Treatment of the disease with radiation exposure
Radiation therapy for cervical cancer involves exposing atypical cells to very high doses of X-rays, which have a destructive effect on them and lead to death.
Important! Scientists have proven that the effect of X-rays on healthy cells causes only minor harm, which is a significant consolation for patients undergoing this therapy.
This type of treatment for cancerous pathology of the cervix can be of two types, namely: external and internal. As a rule, the doctor selects one type for treatment, but often these days specialists have begun to combine these two types. If we talk about the duration of RT treatment, it can range from 5 to 8 weeks, everything will depend on the patient and the stage of the disease.
Radiation irradiation for cervical cancer is also used after surgery, during which a malignant tumor was removed and there is a risk of relapse. In this case, radiation will be combined with chemotherapy, which will only double the effectiveness of treatment.
I would like to talk separately about the consequences after radiation therapy for cervical cancer. It is known that this radiation has an extremely negative effect on the ovaries and for women of reproductive age this may indicate a complete cessation of their ability to work, that is, in practice this leads to infertility.
In addition, all this contributes to the development of early menopause, which usually occurs two, sometimes three months after the start of therapy. If the patient still wants to have the opportunity to give birth to a baby, then she should definitely discuss all these nuances with the doctor. Today, there are special means and procedures that allow you to stop the process of menopause and increase the duration of your reproductive function.
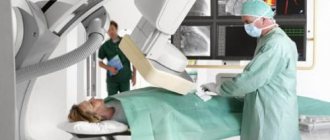
Treatment of cervical cancer with external beam radiation therapy is performed in the inpatient RT department or on an outpatient basis. X-rays are directed to the area of the cancer lesion by a special device. First, procedures are planned, where the patient undergoes a computed tomography scan in order to determine the exact boundaries of the intervention; these boundaries are marked with a marker on the woman’s body.
Typically, irradiation is carried out five days a week from Monday to Friday, usually with a break on weekends. The duration of the procedure will be determined by the doctor, based on the size of the tumor and the type of cancer pathology. The procedure is absolutely painless, but requires complete immobility; however, reviews of radiation therapy for cervical cancer can be read on numerous forums on the Internet.
As for intracavitary radiation therapy for cervical oncology, the cervix itself and nearby areas are exposed to rays. Typically, this course is used after external RT; it can be carried out both in a hospital and on an outpatient basis. Regarding side effects after the procedures, most often patients experience slight bleeding or discharge after completion of treatment. Also, manipulation can lead to diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, inflammatory processes of the skin, fatigue, and narrowing of the vagina.
With the onset of sexual activity, a significant number of women become infected with the human papillomavirus. Serotypes 16 and 18 are oncogenic - capable of transforming normal cells into cancerous ones.
When the body's immune strength decreases, cervical cancer develops. It can grow deeper into the uterine body, rectum, surrounding tissue, and metastasize to the lymph nodes, liver, and bones. In the initial stages, it responds well to treatment. And for prevention, a vaccine has been developed.
Nutrition for uterine cancer after surgery
Nutrition for uterine cancer
Many books have been written about the benefits of a healthy and proper diet, however, few people know that a properly composed diet of healthy foods is one of the main components in the treatment of cancer. A strictly balanced diet for uterine cancer can increase the effectiveness of treatment, and in some cases even slow down the development of the pathological process.
Experts in the field of medicine have proven that the factors that provoke the development of uterine cancer include poor nutrition, namely the consumption of harmful foods that provoke metabolic disorders in the body. Therefore, proper nutrition, that is, a properly formulated diet, is of great importance for women with uterine cancer.
Features of proper nutrition for uterine cancer
The diet of patients with uterine cancer involves the consumption of a number of natural products that have properties to slow down or prevent the development of cancer cells. A properly designed daily diet should be aimed at solving several problems, namely:
- contain components that reduce the development of tumor cells;
- improve the condition of the body, increase its energy;
- increase the body's protective properties;
- improve the functioning of the immune system.
This is possible only with a complete rejection of semi-finished products, fast foods, products containing preservatives or other artificial additives. Thus, nutrition for malignant lesions of the uterus should be based on eating food of plant origin, since it has a positive effect on the functioning of organs and systems, and also improves overall well-being and improves mood.
Avoiding fast food
Cancer cells, when multiplying, absorb large amounts of energy, weakening the body.
The diet for oncology should be designed in such a way as to replenish the affected body with vitamins every day and preserve the energy received as much as possible.
Increasing energy balance helps improve the functioning of the immune system, which allows the body to independently fight the development of cancer.
