What happens to the uterus after childbirth?
After childbirth, all organs and systems of the female body begin to work differently than during pregnancy. Therefore, it will take some time to restore their normal operation. The reproductive system of a woman in labor undergoes especially significant changes, as well as her hormonal levels.
What changes occur in the reproductive system? First of all, these are changes in the uterus.
Just imagine, over the course of all 9 months the muscle tissue of the uterus stretched, the uterus itself gradually increased in size, and eventually became many times larger than before pregnancy. Now think about whether this organ can rapidly shrink within 1.5-2 months, and at the same time not cause a feeling of discomfort or even noticeable pain? For example, immediately after birth the weight of this organ is 1 kg, and after recovery it is about 55 g.
Also, in addition to the fact that the uterus returns to its original size, the processes of healing and restoration of the inner layer take place in it, which is severely damaged during childbirth and represents an open wound. This process lasts about 2 weeks and during this period, bloody discharge is characteristic - lochia, containing blood clots, parts of the placenta and other residual tissue. The peak of these discharges occurs in the first 3 days, then the abundance decreases and disappears.
By the way, after a cesarean section, the recovery process takes longer.
Therefore, if 2 weeks have passed after childbirth, and lochia is still abundant, then you need to consult a doctor.
A little physiology
There are two main symptoms: pain in the vagina after childbirth and pain in the uterus after childbirth. Naturally, each of these points has its own reasons that need to be considered. In certain circumstances, they indicate the development of a pathological condition, so before considering deviations, you need to turn to the physiological norm. This will help to distinguish that fine line where the norm ends and the disease begins.
Immediately after pushing the fetus out of the cavity, the uterus has its own specific parameters:
- weight is about one and a half kilograms;
- volume is 5000 ml;
- the bottom is located in the middle between the pubic symphysis and the navel;
- size - 38 by 24 cm;
- the cavity represents a large wound surface, where the greatest damage is in the area of placental attachment.
During this period, the body itself contains the placenta, umbilical cord, amniotic membranes, which begin to be pushed out by contraction of the muscle layer (myometrium). Against the background of previous attempts, this muscle compression is not as painful as it was during childbirth. The next stage, which takes six to eight weeks, is characterized by gradual involution:
- 1-3 days - the uterus contracts and pushes out the remains of the amnion and blood in the form of a liquid component and clots. All this has a certain appearance (bloody discharge) and is called lochia. The cervical canal allows only one or two fingers to pass through.
- 3-5 days - the lochia lightens and becomes less voluminous, the inner layer (endometrium) completes its restoration. Weight is reduced to 500 grams.
- By the end of the eighth week, complete recovery is observed, the dimensions are the same as before pregnancy with only one difference - the cervical canal is no longer point-shaped, but in the form of a slit. The mass of the organ is 50 grams. This period occupies different time periods.
Read also Why hair grows very strongly and falls out in clumps after childbirth: Reasons
Natural causes of pain
What are the natural causes of lower abdominal pain after childbirth?
Pain in the uterus, which tirelessly attacks only the woman who has given birth, especially during feeding, is a normal and natural phenomenon. They arise as a result of uterine contractions, which are necessary to give the uterus its original pre-pregnant size, as well as to cleanse its cavity from blood clots, placental remnants, and other things. Just imagine, the weight of the uterus should decrease 20 times due to these contractions by the end of the recovery period (involution), that is, in 1.5-2 months!
Often, such contractions are very painful in the first 2-3 days after birth, then the intensity of the pain decreases within a week and then only a feeling of discomfort remains, which also soon passes. The exception is women who gave birth naturally for the first time. They may hardly feel uterine contractions.
In addition, an understandable cause of pain in the lower abdomen is stretched muscles that hold the uterus, so pain may occur with sudden movements, in particular when walking quickly.
As a rule, the most noticeable pain occurs during breastfeeding , when you sit. The pain can be so severe that one has to resort to pain-relieving suppositories, although they, of course, do little to help...
