature during pregnancy occurs due to the work of the placenta. The placenta, the tissue connecting the mother and fetus, produces progesterone. Thus, although the corpus luteum is no longer active, the high temperature is maintained due to the activity of placental progesterone.
Progesterone continues to be synthesized throughout almost the entire period of pregnancy, but usually the mother’s body quickly adapts to this hormonal background, and body temperature drops to normal values.
Thus, if before menstruation the temperature rises to 37 C, and then menstruation is delayed, pregnancy can be suspected. However, the fact that body temperature rises before menstruation is not sufficient to confirm the presence of pregnancy.
It should be noted that when analyzing BT, a more important role is played by the difference in temperatures before, during, and after ovulation, and not by the number on the thermometer on the day before menstruation.
That is, if the temperature before menstruation is 36.9 C, and before ovulation it was 36.7 C, this is less likely to indicate pregnancy than a reading of 36.6 C before menstruation in a woman who is characterized by a decrease in readings before ovulation up to 36.1 C.
In the first case, the difference is 0.2 C, and in the second – 0.5 C. That is why BT can be considered as a diagnostic sign only if the woman monitors her constantly over several cycles.
Measuring rectal temperature in pregnant women
Pregnancy causes extensive changes in a woman's body. He is preparing to bear and feed a child, the mammary glands and even the skeleton are changing. All these processes are controlled by female hormones. In this case, body temperature plays a huge role. And it is often measured rectally, because, as already mentioned, this method gives more accurate readings. This temperature is called basal.
Basal temperature
The temperature in the rectum during pregnancy allows you to monitor the condition of a woman’s body, and it does not depend in any way on the air temperature, which means it is the most accurate. It is called basic or basal. Accurate values can be obtained in the morning, before the woman gets out of bed.
Basal temperature is also the one measured in the vagina or mouth. An experienced doctor, using a schedule of measurement results over a certain time, is able to determine how much progesterone and estrogen are produced in a woman’s body. Using basal temperature readings, you can predict the most accurate time for conceiving a child.
What is the method based on?
A woman’s body temperature depends on many factors, the main one of which is changes in the concentration of sex hormones during the menstrual cycle. Moreover, fluctuations can be observed not even by weeks, but by hours and minutes.
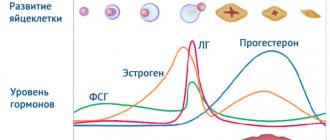
- The first phase of the cycle. It is caused by the work of estrogens, under the influence of which the egg matures. During ovulation, the levels of these hormones, regulated by luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), reach their peak. As a result, the mature egg is released from the follicle for fertilization. An increased concentration of estrogen inhibits metabolic processes. Accordingly, the temperature in the tissues of the pelvic organs decreases.
- Second phase of the cycle. Regulated by progestins. After ovulation, the concentration of these hormones increases and affects the formation of the endometrium. Progesterone is also responsible for the normal course of the gestation period, which is why it received the name “pregnancy hormone”. It stimulates thermoregulatory processes, which causes increased basal temperature during pregnancy, before menstruation.
By regularly measuring your basal temperature over several months, you can determine how the phases of the menstrual cycle change, when ovulation occurs and the most likely days of conception. And also find out whether it took place.
To do this, BT indicators are entered into a special chart every day. You can create it yourself or use separate calendars and electronic applications.
How can you determine ovulation using basal temperature?
The normal temperature in the rectum, vagina and mouth is different for all women. But you can create your own drop chart for each.
In the first half of the menstrual cycle, BT is low, in the second half its indicators rise. This is explained by the effect of progesterone on the body.
1-2 days before ovulation, BT drops sharply, but the very next day its levels rapidly increase. During menstruation the temperature is low, and during fertilization it is high. Knowing the temperature norms in the rectum or vagina, a woman can increase her chance of becoming pregnant if she has not been able to conceive a baby for more than a year. Such measurements can identify disruptions in the endocrine system and restore the production of sex hormones. And most importantly, using basal temperature readings, you can establish the fact of fertilization even before delays in menstruation begin.
Why do you need to measure BT?
Basal temperature demonstrates the amount of heating of the human body only by internal organs. Without taking into account the heat that muscles produce during the work of the lower, upper limbs and torso. Simply put, basal temperature is the body temperature recorded immediately after waking up only the brain, and not the entire body as a whole. You need to measure it immediately after sleep, lying in bed with your eyes still closed.
