Phases of the menstrual cycle
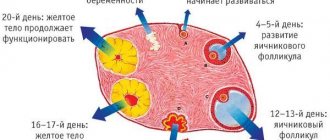
1. Follicular. It starts from the first day of menstrual bleeding and lasts about 14-16 days. In women with a cycle of 30-35 days, its duration is 16-21 days. It is characterized by the maturation of follicles preparing for subsequent ovulation. Their growth is accompanied by an increase in estrogen and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
2. Ovulation. Lasts only 1-2 days. During this period, one or more dominant follicles rupture, releasing the egg.
3. Luteal. Duration – 12-14 days. During its course, progesterone is actively produced, which is necessary to ensure conception.
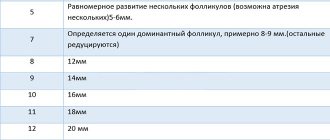
The female cell is located in the follicle and matures on days 12-15 of the cycle. Until this time, it is considered an oocyte. Immediately before ovulation, the diameter of the mature dominant follicle is 18-22 mm. When estrogen reaches peak values, the level of luteinizing hormone (LH) increases sharply, stimulating rupture of the pouch.
The duration of the ovulatory period is 1-2 days. At this time, a sharp change in hormonal levels occurs and the follicle ruptures. The female reproductive cell is viable for 24 hours from the moment it enters the fallopian tubes.
Egg maturation: how it should be
From birth, women have a supply of oocytes - immature eggs, about 400 thousand of them. With the onset of puberty and the onset of menstruation, the number of oocytes gradually decreases. Each cycle, under the influence of luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormone, the follicle matures.
The process of germ cell maturation can be described as follows:
- production of follicle-stimulating hormone;
- maturation of follicles in the ovary;
- rupture of the dominant follicle with release of the egg;
- movement of the reproductive cell towards the uterus;
- formation of the corpus luteum at the site of the follicle.
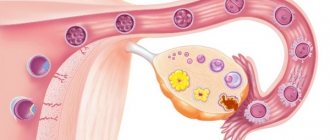
A follicle is a structural component of the ovary. Here the egg matures, surrounded by two layers of connective tissue and a layer of epithelium. Each cycle, several follicles mature in the ovary, but only one of them - the dominant one - will burst, releasing the mature germ cell.
At the site of the follicle, a corpus luteum forms, which produces a small amount of progesterone and estrogen. The work of the corpus luteum is necessary to thicken the uterine mucosa. At the same time, the egg does not stand still - it moves along the fallopian tubes towards the uterus.
This is where the female reproductive cell meets the sperm if attempts are made to conceive. A zygote is formed, which attaches to the prepared, thickened walls of the uterus. The process of conception is facilitated not only by the work of the corpus luteum. Under the influence of hormones, the rectal (basal) temperature rises to 37-37.5 oC - calendars are often compiled based on this criterion, calculating one’s own ovulatory phase for conception.
In female nature there is a place for individual characteristics of the process, but if it deviates from what is described, conception will not occur. For example, if the passage of the egg is blocked by inflamed fallopian tubes, or the cell does not mature.
Mechanisms of female reproduction
A follicle is a natural cavity for the maturation of an egg. It accumulates useful substances, vitamins and everything necessary for the full implementation of this process.
The egg matures from the first day of menstruation (or, in other words, the menstrual cycle as a whole) until the period of ovulation. Next, the mature female cell reaches a large size and breaks its protective shell. Then it enters the uterine space to meet the sperm and form a zygote (embryo).
Absence of rupture - anovulation, can occur as a result of:
- too dense shell of the “house”;
- the absence of a mature germ cell in it.
Both conditions are causes of infertility and require careful consideration, diagnosis and treatment.
The course of the cycle after ovulation
After the egg is released from the ovary, the third phase of the menstrual cycle begins - the luteal phase. The likelihood of successful conception depends on its course. To do this, the corpus luteum, formed at the site of the burst follicle, produces the hormone progesterone. It is necessary for the movement of the egg through the fallopian tubes, securing the fertilized egg in the walls of the uterus. The level of estrogen, FSH and LH gradually decreases at this time.
