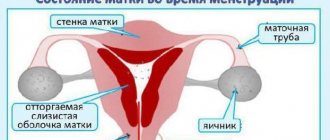
With the appearance of the next monthly discharge, a woman begins a new menstrual cycle. What does discharge after menstruation mean?
The cervix closes after menstruation, since there is no need to remove the remaining endometrium. A common condition is that the uterus shrinks after the discharge stops, but if it is enlarged and the breasts are swollen and painful after menstruation, then you should immediately consult a doctor. There may also be spotting after menstruation. Women may be bothered by an unpleasant odor after menstruation. All these symptoms may be the result of an inflammatory process or tumor. Ultrasound examination will help identify tumors.
But also swollen breasts, enlarged uterus, and blood after menstruation may indicate pregnancy. This may happen if the scanty bleeding allowed in the early stages of pregnancy was mistaken for menstruation.
But still, contrary to the generally accepted opinion that ovulation occurs on days 12-14 of the menstrual cycle, the period when you can get pregnant can occur as early as 8 days after your period. This can be explained by the fact that not all women have a regular cycle, the period of ovulation can be shifted, and therefore the moment of egg maturation is almost impossible to calculate.
What to do if you bleed after menstruation?
If the lower abdomen hurts after menstruation and this is accompanied by bleeding, then there is a possibility of hormonal imbalance, the presence of inflammatory gynecological diseases, and the occurrence of neoplasms. All of the above can become a serious obstacle to the ability to have children in the future or lead to complete infertility in case of untimely treatment.
If it smears after menstruation, you should be examined by a gynecologist as soon as possible and, if necessary, begin treatment. Here are just some of the reasons for bleeding after menstruation:
- polyps;
- injuries of internal genital organs;
- endometriosis, endometritis and other inflammatory diseases;
- uterine fibroids;
- dysfunctional bleeding
So, it becomes clear that it is smeared after menstruation for many reasons, which should be established as early as possible. But in no case should you try to independently determine the nature of the discharge and self-medicate. Only a gynecologist can provide qualified assistance and prescribe effective treatment.
The uterus contracts poorly during menstruation
Did you experience blood clots in your discharge during your period?
Should we panic and what is the reason for this? We will tell you about this in our article. Are you tired of discomfort and poor health due to your period? And then there was also unpleasant discharge, is it really dangerous?
Clots came out during menstruation: a reason to panic?
In most cases, they do not pose any danger; they are produced by the body. During the cycle, the walls of the female uterus are covered with the placenta, and the eggs await fertilization. If this does not happen, during menstruation these formations come out of the uterus in the form of blood and clots. As you can see, there is no danger!
However, we recommend paying attention to the color, size and smell of the clots. If they have colors uncharacteristic of blood and have an unpleasant aroma, it is possible that you may have health problems, so we advise you to consult a doctor as soon as possible. We also advise you to sound the alarm if there are too many clots and menstruation lasts much longer than usual.
Check out our post Why Do Your Breasts Hurt Before Your Period?
Menstruation with clots: reasons
There are several reasons for the appearance of clots, find out them right now:
Endometriosis – if the neoplasms contain light red elements. Most often, menstruation in such cases is accompanied by pain and discomfort. If the disease is not treated, infertility may develop.
The uterus does not contract. Why do clots come out during menstruation? Another reason is problems with uterine contractions; in this case, the doctor prescribes drugs that increase the frequency of contractions.
Remnants of the placenta. If a woman has not given birth, during menstruation the placenta may accumulate in the uterus; in this case, curettage is prescribed.
Congenital anomalies of the uterus . Perhaps your uterus is irregularly shaped or displaced, which is what causes clots to form.
Recent birth. Many women who have given birth may experience blood clots during the month after childbirth; this is a completely normal phenomenon. But if even after a month they continue to be released, consult your doctor, this is a serious violation.
Blood clotting . This is an abnormal process and occurs when any disease appears. Medications can also increase clotting.
Spiral for protection. Perhaps you are using an intrauterine device? Alas, very often those women who choose this method of contraception complain that after its installation too many clots appear in the discharge.
Problems with hormones . Very often, clots cause disturbances in the functioning of a woman’s hormonal system; several tests must be taken to determine the level of hormones. If you do not feel discomfort or pain during menstruation, you should not consult a doctor. But if your period is accompanied by dizziness, sudden mood swings and pain in the lower abdomen, consult a doctor as soon as possible.
If you understand that clots and discharge are not the same as before and are different in color or character, be sure to consult a specialist; do not ignore the problem.
If your period comes with clots: what to do?
It all depends on what is causing the problem. If you have a hormonal imbalance or have been diagnosed with endometriosis, your doctor will prescribe you special medications.
Those women who have an IUD should consult a doctor only if menstruation begins to last longer and there are too many clots. In case of poor uterine contractility, medications are also prescribed, and in the presence of congenital anomalies, surgical intervention may be prescribed.
Do not under any circumstances try to use the drugs yourself, without the advice of a specialist.
If you are concerned about discharge and have not had clots before, this is a reason to sound the alarm. In some cases, they can be a sign of a serious illness and the sooner you seek help, the better.