At later stages of development of the pathology, rapid loss of body weight occurs, and exhaustion of the body occurs. This fact should also be taken into account when drawing up a nutrition plan. Dishes eaten must retain a maximum of nutrients necessary for the functioning of the sick organism.
Diet for uterine cancer
To create the right diet for uterine cancer, you should use products that have anti-cancer properties. It is very important to find the right combination of them, as this will help increase the effectiveness of the diet. These properties have:
- broccoli, cauliflower, white cabbage or Brussels sprouts;
- garlic, onion, asparagus;
- root vegetables - carrots, beets, potatoes;
- legumes – beans, peas, soybeans;
- whole grain or sprouted cereals;
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- spicy greens.
To preserve biologically active components, products should be subjected to minimal heat treatment and steamed, and it is better to try to eat them raw.
In your daily diet, you should try to consume at least 3-4 servings of fresh vegetables and fruits (mostly brightly colored).
Traditional red meat should be replaced with fish rich in polyunsaturated acids or lean poultry.
Nutrition for cervical cancer
Nutrition for cervical cancer
The diet for cervical cancer, as for uterine cancer, has no fundamental differences.
It definitely involves the use of the above products, as well as the consumption of low-fat fermented milk products.
It is imperative to enrich your diet with dishes containing sprouted grains and whole grains. They are a source of valuable nutrients.
The special substance lycopene contained in tomatoes has protective properties. Its digestibility increases when consuming tomatoes with cold-pressed olive oil, which is recommended to be eaten daily. Olive oil has a complex composition that prevents the occurrence of metastases in the body.
An important component of nutrition for uterine cancer is soy and soy products. They are an essential source of protein, as well as special substances that slow down tumor development. Tofu and soy yoghurts are healthy products and perfectly neutralize toxic compounds.
A properly designed diet for cervical cancer is very important for the patient, since it consists only of healthy dishes, and involves the complete exclusion of harmful foods from the diet, which include:
- strong tea and alcoholic drinks;
- chocolate, cocoa, and their derivatives;
- confectionery;
- spicy and salty dishes;
- smoked meats and fatty foods;
- fast foods and semi-finished products;
- products containing artificial additives.
Nutrition for cancerous lesions of the uterus should be supplemented with infusions or decoctions of medicinal herbs, alcohol tinctures prepared at home. However, it should be remembered that only the attending physician should be involved in developing the correct diet.
This is a disease caused by malignancy of the tissue cells of the mucous membrane or walls of the uterus - the endometrium or myometrium.
The inner layer of the walls of this organ is built from endometrial cells, on which a fertilized egg develops, and if this does not happen, the layer is torn off and removed through the vagina to the outside during the next menstruation.
Myometrium is the building material of the muscle tissue of the uterus itself and its cervix, with the help of which the organ makes contractile movements.
Minimum required knowledge about tumors
Cancer of the body or cervix occurs when the normal process of cell growth is disrupted and dead cells are replaced by new, healthy ones.
A failure and cell division occurs, which becomes uncontrolled - their number begins to rapidly increase and form into tumor tissue.
A neoplasm occurs, most often in the cervix, which can be either benign or malignant, giving metastases.
If benign neoplasms are relatively harmless and their timely treatment, for the most part, leads to a complete and final recovery - relapses occur extremely rarely, then malignant tumors, especially the cervix, often lead to surgery to remove the woman’s reproductive organ. And even after such an intervention, not all patients live long.
Source: https://o-kak.ru/pitanie-pri-onkologii-matki-posle-operacii/
Treatment
Recently, more and more people with cancer are beginning to seek help from doctors abroad. Oncology clinics in countries such as Germany and Israel, which are considered one of the best in this field, are in great demand. They have advanced technical equipment, qualified personnel with many years of experience and relatively low prices.
DETAILS: Natural healing system of Galina Sergeevna Shatalova. My SEO implementation.
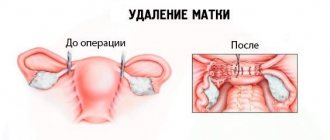
If doctors diagnose a patient with a localized tumor in the uterus, they decide to remove the uterus - a hysterectomy. A similar operation in Israel is performed by laparoscopy, with abdominal access if necessary.
If a malignant neoplasm begins to grow into neighboring tissues, hysterectomy is supplemented by removal of the ovaries and tubes, the upper part of the vagina and lymph nodes - extirpation. It is better to perform such operations using the cavity method.
Immediately before surgery, the doctor may prescribe radiation or chemotherapy to reduce the size of the tumor and destroy distant metastases.
Treatment of uterine cancer in Israel can also be carried out with some modern methods of radiotherapy - IMRT, brachytherapy. Their use depends on the stage of the woman’s disease.
