Compound
One Belara tablet contains 2 mg of chlormadinone acetate and 30 mcg of ethinyl estradiol.
Additional components: lactose monohydrate, K30 povidone, corn starch, magnesium stearate.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcopyrightru
Film shell composition: macrogol 6000, hypromellose, talc, lactose monohydrate, propylene glycol, titanium dioxide, red iron oxide dye.
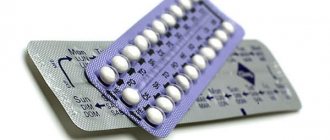
Belara birth control pills are covered with a light pink shell, round, biconvex with a white core. 21 such tablets in a blister, one or three blisters in a cardboard pack.
The composition is characterized by two main components:
- chlormadinone acetate (2 mg);
- ethinyl estradiol (0.03 mg).
Excipients:
- povidone K30;
- lactose monohydrate;
- corn starch;
- magnesium stearate.
The medication is available in solid dosage form - round tablets coated with a light pink film coating. The shell consists of red dye, propylene glycol, talc, macrogol, etc. The pills are sealed in a blister in the amount of 21 pieces. On sale you can purchase one or three blisters in cardboard packaging.
Features of the effect of the drug
Belara contains the hormones progesterone and estrogen. In tablets they are present in the required quantity and certain concentration. For one menstrual cycle you will need 21 tablets. They must be taken at the same time every day. The use of Belara is carried out according to the scheme indicated on the packaging, with strict adherence to all marked days.
Like other drugs, Belar contraceptives change the amount of regulation. This is bloody discharge that appears only in the intervals between taking pills. You should start taking Belara on the first day of your period.
The first course lasts 21 days, then after 7 days you need to take a break. It is during this period that menstruation should occur. On day 8, you need to start taking a new package of contraceptives and repeat the entire course again, according to the scheme.
Some facts
Hormonal contraceptives are up to 99% capable of preventing unwanted pregnancy. These are artificially synthesized analogues of estrogen and progestogen in the female genital organs, which suppress ovulation and exclude the possibility of fertilization of the egg.
Belara is a combination drug from the group of oral contraceptives. Its use causes suppression of ovulation and disrupts sperm motility, preventing their penetration through the cervical canal, thereby preventing conception. In addition to its direct purpose, the product has positive side effects, such as stabilization of the normal menstrual cycle, reduction and even suppression of pain before and during menstruation, as well as the following indications: for the prevention of gynecological diseases.
pharmachologic effect
Contraceptive action.
Chlormadinone acetate is a progestin substance that has antiandrogenic properties. The nature of its action is based on the competitive displacement of androgenic hormones at specific receptors, weakening the severity of the effects of endogenous and exogenous hormones. Daily intake of 1.7 mg of chlormadinone helps to completely suppress ovulation, subject to continuous adherence to a 21-day cycle.
The concentration of chlormadinone reaches its maximum in the blood-forming substance two hours after taking the tablet. During the transformation of the component, active and inactive derivatives are released. Chlormadinone accumulates in adipose tissue, gradually integrating into the circulatory system. The half-life of the substance occurs after 34 hours with a single dose, and on average 38 hours with systematic use of the drug.
Ethinyl estradiol has an inhibitory effect on the secretion of sweat glands of the skin. Like chlormadinone acetate, it provokes the production of globulin, which binds sex hormones, as a result of which the level of testosterone in the blood plasma is significantly reduced. Ethinyl estradiol actively interacts with estrogen receptors in the tubes and cervix, external genitalia, and activates endometrial proliferation. The half-life of metabolites occurs within 14 hours through the kidneys and intestines.
Belara is a reliable monophasic contraceptive. In addition, regular use normalizes hormonal levels, eliminating factors such as menstrual irregularities, premenstrual syndrome, ovarian diseases (cysts), and inflammation of the pelvic organs. The risk of malignant and benign formations is significantly reduced. Prescribing Belara may be associated with these problems, bypassing the main function of the drug to prevent pregnancy.
The nature of menstruation after taking the drug
Taking an oral contraceptive often causes hormonal imbalance, which in turn can cause the following consequences:
- Menstrual delay.