If fertilization is successful, conception itself occurs 7-9 days after ovulation. At this time, the fertilized egg is fixed in the endometrium. Progesterone produced reduces the tone of the uterus, preventing spontaneous miscarriage. Immediately after implantation of the embryo, the level of this hormone begins to increase and continues to increase throughout pregnancy.
In the absence of conception, the concentration of progesterone in the blood decreases, which contributes to the rejection of the endometrium. A few days before menstruation, all a woman’s sex hormones are at their minimum levels.
The nature of the ovulatory period depends on the individual characteristics of the body. In some women, its course differs from the norm, but is not considered a pathology.
Sometimes several follicles mature in one ovary, ready to rupture. This is possible for the following reasons:
- individual characteristics of the body;
- stimulation of ovulation;
- during the first 2-3 cycles after discontinuation of oral contraceptives;
- hormonal disbalance.
This condition can occur spontaneously. In such cycles, the chance of conceiving a child increases, and the likelihood of multiple pregnancies increases.
Usually in this case, one follicle ovulates in each of the ovaries, but there may be more burst bubbles. After the release of the egg, the corpus luteum is formed in each of the appendages.
What to do if there is no egg in the follicles?
The condition when female cells simply do not mature is infertility. In some cases it is adjusted.
The reasons may be:
- premature menopause;
- adolescence;
- polycystic disease, etc.
In the first case, the best solution would be hormonal therapy with estrogen. The dose is selected individually by the doctor.
Polycystic diseases and oncologies are products of unruptured follicles, which increase over time, and in some cases, degenerate into cancer.
Treatment methods are very different, it all depends on the woman’s condition and the size of the foreign formation.
In any case, do not act on your own.
How a follicle can behave
When the follicle ruptures, a small amount of fluid containing the released egg is released. But if the germ cell is not released, an ovarian cyst is formed. This happens due to hormonal imbalances and external factors. The fluid that should have come out accumulates inside, stretching the connective tissue, and a cyst forms.
The development process is similar to multifollicular ovarian syndrome. This happens when there is simply no mature leading follicle - several eggs begin to mature at the same time, but none are released. This happens with a lack of estrogen and progesterone. In place of the follicles that have begun to develop, small cysts form.
Cystic formations are also characteristic of the corpus luteum in pathologies. The egg leaves the follicle, but the corpus luteum, having fulfilled its functions, does not dissolve, but swells and stretches to a cystic formation.
If the corpus luteum persists, pregnancy will also not occur - this is a condition in which the corpus luteum releases progesterone for too long without atrophying. This is also dangerous for a woman’s health in general, since excess progesterone provokes:
- decreased uterine tone;
- rejection of mucous membranes;
- prolonged, heavy bleeding.
The follicle may not mature at all in the egg. This happens with a lack of follicle-stimulating hormone or with hyperandrogenism. A woman is diagnosed with “dormant” ovaries, but this does not mean that attempts to conceive should be abandoned. The condition is corrected by hormonal therapy, the maturation of the dominant follicle is stimulated with the release of the germ cell.
Empty follicles and proper nutrition
In the absence of germ cells, it is also necessary to eat properly. For the ovaries to function fully, you need to provide the body with all the vitamins and nutrients. Protein foods are especially important. A woman’s diet must include products from the following list:
- Bran.
- Citrus.
- Beans.
- Bee products: honey, royal jelly, pollen.
- Beef liver.
- Eggs.
- Dairy and fermented milk products.
- Seafood.
- Rabbit meat, turkey.
- Greens, vegetables.
- Fruits.
Seafood is extremely useful for the prevention and treatment of empty follicle syndrome.
Anything that causes bloating or flatulence should be excluded from the diet. Carbohydrates, baked goods, sweets, and carbonated drinks are not recommended. Alcohol and smoking are prohibited.
Also, when planning a pregnancy, you cannot follow a diet aimed at losing weight.