Have you also felt strong contractions of the uterus after childbirth? Maybe share information about how you dealt with this pain?
The main causes of pain
To find out whether it is normal for the uterus to hurt after childbirth, it is necessary to clarify the reasons why such a sensation may occur.
Uterine pain: natural causes
Contractions after childbirth are not as strongly localized as during labor. Nevertheless, such sensations are noticeable and quite tangible. However, a woman should not worry about this. On the contrary, the absence of contractions immediately after the birth of the baby should cause concern. This can lead to serious complications and stimulation of contractions with the help of medications.
Important!
The more and more often you put your newborn baby to the breast, the faster the uterus can contract, the better for the mother in labor.
Natural causes of uterine pain after childbirth that are not cause for concern include:
- Oxytocin response. The uterus contracts immediately after the baby and birth place (placenta) are removed. This becomes possible only if there is the required amount of oxytocin, which is produced by the female body. Mild but tolerable pain can be clearly observed in the first 5-7 days. These are the kind of contractions that are visible even to a woman in labor: during feeding, the uterus contracts, the stomach literally vibrates.
- Wound surface. The uterine cavity is a solid muscle, which immediately after birth is literally an open wound. When contracted, such a muscle, like any wound, hurts, this is normal.
- Intestinal pain. After pregnancy, the stomach, liver, and pancreas again “learn” to work in the same rhythm, returning to their original place. Therefore, symptoms such as colic, stomach cramps, nausea, and fermentation often occur.
- Contractions of the cervical part. The cervix dilates up to 10 cm so that the uterus can pass the baby's head at the moment of pushing. After pushing out (especially if you do not push correctly), tears may appear in the part where the child passed. After birth, the obstetrician examines all organs and applies stitches if necessary. Of course, for the first 5 days (before discharge) the uterus will ache and ache. After this period, a decrease in pain occurs.
Contraction of the uterus after childbirth and dangerous symptoms
Pain in the lower abdomen in the first few weeks after delivery should cause concern if, along with these symptoms, the following signs appear:
- increase in temperature (as a rule, the increase occurs instantly, and it is virtually impossible to reduce the temperature);
- purulent discharge or blood with a rotten fish or purulent odor;
- there is no reaction to light (the pupils do not constrict);
- the abdomen on palpation is hard, painful, tight (possibly hot to the touch);
- vomiting, nausea, headache;
- uterine contractions acquire an increasingly painful spasmodic effect;
- Breasts swell, nipples are painful to touch.
All of the above symptoms are life-threatening for a woman in labor. For example, symptoms of endometritis develop in just a few hours. As a rule, problems may arise with the presence and development of infection, which after childbirth are deadly diseases.
Important!
Increased mortality among women in labor who decide to give birth at home is associated with the development of peritonitis. 80% of diagnosed complications of home birth are fatal
Pathological causes of pain
Unfortunately, pain in the lower abdomen may not always be caused by natural causes. Due to the fact that childbirth is a rather complex and difficult process for the body, complications caused by pathological reasons may arise.
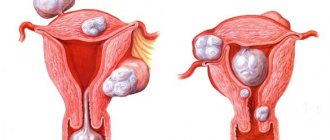
Pathological causes include:
- endometritis;
- improper separation of the placenta;
- intestinal obstruction;
- peritonitis;
- divergence of the pubic symphysis.
Let's take a closer look at these reasons.
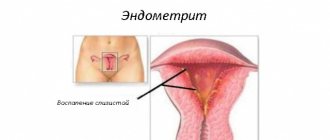
Endometritis
This is a serious inflammatory disease of the inner layer of the uterus, which occurs when an infection enters its cavity during the process of delivery.
This disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- body temperature rises sharply and pulse quickens;
- unpleasant putrid odor of postpartum discharge;
- discomfort when urinating;
- possible discharge mixed with pus;
- general condition worsens;
- Uterine bleeding begins.