After menstruation
A healthy cervix after menstruation begins to prepare again for conception. Immediately after the end of the critical days, the pharynx narrows, because the bleeding has stopped. Simultaneously with the organ being pulled up, the endometrium begins to grow, into which a fertilized egg can be implanted during conception. In addition to its high location, the conditions of the cervix before and after menstruation are similar - the same dryness and tissue density.
But during the period of ovulation, the organ loosens again and begins to secrete mucus. The norm during this period is contraction of the uterus, but if it is still enlarged, then we can talk about pregnancy, a tumor or an infection. There is no need to think that conception during menstruation is impossible - despite the reduced fertility of the organ, there is some probability of becoming pregnant. Therefore, if the uterus has not contracted after the critical days, then it is worth getting tested for hCG or having an ultrasound.
It’s another matter if you are not pregnant, but neoplasms are found on the cervix - we can talk about polyps, erosion or fibroids. However, only a gynecologist can determine whether the uterus is enlarged or not. The woman feels unlikely to be able to independently identify suspicious signs. Naturally, there is a preliminary diagnosis method that is easy to apply at home. This is self-palpation of the cervix. The manipulation must be carried out extremely carefully.
Non-infectious inflammation
Adnexitis, endometritis, adenomyosis and some other non-infectious diseases of the reproductive sphere may hardly bother a woman at normal times, but during menstruation they manifest themselves as cramping pain in the lower abdomen.
, which is necessary to expel blood and particles of rejected epithelium of the inner wall of the reproductive organ, causes pain during menstruation
An additional provoking factor for pain during menstruation is natural fluctuations in hormonal levels, taking into account the phase of the menstrual cycle.
Symptoms
During menstruation, cramping pain radiates:
The intensity of painful manifestations varies. “Contractions” during menstruation can be moderate or can cause almost unbearable pain.
In addition to painful discomfort, menstruation is accompanied by profuse bleeding.
Treatment of gynecological pathologies should be prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the nature of the inflammatory process. And to alleviate the condition during menstruation, it is recommended to drink antispasmodics :
If the pain is unbearable or there is heavy bleeding, you should call an ambulance.
Which doctor treats
Gynecologists deal with pathologies of the female reproductive system.
Rejection of the fertilized egg cannot always be determined; spontaneous abortion is often perceived as the beginning of menstruation and the woman loses the child without knowing that she was pregnant.
Attachment of the fertilized egg occurs with the help of the chorion (embryo of the placenta) and in the first days after implantation the embryo is not well enough attached to the wall of the reproductive organ. The following can provoke embryo rejection :
- stress;
- overwork;
- carrying heavy bags;
- straining with constipation;
- bruises of the abdominal wall.
Sometimes rejection occurs for no apparent reason. Doctors suggest that in this way the body gets rid of a dead or non-viable embryo.
Spontaneous abortion can be suspected by the nature of the pain:
- An aching or nagging pain appears, radiating to the sacrum or coccyx. Lobar discomfort is accompanied by the appearance of spotting vaginal discharge.
- Gradually the pain begins to get stronger, contractions appear during menstruation. Cramping pain develops against the background of severe uterine bleeding.
If a woman always experiences cramping pain during her period, then a miscarriage may go unnoticed.
Help with spontaneous abortion can only be done in a hospital setting. If it is possible to maintain the pregnancy, then drugs are prescribed that relax the walls of the reproductive organ . In addition to the main therapy, a general strengthening course of taking vitamins is carried out.
If the embryo is completely torn from the wall of the uterus, then doctors carry out an inspection (preventive cleaning) of the reproductive organ to prevent complications that arise when the fertilized egg is not completely released.
Who will help
If spontaneous abortion is suspected, hospitalization in the gynecology department is indicated.
Causes of menstrual irregularities due to uterine fibroids
The first sign of tumor formation in the reproductive system is that menstruation with fibroids becomes heavy and irregular. Women experience abdominal pain that reduces their quality of life.
Timely and correct treatment allows you to solve the problem of cycle failure once and for all. It is selected by a gynecologist on an individual basis. Restoring menstruation helps improve a woman’s well-being. In the future she may become a mother.
The effect of uterine fibroids on menstruation
The formation of a myomatous node in the uterine cavity has a negative impact on the activity of neighboring organs - intestinal loops, bladder. The functioning of reproductive structures also changes. The nature of menstruation with fibroids is different:
- longer – over 6–7 days;
- more abundant - with blood clots;
- acyclic - spotting between the main menstrual flows;
- scanty - with intense pain.
In the absence of therapeutic measures for menstruation with uterine fibroids, it is inherent to deplete the female body. Constant blood loss provokes severe anemia, decreased ability to work, a tendency to colds, and exacerbations of chronic pathologies.
Duration of menstruation
The size of the tumor directly determines what your period will be like with fibroids. The intensity of the discharge characterizes the severity of the pathological process. The duration of menstruation and the myomatous node are closely interrelated: the stronger the tumor focus grows, the more significant the changes in the woman’s individual cycle.
Disorders of well-being - bleeding, discomfort in the lower abdomen, decreased libido - are noted in each case.
However, the duration of menstruation is variable.
For some women, this is a difference of 1–2 days compared to the previously observed tissue renewal in the uterus. For other representatives of the beautiful part of the population, the course of menstruation with uterine fibroids changes dramatically.