Basal temperature can be measured to:
- Determine ovulation and favorable days for conceiving a child;
- Determine the days on which you can not use protection during sex;
- Diagnose pregnancy at an early stage;
- Assess the woman's hormonal state.
Today this is the most effective, accessible and cheap method for determining hormonal imbalance and ovulation. It is not very suitable for early diagnosis of pregnancy, only if the woman has a healthy body and a stable menstrual cycle.
How can you determine pregnancy using basal temperature?
In order to determine pregnancy using BT, you need to remember exactly how the menstrual cycle proceeds. It begins with the maturation of the egg in the follicle, while estrogen is actively produced, as the ovaries work with maximum efficiency. The temperature is not very high, approximately 36.1-36.8 degrees. If BT is higher than this value, it means there is little estrogen in the woman’s body.
During ovulation, the follicle ruptures and the egg is released from the ovary. This occurs under the influence of the latinizing hormone. At the same time, BT rises noticeably - up to 37-37.7 degrees Celsius.
In place of the burst follicle, the so-called corpus luteum begins to form. At the same time, it actively produces progesterone.
The next stage is fertilization. At this time, the corpus luteum continues to produce progesterone until the placenta takes over this function. The temperature does not drop.
If there has been no conception, the corpus luteum is destroyed, the level of progesterone, accordingly, decreases sharply, followed by a drop in basal temperature. All measurements of basal temperature during the monthly cycle are carried out either rectally or vaginally. Temperature norms in the rectum and vagina are the same.
Aliis
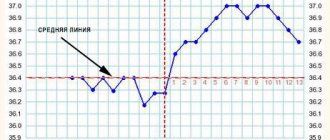
How should BT behave before and during menstruation?
- Normally, 2-4 days before the start of menstruation, BT begins to decrease and by the 1st day of the cycle reaches 37.0-37.1. Then, during normal menstruation, BT continues to decrease, despite the volume of blood released.
- If a woman has a latent ongoing inflammation of the uterine mucosa (endometritis) or the uterus itself (endomyometritis), then during menstruation the BT will go UP, sometimes reaching 37.5-37.6 at normal temperature in the armpit.
- If BT rises at normal times, but then does not fall before menstruation, remains above 37.0 throughout almost the entire menstruation, and decreases in the last days or after the end of menstruation, then this is suspicious for a pregnancy that was interrupted during menstruation.
- If BT in the second phase remains low (36.9-37.0), and by the time of menstruation it begins to rise and remains above 37.0 throughout menstruation, then most likely we are talking about inflammation of the appendages.
- A rise in BT in the last 1-2 days of menstruation (if it lasts at least 4-5 days) may indicate inflammation of the tubes or (much less often) the cervix - without damage to the uterus itself.
- A sharp rise in BT for one day during menstruation does not mean anything: inflammation cannot begin and end so quickly.
- If menstruation is scanty or unusual, and BT remains at an elevated level, pregnancy is possible against the background of the threat of miscarriage.
Is it necessary to measure BT during menstruation?
BT measurements can be started both on the 1st day of the menstrual cycle and on the day the discharge stops (a matter of your convenience).
What should be the BT in the first phase?
- Normally, the temperature of the first phase is kept between 36.5-36.8.
- But often the graphs show estrogen deficiency, which is expressed by a high level of BT in phase 1. In such cases, doctors prescribe estrogens, for example, Microfollin. But only if these suspicions were confirmed by a hormonal blood test.
- Another unusual phase 1 schedule occurs when there is inflammation of the appendages. After an exacerbation during menstruation, inflammation may subside, but from time to time it may cause a slight, purely local exacerbation, which is reflected in the basal temperature. BT may increase to 37.0-37.2 for 1-2 days, and then decrease again.
What could be causing unexpected temperature increases in the first phase?
Stress, travel, drinking alcohol, colds with fever, sex in the evening (and even more so in the morning), measuring BBT at an unusual time, going to bed late (for example, I went to bed at 3 o’clock and measured it at 6 o’clock), sleepless night and many other things affect BT. Eliminate “unusual” temperatures by connecting the normal readings with a dotted line. Try to identify and note in the graph the possible cause of the deviation.
What should be the BT in the second phase?
- Normally, the temperature of the second phase rises to 37.2-37.3. But the difference in average temperatures is more important (read below).
- Low temperature in the second phase (relative to the first) may indicate insufficient function of the corpus luteum (progesterone). To support the second phase (and pregnancy), additional progesterone is prescribed (most often Utrozhestan or Duphaston) - but only if these suspicions are confirmed by a hormonal blood test.
