Inflammation of the appendages is one of the most common pathologies of the female reproductive system. The appendages - fallopian tubes and ovaries - are responsible for the process of fertilization and gestation. For this reason, inflammation of the appendages during pregnancy is particularly dangerous. To prevent the development of the disease, it is necessary to know the causes of its occurrence and ways to combat it.
There is an opinion that inflammation of the appendages and pregnancy are absolutely incompatible. This is explained by the processes that arise as a result of the development of pathology. In the presence of the disease, the hairs located in the fallopian tubes stick together and cannot fulfill their functional purpose. Thus, they will not be able to actively promote the advancement of the egg into the uterus. In addition, bearing a child with such a diagnosis can also be accompanied by serious complications.
However, despite everything, some women, having such a pathology of the reproductive system, become pregnant and also safely bear a child.
Preventive measures:
- protect yourself from sexually transmitted infections
- prevent hypothermia of the body, especially in the pelvic organs
- during menstruation, change the pad more often; When using one pad for a long time, an infection actively develops, and menstrual tracts become a fertile environment for it.
- If possible, avoid thong panties; a narrow strip of panties is a kind of path along which the infection passes from the rectum to the genitals
If you have any persistent pain in the abdominal area or suspicion of inflammation of the appendages, you should see a doctor. Timely treatment will help get rid of harmful microorganisms and other causes that led to the disease.
Acute pain in the ovaries
The ovaries often hurt greatly if there is a threat of their rupture, in advanced forms of the disease.
Hyperstimulation
Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome occurs during the treatment of infertility due to lack of ovulation, or the use of IVF. The process consists of prescribing hormonal drugs in the form of tablets, injections, sprays that promote follicle growth. Hyperstimulation is the result of incorrect dose selection or excessive individual sensitivity of the body to the drug.
Conventionally, hyperstimulation is divided into 3 stages:
- Easy. At the same time, the volume of the abdomen increases, swelling and slight nagging pain in the groin are observed.
- Average. Nausea, diarrhea appear, shooting in the ovary, the stomach protrudes significantly, and body weight rapidly increases.
- Heavy. The listed symptoms are accompanied by shooting, stabbing, pulling pains that are observed at the slightest change in body position. At the same time, the pressure decreases, the heart rhythm is disturbed, and shortness of breath occurs.
At stage 3, there is a high probability of ovarian rupture. The incidence of grade 3 hyperstimulation during pregnancy ranges within 10%.
Apoplexy
Rupture of the ovary, accompanied by acute severe pain, is called apoplexy. Synonyms for this concept are hematoma or ovarian infarction.
Women of reproductive age are at risk.
Factors that increase the likelihood of apoplexy are:
- inflammatory processes occurring in the pelvic organs;
- sclerotic changes in the tissues of the glands, taking drugs that affect blood clotting.
Apoplexy can be triggered by trauma in the abdominal area, the process of irrigating the uterus with a syringe, examination by a gynecologist, or intense sexual intercourse. If the rupture occurs at rest, endogenous factors take place: abnormal location of the uterus, tumor development, adhesions and other disorders.
The main symptom of a glandular infarction is a sharp, sudden pain in the ovarian area caused by the effect of blood on pain receptors.
There are 2 forms of apoplexy:
- Painful, or pseudoappendicular. It is often mistaken for an attack of appendicitis. In addition to unbearable acute pain, nausea begins, blood pressure drops sharply, which is expressed in pale skin and loss of strength.
- Hemorrhagic or anemic. The main signs are lightheadedness, pallor and nausea as a result of blood loss (up to 150 ml in mild cases and more than 500 ml in severe cases).
For mild forms of the disease, conservative treatment is used, but in 85-86% of cases adhesions form, and the probability of relapse is 50%. To preserve reproductive function, laparoscopy with organ preservation, if possible, is recommended.
Ovarian cancer
Secondary cancer is a tumor, a cystic formation with a dense structure. It most often affects women over 40 years of age. As the tumor grows, the following is observed:
- the occurrence of a dull, aching pain;
- pressing sensations in the area of the bladder, rectum;
- constipation, difficulty urinating;
- a significant increase in abdominal size with pronounced asymmetry;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- menstrual irregularities.
At stages 3-4, pain spreads throughout the body due to multiple organ damage.