Selection of methodology
In order for recovery after radiation therapy for cervical cancer to occur as quickly as possible and for the therapeutic effect to be high, medicine provides two types of effects on the patient’s body: internal and external. Often, specialists resort to a combination of techniques, since using one option does not always achieve the desired result.
A malignant focus in the cervix is one of the most frequently detected cancers in the female half of the population. Up to half of all identified cases are in advanced forms, so treatment tactics include not only chemotherapy, but also radiation exposure.
A similar technique can be the main way to get rid of a malignant lesion if it was detected at stages 1-2. To describe the process briefly, the essence is that beams of directed radiation, having encountered an atypical cell, contribute to the destruction of its very basis. As a result, it is unable to fulfill its functional purpose.
It is carried out on an outpatient basis - the cycle of procedures lasts about 5-6 weeks. After a preliminary comprehensive examination and compilation of a three-dimensional image of the tumor focus, markers are placed on the patient’s skin, allowing the equipment to be further directed to the desired area of the body.
As a rule, sessions are held 5 times a week, with intervals of two days off. The duration of one procedure may vary and does not exceed several minutes.
The woman does not feel any discomfort or intense pain impulses. Patients are only required to remain absolutely still. If a session was missed due to a number of objective reasons, then the attending physician may decide to conduct two sessions in one day, with an interval of 7–8 hours.
The essence of the technique is the antitumor effect of rays on the cervical area, or in the immediate vicinity of the uterine tumor. The procedures can be carried out not only in inpatient, but also in outpatient settings.
To achieve the required therapeutic effect, applicator tubes are inserted into the cervix or the uterus itself (if surgery has not been performed). It is from these that irradiation is carried out.
If it is necessary to place the applicator in the uterus itself, manipulations are performed under general anesthesia. Subsequently, the woman is given various medications for pain relief.
If there is no need to place the applicator in this way, then there is no need for pain relief. In order to prevent displacement of the applicator already placed intraorganically, a tampon is additionally inserted into the vagina.
Before the start of the irradiation session, a control CT scan must be performed to ensure that the applicators are positioned correctly. The duration of each session is selected individually by the specialist - one long one or a series of short ones.
There are several types of such radiation therapy - high-dose, low-dose, and pulsed. Which option to resort to is decided only by a specialist - based on the structure of the neoplasm, the age of the patient, as well as the initial state of her health. Possible side effects
Unfortunately for specialists and patients themselves, along with the undoubted benefits of radiation therapy, side effects are also observed. This is due to the high radioactivity of the rays.
Temporary disorders:
- diarrhea – it is recommended to take enough fluids to prevent dehydration;
- moderate bleeding from the vagina - no longer than 5-7 ducks;
- urge to feel sick, loss of appetite - in order to avoid weight loss, experts recommend drinking high-calorie drinks;
- some narrowing of the vagina, making further gynecological examination difficult;
- previously uncharacteristic fatigue, severe weakness - the solution seems to be an increase in rest time after each irradiation procedure.
Such side effects go away quickly. More serious consequences of radiation therapy that require treatment procedures include bladder disorders and lymphostasis. With the right treatment tactics, they can be minimized.
Effective treatment requires pre-radiation preparation, during which the general condition of the patient, the shape and size of the tumor, and its location are studied. Next, the method of exposure is selected, the type of radioactive substance that has the greatest effect on cancer cells. The dose and number of sessions are prescribed.
The goal of radiation therapy for stage 1 cervical cancer is to destroy mutated cells and prevent the spread and development of the process in neighboring organs in the pelvis - rectum, bladder. The effect is applied at two points - directly on the tumor and the inguinal lymph nodes. The negative consequences of the procedures disappear with normalization of nutrition, proper rest, and consumption of water and vitamin complexes.
Radiation therapy for stage 3 cervical cancer is the final stage of treatment to eliminate the possible risk of cancer recurrence and metastases. If you carry out all therapeutic measures, give up bad habits, eat a balanced diet, and take vitamins, the prognosis is favorable. Relapses can occur due to violation of the rest regime, heavy physical activity, changes in diet, drinking alcohol and smoking.
Treatment is prescribed by a radiologist. The following data is recorded in the referral for the radiological technician who will directly perform the procedure:
- irradiation area;
- dose per fraction;
- number of doses per day, week;
- beam energy;
- total dose;
- description of the irradiated field.
Instructions are given on the need to monitor tests and general condition.