Often such days occur 2-3 times a month.
Less often, delays between menstruation are possible due to changes in the structure of the endometrium in the organ cavity. In addition, hormonal levels have a huge impact - the entire woman’s body suffers from its fluctuations.
Causes of heavy periods
Despite its benign quality, a myomatous neoplasm certainly affects the volume of uterine discharge. Women are more likely to experience heavy periods due to fibroids. Causes of this disorder:
- due to hormonal fluctuations immediately before menstruation, the tumor also increases in size;
- the endometrium thickens and its rejection occurs unevenly;
- the submucosal node stretches the tissue, the vessels that feed the neoplasm burst, and blood comes out together with the menstrual fluid.
The nature of the discharge also changes - it can be either liquid, almost watery, or thick, with pieces of mucous membrane and clots. The color can be either scarlet or dark cherry.
In general, heavy periods themselves cause deterioration in the reproductive system. The body does not have time to recover, and its energy reserves are depleted.
Delayed periods
At the early stage of fibroid formation, monthly ailments in women change little. Sometimes women who are attentive to such disorders in their body note that menstruation periods are shortened - by at least 1-2 days. This condition requires medical intervention, as does abundant acyclic metrorrhagia.
The main reasons for delayed menstruation due to uterine fibroids:
- changes in the structure of the tissue inside the uterus;
- ovarian dysfunction;
- disruption of blood circulation in the endometrial vessels;
- fertilization of the egg has occurred.
A monthly discharge of less than three days is considered to be scanty, with barely noticeable smear marks on a sanitary pad or underwear. In the future, they are usually replaced by painful and profuse blood loss from the uterine cavity. Sometimes they even develop into bleeding, which requires immediate medical attention in a hospital setting.
Lack of menstruation
It is extremely rare that menstruation with uterine fibroids is completely absent. The explanation for this situation is a severe change in the structure of the muscular layer of the organ - against this background, the endometrium is not able to fully separate. A small amount of blood accumulates inside the uterus, which is accompanied by intense pain, inflammatory symptoms, and a sharp deterioration in well-being.
There are cases where amenorrhea was the result of cessation of blood supply to a myomatous tumor, both natural and artificial.
For example, a woman was recommended for therapeutic purposes to take medications that prevent menstruation, or embolization of the uterine arteries was performed. Short-term menopause is completely reversible.
Another understandable reason for the absence of menstruation in women with fibroids is the onset of pregnancy. After all, the tumor itself does not prevent the fertilization of the egg.
It subsequently complicates the proper development of the fetus and the birth process.
The expectant mother must be under the supervision of an experienced obstetrician-gynecologist, who will select the optimal method of delivery and elimination of the myomatous neoplasm.
Actions for delayed menstruation due to fibroids
If a delay in menstrual flow is detected due to uterine fibroids, the woman is first recommended to seek advice from her treating gynecologist. Already at this stage, you can perform a number of diagnostic procedures that will help establish the root cause of the malfunction in the female body:
- perform a pregnancy test - acceptable at home;
- take a blood test for hCG concentration;
- undergo an examination in a gynecological chair;
- examine the structures of the pelvis with ultrasonic waves.
In the absence of a fertilized egg both in the uterine cavity and in its appendages, the specialist will select the optimal treatment regimen for amenorrhea. As a rule, a course of medications with a minimum amount of female sex hormones is sufficient. They will simultaneously help normalize the menstrual cycle and also reduce the size of the tumor.
Additionally, you can resort to traditional medicine recipes - decoctions and infusions of medicinal plants that can correct blood flow in the pelvis. Each remedy must be agreed upon with the attending physician. Chamomile and calendula, red brush and parsley have proven themselves to be excellent.
Surgical removal of fibroids is resorted to in extreme cases - for example, when a tumor is suspected of malignancy or in cases where the absence of menstruation is due to the presence of a node in the cervical region, which threatens organ rupture.
Actions for heavy periods with fibroids
Excessively heavy menstrual blood loss certainly depletes the female body. First of all, the actions of specialists are aimed at stopping discharge from the uterine cavity.
After assessing the patient’s health, the gynecologist makes a decision: to fight the disease with conservative methods, for example, pills, or to perform a minimally invasive intervention to preserve the integrity of the organ. Pharmaceutical subgroups that can stop blood loss include:
- drugs that help increase contractile activity of the uterus;
- agents that increase blood viscosity;
- hormonal medications;
- anti-inflammatory medications.
In the absence of a positive result—menstruation remains acyclic and heavy—the issue of surgical removal of the pathological focus is considered. In most cases, they resort to embolization or FUS ablation of the uterine arteries. The procedure is completely safe for the reproductive system, leaving women the opportunity to become a mother in the future.
Traditional medicine is also effective - since ancient times, decoctions of nettle, knotweed, barberry and shepherd's purse have restored menstruation and improved the well-being of representatives of the fair part of the population.
Ectopic pregnancy
The egg is fertilized in the fallopian tube, and then descends into the uterus and implants into the wall of the organ. But sometimes attachment occurs not in the uterus, but in an organ that is not adapted for this - then an ectopic pregnancy occurs.