Why is endometritis so dangerous?
This pathology can not only leave a woman infertile in the future, but also exposes her life to great danger.
In case of incorrect or incomplete separation of the placenta
Severe pain in the uterus is also possible. Why do they arise?
Let's start with the fact that physiologically the placenta during pregnancy is attached to the inner layer of the uterus, but when, for some reason, it is attached deeper, it accretes, which subsequently causes difficulties in its passage. However, this situation is quite rare. The picture is more often observed, for example, with weak labor, when this process does not want to go through on its own. Then the doctor decides to separate the placenta manually. As a result of manual separation of the placenta, fragments of the placenta may remain inside the uterus.
In order to solve this problem, various methods are used:
- scraping out residues;
- taking medications that stimulate uterine contractions.
Intestinal obstruction
The problem of constipation after the birth of a baby affects only the lucky ones. As you already understand, constipation is a fairly common occurrence among new mothers. It can be caused by both disturbances in hormone levels and physiological changes in the intestines during pregnancy and childbirth:
- the intestines gradually assume their usual position;
- the perineal muscles are stretched and are not able to fully perform their function;
- The abdominal muscles are also stretched, therefore creating weak intra-abdominal pressure.
In addition, a woman is even scared to imagine the process of bowel movement, because the muscles of the perineum hurt after childbirth, and if there are still tears and stitches, then fear takes its toll.
What to do in this case?
A microenema will cope perfectly with your problem; as an option, you can use glycerin suppositories.
Peritonitis
This is a very dangerous disease, which is characterized by inflammation of the abdominal organs. After childbirth, this disease can appear as a result of inflammation of the uterus and its appendages, if not diagnosed and treated in a timely manner, the source of infection spreads to the abdominal cavity and peritonitis occurs.
Divergence of the pubic symphysis
Quite a common occurrence in pregnant women. It occurs for several reasons:
- heavy workload during pregnancy;
- relaxing effect on progesterone ligaments.
Divergence of the pubic symphysis can occur both during pregnancy and during childbirth.
In addition to the reasons listed, a complication may occur such as blockage of the cervical canal with a large blood clot or a piece of amniotic membrane. In this case, cleaning or taking special medications is also prescribed.
It also happens that 2-3 months have passed, and the painful sensations are still present. In this case, there is no need to hesitate, but immediately consult a doctor.
What is really the norm?
It is worth noting here that all of the above points may be accompanied by a complaint that the uterus hurts after childbirth.
It is important to distinguish between mildly painful discomfort, which is normal at the moment, and when it really hurts.
The second may indicate the development of the disease - inflammation of the endometrium, accumulation of lochia, and even atonic bleeding, which is life-threatening. At this point, it is important to seek professional help from a doctor.
The sensation of discomfort is more like aching soreness, sometimes requiring the use of antispasmodic drugs.
Most often this happens after the second birth. It also intensifies during feeding, since a large amount of the hormone oxytocin is released into the blood, which is responsible not only for attachment to the baby, but also for regulating the activity of the uterine muscle fibers.
Young mothers wonder how much pain there is in the lower abdomen after childbirth. It hurts for no more than seven days, but mild discomfort is observed for about two months, since during this period the pelvic ligaments have not yet fully returned to normal and even slight overfilling of the bladder can lead to unpleasant sensations.
Signs of pathology
All these conditions are very dangerous for mommy and require immediate medical attention. Therefore, at the slightest suspicion of poor health, you should seek help from specialists. And even more so if you have at least one of these symptoms:
- unbearable pain;
- increased body temperature, chills;
- the discharge is copious, possibly with purulent impurities, and has an unpleasant odor;
- severe symptoms of body intoxication (headache, dizziness, nausea, fatigue);
- bleeding.
Why is this happening?