Irradiation is carried out at two conventional points:
- A – main focus, primary tumor;
- B – effect on parametric tissue, pelvic lymph nodes.
| Stage | Point A | Point B |
| 1 | 65-70 | 40-45 |
| 2 | 75-80 | 50-55 |
| 3 | 80-85 | 55-60 |
The use of curly fields gives a good effect. To do this, an x-ray is taken, where the doctor marks areas that should not be exposed to radiation. According to their outlines, a blank is cut out of foam plastic, which is then made from an alloy of lead, bismuth and cadmium.
The basis of treatment is intracavitary irradiation, which is performed 2-3 times a week for a month.
Several radiation methods are used to treat cervical cancer:
- External therapy is carried out in a hospital setting, but the patient may not be there around the clock, but come from home. The beams are directed to the desired area using a linear catalyst. Before starting therapy, marks are applied to the body to serve as a guide.
The procedure is carried out daily with a break on weekends. If one day was missed, the irradiation can be repeated twice a day with an interval of 8 hours. The process takes a few minutes. After the procedure, the patient does not become radioactive.
- Internal irradiation is carried out using a special applicator - a hollow tube in which the radiation source is placed. It is placed in the vagina, the entrance is covered with a gauze swab to avoid displacement. The correct position is monitored using MRI. The radiation source is then inserted into the tube. The procedure can be performed as an inpatient or outpatient procedure.
Irradiation can be of three types:
- high-dose – internal irradiation is carried out with a large dose for 10-15 minutes. There is a break of several days between sessions. The applicators are not removed.
- low dose – this is usually one session lasting 12-24 hours. The woman is on bed rest and a urinary catheter is installed. Visits are prohibited, because irradiation of others occurs.
- Pulse is carried out like low-dose, but periodically. The applicator cannot be removed during breaks.
In this case, the cervix and surrounding areas are directly exposed to radiation. As a rule, a course of such treatment is prescribed after external radiation therapy. The course can be conducted both inpatient and outpatient.
To irradiate these organs, the radiation source is placed in specially designed hollow tubes - applicators - which are placed as close as possible to the cancer.
If the patient has not undergone a hysterectomy, intrauterine radiation therapy will be performed. In this case, the doctor places applicators in the vagina and passes them through the cervix into the uterus. In some situations, it may be advisable to place additional applicators near the cervix. The applicators are placed surgically, the patient is under anesthesia.
If the patient has undergone a hysterectomy, a large applicator will be placed in the vagina - no anesthesia is required in this case.
X-rays or computed tomography are used to control the position of the applicators. Once the correct placement of the applicators is confirmed, the source is installed and treatment begins.
This type of radiation therapy can be carried out either using a single long-term irradiation technique or in the form of several short-term sessions - the specific choice depends on the situation and the systems used.
High dose treatment
The most common method of delivering internal radiation therapy. The patient receives a large dose of radiation over several minutes. As a rule, the session takes 10-15 minutes. The course of such therapy includes a small number of sessions repeated at intervals of several days.
High dose treatment
Nutrition after hysterectomy, diet for uterine cancer
Proper nutrition when diagnosing cancer is not a separate treatment method, but diet therapy helps to activate the body's defenses.
The diet is also prescribed for uterine cancer. Preference is given to products containing antioxidants, alkalis, and natural acids. But this is not enough. In order for diet therapy to produce results, it is important to follow the rules of nutrition when undergoing chemotherapy, before a hysterectomy, and during radiation treatment.
Nutrition for uterine cancer
When diagnosed with uterine cancer, nutrition should be changed as much as possible. The food consumption regime also requires adjustments.
Authorized Products
The first nutritional requirement when treating uterine cancer is to consume only natural, fortified foods. It is important that they strengthen the immune system, helping the body fight a dangerous disease.
It is important for a patient with this disease to prefer:
- Fruits - apples, pears, oranges, lemons. Heat treatment is not recommended.
- Vegetables – pumpkin, cauliflower, spinach, greens, lettuce.
- Berries - plum, black currant, rose hips. They contain antitumor substances and help remove carcinogens and free radicals from the body.
- Cereals - oats, flaxseeds, lentils.
- Low-fat meat and fish - chicken, beef or veal, salmon.
- Some types of spices are coriander, red pepper.
- Honey, ginseng root, and turmeric will also be beneficial for uterine cancer.
Prohibited Products
A woman with cancer of the reproductive organ is prohibited from consuming:
- any types of sausages;
- semi-finished products;
- baking;
- sweets, desserts;
- packaged juices;
- alcohol;
- carbonated drinks;
- fast foods;
- cocoa;
- chocolate;
- caffeinated drinks.
Refusal of salted, smoked, fried foods is mandatory. Canned food - vegetables, meat or fish - falls under the taboo.