Many women are concerned about the fact that after taking Belara there are no periods or they are delayed. Most often this happens in the first month of taking the pills. This deviation can easily be explained by the woman’s body becoming accustomed to excess hormones. Under the influence of the contraceptive, active production of luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones is observed, which help suppress ovulation.
Along with the production of hormones, the consistency of the mucus in the cervix changes. It becomes viscous and thick and therefore interferes with the movement of sperm. The same changes occur in the endometrium, which becomes completely unsuitable for embryo attachment. After the start of the course, menstruation occurs from the 21st to the 28th day of the cycle. During this period, after stopping taking the pills, there will be a decrease in sex hormones. The mucous layer will begin to be rejected in the uterus, and bleeding will appear, reminiscent of menstruation.
- Light discharge.
While taking Belara, scanty discharge is normal. The amount of discharge decreases to 60 ml for all days of menstruation. The number of days of menstruation is also reduced. All these phenomena are due to the pharmacological action of the drug and the influence of hormones on the female body.
The decrease in menstruation under the influence of the drug is also due to a decrease in the endometrial layer. It will differ from normal in its structure. But the amount of its remains will be insignificant. All of them will be pushed out by the uterus within a short time.
- Lack of menstruation.
After completing the course for 21 days, menstruation may not occur. In this case, after 7 days, you should continue taking the drug. Disruptions in the menstrual cycle can be observed for six months. After 6 months, the body should get used to the hormones taken, and menstruation will normalize.
If menstrual flow does not appear at the strictly prescribed time while taking Belara, you should immediately consult a doctor.
This can happen for various reasons, for example:
- When pregnancy occurs.
- When the drug is ineffective (in this case it must be replaced with another).
- There is a disease of the reproductive system.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Pharmacodynamics
A combined contraceptive drug taken orally.
Long-term use of the drug leads to a decrease in the secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone, and, consequently, to suppression of the ovulation process. At the same time, proliferation and secretory transformation of the endometrium occurs, preventing the fixation of the fertilized egg.
Chlormadinone acetate included in the drug is a gestagen with antiandrogenic properties. Its effect is based on the ability to compete with androgens at specific receptors, weakening the effect of androgens. The Pearl index (the probability of becoming pregnant in 12 months) ranges from 0.291-0.698 and depends on how carefully the woman follows the medication regimen.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytdevru
To completely block ovulation, approximately 1.7 mg of chlormadinone acetate is required daily. The required dosage per cycle is 25 mg.
Pharmacokinetics
Chlormadinone acetate. Quickly and completely absorbed. The maximum concentration occurs in an hour and a half. 95% binds to human blood proteins, mainly albumin.
During the transformation process, many metabolites are formed, the main of which are 3-beta and 3-alpha-hydroxy-chlormadinone acetate.
The average half-life from the blood is 34 hours. Chlormadinone acetate and its metabolites are excreted in approximately equal quantities in the urine and through the intestines.
Ethinyl estradiol. It is quickly and almost completely absorbed from the intestine, reaching maximum concentration in plasma after an hour and a half. Absolute bioavailability is about 40%.
About 98% of the substance binds to blood proteins. Ethinyl estradiol is transformed through hydroxylation of the aromatic ring. The main derivative is 2-hydroxy-ethinyl estradiol.
The average half-life of ethinyl estradiol from the blood is 13 hours. Excreted by the kidneys and feces in a ratio of 2:3.
Belara 2/0.03 No. 1*21 film-coated tablets
Belara (BELARA)
Compound
One tablet contains 0.030 mg ethinyl estradiol and 2 mg chlormadinone acetate.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
progestogens and estrogens, fixed combinations
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Continuous use of Belara for 21 days suppresses the secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) by the pituitary gland and, as a result, suppresses ovulation. Proliferation of the endometrium and its secretory transformation are observed. The consistency of cervical mucus also changes. This makes it difficult for sperm to pass through the cervical canal and leads to impaired motility.
Pharmacokinetics
Chlormadinone acetate (CMA): After oral administration, CMA is rapidly and completely absorbed. Max. concentration in blood plasma is achieved after 1-2 hours. More than 95% of CMA binds to blood plasma proteins. CMA accumulates predominantly in adipose tissue. The half-life of CMA is approximately 34 hours (after a single dose) and approximately 36-39 hours (after multiple doses).