Difficulty in the passage of the fertilized egg through the fallopian tubes may be caused by:
- obstruction;
- the presence of pathological narrowings;
- inability of the walls of the reproductive organ to attach a fertilized egg (implantation occurs in the cervix).
Unable to gain a foothold in the reproductive organ, the fertilized egg implants into the fallopian tube or uterine cervix, and less often into other organs that are also unsuitable for bearing a child.
Ectopic pregnancy is characterized by:
- cramping pain in the lower abdomen before menstruation;
- the appearance of heavy bleeding against the background of intensified contractions.
During tubal implantation, there is additional pain on the right or left (at the site of embryo attachment).
Almost always, symptoms develop after a missed period and the woman already knows about pregnancy. But, unfortunately, with the help of the test it is possible to determine only the fertilization that has occurred, and not the place of implantation of the embryo, and during an external examination it is impossible to distinguish an ectopic pregnancy from a miscarriage.
Doctors decide what to do in a hospital setting. The cervical implant comes out on its own under medical supervision or is removed by cleaning the reproductive organ under local anesthesia.
With tubal insertion, spontaneous evacuation is impossible, and cramping pain can lead to rupture of the fallopian tube . In this case, abdominal surgery or endoscopic removal of the tube along with the embryo is performed.
Where to contact
If your period is heavy, accompanied by severe cramping pain, you must call an ambulance. Doctors will take you to the emergency department of a gynecological hospital.
the uterus does not contract after menstruation
Hi all! Here is the situation. My period started 5 days earlier, but it went on for 2 days and just stopped for a day and it wasn’t even masolo, then another day it went on for maybe 6 hours, and now I don’t have my period, it ended abruptly, it’s just clear and that’s it .usually I decrease and the cabbage soup ends, but here it’s not like that. And now the uterus doesn’t contract, what is it? At the same time, the nausea is very strong, I can’t stand the smells and I eat like an animal. Usually I’m in control, I could even abstain from food, for the sake of my figure. I feel heaviness in stomach.
Girls, thank you in advance for your advice! I took the test immediately after my period and showed one line.
Fibroids rejection
A benign pedunculated tumor growing inside the uterus can spontaneously be rejected.
Provoking factors
The main reason is considered to be: spontaneous detachment of the tumor, which occurs in a number of cases:
- when jumping from a great height;
- abdominal bruises;
- overstrain of the abdominal wall.
Detachment is possible only for small tumor formations. The risk of spontaneous fibroid rejection increases during menstruation.
When fibroids are “born,” pain appears during menstruation, like contractions, and then the volume of bloody discharge from the vagina increases.
Rejection of a fibroid node is similar in symptoms to a miscarriage, but the process ends with the release of a homogeneous formation.
After self-removal of the tumor, the cramping pains lose intensity and gradually disappear, and the volume of bloody discharge decreases. If the bleeding does not decrease, this may indicate damage to the blood vessels inside the uterus or internal ruptures.
Regardless of the outcome of the expulsion of the fibroid formation: the node has come out and the contractions have stopped, or the process is actively continuing, the woman must be hospitalized. In this case, the “born” neoplasm is also taken for subsequent cytological examination.
In a hospital setting, an ultrasound scan of the uterus is performed and the size of the detached tumor is determined - the treatment tactics depend on this. After obtaining the necessary information, the fibroids are removed under local anesthesia and the uterus is inspected .
For bleeding from large vessels that cannot be stopped by curettage or cauterization, surgery is indicated.
If the node has already come out and there is bloody discharge, as during menstruation or after childbirth, then the patient is left under observation and the examination is carried out as planned.
Who will help
The necessary assistance will be provided by doctors in the gynecological surgery department.
Principles of self-palpation
It is best, even for the simplest examination, to contact a professional gynecologist, no matter how much time or money it costs you, but if you are impatient and decide to be examined yourself before visiting a doctor, it is important to listen to the recommendations of specialists:
- It is strictly undesirable to conduct a vaginal examination two days before and during menstruation;
- Hands should be clean, with fingernails cut short;
- It is most convenient to carry out the procedure in a sitting position, for example, on a toilet or bidet. Alternatively, you can squat down or use an elevated platform with one foot on it;
- Movements should be as smooth and careful as possible to avoid injury to a delicate organ.
So, you have taken a comfortable position and begin the palpation procedure. Insert the middle and ring finger, dressed in a sterile rubber glove, into the vagina and rest against the tubercle - this is the cervix.
If the middle finger easily rests on the cervix, this means that it is in the lower position, corresponding to the period before the menstrual period. If it is difficult to reach the cervix, this means that it has contracted to its normal state, as after menstruation.
It is important to remember that independent research can only give a very general and incomplete picture of the condition of the internal genitalia, especially when it comes to determining the degree of density and size of the uterus. This is explained by the fact that in addition to tactile sensations, it is very important to conduct a visual examination of the condition of the genital organs, and this is only available during an examination by a specialist.
Based on the above, we draw a reasonable conclusion - no amateur activity can cancel a visit to a competent gynecologist, and especially not worth your health.
What else provokes cramping pain during menstruation?
Let's see what other causes of cramping pain during menstruation may be:
- Intestinal diseases. The intestinal loops are located next to the uterus and the symptoms of organ pathology intensify during menstruation due to the fact that the reproductive organ begins to shrink slightly. A characteristic feature is that cramping pain is accompanied by nausea, flatulence and other dyspeptic disorders.