Diet
Eat fractionally, in small portions. The interval between meals is 4-5 hours. The weight of one serving is no more than 300 g.
Menu
Despite the described food prohibitions, a woman still has a large selection of products to create a healthy and tasty menu for the week. Here is an example of a diet.
- Breakfast: a glass of freshly squeezed single- or multi-ingredient juice.
- Second breakfast – 1 apple, a cup of rosehip infusion (chamomile sage, valerian), low-fat cottage cheese.
- Lunch – vegetable soup, a small piece of boiled meat, porridge from any type of cereal, a cup of green tea.
- Afternoon snack – 1 fruit or vegetable, a glass of juice.
- Dinner – a small portion of salad with a piece of baked fish, a cup of tea. Before going to bed, you are allowed to drink a glass of kefir or freshly squeezed juice.
If you alternate products daily, the menu for the week will be complex and varied.
It is important to include soups and cereals in the menu every day, as well as juices, raw fruits or vegetables. Meat and fish are allowed to be eaten at intervals of 1-2 days.
Nutritional considerations before surgery
Preparing for a hysterectomy for uterine cancer requires adherence to a diet. The day before surgery, the patient is recommended to:
- exclude indigestible foods that irritate the intestinal mucosa;
- Avoid foods that cause increased gas formation (beans, peas, beans, cabbage).
Food should be easily digestible and contain vitamins. Before surgery, it is recommended to eat vegetables, fruits, and a small portion of cereal porridge. Exclude fermented milk and dairy products.
Diet after hysterectomy
Nutrition after surgery to remove the uterus should be gentle. The body needs to recover from the stress that surgery has caused it.
You can’t suddenly return to your usual serving sizes. After recovering from anesthesia, the patient is allowed to drink exclusively clean water without gas. Only after a few hours, and sometimes after a day, is the first meal allowed.
Prohibited during the postoperative period
During the rehabilitation period, foods that irritate the intestinal mucosa are excluded from the menu. Until the body fully recovers after a hysterectomy, avoid:
- coffee,
- desserts,
- tea,
- chocolate,
- ice cream,
- white bread.
Healthy foods
During the rehabilitation period it is recommended to use:
- cereal porridge;
- fermented milk products;
- low-fat meat broths;
- nuts.
Fruits and vegetables are an essential element of the daily diet (they help avoid constipation).
We must not forget about the drinking regime. 1.5 liters of liquid, including juices and pure still water, will be enough for a speedy recovery of the body after surgery.
Approximate diet
An approximate menu in the postoperative period looks like this:
- Breakfast: fresh multivitamin – vegetable or fruit.
- Second breakfast – an apple or other fruit, a handful of nuts.
- Lunch – low-fat chicken or veal broth with a small slice of bread, or cereal porridge.
- Afternoon snack – fruit or vegetable, glass of fresh juice.
- Dinner – low-fat cottage cheese.
- Before going to bed, you are allowed to drink a glass of low-fat yogurt or fermented baked milk.
Diet during radiation therapy
Radiation therapy also requires a woman to review her diet. A rationally developed menu will help reduce the intensity of side effects of treatment - nausea, vomiting, and general malaise.
Attention should be paid to foods high in calories. You need to use it little by little, fractionally. Foods high in calories will give the body strength to fight a dangerous disease.
After radiation therapy sessions, eating is sometimes accompanied by a burning sensation or sore throat. In this case, it is recommended to grind food through a sieve or knead with a spoon before use.
useful to use the following when undergoing a course of radiation therapy:
- kefir;
- cottage cheese;
- fermented baked milk;
- biphylux;
- homemade yoghurts;
- whole grain bread;
- porridge made from lentils, barley, oats, buckwheat;
- soups and broths with lean meat;
- fatty fish (enrich the body with Omega-3 acids).
Drink as many freshly squeezed juices as possible. They need to be prepared from fruits, berries, herbs and vegetables. List of fresh juices that are beneficial for the body of a woman undergoing radiation treatment:
- apple,
- pear,
- cherry,
- orange,
- citric,
- potato,
- celery,
- cucumber and others.
A patient who is treating uterine cancer with radiation therapy is advised to stop using :
- coffee and other drinks containing caffeine (including black tea, cocoa);
- fried, spicy, smoked, salted;
- conservation;
- marinades;
- sour products;
- dairy products.
Despite the benefits of legumes, cabbage and mushrooms, if you have cancer, they will also have to be removed from the menu. These foods cause increased gas formation, which aggravates the woman’s condition and increases the manifestation of unpleasant symptoms.
It is useful to periodically consume jelly, green and white tea, and herbal infusions. Make sure that the drink is not too sweet, as this can cause nausea.