Ethinyl estradiol (EE): EE is rapidly and completely absorbed after oral administration, reaching max. concentrations in blood plasma after 1.5 hours. About 98% of ethinyl estradiol is bound to plasma proteins. The average half-life of EE from blood plasma is approximately 12-14 hours. EE is excreted by the kidneys and through the intestines in a ratio of 2:3.
Indications
Hormonal contraception.
Directions for use and doses
One film-coated tablet should be taken every day at the same time (preferably in the evening) for 21 days in a row, then a 7-day break from taking the tablets should be taken; two to four days after taking the last film-coated tablet, withdrawal bleeding similar to menstrual bleeding will occur. After the end of the seven-day break, you should start taking Belara from the next pack, regardless of whether the bleeding has stopped or not. Film-coated tablets should be taken every day, following the direction indicated by the arrow.
If hormonal contraceptives have not previously been used
The first film-coated tablet should be taken on the first day of a woman’s natural cycle, i.e. on the first day of the next menstrual bleeding. If the first tablet is taken on the first day of menstruation, the contraceptive effect of the drug begins on the first day of administration and continues during the seven-day break in taking tablets. The first film-coated tablet can also be taken on days 2-5 of menstruation, regardless of whether the bleeding has stopped or not. In this case, during the first seven days of admission it is necessary to use additional barrier methods of contraception.
If menstruation began more than five days ago, the woman should be advised to wait until the start of her next menstruation before starting to take Belara.
Switching from another combined oral contraceptive
A woman should start taking Belara the next day after a seven-day break from taking pills or taking placebo pills from the package of a previously used combined oral contraceptive.
After spontaneous or medical abortion in the first trimester
You can start taking Belara immediately after a spontaneous or medical abortion in the first trimester. In this case, there is no need to use additional contraceptive measures.
After childbirth, spontaneous or medical abortion in the second trimester
After giving birth, women who are not breastfeeding can start taking the drug 21-28 days after birth. In this case, there is no need to use additional barrier methods of contraception. If the drug was started more than 28 days after birth, additional barrier methods of contraception should be used during the first seven days.
If a woman has already had sexual intercourse, pregnancy should be excluded, or wait until the start of the next menstrual cycle before starting to take the drug.
After stopping taking Belara
After you stop taking Belara, your current cycle may lengthen by about one week.
Irregular taking of pills
If the patient forgot to take the film-coated tablet, but took it within the next 12 hours, no additional contraceptive measures are required. The patient should continue taking the drug as usual.
If the patient forgot to take the film-coated tablet, but took it after 12 hours, contraceptive protection may be reduced.
The last (forgotten) film-coated tablet should be taken immediately, even if this means taking 2 tablets at the same time. Other tablets should be taken as usual. Over the next seven days, it is necessary to additionally use barrier methods of contraception.
Contraindications
Combined oral contraceptives (COCs) should not be used if you have a medical condition or if one of the following conditions occurs while taking them:
- existing or existing thrombosis of veins or arteries;
- prodromal period or first signs of thrombosis, thrombophlebitis or symptoms of embolism (for example, transient ischemic attack, angina pectoris);
- planned surgery (at least four weeks before surgery), period of immobilization;
- diabetes mellitus accompanied by vascular complications;
- diabetes;
- arterial hypertension;
- hepatitis, jaundice, liver dysfunction until normalization of liver function indicators;
- generalized itching, cholestasis;
- Dubin-Johnson syndrome, Rotor syndrome, bile secretion disorders;
- history of liver tumors; porphyria;
- malignant hormone-dependent tumors of the mammary glands or uterus;
- serious disorders of lipid metabolism; pancreatitis;
- migraine with a history of focal neurological symptoms (a form of migraine combined with paresthesia, convulsions, aphasia);
- amenorrhea of unknown etiology; endometrial hyperplasia;
- bleeding from the vagina of unknown etiology;
- hypersensitivity to the active substances or to any other component of the drug, lactation.