- Approximately 2-4 days before the start of menstruation, BT begins to decrease and by the 1st day of the cycle reaches 37.0-37.1.
- If BT rises at normal times, but then does not fall before menstruation, remains above 37.0 throughout almost the entire menstruation, and decreases in the last days or after the end of menstruation, then this is suspicious for a pregnancy that was interrupted during menstruation.
- If BT in the second phase remains low (36.9-37.0), and by the time of menstruation it begins to rise and remains above 37.0 throughout menstruation, then most likely we are talking about inflammation of the appendages.
If the second phase temperature is not high enough (no difference of 0.4 degrees), does this mean that I have a second phase deficiency?
Possibly, but not necessarily. BT does not provide any information about the full function of the corpus luteum - neither about the length of the phase (the temperature can rise several days after ovulation), nor about the level of progesterone produced by the corpus luteum (the thermometer readings do not allow determining the quantitative level of progesterone in the blood - to assess the level Progesterone levels must be tested a week after ovulation).
On what day relative to the rise in temperature does ovulation occur?
Before ovulation, the temperature decreases, and after it it increases. A rise in basal temperature means that ovulation has already occurred.
A drop in temperature at the time of ovulation occurs only in a very small number of women. Since a sharp drop in temperature occurs extremely rarely, this sign cannot be absolutely reliable in determining the ability to conceive; therefore, it is better to use two other signs to determine the approach of ovulation.
If ovulation is not visible on the chart, does this mean that it did not happen or that I have problems with hormones?
The BT measurement method is very unreliable! Under no circumstances should you rely on it when diagnosing any disorders or when prescribing hormonal medications! In cases where there is no obvious second phase on the graphs, it is necessary to carry out ultrasound monitoring, and if there is ovulation according to ultrasound, take a blood test for progesterone a week after ovulation, if the results of both studies are normal - you can consider such graphs a “feature” of the body and stop measuring temperature, if it is not indicative;
Do you ovulate more than once per cycle?
Cases where two (or more) eggs are released from the ovaries during one cycle constitute a very small percentage of the total number of ovulations. However, such withdrawal always occurs within 24 hours. Multiovulation leads to the birth of twins.
If the schedule is perfect, does this mean that ovulation occurred? Does this mean that you can accurately guess the day of ovulation?
The method does not provide accurate information about the presence of full ovulation even in the presence of two-phase graphs (for example, in the case of premature luteinization of the follicle), as well as accurate information about the timing of ovulation (the temperature may rise the next day or a few days after ovulation - this is in within normal limits),
What should be the temperature difference between the first and second phases?
- The difference between the average BT of the second phase and the average BT of the first phase should be at least 0.4-0.5. Except in cases where a small temperature difference is only a feature of a woman’s body, and not an indicator of the presence of any disorders. This is usually checked by additional examination methods - ultrasound, blood tests for hormones, etc.
- If throughout the entire cycle the temperature on the graph remains at approximately the same level or the graph looks like a “fence” (low temperatures constantly alternate with high ones), and not two-phase, then this means that there was most likely no ovulation in this cycle - anovulation. To confirm this fact, it is necessary to conduct ultrasound monitoring over several cycles to determine the presence or absence of ovulation. Healthy women are allowed to have several anovulatory cycles per year, but if this pattern is observed in all cycles, you need to consult a doctor. In the complete absence of ovulation, a woman does not have full menstruation - only “menstrual-like bleeding” (which can be either regular or irregular).
How many days should the climb last?
Normally, the rise takes no more than 3 days. A gentler rise reflects a lack of estrogen and weakness, inferiority of the egg. Fertilization in a cycle when BT in the first phase is high and the rise takes more than 3 days is very problematic.
What is the duration of the phases and why is the cycle always different?
The first phase (preceding ovulation) can be very different in duration, both in different women and in the same woman. Typically, the length of this particular phase of a woman’s cycle affects the delay of menstruation - for example, if the maturation of the follicle occurs more slowly or does not occur at all. The second phase (after ovulation) varies among different women (from 12 to 16 days), but is almost constant among the same women (plus or minus 1-2 days).
- Lengthening the first phase of the cycle is an atypical phenomenon, but this does not affect the normality of the cycle. A cycle with an extended first phase is normal.
- If the second phase is shorter than 12 days, then this is a sign of insufficiency of the second phase, low progesterone levels.
Which BT indicates pregnancy?