Along with changing the menu, it is important to adjust your lifestyle. Quitting smoking, alcohol, and the use of toxic substances are conditions that must be met. Thanks to this, it will be possible to eliminate ailments caused by radiation and speed up the healing process.
Diet therapy for oncological processes in the tissues of the uterus is an auxiliary method of treating a dangerous disease. The principles of nutrition and the menu for every day are similar, but different types of treatment require different approaches to the diet.
Every patient should follow the stated rules of rational nutrition during the treatment of cancer of the reproductive organ. This approach will help improve your well-being, give the body strength to fight the disease, and promote weight loss. This is also important for the successful fight against cancer, because in many women it develops and rapidly progresses against the background of excess body weight.
If you cannot independently develop a menu for every day, an oncologist and nutritionist will help you cope with the task.
Diet therapy for uterine cancer: menu features Link to main publication
Source: https://onko-24.ru/cancer/zhenskie-organy/dieta-rak-matki
Preparation for the procedure
When deciding whether a cancerous lesion has been identified and needs to be treated, the specialist focuses on the structure of the tumor, whether it is malignant, its size, and the age category of the patient.
The fact that radioactive rays pose a direct threat to tissues not affected by atypia is also taken into account. Such therapy is necessarily carried out in several stages - with breaks of several weeks between procedures. If necessary, separate procedures are applied to target specific areas.
Preliminary setup of equipment is a mandatory step. A careful selection of the correct direction of the rays is carried out to accurately hit the tumor site. After taking a series of images, the information is displayed on the screen, and the specialist identifies the location of the carcinoma, its boundaries, and calculates the radiation therapy load.
Then the device system itself will manage the process of placing and subsequent rotation of the patient, the emitter itself, and also adjusts the position of the protective devices. If the contours of the tumor were clearly marked on the pictures, then the laser beam will highlight the point of direct impact on the body of the irradiated person.
It is somewhat more difficult if the malignant lesion has moved to neighboring tissues and organs. However, modern equipment makes the task easier for specialists - tomographs make it possible to obtain a three-dimensional image of the tumor, followed by a radiation treatment program.
The history of radiation therapy begins with the discovery of special rays in 1895 by V.K. Roentgen. This was followed by the discoveries of radioactive elements by Becquerel, Marie and Pierre Curie. In 1898, Rutherford identified two types of rays - alpha and beta, which have different penetrating powers.
Skin lesions among physicists involved in the study of radioactivity suggested the damaging ability of radiation on living organisms. At the same time, ideas arose about using radiation to get rid of tumors.
Radiation therapy was first used in 1896 to treat inoperable breast tumors. In 1908, they began to treat uterine cancer using radium, which was placed in the vagina. Each scientist had different approaches, but the results were approximately the same.
Methods of influence were gradually improved. Radioactive substances were sealed in glass tubes and placed in gold and copper needles and applicators, which were convenient for use in gynecology.
At the same time, the main law of radiation therapy was formulated: radioactive radiation has a stronger effect on cells, the more actively they divide and the less differentiated.
For treatment, various installations are used, which differ in the type of emitted rays and power. Their choice depends on the type of tumor and its location.
In terms of preparation for the procedure, dose planning is mandatory. This is done by a team of doctors and physicists who calculate the required dose. Markings are applied to the skin with a special marker, which serves as a guide for installing the emitters and directing the rays.
A few days before the start of the course, you should not use iodine tincture or irritating substances. If you have diaper rash on your skin, you should definitely tell your doctor. Under no circumstances should you sunbathe.
A week before the start and during treatment, you must follow the following rules:
- eat well, drink enough fluids;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- clothing should not fit tightly to the irradiated area;
- use underwear made of cotton fabric, do not wear woolen or synthetic items;
- do not use cosmetics, shampoos, soaps, deodorants, powders, creams on the irradiated areas;
- Do not rub, heat or cool the irradiation site.
After radiation therapy, you definitely need high-calorie food. The energy value can be increased by eating sweet, rich baked goods. Therefore, you can take chocolate, marshmallows, marmalade, favorite sweets and buns with you.
Internal irradiation is carried out after remote irradiation no earlier than 2 weeks. The applicator is inserted under general or spinal anesthesia. Before administration, an examination is carried out to clarify the effect of remote irradiation. A radiopaque mark is applied to the neck. The uterine cavity is measured with a uterine probe. The cervical canal is expanded and an applicator is inserted. The vagina is tamponed.
Later, a 131Cs source is inserted into the applicator. The bladder is catheterized and 7 ml of radiopaque contrast agent is injected into it. Marks are applied to the anus. If possible, a dosimeter is inserted into the anus.