After the birth of a child, the body experiences very serious stress, because all the organs inside the abdominal cavity, as well as muscles and ligaments, were subjected to almost maximum stress, which cannot pass without consequences. This explains why the stomach hurts during the recovery period. Of course, this condition causes discomfort, anxiety, and overshadows the joy of communicating with the baby, but it is natural. However, you need to monitor yourself, and if the pain becomes unbearable or continues for a long time, you need to consult a doctor.
What to do if your stomach hurts after childbirth? Be sure to go to the doctor!
How long your stomach hurts after the baby is born depends on many factors. In most cases, the causes of this condition are absolutely physiological, but pathology is also possible, so it is very important to accurately determine your feelings and, if necessary, take adequate measures.
The reasons for this condition may be different:
- Drawing spasms, like contractions that occur immediately after the completion of the labor process, are natural and indicate contraction of the uterus. During this period, a very active production of the hormone oxytocin occurs in the female body, which is responsible for stimulating the contractile process. If the birth took place by caesarean section, then this hormone is injected into the body intramuscularly to artificially stimulate the process of contraction of the walls of the uterus. As a rule, the most severe pain is observed in the first three days, but residual weak contractions may appear after two weeks.
- The stomach may ache and pull during breastfeeding, which is also associated with the synthesis of oxytocin. When a baby pulls milk from the breast, the mammary glands are irritated, which further stimulates the production of the hormone.
- If one month has passed, and fairly strong cramps are felt in the lower abdomen, this may indicate the presence of a pathology. In such a situation, you should immediately consult a doctor. The condition can be dangerous not only for a woman’s health, but also for her life. The most common cause of this disorder is incomplete cleansing of the uterine cavity and the presence of blood clots or placental remains that could not be expelled on their own. If in this case you do not consult a doctor in time, then rotting processes may begin inside the uterus, which will require not only cleaning, but also long-term complex treatment.
- Another reason can be called endometritis - inflammation of the uterine mucosa. This process can progress quite quickly, but, as a rule, it is observed very rarely in women who gave birth naturally. More often, young mothers who have undergone a cesarean section are susceptible to it, since pathogenic microorganisms can enter the uterine cavity during surgical intervention. Therefore, if two months have passed since the birth of the baby, and the discomfort in the lower abdomen persists or intensifies, the temperature rises and severe bleeding with clots and pus appears, you should immediately consult a doctor. As a rule, such symptoms appear precisely at the end of the second month after childbirth, since pathogenic microorganisms require time to reproduce.
Abdominal pain, as during menstruation.
Pain in the lower abdomen, as during menstruation, may indicate inflammation of the appendages - salpingoophoritis. In this case, the pain is nagging in nature and varies in intensity; it can be quite tolerable, but does not go away on its own.
Very severe pain at high temperatures may indicate the development of peritonitis, a very dangerous inflammatory disease. This condition requires urgent hospitalization.
If pain in the lower abdomen moves to the lower back, hindering movement and radiating to the spine, postpartum injury is possible. Most often, displacement of the lumbar vertebrae occurs. This can be a concern even when three months have passed after the birth of the baby, and sometimes the problem persists for several years, causing discomfort under any load on the back.
Quite often, the cause of discomfort and pain in the abdomen during the rehabilitation period is poor nutrition, as well as non-compliance with a certain diet recommended for nursing mothers. In this case, increased gas formation may be observed, caused by fermentation processes in different segments of the intestine, which causes discomfort.
We recommend reading: How long does discharge last after childbirth: normal and abnormalities
Another reason for this condition may be a strong divergence of the pelvic bones during the birth process, which requires proper and very long recovery. On average, this period can take from 5–6 months to a year.
What to do if your stomach hurts after childbirth? See a doctor immediately.
Physiological reasons
Irritation of pain receptors in the lower abdomen can be caused by the following phenomena:
- Removal of lochia and contraction of the uterus are often accompanied by discomfort and nagging pain, which becomes especially pronounced during breastfeeding.