- Scars or adhesions on the uterus. Due to abortion, gynecological diseases or surgical interventions, scar changes appear, so the walls of the reproductive organ cannot contract evenly during menstruation. This causes cramping pain in the lower abdomen.
- Individual pain sensitivity. Some girls have an increased reaction to pain and physiological contractions of the reproductive organ during menstruation begin to be perceived as cramping painful manifestations.
- Puberty. Girls may experience cramping pain for 1-2 years from the beginning of their first menstruation until the menstrual cycle is fully established.
The appearance of cramping pain almost always indicates the development of pathology. You should not ignore the symptoms that arise - this can lead to the development of complications.
What to do when cramping pain appears during menstruation
First of all, assess your condition:
- Pain intensity. If the pain during menstruation is severe, then immediate medical attention is required.
- The nature of menstrual bleeding. Heavy bleeding during menstruation may indicate a miscarriage or uterine bleeding. If the cramping pain intensifies, then hospitalization is required.
- When it started to hurt. If painful cramping sensations appear during menstruation regularly for several years, then this may be a sign of a hidden chronic process in the reproductive sphere or an incorrectly installed intrauterine device. No emergency assistance is required, but it is necessary to undergo an examination by a gynecologist.
- Duration of pain. If it hurts throughout the entire menstruation and moderate pain persists after menstruation, then this is an alarming sign that requires attention.
The appearance of cramping pain during menstruation, with rare exceptions, indicates a pathological process. Contacting a gynecologist will help make periods less painful and preserve women's health.
Found an error? Select it and press Ctrl+Enter.
Sequences of changes in the uterus during menstruation
The condition of the uterus changes during menstruation. The change is aimed at facilitating the exit of exfoliated endometrium. The neck expands and the pharynx opens. The uterus is usually enlarged and prolapsed during menstruation. This only happens if fertilization has not taken place. Rejection of the endometrium occurs approximately on the 29th day of the cycle. Deviations of several days are possible based on the individual characteristics of a particular woman’s body. The condition of the uterus during menstrual periods helps to assess women's health. The organ is used to verify the absence or, conversely, the presence of infectious processes. It is recommended to check the organ using ultrasound during menstruation.
Naturally, the uterus changes during menstruation
Cervix during menstruation
We found out what the condition of the cervix is before menstruation, now we will find out what it looks like directly on menstruation days. At this time, the pharynx expands slightly, as during ovulation, but the purpose of this opening is different - not readiness for fertilization, but the desire to erupt blood clots. This position of the cervix during menstruation creates fertile ground for the proliferation of bacteria and the addition of infection. That is why on critical days it is not recommended to swim in open water, visit the pool, have unprotected sex and insert foreign objects into the vagina - fingers, a speculum. Although the moderate mucous discharge that is observed during this period is designed to protect the woman from infection, it is still not worth the risk.
The condition of the cervix during menstruation requires external hygiene . Ideally, you should wash yourself twice a day, not counting the procedures after bowel movements. You cannot wipe the anus in a forward direction - such actions are fraught with infection. It is also strongly recommended not to carry out water procedures inside the vagina during this period - no douching or insertion of intimate hygiene products. Often during menstruation, women experience pain in the uterus. Most often they are associated with the rejection of blood clots. In this case, conventional antispasmodics help. But sometimes painful contractions of the cervix signal an infection or pathology in the development of the organ. Therefore, do not neglect routine examinations with a gynecologist, so as not to lead to infertility from a common illness.
By the way, it is not so much pain, which is often a sign of dysmenorrhea, as heavy discharge that warns of abnormalities - fibroids, endometriosis, bleeding disorders and acute infections. In any case, after your period, especially if the pain in the uterus has not stopped, you should consult a doctor and do an ultrasound. If the cause of discomfort is dysmenorrhea, then it makes sense, along with painkillers or contraceptives, to take a course of vitamins and Omega-3 complex. If the cause of the pain is a serious illness, you should immediately begin treatment prescribed by the gynecologist.
What are periods
Menstruation is characterized by the monthly appearance of natural bleeding. The duration of the process is 3-7 days. It is from the first day of critical days that the menstrual cycle begins.
Features of the first menstruation are presented in the table.
Menstruation is accompanied by natural changes in hormonal levels. The endometrium begins to peel off if the egg moving through the fallopian tubes has not been fertilized. If you become pregnant, you should not have periods.
Normally, menstrual bleeding lasts up to 7 days. A longer presence of discharge may indicate bleeding due to pathological processes existing in the body.
Menstruation completely disappears in women by the age of 45-50. This period is usually called menopause. The girl loses the function of childbearing. The supply of her eggs for a man to fertilize is running low.
The uterus retains its reproductive function only at a young age
The menstrual cycle lasts 28-32 days. Possible insignificant deviations depending on individual characteristics. Delays can be explained by a low standard of living, bad habits or the presence of diseases of the reproductive system.
Menstruation reflects the state of the female reproductive system. Any violations should not be ignored. It is important to see a doctor for diagnosis. The doctor will make a diagnosis and, if necessary, select effective treatment.