Photographs of the pelvis are taken in direct and lateral projections. Calculate the dose for points A and B, bladder, rectum. According to indications, antibiotics, anticoagulants, and corticosteroids are prescribed.
Foods you should avoid
The diet after irradiation does not limit the patient in any way. However, there are products that cause irritation of the mucous membrane, increase gas formation and are undesirable on the patient’s table.
During radiation therapy, certain foods are strictly prohibited
These include the following:
- Rich and fatty broths;
- Hot herbs and spices;
- Marinades and canned food;
- Fast food;
- Alcohol, tobacco;
- A large number of confectionery products and carbonated sweet drinks;
- Cabbage;
- Rough food in large pieces.
Proper nutrition after radiation therapy is the basis for the body’s recovery. If there are problems absorbing food by mouth, patients may be temporarily prescribed parenteral mixtures administered intravenously. In any case, you need to replenish your reserves of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. The main thing is to improve the patient’s well-being and create optimal conditions for his rehabilitation.
Indications for radiation therapy
At the first stage of oncology, radiation therapy is used as the main method of treatment or in addition to the surgical method.
In almost all cases of cervical cancer, radiotherapy is performed. In the initial stages, the method may be the only treatment. At stages 2 and 3 - in combination with other methods.
A feature of cervical cancer in women is its problematic diagnosis in the early stages. In order to detect the disease in time, it is necessary to be constantly observed by a gynecologist. Practice shows that most patients complain of stages 2 and 3 of cancer, when pain appears. Therefore, treatment requires the use of several methods at once: surgery with chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
In cases of inoperable cervical cancer, palliative therapy is prescribed to relieve pain and improve quality of life.
Contraindications
The patient's serious condition after surgery and chemotherapy, and the development of fever are also temporary contraindications to radiation.
Radiation therapy is currently used in 90% of patients with cervical cancer:
- at stages 1-2a, complements surgical operations if necessary;
- at 2b-3 a mandatory stage of complex therapy;
- when the tumor moves to the uterine body, periuterine tissue;
- poorly differentiated tumors;
- severe somatic pathology, in which surgery is contraindicated;
- resectable cancer with deep invasion into adjacent organs.
Radiation therapy is contraindicated in the following cases:
- prolonged fever;
- anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia;
- radiation sickness;
- Stage 4 cancer, when there are multiple metastases, tumor decay and bleeding;
- severe diseases - renal failure, diabetes mellitus, pathology of the heart and blood vessels.
Target
What tasks are set before the procedure depends on the stage of the tumor, its size, and the presence of metastases.
- Complete destruction of cancer cells is possible at an early stage without tumor growth deep into tissues and without metastases.
- Reducing the size of the pathological lesion is necessary for further surgical treatment in order to reduce the volume of tissue removed.
- Consolidation of the results of surgery and chemotherapy, destruction of possible remaining tumor cells.
- Palliative care in case of advanced inoperable cancer to alleviate the patient’s condition.
Benefits of Radiation Therapy
Against the background of targeted impact of hardware beams directly on the focus of mutated cells, under the influence of high doses of radiation they are no longer able to divide, and the tumor stops growing. Healthy structures receive minimal damage and are quickly restored.
Oncologists necessarily take into account many facts at the preparatory stage for such a method of treating cervical cancer - after all, each woman has her own characteristics of the body. The structure of the tumor, its size, localization, and the presence of metastases in other organs are of great importance.
Benefits of radiation therapy:
- ionizing rays practically do not affect healthy cells;
- high effectiveness in fighting cancer;
- rays have access to even the most difficultly located tumors;
- significant reduction in the risk of relapse of pathology;
- the general health of patients is not too depressed;
- The technique is more tolerant compared to the effects of chemotherapy.
However, radiation therapy has its disadvantages and consequences. Therefore, it is so important to undergo a comprehensive diagnostic examination, recommended by a specialist at the stage of preparation and drawing up a treatment plan.
Treatment of oncology with radiation therapy has both positive and negative sides. The use of outdated equipment leads to greater intoxication of the body and a larger irradiation surface. Complications manifest themselves in women in the form of early menopause and cessation of ovarian function, narrowing of the vagina, bleeding, and damage to the bladder.
Currently, there is an IMRT device that forms a 3D image of the tumor, creates a powerful beam of radiation and directs it to the tumor site without affecting healthy areas. The doctor performing the procedures monitors the process on the monitor screen. Treatment of cervical cancer with radiation therapy using this equipment allows you to avoid dangerous consequences or reduce them to a minimum.
Attention! The use of three-dimensional control over treatment makes it possible to radically influence the diseased organ, while simultaneously monitoring the patient’s basic vital parameters.