Ovarian tecomatosis
With oncological diseases of the reproductive organs, ovarian tecomatosis is observed in 85-87% of cases. This is a condition in which the ovarian tissue grows. Hyperplasia should not be confused with cancer. In most cases, cell degeneration is not observed. The main problem is excessive androgen production. The disease itself does not cause pain.
Question: “Why do the ovaries hurt and what to do?” in case of severe and acute pain, it is not just inappropriate. Seek emergency medical help immediately - this is what you need to do in such a situation. Such pain signals the following pathologies requiring immediate hospitalization:
- apoplexy and rupture of the ovary, which can even occur as a result of the release of an egg from an inflamed ovary;
- pelvioperitonitis - a purulent process in the peritoneum;
- ruptured cystic capsule or torsion of its legs;
- ectopic pregnancy.
Only regular general medical examinations, mandatory annual examinations by a gynecologist, adherence to a healthy lifestyle and prompt, responsible treatment are a relative guarantee of preserving a woman’s health and fertility.
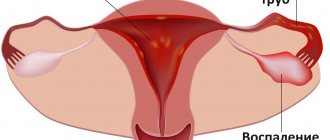
What is ovarian inflammation
A disease accompanied by inflammation in the female appendages is called adnexitis. Like any other inflammatory process, this disorder can be acute or chronic. Pathology occurs against the background of the formation of a focus of infection with reduced immunity.
The clinical picture depends on the cause of the inflammatory process, its form and stage of development. Before making a diagnosis, diagnostics are carried out, which includes laboratory research methods, gynecological examination and ultrasound. This disease has many serious complications, especially if the inflammation of the ovaries becomes chronic with the formation of adhesions.
Symptoms of adnexitis
If a woman develops adnexitis during pregnancy, its symptoms will depend on the form and severity of the pathology. Manifestations of adnexitis during pregnancy are as follows.
- Leucorrhoea (pathological discharge) from the vagina.
- Pain localized in the lower abdomen.
- Bloating.
- Slight increase in temperature, chills.
- Painful sexual intercourse, persistent discomfort after intercourse with a partner.
Adnexitis of pregnant women in the acute phase of its development has the following symptoms.
- Heat.
- Problems with urination.
- Pain in the anus, discomfort in the lower back.
- Fever.
- General weakness.
- Nausea (usually this symptom is not accompanied by vomiting).
Untimely treatment of the acute stage of adnexitis leads to the transition of the disease to the chronic stage.
Is it possible to get pregnant with adnexitis?
No doctor can say with 100% certainty and guarantee that pregnancy will occur. Even if, during delayed ovulation, which is a consequence of inflammation, fertilization of the egg occurs, then, according to physiological norms, the fertilized egg must move towards the uterine cavity in order to attach to the wall there and begin its development. It is at this stage that a failure in this system may occur, the cause of which is obstruction of the fallopian tubes.
Also, pathogenic microorganisms can become a provocateur, causing disruption of the functioning of the egg and preventing its movement to the uterus. In such a case, there is a high risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy. Due to the unfavorable conditions created, the fertilized egg simply does not have time to reach the uterine cavity and attaches to the wall of the ovary or fallopian tube. Naturally, in such conditions the child cannot develop and the pregnancy is terminated.
Whether pregnancy occurs or not in this case depends on many factors. Here you should take into account the woman’s age and her physiological characteristics. The general state of health and the presence of complications arising from ovarian inflammation are also taken into account. In any case, before conceiving a child, it is necessary to undergo a full course of examination and, if pathology is present, it is better to cure all lesions, and only then begin to plan the birth of a child.
Location
The structure of the internal genital organs of a woman
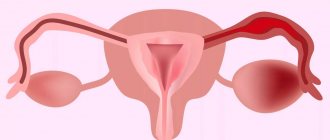
Judging by its appearance, the ovary is comparable to a peach pit, the length of which does not exceed 4 centimeters and 2.5 centimeters in width. In this case, the thickness of the paired organ is 1-1.5 cm.
The outer layer is well protected by the tunica albuginea. It has appropriate properties, so pathogens do not penetrate inside the ovary. Thanks to this membrane, inflammatory processes develop less frequently than in the fallopian tubes and the uterus itself.