Preparing the body for menstruation
During desquamation, the functional layer of the endometrium is rejected. The process occurs on the 28-29th day of the cycle. It lasts 5-6 days. The functional layer looks like areas of necrotic tissue, and with the arrival of menstruation, the endometrium is completely rejected in 1-2 days.
At the very beginning of menstruation, the uterus in its normal state has a smooth and tactilely dense cervix.
Its normal size in nulliparous girls is: length – 45 mm, width – 46 mm, thickness – 34 mm; and for those who gave birth: length – 53 mm, width – 50 mm, thickness – 37 mm.
During ovulation, the cervix opens a little and becomes loose. After a failed conception, the process of menstruation begins. The cervix begins to straighten and descend into the vagina.
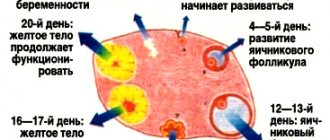
It is the process of shedding the endometrium and leaving it from the uterus that is called menstruation. The phases of the menstrual cycle are regulated by follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones of the pituitary gland, due to which active substances are released: progesterone, estrogen. These hormones prepare the body for conception and regulate the menstrual cycle.
The period of menstruation usually lasts 2-7 days, and the duration of the menstrual cycle is approximately a month. However, some deviations in its duration are acceptable, but the cycle must be regular.
The pain and duration, various characteristics of menstruation, as well as the menstrual cycle are mainly influenced by heredity.
How its dimensions change
The size of the uterus can be determined by a doctor in a hospital setting. It is impossible to do this on your own.
Enlargement of the uterus occurs 14 days before the onset of menstruation. The process is normal and should not cause concern. The cervix softens before menstruation. It also opens slightly if the woman has already given birth.
The length of the cervix changes during menstruation. This is due to the fact that the organ not only increases, but also decreases slightly.
The size of the uterus varies from person to person. The organ is smaller in girls who have not given birth. Also, the dimensions directly depend on the general condition of the woman’s body.
Uterus after menstruation
After the separation of the endometrium is completed, the bleeding stops, the cervix closes, and the woman’s body enters the phase of preparation for the next potential fertilization. During this period, the reproductive organ rises higher and the decidual layer grows again, into which, upon successful conception, the embryo is implanted. This happens gradually, until the middle of the menstrual cycle - before the ovulatory phase.
A significant increase in the uterus during this period indicates a possible pregnancy or some kind of disease.
What does the change depend on?
Changes in the uterus during the menstrual period depend on many factors. The growth of the organ is determined by hormonal levels. Progesterone and estrogen have a direct effect.
The video describes what happens in the body during menstruation:
The size of the uterus returns to normal immediately after menstruation. If this does not happen, then pregnancy should be suspected. Progesterone has an effect during critical days. The hormone has the following actions:
- affects the condition of the endometrium, namely makes the layer softer and looser;
- increases blood flow in a woman’s internal organ;
- activates the process of fat accumulation;
- responsible for enlarging the internal organ;
- promotes fluid retention in the body.
Thanks to these actions, the natural growth of the uterus occurs. This is a natural process that does not require any treatment.
The uterus can also enlarge during pregnancy.
The following signs indicate successful fertilization:
- increased sensitivity of the mammary gland;
- frequent urination;
- nagging discomfort in the lower abdomen;
- change in gastronomic preferences;
- change in emotional background.
Pain in the lower abdomen may indicate pregnancy.
Only a doctor can determine the true cause of organ growth.
Condition of the uterus after menstruation
The uterus undergoes some changes after menstruation. She again begins to prepare for a possible pregnancy. The endometrium, the inner uterine layer into which the fertilized egg is implanted, grows day by day. And if the uterus is slightly open before menstruation, then at the beginning of the next menstrual cycle it closes again, as the discharge stops.
Based on the condition of this organ, some pathologies can be diagnosed. For example, if the uterus is enlarged after menstruation (and, in principle, in any other phase of the cycle, if there is no pregnancy) - this may indicate the presence of neoplasms in it. Typically, with this pathology, the reproductive organ takes on asymmetrical shapes. Uterine tumors are diagnosed using ultrasound examination. The most common benign tumor is fibroid, which increases the size of the organ.
It’s another matter if no pathologies are identified, but the woman says that the uterus contracted poorly during menstruation. There were very few allocations. And the doctor notices that the uterus is larger than normal in size, and there are other signs of pregnancy, such as, for example, cyanosis of the walls of the vagina and cervix. Yes, this happens too. Conception is possible only in the middle of the menstrual cycle. But bleeding is possible in the early stages of pregnancy. And women mistake them for menstruation.
Some women try to find out in a non-standard way whether they are pregnant, or whether they simply had scanty menstruation. For this purpose, tests are not purchased, but an independent vaginal examination is performed. During pregnancy, the cervix is normally always closed and located deep in the vagina. After menstruation, the cervix is filled with thick mucus, which serves as a kind of protection against infection. During ovulation, the mucus becomes thinner, allowing sperm to pass through.