Recommended Products
The basic rule for the appropriate condition is to include light and maximally nutritious dishes, which include eggs, yeast-free bread, walnuts and sunflower or pumpkin seeds, lean sea fish, dried fruits and apples, vegetables, fresh herbs. Very useful products for such patients are those based on sour milk, especially cottage cheese.
It is important to enrich the diet with berries in any form: black currants, rowan berries, cherries, cranberries, lingonberries, rose hips, gooseberries.
During radiation exposure, one should not forget to include the patient's favorite foods, even if they are not on this list.
External exposure
External beam radiation therapy is usually provided to outpatients as a series of short treatments in an inpatient radiation therapy department. X-rays are sent directly to the area of the cancerous lesion by a special device called a linear catalyst.
Treatment planning
Planning is a very important part of the upcoming treatment, which is why it can be carried out over several visits. Proper planning is the key to ensuring that treatment is as effective as possible.
During the first visit to the radiation therapy department, the patient undergoes a computed tomography scan, which gives the doctor a three-dimensional image of the area to be treated. The data is used to determine the precise boundaries of the intervention.
Once the treatment area is determined, small markers are placed on the patient's skin to help the radiologist ensure that the patient is positioned correctly. The markers are permanent, but they are tiny dots and are virtually invisible. The patient may experience some discomfort when the markers are applied, but they are necessary.
Start of treatment
As a rule, irradiation is carried out from Monday to Friday, with a break on weekends. If the patient accidentally missed the daily procedure, two sessions can be performed on the same day with an interval of 6-8 hours.
The duration of sessions directly depends on the type of cancer and the size of the malignant neoplasm; the entire course usually takes 5-6 weeks. Before starting the procedure, the radiologist will check that the patient is in the correct position on the couch. During the procedure, the patient is alone in the room, but the doctor can observe her through a special glass. The session lasts several minutes.
The procedure is painless, but you should remain completely still during the irradiation process. Radiotherapy does not make the patient radioactive - contact with other people (including children) is absolutely safe.
Start of treatment
To the beginning ⇑
Rehabilitation
Completing a course of radiation therapy, even if it ended in complete victory over cancer, does not mean an instant return to your past life, without any restrictions and rules. The patient will have to limit himself for a long time, since relapse with oncology is very possible. In addition, an organism with a significantly weakened immune system is practically not protected from all kinds of negative factors. During this period, you must continue to take medications prescribed by your doctor, take walks in the fresh air, avoid hypothermia and, of course, follow a diet.
If you follow all these rules, it will be possible to defeat cancer and once again experience all the joys and pleasures of a full life.
Long-term consequences
Radiation therapy is a big burden on the body. Therefore, increased fatigue and weakness are normal. To reduce these phenomena, shortly before the start of the radiation course, it is recommended to switch to nutritious, high-calorie foods, and be sure to drink a lot of water.
As already mentioned, radiation has the greatest effect on rapidly dividing cells. In addition to tumor cells, epithelial cells, including cells of the intestinal mucosa and bladder, have such properties. Consequences of irradiation - the mucous membrane becomes thinner and is easily injured, which is manifested by the admixture of blood in the urine and feces.
Other possible consequences of radiation therapy for cervical cancer:
- diarrhea;
- bleeding from the vagina; “spotting” should not last more than 5-7 days in a row, otherwise you need to consult a doctor;
- loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting;
- dryness and narrowing of the vagina, possible scarring;
- premature onset of menopause - due to irradiation, the ovaries cease to perform their function;
- lymphostasis and swelling in the legs;
- hematopoietic disorder - part of the red bone marrow, which creates blood cells, is located in the pelvic bones and lumbar vertebrae.
- Vaginal bleeding.
- Diarrhea.
- Nausea.
- Skin inflammation.
- Weakness.
- Narrowing of the vagina.
- Damage to the bladder.
- Swelling of the legs.
- Menopause.
In some patients, radiation therapy can make blood vessels in the intestines and bladder more fragile, leading to blood in the stool or urine. Such effects may appear months or years after treatment, and you should consult a doctor as soon as they are noticed.
In rare cases, radiation therapy causes a narrowing of the intestines and an intestinal obstruction, which can cause vomiting, constipation and abdominal pain. To treat this problem, the patient will most likely have to be hospitalized.
Radiation therapy may cause vaginal bleeding or chronic narrowing of the vagina. A gynecologist treats these types of problems.
Radiation therapy can affect the lymph nodes located in the pelvic region, which leads to lymphostasis. This complication is most likely to occur during combined treatment: surgery and radiation therapy.