The next layer is the cortex. Several follicles of unequal maturity are constantly present on its surface. These capsules look like bubbles filled with liquid, and a full-fledged egg should grow in them. When this process is completed, ovulation occurs. As a result, the follicle wall is destroyed, and the egg is ready to meet sperm for the purpose of fertilization. If conception does not occur, it dies, and if not, it begins to move through the tubes to gain a foothold in the uterus.
As for the ovaries themselves, they are responsible for the formation of key female hormones - progesterone and estrogen. Thanks to these hormones, reproductive function is carried out.
Inflammation is often called an ovarian cold. If the body is overcooled, then it is much easier for pathogenic microorganisms to enter the genitourinary system.
In the presence of a focus of infection, inflammation of the ovaries develops. In most cases, the source of infection is the omentum or fallopian tube.
How does ovarian inflammation affect pregnancy?
If pregnancy does occur with such a serious pathological disorder, there is a high risk of premature birth, miscarriage and uterine bleeding. This is due to the fact that during pregnancy the inflammatory process reduces the protective functions of the uterus and damages its internal tissues. Under such conditions, the fetus can be most actively attacked by viruses and bacteria. In addition, the mother's excited immune system can create additional difficulties.
Bleeding can occur due to the attachment of the fertilized egg to the lower part of the uterus, and with inflammation of the ovaries, the fertilized egg tends to attach itself to this part of the organ. It can also be noted that this pathology provokes the production of antibodies, which can result in the development of thrombohemorrhagic syndrome. The danger of such a violation is expressed in the formation of a large number of blood clots and premature placental abruption.
Adnexitis causes the following pathological conditions during pregnancy:
- fetal infection;
- premature birth;
- miscarriage;
- hydatidiform mole;
- frozen pregnancy.
In the chronic course of the disease, hormonal disruptions occur, as a result of which the development of the fetus is disrupted and the most serious complication is infertility.
Before planning a pregnancy, you need to consult a gynecologist, take tests and smears to identify the presence of an inflammatory process. If the test results reveal that a pathological disorder is present, the doctor will prescribe a course of conservative therapy.
Further, after completing the course, diagnostics are carried out again and, if everything is in order, the woman first needs to completely restore her reproductive function and ensure its physiological functioning. To do this, a sleep and rest schedule is observed, and hormonal levels are adjusted by taking medications. You also need to normalize your metabolism and strengthen your immune system.
To prevent the occurrence of such a pathological disorder, you need to especially carefully monitor your health and not expose yourself to unfavorable factors. And if a disease occurs, do not despair. Modern medical methods make it possible to cure the inflammatory process in a fairly short period and give a chance for the birth of a healthy child.
Ovarian inflammation is a gynecological disease that reduces a woman’s reproductive ability. It is important to contact a specialist in time; only in this case will it be possible to restore it. The disease often interferes with conception and often causes various complications.
Inflammation of the ovaries is a common gynecological disease. Often the inflammatory process becomes chronic. It is noteworthy that diagnosed patients are predominantly young nulliparous girls.
Causes of pain
During pregnancy, the ovaries continue to function, supporting the activity of the corpus luteum. Such a load on the appendages can cause pain. The causes of pain can be grouped into three categories: physiological, pathological and non-obstetric.
Physiological pain in the ovaries
Are a normal process. This is the body’s response to some inconveniences that it begins to experience after pregnancy, however, such sensations are in no way connected with the development of serious pathology.
The causes of pain may be the following:
- Sprains of ligaments and muscles, which are caused by displacement of internal organs due to the growth of the uterus. The ovaries do not hurt much during pregnancy, the pain is tolerable, aching in nature, and is not accompanied by other alarming symptoms.
- Awkward movements can also provoke discomfort in the ovarian area, but such pain is almost always explainable - women feel that the pain is due to a sharp turn, bending or other actions.
Pathological pain
They indicate that there is something wrong with the ovary.
The causes of pathological sensations may be the following:
- The presence of an inflammatory process is almost always accompanied by painful sensations. With mild or chronic inflammation, the pain is aching, can radiate to the sacral spine, spread to the entire lower abdomen and intensify with urination.
- A cyst in the ovary can occur under the influence of pregnancy. Usually the pain is of a pulling nature and appears on the side where the affected organ is located.
- Ovarian apoplexy is a rupture of the appendage, most often accompanied by increased pressure in it.
Non-obstetric pain
Discomfortable sensations in the appendages, which are associated with pathologies of other organs, however, manifest themselves from the localization of the appendages. If such pain occurs during pregnancy, women may quite reasonably think that the ovary hurts.