Side effect
The most common side effects of the drug were nausea, vomiting, lower abdominal pain, breakthrough bleeding, minor spotting, dysmenorrhea, amenorrhea, headache, dizziness, migraine, discomfort in the mammary glands, skin allergic reactions, depressed mood, irritability,
fatigue abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea. The likelihood of irregular bleeding decreases with long-term use of Belara.
Special instructions and precautions
Smoking increases the risk of serious cardiovascular complications associated with combined oral contraceptives (COCs). Women over 35 who smoke should use other methods of contraception.
The use of COCs is associated with an increased risk of various serious diseases, such as myocardial infarction, thromboembolism, stroke or liver neoplasms. Other risk factors such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, obesity and diabetes significantly increase the risk of complications and mortality.
If you have one of the following diseases/risk factors, you should weigh the potential risk and expected benefits of using Belara.
Interaction with other drugs
The following medicinal products may reduce the serum concentration of ethinyl estradiol: all medicinal products that increase gastrointestinal motility (eg metoclopramide) or impair absorption (eg activated charcoal); substances that induce liver microsomal enzymes, such as rifampicin, rifabutin, barbiturates, anticonvulsants (for example, carbamazepine, phenytoin or topiramate), griseofulvin, barbexaclone, primidone, modafinil, some protease inhibitors (for example, ritonavir) and St. John's wort preparations; some antibiotics (eg, ampicillin, tetracycline) in some women, possibly due to decreased enterohepatic circulation of estrogens. With the simultaneous short-term use of these drugs with Belara, it is necessary to use additional barrier methods of contraception, both during treatment and during the first seven days after its completion. When taking active substances that reduce the concentration of ethinyl estradiol in the blood serum due to the induction of microsomal liver enzymes, additional barrier methods should be used within 28 days after the end of treatment.
Ethinyl estradiol may affect the metabolism of other substances:
suppress the activity of microsomal liver enzymes and, accordingly, increase the concentration in the blood serum of such active substances as diazepam (and other benzodiazepines, the metabolism of which is carried out through hydroxylation), cyclosporine, theophylline and prednisolone; induce glucuronidation in the liver and, accordingly, reduce the concentration in the blood serum of substances such as clofibrate, paracetamol, morphine and lorazepam.
The need for insulin and oral antidiabetic agents may change because the drug affects glucose tolerance.
Package
1x21 or 3x21 film-coated tablets.
Contraindications
The need for oral contraception.
Prescribing the drug is prohibited if there are the following contraindications:
- diabetes mellitus in an uncontrolled phase;
- liver dysfunction caused by various diseases;
- hypertension, blood pressure instability;
- pancreatitis;
- inflammatory pathologies of the female genital organs;
- epilepsy; malignant tumors;
- autoimmune processes;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- sclerosis.
Treatment cannot be prescribed if there is an individual intolerance to the components.
Manifestations of an overdose may include nausea and vomiting, as well as bleeding. They are relieved symptomatically.