Lack of ovulation
Anovulation is not considered a pathology if it occurs 1-2 times a year. This process can occur both for natural reasons and as a result of stress or past illnesses - sore throat, flu, ARVI, etc. If it occurs regularly, you should be diagnosed by a gynecologist.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iuyF5eO-rpM
In case of one-time absence of ovulation, menstruation comes on time. They are menstrual-like bleeding, the nature of which differs from normal menstruation. This phenomenon occurs in the absence of follicle rupture, which entails a decrease in estrogen levels against the background of progesterone not produced by the ovaries.
Pathological reasons that the egg does not leave the ovary:
- hormonal imbalance due to pathologies of the endocrine organs;
- inflammatory processes of the genital area;
- genital tract infection;
- recent childbirth, abortion, cessation of lactation;
- the presence of tumors on the ovaries or in the uterus.
During pregnancy, ovulation does not occur. At this time, the ovaries produce sex hormones, and the follicles temporarily stop maturing. This is considered the body's natural defense against a new pregnancy that could harm an already developing fetus.
In women immediately before menopause, the number of anovulatory cycles increases. This is not considered a deviation. Often this phenomenon is accompanied by minor disruptions in menstruation. Later, during menopause, the cycles will stop completely.
Why doesn't she ripen?
There are several reasons why the egg does not mature. They are conventionally divided into internal factors - causes directly in the woman’s body, as well as external factors - the influence of lifestyle and the environment.
Internal reasons:
- inflammation in the pelvic organs;
- deficiency of progesterone and estrogen;
- inflammation of the membranes of the brain;
- dysfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary system;
- infections of the abdominal cavity or genitals.
Sometimes the reason is hormonal imbalance. But the disruption of hormone production itself can be provoked by external factors:
- depression;
- severe stress;
- strict diet;
- clinical obesity;
- sudden climate change;
- frequent change of sexual partners.
Dysfunction is also observed in women with bad habits; they are more susceptible to early menopause.
Any acute disease in the body will lead to the fact that the level of hormones will be reduced and the egg will not mature. This is how nature protects the human species from extinction, because if conceived in the acute phase of illness, a child may be born with defects.
Cycles in which the egg does not mature also occur in young, healthy women. This happens 2-3 times a year. The cell begins to prepare for release, the follicle also grows under the influence of estrogen and FSH, but LH is not released and the vesicle does not burst. The rupture occurs later, when the egg is no longer capable of fertilization, and menstrual flow begins almost immediately.
This is not a pathological process and it occurs even in healthy women. But if the frequency of anovulatory cycles increases, you need to undergo examination.
For the maturation of the egg and its full release, the following hormones are needed:
- estrogen;
- progesterone;
- follicle-stimulating hormone;
- luteinizing.
Stress
Prolonged experiences, depression, lack of sleep and severe stress not only lead to the fact that the egg does not mature, but also provoke a complete absence of ovulation until the condition returns to normal. During such periods, the level of estrogen and FSH decreases, and natural mechanisms to prevent pregnancy are triggered.
Nature “does not allow” to conceive a child if the environment around a woman is so tense and depressing. The balance of hormones is restored when the psycho-emotional state also returns to normal, since the hormonal background is a complex. Here, LH, FSH, and estrogen depend on serotonin, endorphin and other mediators.
Non-ripening of the egg can also be caused by the following pathologies:
- infections of female genital organs;
- adhesions, chronic foci of inflammation;
- inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract.
With intestinal inflammation or hemorrhoids, rectal body temperature increases significantly. This affects the condition of the ovaries and fallopian tubes, the follicle will not mature and release the egg.
Infections, if left untreated, become progressive. From the mucous membranes they penetrate the uterus, tubes and ovaries, provoking an extensive inflammatory process. Sensitive membranes react by forming adhesions and moving into the chronic phase.
Signs of anovulation
The normal menstrual cycle in healthy women is 25-30 days. The egg is released from the ovary in the middle of the cycle, somewhere on days 9-14, if you count from the first day of your period. The onset of ovulation is indicated by the following indicators:
- discharge from the genital tract becomes more abundant, mucous and transparent;
- Rectal body temperature increases;
- pain may be observed in the area of the ovulating ovary;
- increased content of sex hormones in the urine.