In fact, the causes of non-obstetric pain lie in the following:
- Kidney problems, most often an exacerbation of a chronic pathology that existed before pregnancy.
- Exacerbation of cholecystitis.
- Cystitis.
- Pyelonephritis.
- Appendicitis.
In any case, no matter what pain a pregnant woman begins to experience, she must be examined by a gynecologist. For example, if the right ovary hurts during pregnancy, this may indicate appendicitis, for which help should be provided on the first day of the disease, or even earlier. Only with early diagnosis and timely treatment is a favorable outcome possible.
Is it possible to get pregnant with ovarian inflammation?
It is difficult to get pregnant with inflammation of the ovaries, since there is a change in the woman’s hormonal levels and the process of egg maturation.
If it is ripe and occurs, women with the disease have a high probability of ectopic pregnancy, the development of pathologies, and miscarriage.
Therefore, when a doctor diagnoses inflammation, it is necessary to stop planning pregnancy.
Chronic form
If inflammation of the ovaries has a long course, it is called chronic. As a rule, over a long period the disease does not manifest itself in any way, there are no obvious signs. Unfortunately, this is where the danger of the disease lies, since it is asymptomatic and as a result is fraught with serious consequences, for example, infertility. As a rule, this diagnosis is the reason for the patient to contact a specialist.
Symptoms of the disease:
- nagging pain;
- decreased sexual function;
- unpleasant sensation during sexual intercourse;
- disruption of the menstrual cycle;
- depressed emotional state.
Acute form
An acute form of ovarian inflammation involves the use of antibacterial drugs, as well as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The presence of the disease can be determined during a routine examination by a gynecologist.
Of course, therapy copes with the disease. However, in the event of pregnancy, they will have a direct negative effect on the embryo.
Before starting antibiotic therapy, pregnancy should be ruled out. For this, the results of an ultrasound and a blood test for hCG are quite sufficient.
Nature of pain in the ovarian region
The pain can be of different types: stabbing, sharp, aching or shooting.
Stitches in the left or right ovary with sudden movement
Sometimes sudden movements cause unpleasant pain. One of the reasons is a sprained ligament. In itself, this is an unpleasant process that causes discomfort. From the first weeks of pregnancy until the end of the term, it is considered normal. The pain is tolerable and does not subside immediately, within a few minutes. It does not require treatment, as this is a physiological process.
Whining in the early stages
At the beginning of pregnancy, discomfort in the appendage area is common. One of the reasons is implantation of the fertilized egg. When it takes hold in the uterus, it forms an embryonic bud and destroys the integrity of the blood vessels, causing slight bleeding and nagging pain. The ovaries begin to mix a little, also causing slight discomfort.
Along with the enlargement of the uterus, the ligamentous apparatus is stretched, causing discomfort. This often happens when a woman in labor suddenly changes position or, conversely, remains on her side for a long time. The pain persists for several minutes.
In the first trimester, a woman should carefully treat any ailment, because constant pain can be due to an ectopic pregnancy, spontaneous miscarriage, or the threat of losing a child. It is imperative to inform your doctor about any changes in your health.
Tingles after sleep
After waking up, you may sometimes experience a slight tingling sensation. This is due to being in one position for a long time, when the pregnant woman stands up, the ligaments and uterus become tense and cause pain. This is normal. Such sensations appear especially often when the stomach acquires an impressive size. The uterus puts pressure on the internal organs, causing discomfort.
If the pain is acute and regular, then you need to seek medical help to rule out serious problems and diseases.
Pulling on the left or right side in the ovarian area
Pain in the sides may indicate inflammatory processes. The disease happens:
- Spicy.
- Chronic.
At the moment of bearing a child, a woman is most vulnerable and inflammation can be a consequence of a common cold or infections that are transmitted through the sexual tract. Treatment at this time is difficult, since antibiotics and many medications are prohibited for pregnant women. Therefore, experts recommend a thorough examination during the period of planning conception.
Also, the initiator of pain in the sides or lower back can be inflammation of the bladder or kidneys.
Is it possible to get pregnant with adnexitis: what doctors say
Adnexitis is an inflammatory process in the ovaries and fallopian tubes. The development of the inflammatory process is provoked by:
- hypothermia;
- prolonged overwork;
- stress;
- pathologies of the genitourinary system;
- surgical interventions in the uterine cavity;
- abortion, etc.