- The process of childbirth involves not only the internal organs of the female reproductive system, but also the muscular-ligamentous apparatus. Abdominal pain can be the result of too much strain on the abdominal muscles.
- Diastasis that occurs in the third trimester of pregnancy and persists during the first period after childbirth is considered to be a physiological norm. One of the signs of divergence of the superficial rectus muscles is pain in the abdomen.
- The cause of pain can be sprained muscles and ligaments due to bone separation as the newborn passes through the birth canal.
Abdominal pain after childbirth, spreading to the lumbar spine, appears as a result of excessive stress on the lower back with a sharp increase in the abdomen and an unnatural shift in the center of gravity during this period.
Signs of the disorder
If after childbirth the lower abdomen hurts for more than a month after childbirth, the woman should consult a doctor. There is a high probability of having diseases that require timely treatment. Otherwise, discomfort and pain may increase and gain new momentum in the form of complications.
We recommend reading: Bandage after childbirth: types, how to put on, how long to wear?
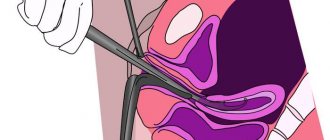
After scraping
Mechanical cleaning of the uterine cavity after childbirth is carried out to remove remnants of the placenta, fetal membranes or large blood clots. In a healthy woman, foreign tissues come out during the first 2-3 days with intense contractions of the uterus. In case of excessive stretching, thinning of the walls of the uterus, atony of its muscular layer, accretion of the placenta to the inner layer of the organ, the gynecologist has to do this during a mini-operation. According to statistics, after a caesarean section, curettage is indicated for almost every woman in labor. If the cleansing of the uterine cavity is successful, the lower abdomen may continue to hurt until the reproductive organ contracts completely. The pain, within normal limits, has a mild aching character, its intensity decreases every day. The following signs indicate the development of postoperative complications:
- increased pain in the absence of discharge;
- sometimes there is severe bleeding;
- lochia has an unpleasant distinct odor;
- hyperthermia is observed - an increase in body temperature to 38 degrees and above.
If at least one of the listed symptoms appears, a woman should immediately contact an antenatal clinic.
Endometritis
Pain in the lower abdomen after childbirth may be accompanied by brown discharge that does not resemble blood. In some cases, the bleeding only intensifies and resembles menstruation. The nature of the pain in this case is nagging, and in addition to it the following symptoms may occur:
- increased body temperature;
- intoxication;
- purulent vaginal discharge;
- symptoms of uterine subinvolution;
- increased heart rate.
Some of the causes of pain are physiological in nature, while others are associated with certain pathological conditions.
The cause of the symptoms in this case is postpartum endometritis, most often developing after a cesarean section. Endometritis requires timely treatment, as it is an infectious complication. This occurs due to impaired contractility of the uterus and retention of membranes or parts of the placenta in it. Abdominal pain after childbirth will only increase if endometritis is ignored; this can lead to inflammation of the periuterine tissue, pelvic peritoneum, and even peritonitis.
Symphysitis
Wondering why the lower abdomen hurts after pregnancy, a woman often sees a traumatologist and radiologist. It's all about symphysitis - separation of the bones of the pubic symphysis. The stomach hurts a month after childbirth in case of symphysitis due to the peculiarities of physiology. During the increased work of progesterone and other hormones, the pelvic bones soften and move apart, this is necessary for the free passage of the fetus during the birth process. The normal distance between the bones of the symphysis does not exceed one centimeter. During childbirth, the distance can increase to 5-6 mm, and in some cases the value reaches critical values. Bone discrepancy is divided into three degrees:
- 1st degree - distance 5-9 mm;
- 2nd degree - distance 1-2 cm;
- Grade 3 - distance greater than 2 cm.
If two days have passed after childbirth and pain occurs, the woman cannot walk or raise her legs on the bed, most likely the woman in labor has symphysitis. An accurate diagnosis will be made only after an x-ray.