To record the moment the egg is released, you can use a rapid urine test to determine ovulation.
Important! If a malfunction occurs in the female body and the egg for some reason does not come out of the follicle, then this can be determined by the following characteristic features:
- absence of menstruation;
- changes in the composition and volume of menstruation, a shift in the interval between them;
- throughout the entire month, discharge from the genital tract has an opaque milky structure, there is no colorless mucus in it;
- there is no increase in rectal temperature in the middle of the cycle;
- a urine test for hormones shows a negative result;
- the appearance, condition of the skin and hair have deteriorated.
The more strongly the reproductive function is impaired, the more clearly and for a long time external signs will indicate this. To cure such infertility and have the desired offspring, you need to consult a doctor. In addition, chronic anovulation can negatively affect the condition of the entire body and lead to diseases of the mammary glands, cardiovascular system and cause endometrial hyperplasia.
Some women can tell when ovulation is approaching by its symptoms. To do this, you need to listen to your own condition more often and respond to the slightest changes in the body. Sometimes there are no signs of egg release at all.
Symptoms of ovulation:
- Changes in the nature of vaginal discharge. Immediately at the moment of release of the female cell or 1-2 days before, a woman can observe the appearance of transparent discharge - a consequence of the work of hormones. Their consistency resembles the white of a chicken egg and stretches well. Such secretions are the optimal environment for the functioning of sperm. Their presence simplifies the entry of male germ cells into the uterus.
- Pain in the mammary glands. A sign that ovulation has occurred, as it signals an increase in progesterone. The presence of pain is not necessary - some women simply experience increased breast sensitivity.
- Increased libido. The increase in sexual desire is explained by the maximum concentration of female sex hormones during this period.
- Vaginal moisture. The amount of natural lubrication produced during intimacy increases. Such discharge is present throughout the day. This is felt by wetness in the vagina, the presence of small wet spots on the underwear.
- Blood impurities in the discharge. Indicates follicle rupture. The amount of blood usually does not exceed a few drops.
- Change in position of the cervix. Throughout the menstrual cycle, the cervix constantly changes position. Before ovulation occurs, it softens and rises higher. This is necessary to simplify the movement of sperm through the cervical canal. You can check the position of the cervix yourself, with clean fingers.
- Headache. Indicates hormonal changes. Often present before ovulation and menstruation.
- Pain in the lower abdomen. Usually occur on one side. They are characterized by low intensity. Before the release of the egg, a woman may feel a tingling sensation in the ovary area or a slight aching pain.
- Bloating. It is explained by changes in hormonal levels and increased blood circulation in the pelvis.
- Nausea. Slight nausea indicates hormonal changes.
Signs that the egg has not been released
Many women feel the onset of this phase. It usually occurs on days 9–14 of the cycle (based on the first day of menstruation) and is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- mucus discharge (which lasts several days in the middle of the cycle);
- light bleeding is possible (or rather, streaks of blood are a sign of a burst body);
- pain and heavy sensation in the working ovary;
- lower back pain;
- rectal body temperature rises;
- hormones in the urine go off scale;
- increased libido.
But there is also a type of woman who feels absolutely the same during ovulation as during any other period. A special test will help them (more on this below).
When the follicle ruptures, a “corpus luteum” is formed in its place, producing progesterone right up to menstruation, as well as in the first trimester of pregnancy.
Therefore, a characteristic sign that the vessel has ruptured will be breast swelling in the second half of the cycle, which reaches its maximum two to three days before menstruation.
If the cell is not released, then there will be no changes in the body.
Summarizing the above, we note the characteristic signs of lack of ovulation:
- lack of mucous discharge in the middle of the cycle;
- delay of menstruation (unreasonable);
- irregular menstruation;
- negative ovulation test result.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Since there are many reasons for an unripe egg, the symptomatic complex is also extensive. What can the condition be associated with:
- fluctuations in body weight for no apparent reason;
- mood changes, apathy, tearfulness, irritability;
- swelling of the limbs;
- increased appetite;
- poor sleep;
- pain in the pelvic area;
- atypical discharge, an increase in its volume;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.