Experts warn that ignoring adnexitis is dangerous because the disease often becomes chronic, causing women to experience difficulty conceiving.
Treatment options to promote pregnancy with ovarian inflammation
To cure inflammation of the ovaries, there are quite a lot of options, both traditional and folk medicine.
Drug treatment involves taking antibiotics. The drugs are available in the following forms:
- ointments;
- creams;
- candles;
- injections.
In tandem, the doctor prescribes medications to prevent dysbiosis.
Before taking an antibiotic, you should find out what pathogen caused the disease.
Before the stage, the girl must take tests and undergo a full examination. Only a doctor can choose a course of treatment. Upon completion, you should not immediately proceed to planning.
The main purpose of a woman is considered to be procreation, that is, the birth of a child. To perform this biological task, the body has a reproductive system. If it functions without failures, then there are no problems with pregnancy. However, various diseases of the organs of this system can prevent or even make it impossible for the birth of a new life.
Adnexitis: causes and mechanisms of development
Most often, this is the name of the inflammatory process in the uterine appendages: the ovaries and (fallopian) fallopian tubes. Another name for this pathology is salpingoophoritis. Inflammation begins against a background of reduced immunity from a small infectious focus, developing into a serious disease. Many patients, when voicing a diagnosis, have a question: is it possible to get pregnant with inflammation of the appendages? To answer, you need to understand the causes and manifestations of the disease.
To make a correct diagnosis, a woman needs to undergo the necessary tests, undergo an examination by a gynecologist, as well as an ultrasound examination. It is advisable to identify the disease as early as possible and begin therapy, since advanced inflammatory processes in the appendages and ovaries almost always become chronic, which leads to the formation of adhesions and other complications.
Experts identify several risk factors for the development of adnexitis:
- inflammatory processes in neighboring organs;
- infectious diseases of the genital area;
- decreased immunity;
- general hypothermia;
- tension in the functioning of the nervous system (stress, overwork);
- history of unsuccessful abortions;
- careless implementation of hygiene rules.
The immediate cause of adnexitis is infection with pathogenic viruses and bacteria during unprotected sex (chlamydia, streptococci, staphylococci and gonococci, as well as mycoplasma and ureaplasma are especially dangerous). Activation of one’s own flora against the background of reduced immunity is not excluded. The likelihood of developing adnexitis increases after abortions and miscarriages.
Chronic adnexitis
Chronic adnexitis and pregnancy are 2 conditions of the female body, the combination of which is extremely undesirable. If a doctor diagnoses a woman with “chronic adnexitis,” she should first cure the pathology and only then start planning a pregnancy.
Is it possible to give birth with chronic adnexitis?
The danger of chronic adnexitis is that it occurs latently and is often asymptomatic. A gynecologist can detect pathology in a woman who is already pregnant. Due to weakened immunity and hormonal changes, the disease worsens, becoming more dangerous to the health and life of the baby. The question of whether it is possible to give birth with chronic adnexitis worries many expectant mothers. Doctors advise treating the disease first, and only then thinking about the child. But if it so happens that a woman learned about the diagnosis of “chronic adnexitis” after conceiving a baby, she should be under the supervision of a doctor throughout her pregnancy, be tested for genital tract infections and undergo a course of gentle anti-inflammatory therapy. Natural childbirth for chronic adnexitis is not recommended. A caesarean section is performed.
Pregnancy with adnexitis: are there any chances?
This possibility exists, but it is small. First of all, due to inflammatory processes, ovulation, i.e., the maturation of the egg, slows down. Further, even if fertilization has occurred, an impassable obstacle may appear on the way of the egg to the uterus for attachment due to the appearance of adhesions in the lumen of the fallopian tubes. Pathogens also interfere with the normal physiology and progression of eggs. In such cases, the probability of occurrence is high, since in unfavorable conditions, due to inflammatory processes, the egg moves slowly and attaches not in the uterus, but along the way - on the walls of the ovaries or fallopian tubes. The result is always the same - the earliest possible surgical termination of such a pregnancy and possible infertility.
The answer to the question of whether it is possible to become pregnant with inflammation of the ovaries depends on a number of other factors: the type and duration of the existing inflammatory process in the genital area, the presence of concomitant diseases, the age of the patient and the individual characteristics of her body.