The use of the drug is contraindicated in the following diseases:
- the presence of initial signs of thrombophlebitis, thrombosis or symptoms of embolism (including temporary ischemic attacks);
- thrombosis and thromboembolism during or in history (myocardial infarction, pulmonary embolism, venous thrombosis, cerebrovascular changes);
- planned surgical intervention (4 weeks before) and period of immobilization;
- uncontrolled arterial hypertension;
- acute or chronic severe liver damage (until normalization of liver function);
- uncontrolled diabetes mellitus;
- predisposition to the appearance of venous and arterial thrombosis: APC resistance, protein S deficiency, protein C deficiency, antithrombin 3 deficiency, antiphospholipid antibodies and hyperhomocysteinemia;
- itching of the entire body, cholestasis, especially during a previous pregnancy or use of sex hormones in the past;
- liver tumors, including a history of;
- severe epigastric pain, hepatomegaly or signs of intra-abdominal bleeding;
- Rotor syndrome, Dubin-Johnson syndrome, slowing of bile flow;
- porphyria in all forms and manifestations;
- hormone-dependent malignant tumors or suspicion of their presence;
- pancreatitis, in combination with severe hypertriglyceridemia;
- pronounced changes in lipid metabolism;
- migraine attacks;
- acute sensory disturbances;
- increased frequency of epilepsy attacks;
- movement disorders;
- severe depression;
- complication of otosclerosis during previous pregnancies;
- endometrial hyperplasia;
- cryptogenic amenorrhea;
- vaginal bleeding of unknown etiology;
- lactation period;
- pregnancy and suspicion of it;
- addiction to smoking at the age of 35 years;
- lactase deficiency, lactose intolerance, glucose-galactose malabsorption;
- the presence of multiple risk factors for arterial or venous thrombosis;
- sensitization to the components of the drug.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=upload
It is necessary to prescribe the drug with caution in the presence of the following diseases (including a history):
- multiple sclerosis, epilepsy;
- bronchial asthma;
- convulsive syndrome;
- migraine without neurological symptoms;
- renal or heart failure;
- uncomplicated diabetes mellitus;
- chorea;
- mild liver diseases;
- dyslipoproteinemia, lipid metabolism disorder;
- autoimmune diseases;
- obesity;
- endometriosis;
- controlled arterial hypertension;
- phlebitis of the superficial veins of the legs, varicose veins;
- changes in blood clotting;
- uterine fibroids;
- mastopathy;
- herpes pregnant women;
- chronic inflammatory bowel diseases;
- depression.
When taking birth control pills that contain high levels of hormones, you need to understand the degree of risk to the body. A sharp change in hormonal levels negatively affects all organs and systems.
Women with existing systemic diseases of the endocrine and genitourinary systems (diseases of the liver and kidneys, biliary tract, Crohn's disease) are especially sensitive to hormonal imbalance.
The following factors are absolute contraindications to the use of emergency contraception:
- current pregnancy;
- lactation period;
- existing blood diseases (coagulation disorders, thrombosis, bleeding of unknown etiology);
- severe liver disease;
- epilepsy;
- individual intolerance to the drug;
- diabetes mellitus (severe form);
The presence of at least one provoking factor creates the prerequisites for additional consultation with the attending physician.
A decrease in effectiveness is noted with functional disorders of the digestive system (Crohn's disease).
Memo
A systemic contraceptive taken in a timely manner prevents unplanned pregnancy. Contraceptives used topically reduce the likelihood of fertilization in the absence of systemic therapy. When deciding on emergency preventive measures, you need to realistically assess the risk of complications due to sudden changes in hormonal levels. Consulting a gynecologist will be the best option to resolve this situation.
Belara price, where to buy
Each package contains detailed instructions with the dosage of the tablets. Before you start drinking Belara, you must carefully read the rules of administration. For convenience, all tablets in the blister are marked by day of the month.
According to the annotation, contraceptives should be taken daily, without skipping, at the same time (evening is recommended). If the drug was prescribed for the first time, the first pill should be taken with a small amount of liquid on the initial day of the cycle, but no later than the fifth day. The course lasts twenty-one days, then you need to stop for seven days.
When switching from another contraceptive to Belara, there are several nuances. So, in case of discontinuation of drugs containing gestagen, a break between them and the use of Belara is not required. The same applies to medications in a dosage of 21-22 pieces. They need to be consumed to the end, and the next day you should start a new prescription.
After an abortion in the first trimester, you can start taking Belara on the day of termination of pregnancy. If the period exceeds three months, or childbirth has occurred, the medicine is prescribed for the fourth week. If you miss your due date, you must use barrier methods of contraception or wait until the next cycle begins.
- You cannot take a break for more than a week.
- Contraceptive properties are restored after seven days of continuous use of the drug.
- A dose of two tablets is allowed with a one-time pass, then follow the standard regimen.
Instructions for use of Belara prescribe taking birth control pills orally. They should be removed from the blister and swallowed whole, if necessary with a small amount of liquid. The tablets should be taken every day at the same time (preferably in the evening) for 21 days in a row, then you should stop taking them for 7 days; approximately 2-4 days after taking the last tablet, withdrawal bleeding similar to menstrual bleeding develops.
After completing the 7-day break, you must start using the drug from the next pack, regardless of whether the bleeding has stopped.