For diagnosis, the gynecologist will prescribe:
- general clinical analysis of blood and urine;
- study of FSH and LH levels;
- determination of estrogen and progesterone;
- determination of androgen levels;
- bacterial culture from the vagina;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
Empty follicle syndrome
Empty follicle syndrome is a diagnosis that is increasingly encountered by married couples who have been trying to conceive a baby for a long time. This pathology is usually detected during infertility examinations. Usually these are diagnostic techniques such as ultrasound, various laboratory tests, etc.
The most accurate information is provided by follicular fluid analysis, which is carried out only at the level of in vitro fertilization. According to doctors, it is with the help of this type of examination that it is possible to identify the disorder, although it sometimes gives unreliable results. However, not all doctors recognize the fact of such a pathology. For what reasons this happens, we will consider further.
Causes of egg failure from the ovary
Under normal conditions, in the middle of the menstrual cycle, the egg matures in the follicle, leaves the ovary and waits for fertilization. This phenomenon is called ovulation. If fertilization of the released germ cell does not occur, then menstruation begins. But the egg may not leave the ovary on time. This process is called anovulation.
The causes of anovulation can be the following processes:
- The growth and maturation of the follicle and the egg in it are disrupted, so the female gamete is simply absent.
- The formed germ cell could not be released due to the dense lining of the ovary.
Without the released gamete, fertilization and pregnancy are impossible. Therefore, anovulation is one of the main causes of infertility. It can be temporary (physiological) and chronic (pathological). The periodic absence of ovulation is natural and may be due to physiological reasons:
- puberty: after the first menstruation, girls may not ovulate for up to several years;
- pregnancy period;
- postpartum and lactation period;
- changes associated with menopause;
- the body's rest period is normally no more than 2 times a year.
The chronic absence of an egg ready for fertilization can be caused by a pathology in the structure of the internal genital organs or a malfunction of the endocrine glands. Most often, pathological anovulation becomes the cause of infertility. It can be triggered by the following factors:
- stressful situations;
- excessive physical activity;
- injuries, infections and inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system;
- gynecological diseases;
- impaired blood flow in the brain;
- disruptions in the functioning of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland reduce hormonal stimulation of the ovary;
- overweight or underweight;
- early menopause;
- thyroid diseases;
- liver diseases;
- uncontrolled use of medications;
- the use of hormonal contraceptives that suppress ovulation;
- age: after 30 years, the number of ovulations begins to decrease;
- genetic abnormalities;
- ovarian depletion;
- excess male hormones.
Hormones control the growth and maturation of gametes. If there is a hormonal imbalance in the body, the eggs do not mature. Due to gynecological diseases, for example, polycystic ovary syndrome, the female reproductive cell matures on time, but cannot leave the unruptured follicle. In order to identify infertility and seek medical help in time, you need to be able to determine your ovulation.
Ovulation is highly individual. In most women, one of the ovaries, which has a single mature follicle, ovulates more often. For some, several eggs are ready for fertilization at once.
In the right appendage
Ovulation in the right ovary occurs most often. This organ is considered dominant in most women. It is responsible for both the maturation of follicles and the production of hormones. The left appendage at this time is necessary only for endocrine function.
In the left appendage
Ovulation in the left ovary is less common than in the right. However, the chances of getting pregnant with increased activity of the left organ remain the same. The location of the dominant appendage does not affect the reproductive ability of a woman.
The appendages are capable of ovulating alternately. In one of the cycles, the female cell will come out of the left ovary, in the other - from the right. The sizes of the appendages during the alternating ovulatory process are approximately the same.
To determine in which ovary ovulation occurs, you need to monitor your own health or perform an ultrasound. In the first case, discomfort and mild pain will appear on the side of the abdomen in which the dominant appendage is located. An ultrasound examination more accurately determines the location of the organ in which the follicles mature. You can undergo diagnostics at any phase of the cycle - the ovary that released the egg will have a corpus luteum.
This is considered the norm for the vast majority of women. In this case, ultrasound determines the growth of follicles in only one appendage. Activity of two organs at once is extremely rare.