Complications of pregnancy with adnexitis
The presence of pathological inflammatory processes in the appendages is not a 100% obstacle to pregnancy. However, the subsequent pregnancy often occurs with many complications.
The most common complications of pregnancy against the background of chronic adnexitis are presented in the table.
| Gestational age | Complications | Correction |
| I trimester (up to 12 weeks) | Spontaneous miscarriage, regressive pregnancy, intrauterine infection of the fetus | Treatment aimed at maintaining pregnancy, antibacterial therapy |
| II trimester (13-24 weeks) | Spontaneous miscarriage, placental insufficiency, placenta previa | Conservation therapy, means to improve uteroplacental blood flow |
| III trimester (25-40 weeks) | Premature birth, placental insufficiency, fetal hypoxia, fetal growth restriction, polyhydramnios | Conservation therapy, means to improve uteroplacental blood flow, antibacterial therapy, resolving the issue of delivery |
| Postpartum period | Postpartum endometritis | Antibacterial therapy |
Consequences and their prevention
It is best, without waiting for trouble, to prevent diseases of the female genital area and not be exposed to risk factors for inflammation. Then you can plan your pregnancy at any time.
If inflammation of the ovaries or appendages has already been diagnosed - with the help of tests, vaginal smears, as well as an ultrasound examination that showed the presence of inflammation - do not despair. In modern gynecology, there is a whole area dedicated to the treatment of inflammation of the uterine appendages. Its goal is to stop pathological processes, cure their consequences and restore normal functioning of the female reproductive system for the onset of physiological pregnancy and successful delivery. Therapy is carried out conservatively, with the help of medications and physical therapy. Herbal medicine can also be used in doses as support.
After the normal functioning of the uterine appendages has been restored, hormonal levels are adjusted with medication (usually with the help of oral contraceptives), metabolism is normalized (with the help of a balanced diet) and the immune system is strengthened (with the help of vitamin therapy).
After recovery, confirmed by tests and visual examination by a gynecologist, at least 3-6 months of physiological functioning of the ovaries should pass, after which you can begin planning a pregnancy and prepare for the birth of a healthy child.
Inflammation of the appendages is a disease in which the inflammatory process is localized in the ovaries and/or fallopian tubes.
Usually it is a consequence of infection in the sterile environment of the genital organs, which can be caused by non-compliance with hygiene rules, including during sexual intercourse, previous abortions, childbirth, hypothermia, etc.
Is pregnancy possible with inflammation of the appendages?
Many women who are faced with such a disease as inflammation of the appendages are interested in: is it possible to get pregnant with this diagnosis?
If a concomitant diagnosis of infertility is not made, then the theoretical probability of pregnancy cannot be excluded, although the maturation and fertilization of the egg is associated with significant difficulties due to hormonal disorders.
But even if fertilization occurs, due to disturbances in the patency of the fallopian tubes, the egg may not reach the uterine cavity, and then an ectopic pregnancy will occur, which in all respects is dangerous for the woman’s life.
In addition, even if the egg has successfully implanted in the uterus, pregnancy has occurred and is proceeding normally at first glance, the danger has not yet passed. Unfortunately, with untreated inflammation of the appendages, miscarriage can occur at any time. Pathologies of fetal development cannot be excluded. The likelihood of carrying and giving birth to a healthy child, alas, is not very high.
How to cure inflammation of the appendages?
Treatment of adnexitis is a long and complex, but necessary, process, including restoration of the reproductive system, normalization of hormonal levels, metabolism and strengthening of the immune system.
Treatment is carried out either in a hospital or at a antenatal clinic.
The basis is the prescription of antibiotics selected in accordance with the individual course of treatment. If necessary, the adhesions of the fallopian tubes are dissected.
A variety of physiotherapeutic procedures are also used, a special diet and a special lifestyle are prescribed. During the recovery period, sanatorium-resort treatment is desirable.
Is it possible to get pregnant with ovarian inflammation?
The reproductive system of a woman is the most complex and most amazing system of the human body, because it is in it that a new life is born and its development occurs until birth. But at the same time, female organs are susceptible to a variety of diseases, which often affect the course of pregnancy itself and the ability to become pregnant in general. One of the most common female diseases is inflammation of the ovaries, so very often women planning pregnancy are interested in whether it is possible to get pregnant with inflammation of the ovaries
.