And if the uterus hurts after menstruation, is this normal? More often than not, no. Moderate pain during menstrual bleeding is quite normal and predictable for many women. But if pain persists after menstruation, you should think about a possible gynecological disease or pathology of the genitourinary system. For example, painful contractions of the uterus can occur with cystitis (another sign of this disease is frequent and painful urination). Severe pain can be caused by uterine fibroids, endometriosis, and adhesions. Some women experience pain in the lower abdomen after sexual intercourse.
The uterus contracts poorly during menstruation
Did you experience blood clots in your discharge during your period? Should we panic and what is the reason for this? We will tell you about this in our article.
Are you tired of discomfort and poor health due to your period? And then there was also unpleasant discharge, is it really dangerous?
Clots came out during menstruation: a reason to panic?
In most cases, they do not pose any danger; they are produced by the body. During the cycle, the walls of the female uterus are covered with the placenta, and the eggs await fertilization. If this does not happen, during menstruation these formations come out of the uterus in the form of blood and clots. As you can see, there is no danger!
However, we recommend paying attention to the color, size and smell of the clots. If they have colors uncharacteristic of blood and have an unpleasant aroma, it is possible that you may have health problems, so we advise you to consult a doctor as soon as possible. We also advise you to sound the alarm if there are too many clots and menstruation lasts much longer than usual.
Check out our post Why Do Your Breasts Hurt Before Your Period?
Menstruation with clots: reasons
There are several reasons for the appearance of clots, find out them right now:
Endometriosis – if the neoplasms contain light red elements. Most often, menstruation in such cases is accompanied by pain and discomfort. If the disease is not treated, infertility may develop.
The uterus does not contract. Why do clots come out during menstruation? Another reason is problems with uterine contractions; in this case, the doctor prescribes drugs that increase the frequency of contractions.
Remnants of the placenta. If a woman has not given birth, during menstruation the placenta may accumulate in the uterus; in this case, curettage is prescribed.
Congenital anomalies of the uterus . Perhaps your uterus is irregularly shaped or displaced, which is what causes clots to form.
Recent birth. Many women who have given birth may experience blood clots during the month after childbirth; this is a completely normal phenomenon. But if even after a month they continue to be released, consult your doctor, this is a serious violation.
Blood clotting . This is an abnormal process and occurs when any disease appears. Medications can also increase clotting.
Spiral for protection. Perhaps you are using an intrauterine device? Alas, very often those women who choose this method of contraception complain that after its installation too many clots appear in the discharge.
Problems with hormones . Very often, clots cause disturbances in the functioning of a woman’s hormonal system; several tests must be taken to determine the level of hormones. If you do not feel discomfort or pain during menstruation, you should not consult a doctor. But if your period is accompanied by dizziness, sudden mood swings and pain in the lower abdomen, consult a doctor as soon as possible.
If you understand that clots and discharge are not the same as before and are different in color or character, be sure to consult a specialist; do not ignore the problem.
If your period comes with clots: what to do?
It all depends on what is causing the problem. If you have a hormonal imbalance or have been diagnosed with endometriosis, your doctor will prescribe you special medications.
Those women who have an IUD should consult a doctor only if menstruation begins to last longer and there are too many clots. In case of poor uterine contractility, medications are also prescribed, and in the presence of congenital anomalies, surgical intervention may be prescribed.
Do not under any circumstances try to use the drugs yourself, without the advice of a specialist.
If you are concerned about discharge and have not had clots before, this is a reason to sound the alarm. In some cases, they can be a sign of a serious illness and the sooner you seek help, the better.
Features of the uterus during, before and after menstruation
Monitoring the condition of the cervix in gynecology is one of the main aspects of monitoring the health of the female reproductive system. Any changes in this organ can serve as evidence of puberty, pregnancy, ovulation with the approach of critical days, as well as a picture of various pathologies, infectious diseases and other various alarming symptoms.
A cervical check should be done regularly (at least once a year), preferably before your period or during ovulation. At this time, the organ is most sensitive and maximally manifests outwardly noticeable problems with women’s health - various benign and malignant neoplasms, endometriosis, erosions and other diseases.
Non-infectious inflammation
Adnexitis, endometritis, adenomyosis and some other non-infectious diseases of the reproductive sphere may hardly bother a woman at normal times, but during menstruation they manifest themselves as cramping pain in the lower abdomen.
, which is necessary to expel blood and particles of rejected epithelium of the inner wall of the reproductive organ, causes pain during menstruation
An additional provoking factor for pain during menstruation is natural fluctuations in hormonal levels, taking into account the phase of the menstrual cycle.
Ectopic pregnancy
The egg is fertilized in the fallopian tube, and then descends into the uterus and implants into the wall of the organ. But sometimes attachment occurs not in the uterus, but in an organ that is not adapted for this - then an ectopic pregnancy occurs.
Difficulty in the passage of the fertilized egg through the fallopian tubes may be caused by:
- obstruction;
- the presence of pathological narrowings;
- inability of the walls of the reproductive organ to attach a fertilized egg (implantation occurs in the cervix).
Unable to gain a foothold in the reproductive organ, the fertilized egg implants into the fallopian tube or uterine cervix, and less often into other organs that are also unsuitable for bearing a child.
Ectopic pregnancy is characterized by:
- cramping pain in the lower abdomen before menstruation;
- the appearance of heavy bleeding against the background of intensified contractions.
During tubal implantation, there is additional pain on the right or left (at the site of embryo attachment).