Slight fluctuations in cycle length are possible for all women. This happens during the course of diseases or under the influence of external factors. Along with the duration of the menstrual cycle, the day of ovulation also changes.
Normally, follicle rupture occurs 12-15 days from the start of the cycle. At this time, a gradual decrease in values is noted in the basal temperature graph; the ovulatory period indicates the following:
- immaturity of the egg released from the ovary - exit from the oocyte follicle;
- unpreparedness of the endometrium to accept the fertilized egg;
- lack of vaginal discharge favorable for the life of sperm;
- the presence of a dense plug in the cervix, preventing the penetration of male cells.
Therefore, early ovulation reduces the chance of pregnancy. Its one-time course does not affect the woman’s further reproductive ability. When it occurs regularly, there is insufficiency in the first phase of the menstrual cycle, requiring the prescription of hormonal drugs.
Reasons for early release of the egg:
- stress, chronic fatigue;
- hormonal disbalance;
- age over 40 years;
- abuse of bad habits;
- course of gynecological diseases.
There is a possibility of a female cell being released during or immediately after menstruation. This is possible due to hormonal imbalance or maturation of follicles in two ovaries at once. In the latter case, the release of the egg from the appendages occurs at different times, so some women may become pregnant during intercourse during menstrual bleeding or immediately after it.
Late ovulation
This condition is considered normal for women with a menstrual cycle lasting more than 30 days. In other cases, this is a sign of the following violations:
- hormonal imbalance;
- approaching menopause;
- stress;
- taking hormonal drugs.
With late ovulation, the egg develops longer than expected. This is fraught with a change in the number of chromosomes in it, which can cause intrauterine malformations of the fetus. Most often, such pregnancies end in spontaneous abortion in the early stages. In this way, the body gets rid of non-viable and weak offspring.
During breastfeeding, late ovulation is also considered normal. This is due to natural hormonal imbalance. Menstrual cycles in lactating women are irregular, have a long first phase, and are often anovulatory. That is why during this period the risk of a new pregnancy is significantly reduced.
Treatment
The examination of the patient begins with the collection of data about the problem, the composition, quality and cyclicity of menstruation is determined. If the menstrual cycle is irregular, then this indicates anovulation and is the basis for further research. To identify the reasons for the failure of the egg to leave the ovary, an examination by a gynecologist, endocrinologist and instrumental examination may be prescribed:
- biochemical blood test and blood test for hormones;
- ultrasound examination of the internal reproductive organs, mammary glands and thyroid gland;
- radiography and tomography of the brain.
The results of the study will allow us to establish the cause of egg failure and make a correct diagnosis. Only by knowing the cause of the disease can the correct treatment be prescribed. In healthy women, lack of ovulation can be caused by stress and poor diet. In such a case, treatment consists of rest, healthy eating and taking vitamins.
Please note: If infectious diseases of the pelvic organs and obstruction of the fallopian tubes are not detected, ovulation stimulation is prescribed to treat infertility. Stimulating egg production does not affect the size of a woman's follicle supply. If anatomical defects of the internal reproductive organs and tumors are detected, surgical intervention is prescribed to eliminate them.
Qualified medical care and correct diagnosis are very important in the treatment of infertility. You should not self-medicate or use various medications uncontrollably. Incorrect treatment can only make the situation worse.
We recommend you find out: How they develop
polyps in the ovaries
Most often, hormonal therapy is required to eliminate the resulting disorders. It is selected individually and determined based on test results, taking into account the patient’s age, the cause of the development of the deviation and the need for pregnancy.
When taking oral contraceptives, the work of the ovaries is temporarily suspended. This effect is achieved by taking pills containing hormones that regulate the menstrual cycle. The endocrine function of the appendages almost completely stops at this time, and follicle maturation does not occur. Treatment with oral contraceptives is prescribed to patients with hormonal imbalance and the presence of certain other gynecological diseases.
The duration of therapy is 3-6 months. In the future, a woman can take pills as a contraceptive. After discontinuation of the drug, the likelihood of pregnancy increases sharply.