Inflammation of the ovaries most often occurs as a result of microbes entering the female organs, which penetrate during sexual intercourse, or as a result of non-compliance with basic rules of hygiene and self-care. Other causes of inflammation of the appendages include previous abortions and childbirth, infectious diseases, reduced immunity of women, hypothermia, constant stress, and overwork.
Most often the disease is caused by:
- mycoplasma;
- gonococci;
- staphylococci;
- streptococci;
- chlamydia;
- other pathogenic organisms.
Ovarian inflammation, especially its chronic form, is fraught with irreversible consequences, including infertility and ectopic pregnancies. It is very difficult to get pregnant with inflammation of the ovaries, because the woman’s hormonal levels are disrupted, as well as the process of maturation of the egg, the main participant in fertilization. As a result, pregnancy with ovarian inflammation can be accompanied by pathologies, disturbances in fetal development, as well as miscarriage, which can occur at any stage of pregnancy.
In answer to the question: Is it possible to get pregnant with inflammation of the ovaries? you should immediately formulate a counter question: Is it necessary?
Modern medicine offers innovative ways to treat inflammatory processes of the female organs, which in a fairly short time normalize the functioning of the entire reproductive system and give a woman the opportunity to conceive and bear a healthy child. You should not rely on chance and, when planning a pregnancy, it is imperative to seek advice from specialists.
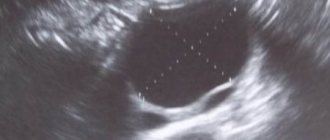
Cyst
Pain in the appendages in pregnant women can be caused by a cyst - a benign neoplasm filled with fluid. When making such a diagnosis, a pregnant woman should not worry too much, because this disease is treatable with medication.
© shutterstock
Signs of illness
In the early stages of pregnancy, an appendage cyst can only be detected by ultrasound examination, since the disease does not show any symptoms.
When the tumor increases in size, the woman begins to worry:
- Abdominal pain;
- Bloating;
- Edema;
- Frequent urination;
- Fever.
Treatment options
During pregnancy, you can get rid of the pain of the appendages caused by a cyst thanks to hormonal drugs. Their use must be prescribed by a doctor, since self-medication will lead to unforeseen consequences.
In extremely rare cases, surgical intervention is performed - laparoscopy.
Is it possible to get pregnant after inflammation of the uterine appendages?
Why is inflammation of the appendages dangerous?
Inflammatory diseases of the fallopian tubes and ovaries - adnexitis and salpingoophoritis. They are usually the result of promiscuous sex life, the hidden course of chronic diseases, poor personal hygiene and weakened immunity. In a healthy woman, the appendages and uterine cavity are sterile, as they do not have their own microflora. They can become inflamed when exposed to pathogenic microbes. Sexually transmitted microorganisms are especially dangerous: gonococci, trichomonas, chlamydia, mycoplasma, ureaplasma. They are extremely hardy and stubbornly resist the immune system. Often, signs of the disease can appear when the inflammatory process has already become chronic. Typically, women are bothered by sharp and aching pain in the lower abdomen, menstrual dysfunction, fever and weakness. The functioning of inflamed fallopian tubes and ovaries is seriously impaired if the process continues for a long time. It is worth noting that hypothermia cannot cause inflammation of the appendages; it only serves as a provoking factor when the inflammatory process begins.
What is the likelihood of pregnancy after inflammation of the appendages?
Untimely treatment of the inflammatory process leads to the formation of dense connective tissue, which replaces dead cells. As a result, the already thin lumen of the tube may become “overgrown” and it will become impassable for the egg.
In addition, inflammation causes damage to the cells of the inner surface of the fallopian tubes and the death of ciliated cilia, leading to impaired peristalsis and complete loss of tube function.
Many microorganisms, such as chlamydia and mycoplasma, can penetrate the pipe wall, thereby disrupting its function. If a woman has had two tubal pregnancies, IVF may be one of the ways to conceive.
Inflammation of the appendages is not a death sentence!
These factors significantly reduce the possibility of intrauterine pregnancy, making it difficult for the fertilized egg to move from the tube into the uterine cavity. This can lead to ectopic pregnancy and infertility, which is difficult to treat. However, there is a chance of getting pregnant, so don’t despair ahead of time! You can take advantage of specialist consultations, and patience and faith in your own strength will lead to long-awaited motherhood!