Almost always, symptoms develop after a missed period and the woman already knows about pregnancy. But, unfortunately, with the help of the test it is possible to determine only the fertilization that has occurred, and not the place of implantation of the embryo, and during an external examination it is impossible to distinguish an ectopic pregnancy from a miscarriage.
Doctors decide what to do in a hospital setting. The cervical implant comes out on its own under medical supervision or is removed by cleaning the reproductive organ under local anesthesia.
With tubal insertion, spontaneous evacuation is impossible, and cramping pain can lead to rupture of the fallopian tube . In this case, abdominal surgery or endoscopic removal of the tube along with the embryo is performed.
Where to contact
If your period is heavy, accompanied by severe cramping pain, you must call an ambulance. Doctors will take you to the emergency department of a gynecological hospital.
Palpation of the uterus at home: recommendations and precautions
If something is bothering you, it is easier to conduct a preliminary examination at home than to be nervous before going to the gynecologist. It is better to cut the nails on the index and middle fingers of your right hand and put on a sterile glove before starting palpation. The easiest way to feel the uterus is while sitting on the toilet, squatting or placing one foot on the sofa, the edge of the bathtub, etc. You can try to take a position similar to the one you take in the gynecological chair.
So, insert two fingers into the vagina and feel the tubercle. This is quite easy, the main thing is not to make sudden movements to avoid injury to the organ. But determining the consistency of the cervix is not so easy if you are not a professional. Only the comparison method will help the amateur. And yet, you can find out something on your own - if the middle finger literally rests on the cervix, it means that it is located quite low, as before menstruation. If you can barely reach it, then the uterus has contracted, as it should after menstruation. Remember, before starting and especially during menstrual periods, it is not recommended to palpate the organ.
What are the risks of self-examination?
If you are used to constantly palpating the cervix, refrain from manipulation at least 2-3 days before menstruation. Even the doctor will prefer to postpone the examination until the end of menstruation and here’s why:
- At this time, the cervix begins to partially dilate, so it is easy to get infected and get inflammation of the ovaries or fallopian tubes. Against this background, adhesions can form, leading to infertility.
- Even if you use sterile gloves, there is a risk of damaging the cervix. Typically, such injuries heal quickly, unless, of course, an infection occurs.
- For the most part, independent palpation of the organ does not give anything, and only a doctor can identify the pathology. After all, the gynecologist not only feels the cervix, but also examines it with a mirror.
These warnings do not directly prohibit self-palpation, but suggest that in case of any suspicious symptoms, it is better to consult a doctor and clarify the diagnosis professionally.
Educational video: Cervical erosion
Fibroids rejection
A benign pedunculated tumor growing inside the uterus can spontaneously be rejected.
Provoking factors
The main reason is considered to be: spontaneous detachment of the tumor, which occurs in a number of cases:
- when jumping from a great height;
- abdominal bruises;
- overstrain of the abdominal wall.
Detachment is possible only for small tumor formations. The risk of spontaneous fibroid rejection increases during menstruation.
When fibroids are “born,” pain appears during menstruation, like contractions, and then the volume of bloody discharge from the vagina increases.
Rejection of a fibroid node is similar in symptoms to a miscarriage, but the process ends with the release of a homogeneous formation.
After self-removal of the tumor, the cramping pains lose intensity and gradually disappear, and the volume of bloody discharge decreases. If the bleeding does not decrease, this may indicate damage to the blood vessels inside the uterus or internal ruptures.
Regardless of the outcome of the expulsion of the fibroid formation: the node has come out and the contractions have stopped, or the process is actively continuing, the woman must be hospitalized. In this case, the “born” neoplasm is also taken for subsequent cytological examination.
In a hospital setting, an ultrasound scan of the uterus is performed and the size of the detached tumor is determined - the treatment tactics depend on this. After obtaining the necessary information, the fibroids are removed under local anesthesia and the uterus is inspected .
For bleeding from large vessels that cannot be stopped by curettage or cauterization, surgery is indicated.
If the node has already come out and there is bloody discharge, as during menstruation or after childbirth, then the patient is left under observation and the examination is carried out as planned.
Who will help
The necessary assistance will be provided by doctors in the gynecological surgery department.
What else provokes cramping pain during menstruation?
Let's see what other causes of cramping pain during menstruation may be:
- Intestinal diseases. The intestinal loops are located next to the uterus and the symptoms of organ pathology intensify during menstruation due to the fact that the reproductive organ begins to shrink slightly. A characteristic feature is that cramping pain is accompanied by nausea, flatulence and other dyspeptic disorders.
- Scars or adhesions on the uterus. Due to abortion, gynecological diseases or surgical interventions, scar changes appear, so the walls of the reproductive organ cannot contract evenly during menstruation. This causes cramping pain in the lower abdomen.
- Individual pain sensitivity. Some girls have an increased reaction to pain and physiological contractions of the reproductive organ during menstruation begin to be perceived as cramping painful manifestations.
- Puberty. Girls may experience cramping pain for 1-2 years from the beginning of their first menstruation until the menstrual cycle is fully established.
The appearance of cramping pain almost always indicates the development of pathology. You should not ignore the symptoms that arise - this can lead to the development of complications.