Ovulation stimulation
This type of treatment is required in the complete absence of natural rupture of the follicle. Stimulation of ovulation for subsequent conception requires the prescription of medications containing female hormones. Before the immediate start of treatment, the following diagnostics are carried out:
- blood tests for hormonal levels;
- Ultrasound of the internal genital organs;
- folliculometry for 2-3 cycles;
- vaginal smear.
Types of drugs for stimulation:
- estrogen-containing – normalize the course of the first phase of the menstrual cycle, support the growth of follicles;
- reducing estrogen levels - necessary to stimulate the production of FSH and LH;
- gonadotropins - synthetic analogs of FSH that accelerate follicle growth;
- hCG hormone - used immediately after ovulation to maintain progesterone production.
Throughout treatment, monitoring of ovarian function using folliculometry is necessary. The effect of the drugs is assessed by performing a hormonal analysis.
Used as a last resort. Their use is necessary when other treatment methods are ineffective. Indications:
- inability to get pregnant naturally;
- lack of ovulation;
- ineffectiveness of drug stimulation of follicle growth for their subsequent rupture.
The most common method is in vitro fertilization, or IVF. To carry it out, it is necessary to collect biomaterial from both partners - the egg and sperm. Conception occurs artificially in a test tube, after which the fertilized egg is placed in the uterus. Most often, several of these fertilized cells are used simultaneously, which increases the chance of multiple pregnancies. IVF is highly effective.
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine recipes are used for minor deviations during ovulation. Sometimes they are an auxiliary method of therapy and are used simultaneously with medications. The most effective are herbal decoctions containing estrogens:
- sage;
- clover;
- hop;
- sweet clover;
- licorice;
- oregano;
- Linden;
- mistletoe.
The course of ovulation determines a woman's likelihood of becoming pregnant. It is during this phase of the cycle that the chance of conception is greatest. Violations can be identified by performing ultrasound diagnostics and taking a blood test to determine the functionality of the endocrine organs. Treatment requires hormonal therapy.
To treat dormant ovaries, a course of the FSH hormone or complexes is prescribed that will stimulate the functioning of the reproductive system. Cystic formations are treated depending on the stage and extent. Complexes of progesterone with estrogen and anti-inflammatory drugs in tablets and suppositories are prescribed:
- Duphaston;
- Anteovin;
- Janine;
- Ibuprofen;
- Paracetamol;
- Logesta et al.
Only a gynecologist is involved in the selection, since such medications without the supervision of a doctor can seriously harm hormonal levels.
If the disease is infectious, antiseptic and antibacterial drugs and anti-fungal drugs are first prescribed:
- Terzhinan;
- Polygynax;
- Hexicon;
- Betadine;
- Ketoconazole and others.
The reasons why the egg does not mature are identified by the gynecologist during examination and during diagnosis. Most of them can be treated, after which ovulation is restored, and attempts to conceive end in a successful pregnancy.
Advantages of treatment at the SM-Clinic Reproductive Health Center
In the multidisciplinary holding center for reproductive health "SM-Clinic", consultations are conducted not only by gynecologists, but also by doctors of other specialties, whose task is to “tune” the woman’s body to the correct functioning and successful implementation of the reproductive function. Diagnostics are performed using expert-class equipment, which allows us to identify even minor deviations in the functional state of organs. In our own laboratory, we evaluate various indicators that reflect the state and functioning of the reproductive system.
The SM-Clinic Reproductive Health Center is a center where qualified specialists will help assess your fertility and, in case of existing disorders, select the most optimal method of correction.
Why determine the ovulatory period?
You can determine the onset of the ovulatory process yourself by its symptoms. The calendar method is considered less accurate. Factors requiring determination of the period:
- Pregnancy planning. In order to successfully conceive a child, you need to know exactly the day of ovulation. 3-7 days before the expected event, you need to start leading an active intimate life. Doctors consider the optimal option to have sexual intercourse every other day - this is the time it takes for sperm to mature. You should continue trying until the day the egg is released, inclusive.
- Protection against unwanted pregnancy. In order to protect yourself from conception, you should avoid intimacy 7 days before ovulation and 2 days after it. The absence of sperm in the uterus during this period will prevent pregnancy. In order for this method of protection to work, you need to know exactly the day the ovulatory period begins.