How to treat conjunctivitis at home
At the first symptoms of conjunctivitis, it is important to consult a doctor promptly, who will subsequently prescribe antibiotics that destroy the infection.
- How to remove unpleasant odor from shoes
- Irritable bowel syndrome: treatment with folk remedies
- How to effectively treat hemorrhoids at home
- How to get rid of acne on the scalp
The danger of adnexitis in early pregnancy
Inflammatory processes in one of the reproductive organs can have a negative impact on the course of pregnancy in almost all trimesters. So, in the first trimester, a miscarriage is possible due to impaired ovarian function. The fact is that ovulation with inflamed appendages does not occur or occurs with a clear delay. If in a healthy woman ovulation begins in the middle of the menstrual cycle, then with adnexitis it shifts and occurs almost before menstruation. Normally, after ovulation, a corpus luteum appears in place of the egg, which is responsible for the production of progesterone. This hormone not only allows you to get pregnant, but also supports pregnancy in the first trimester. With inflamed ovaries, the corpus luteum cannot work fully, as a result of which too little progesterone is produced. For this reason, the pregnancy is terminated. This can only be avoided with timely administration of maintenance hormone therapy.
Note:
Many patients who were able to become pregnant with adnexitis are faced with such an unpleasant consequence as ovarian pregnancy. The inflammatory process in the ovaries leads to an increase in connective tissue and a narrowing of the lumen in the fallopian tubes.
This pathological condition also leads to impaired functioning of the cilia located in the ciliated epithelium. These organs lose the ability to promote a fertilized egg to the uterine cavity. In this case, a pregnancy test may give a positive result, and the woman will experience exactly the same sensations as during a normal pregnancy. If you were diagnosed with adnexitis before pregnancy and managed to get pregnant, you should contact a gynecologist as soon as possible to rule out or confirm an ectopic pregnancy.
Often, inflammation of the appendages leads to miscarriage due to the fact that the inner layers of the uterus are damaged and its protective system undergoes changes. The layers of the uterus, trying to protect the organ from microorganisms that cause inflammation, begin to mistake the embryo for a foreign agent. As a result, the embryo is rejected and a miscarriage occurs. Even if the fertilized egg is implanted, most often it remains in the lower part of the uterus. This results in placenta previa or low attachment. Such conditions often cause bleeding during pregnancy.
Is it possible to get pregnant after inflammation of the uterine appendages?
Of course, it can, but it’s better to see good doctors before planning and have everything healed properly. If there are a lot of adhesions, then they can interfere. Also, God forbid, an ectopic pregnancy may occur, which will then lead to the removal of the tube. Therefore, I do not advise you to take risks, but to consult a doctor about this. It’s possible that you’re pregnant, so don’t beat yourself up about it!
I know a lot of examples from my friends. We became pregnant more than once, and each one experienced this disease differently. One was cured after completing a course of 10 injections. The other one took longer to be treated, I don’t remember with what. but it wasn’t limited to injections. And they gave birth to children. not immediately after illness. It worked out that way, and after 2 - 3 years.
Is it possible to get pregnant with adnexitis?
Hello, dear forum members! My question is: is it possible to get pregnant and how will pregnancy proceed with chronic adnexitis? I have bilateral acute adnexitis, which I treated a month ago, but was not cured. My friend says that it is difficult to get pregnant, and if you do get pregnant, you will suffer from periodic pain in the uterus and ovaries. Tell me, is it possible to get pregnant with such a disease, is it worth it, and what could be the consequences?
Sources: gynecologist.com.ua, medinote.ru, www.kakprosto.ru, www.bolshoyvopros.ru, mamapluspapa.ru
Signs of adnexitis
Adnexitis in a pregnant woman can be caused by various reasons. Depending on them, the disease will manifest itself externally in the form of certain signs. Adnexitis of any form not only disrupts female reproductive function, but also leads to serious pathologies of pregnancy if it occurs. For example, in the 1st trimester, a woman with adnexitis risks losing her baby as a result of a miscarriage, or the pregnancy may be frozen. With adnexitis in the 6th month of pregnancy, the signs and symptoms of the disease are often mild or absent altogether. The adverse effects of inflammation can be avoided if you pay attention to the symptoms of the disease in time.