Salpingo-oophoritis - inflammation of the appendages
Salpingoophoritis is an inflammation of the fallopian tubes and appendages. Tandem organ damage occurs very often. Less commonly, inflammation is localized only in the fallopian tubes (salpingitis) or only in the appendages (oophoritis). The development of the disease is provoked by pathogenic microorganisms - staphylococci, gonococci, Escherichia coli and streptococci.
During the course of the disease, acute, chronic and latent forms are distinguished. The latent form is asymptomatic. In the chronic form, periods of exacerbation and remission are distinguished. At the same time, the symptoms are blurred. Signs of postpartum inflammation of the appendages are clearly expressed only in acute form.
The disease manifests itself:
- Increasing temperature indicators
- Copious foamy discharge
- Aching sensations in the lower abdomen
Usually it hurts either the left side or the right. Bilateral inflammation of the appendages is less common.
Suppuration of sutures after cesarean section
Incorrect postoperative care or infection of the suture starts the process of suppuration. Along with a high temperature, when the sutures suppurate, pain appears as during menstruation. Their intensity is higher after the second birth, which was performed by caesarean section.
Intestinal problems
Adaptation processes in connection with childbirth affect almost all systems and organs. Immediately after childbirth, intestinal motility is slowed down, and it will take time to bring the process of fecal excretion back to normal. Delayed bowel movements are most often associated with the mother’s fears of damaging the sutures or causing an exacerbation of hemorrhoids. As a result, compressed feces accumulate in the rectum and cause nagging pain in the lower abdomen and bursting pain that spreads over the entire surface of the anterior abdominal wall.
Peritonitis
This pathology is represented by an infectious disease that occurs as a result of rupture of the uterine suture after cesarean section. As a result, infection of the abdominal cavity occurs. The complication is manifested by acute pain and a rapid increase in temperature.
Placental polyp
Often after childbirth, the stomach hurts severely due to retention of placental remains in the uterine cavity, which can lead to bleeding. Sometimes chorionic villi help the uterus contract, which delays the pathological process for several weeks. After 4-5 weeks have passed, the clinical picture begins:
- signs of bleeding (pallor, weakness, decreased blood pressure, decreased hemoglobin, tachycardia);
- a month after giving birth, your stomach hurts due to infection (this indicates the development of endometritis).
Further symptoms develop in the classic “style” of uterine inflammation.
Vertebral displacement
A spinal injury can be judged if, after childbirth, the lower back hurts for no apparent reason. Women who are overweight are more susceptible to this diagnosis. Also, vertebral displacement often occurs during childbirth with pain relief.
Pain occurs when walking or doing physical exercise. Discomfort below can be felt even several 4-5 months after childbirth.
Osteochondrosis
So, a month has passed since giving birth, and my lower abdomen hurts. In addition to the above, osteochondrosis may also be to blame. The fact is that the back during this period undergoes a large load caused by an increase in the girl’s body weight. If the expectant mother did not use a special bandage, her back may hurt very badly. Even if quite a long time has passed after childbirth, the pain may persist due to compression of the nerve endings. With osteochondrosis, the lower abdomen and lower back most often hurt, so it’s not easy for a woman.
We recommend reading: Pads for women in labor: which ones to take to the maternity hospital, sterile models after childbirth, how to use them
Static and dynamic overloads, as well as vibration, contribute to the development and exacerbation of spinal osteochondrosis.
There are several other causes of postpartum abdominal pain:
- often after childbirth the right side of the lower abdomen hurts due to inflammation of the ovaries;
- after childbirth, the left side in the lower abdomen hurts - most likely, it is due to inflammation of the ovaries or appendages. Pain on the left and right can be bilateral;
- A gastroenterologist will tell you why your stomach hurts after childbirth. This could be irritable bowel syndrome, gastritis, gastroduodenitis, gastroptosis or an ulcer. After pregnancy, irritable bowel syndrome most often occurs because the diet is changed and bowel function becomes much more difficult.