- Prediction of the sex of the unborn child.
There is a belief that making love 2-7 days before the release of the egg will help you conceive a girl, and intercourse directly on the day of ovulation will help you conceive a boy. This is explained by the high speed of sperm with male chromosomes. The reproductive cells capable of conceiving a girl are slower, but have high endurance. This method is not considered a 100% way to choose the gender of the unborn child.
- Taking medications. Preparations containing progesterone should be used only in the luteal phase of the cycle. Starting treatment earlier may suppress follicular growth. Therefore, to increase efficiency, it is necessary to accurately determine the period of ovulation.
Diagnostic methods
You can determine the course of the process yourself or with the help of a gynecologist. This is possible both by external signs and by laboratory diagnostics.
External signs
There are several ways to check the functioning of your ovaries yourself. They do not require consultation with a doctor:
- Pharmacy ovulation test. It has high accuracy and responds to the release of luteinizing hormone into the blood. It does not guarantee a 100% release of the egg, since an increase in LH levels does not always provoke rupture of the follicle. This method is informative for women who do not have problems with the ovulation period.
- Basal temperature chart. The temperature in the rectum varies throughout the cycle.
Measurements should be taken in the morning, at the same time, without getting out of bed. At the moment the follicle ruptures, the temperature becomes minimal. If the process is successful, it increases in the second phase of the cycle. The onset of pregnancy can be determined by the absence of a decrease in values and the subsequent delay of menstruation. The method of charting your basal temperature and recording your symptoms is considered one of the most accurate home methods for determining ovulation. With its help, you can identify other menstrual cycle disorders - phase insufficiency, hormonal imbalance, etc.
- Elasticity of cervical mucus. Most often the method is performed in a hospital setting, but is also suitable for home use. To carry it out, vaginal discharge is stretched using special gynecological tweezers - forceps - or regular ones. During ovulation, mucus can stretch up to 8-12 cm, while at other periods of the cycle it can stretch no more than 6 cm.
These methods must be used over several cycles. After studying your own body in this way, it becomes easier to determine phase changes.
Laboratory methods
To identify some signs of approaching ovulation, you need to visit a doctor. A woman needs to undergo a gynecological examination and take a blood test:
- Pupil symptom. It is carried out during examination using a vaginal speculum on a gynecological chair. The moment of ovulation can be determined by the expansion of the cervical canal and the presence of transparent discharge around it. Outwardly, it is similar to the pupil of the eye. The method is not highly accurate.
- Karyopyknotic index. To carry it out, you need to take a smear. In the resulting biomaterial, the ratio of cells with pyknotic nuclei to surface epithelial cells is determined. The concentration of the former increases sharply at the moment the egg is released. To increase accuracy, the study must be carried out every 2-3 days from about the 10th day of the cycle.
- Blood test for hormonal levels. Helps determine the rate of estrogen growth and the moment of release of luteinizing hormone. With a subsequent increase in progesterone, ovulation is considered successful. At least 2 such laboratory tests must be carried out in one cycle.
To monitor the growth of follicles and their subsequent rupture, folliculometry is necessary. This study should be carried out every 2-3 days, starting from the 5th day of the menstrual cycle. During the first folliculometry, a full ultrasound is performed with measurements of the sizes of all organs and assessment of other parameters. During subsequent ultrasound diagnostics, only the diameter of the growing follicles is measured. The study is repeated after the release of the egg - the resulting corpus luteum confirms the normal course of the ovulatory process.
This method is highly informative and helps to identify concomitant pathologies of the genital organs. With its help, it is determined in which ovary the egg will mature, the day the follicle ruptures, and the number of mature vesicles. Ultrasound is considered the optimal diagnostic method due to the possibility of identifying errors in other methods:
- increase in basal temperature in the presence of a persistent follicle;
- lack of conception due to the small thickness of the endometrium against the background of the normal course of the ovulatory process;
- false positive result of pharmacy ovulation tests;
- graph of basal temperature with values that do not correspond to the phase of the cycle.