- If there is no menstruation, and BT remains in the second phase for more than 18 days, this indicates a possible pregnancy.
- You can be sure of pregnancy if the level of high temperatures persists for 3 days more than your normal corpus luteum phase. For example, if it usually lasts 12 days (maximum 13), but one day lasts 16 days, then almost
- If a third level of temperature appears during a normal two-level cycle, then you are almost certainly pregnant. This third level of temperature occurs due to additional progesterone in the body of a pregnant woman. Unfortunately, however, not all women have such a three-level schedule.
- If menstruation is scanty or unusual, and BT remains at an elevated level, pregnancy is possible against the background of the threat of miscarriage.
- If BT rises at normal times, but then does not fall before menstruation, remains above 37.0 throughout almost the entire menstruation, and decreases in the last days or after the end of menstruation, then this is suspicious for a pregnancy that was interrupted during menstruation.
When does implantation occur and how does BT behave at this time?
Implantation of the fertilized egg occurs on days 6-8. It happens that at this time the temperature drops by 1, maximum 2 days. When you see a decrease in temperature in the middle of the luteinization phase on your graph, this does not mean that you are pregnant. Moreover, such a picture is not necessary during pregnancy.
Is it necessary to measure BT while taking OCs or other hormonal drugs?
You should not measure BT while taking OCs - under the influence of the hormones you take, it will not be indicative.
How are measurements taken?
In order for all measurement readings to be as accurate as possible, certain rules must be followed:
- Temperature measurements should be taken in the morning at the same time, before getting out of bed.
- Measurements are carried out with the same thermometer. First you need to lubricate its tip with Vaseline.
- During the day, the temperature changes several times under the influence of various factors, including mild stress and mood swings. Therefore, it is not recommended to measure BT in the middle of the day.
- The thermometer should be in the anus or vagina for at least 5-6 minutes. In this case, the woman should lie on her side, pulling her knees to her chest.
- You need to start plotting the changes the next day after the monthly cycle.
What factors influence the correctness of measurements?
During the period of constructing the BT chart, you need to remember that there are factors that significantly distort the readings. First of all, it is alcohol, and in any quantity. In addition, you need to remember that alcohol destroys follicles with eggs, so if a woman wants to have children, then she should not drink alcohol in principle, since the number of eggs in her body will be limited.
You cannot have sex 10-12 hours before measurements. Temperature levels are affected by stress, so situations that could affect a woman’s mental state should be avoided.
With any infection, the body temperature rises, so it will be impossible to determine ovulation or pregnancy under such conditions.
Although it is believed that BT is not affected by the environment, you need to understand: the presence of a heating pad nearby or frozen feet will in any case have some effect on the temperature readings. At the time of measurement, the woman should feel comfortable, she should not be cold or too hot.
BT in the second phase of the cycle
From the moment of ovulation, the luteal phase begins, also known as the corpus luteum phase. It lasts as long as the corpus luteum remains active (12-14 days).
BT increases after ovulation, remaining at a level approximately 0.4 C higher than before ovulation for approximately 10 days. The corpus luteum gradually degrades and progesterone levels drop. At this stage, there are 2 possible scenarios:
1. If fertilization does not occur during the existence of the egg, that is, the woman does not become pregnant, the BT decreases, and after a few days menstruation begins, and the cycle begins from the beginning.
2. If fertilization has occurred, the basal temperature rises in the period before menstruation; after this, BT continues to remain at an elevated level (about 37 C), and menstrual bleeding does not occur.
When is basal temperature not indicative?
There is such a situation as an ectopic pregnancy. In this case, the fertilized egg does not reach the uterus and attaches to the wall of the fallopian tube. At the same time, progesterone and other hormones produced during pregnancy are produced in full. Such a pregnancy is futile, and it will end very quickly in a miscarriage with large blood loss. A very life-threatening situation for a woman. In this case, BT will reflect the temperature that occurs during pregnancy. Therefore, you cannot rely only on the obtained measurement results. After checking conception using rectal or vaginal temperature measurements, an ultrasound examination should be performed.
Another situation when basal temperature is not informative is the 2nd and 3rd trimester of pregnancy. During this period, the temperature changes constantly, so there is no point in continuing to measure it.
In some cases, increased temperature in the rectum may indicate malfunctions in the body, for example, associated with an inflammatory process. Before starting measurements, you should consult your doctor. He will be able to point out all the subtleties and nuances of this procedure. It is undesirable to draw independent conclusions, and sometimes it is simply dangerous.