The first tablet must be taken on the first day of a woman’s physiological cycle (the first day of the next menstruation). In this case, the contraceptive effect begins on the first day of use and lasts during a week-long break in use.
The first tablet can be taken on days 1-5 of menstrual bleeding (whether the bleeding has stopped or not). In this case, during the first seven days of use, you must also use barrier methods of contraception.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=https:accounts.google.comServiceLogin
If menstrual bleeding appeared more than 5 days ago, it is recommended to wait until the next menstruation begins and then begin the cycle of taking the drug.
Transition from another hormonal contraceptive (combined) to Belara
Switching from products containing 21-22 tablets. It is necessary to finish using all tablets from the previous package. Next, you need to take the first Belara tablet the next day. There should be no break in the use of the pills, and the woman is not advised to have her next menstruation. Additional methods of contraception are not required in this case.
Transition from products containing one gestagen (mini-pill)
In this case, the first Belara tablet should be taken the next day after using the last tablet, which includes only gestagen. During the first seven days, it is also recommended to use barrier methods of contraception.
Switching from hormonal contraceptives, injection or implant
You can start taking Belara on the first day of implant removal or on the first day of the planned injection. During the first seven days, it is recommended to use barrier contraceptive methods.
After an abortion (spontaneous or medical) in the first 3 months of pregnancy
You can start using Belara on the day of the abortion. In this case, you may not need to use additional methods to prevent pregnancy.
After childbirth or abortion (spontaneous or medical) at 3-6 months of pregnancy
It is recommended to start taking Belara in the fourth week after birth, if lactation is not occurring, or after an abortion in the second trimester of pregnancy. In this case, it is not necessary to use additional methods of contraception.
If the use of the drug is started later than the fourth week after childbirth or abortion, it is recommended to use additional methods of contraception during the first week.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytadvertiseru
If you have already had sexual intercourse, it is advisable to exclude pregnancy or wait until the next menstrual cycle before taking the drug.
If a woman forgot to take the pill, but took it 12 hours later, the contraceptive effect may be weakened.
If you miss a pill, you must follow the rules below:
- Do not stop taking the medication for more than a week;
- 7 days of continuous medication is necessary to achieve reliable suppression of the regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian system.
It is advisable to take a missed tablet immediately, even if this means that you need to take two tablets at a time. Then follow the standard scheme. Over the next week, it is necessary to use barrier methods of contraception.
If there are less than seven tablets left in a pack, immediately after finishing taking tablets from this pack, you must start taking tablets from a new pack - there should be no break between packs. Withdrawal bleeding will usually not occur until all the tablets in the second pack have been used, but exceptions may occur. If withdrawal bleeding does not appear after the end of the cycle of taking the second package, then you need to perform a pregnancy test.
Typically, overdose does not cause severe toxic effects. Symptoms: possible vomiting, nausea, bloody discharge from the vagina.
Treatment: symptomatic. There is no selective antidote.
The price of Belara in Russian pharmacies (21 tablets per package) is 491-536 rubles. The price of tablets No. 63 starts from 710 rubles.
Buying similar contraceptive pills No. 21 in Ukraine will cost 250-650 hryvnia, and the minimum cost of package No. 61 will be 910 hryvnia.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
- Online pharmacies in KazakhstanKazakhstan
ZdravCity
- Belara tab. n21Grunenthal GmbH/Gedeon Richter OJSC
- Belara tab. n63Grunenthal GmbH/Gedeon Richter OJSC
Pharmacy Dialogue
Europharm* 4% discount using promo code medside11
- Belara n21 tableGedeon Richter OJSC
show more
Pharmacy24
- Belara No. 21 tablets VAT "Gedeon Richter", Ugorshchina
PaniPharmacy
- Belara tablets Belara tablets. No. 21 Hungary, Gedeon Richter
show more
BIOSPHERE
- Belara 2 mg/0.03 mg No. 21 tablet p.o. Gedeon Richter (Hungary)
show more
How can you delay or delay your periods using folk remedies?
Some women resort to a variety of traditional medicine to delay menstruation. On forums in reviews you will read different opinions about this or that plant: it helped some, but not others.
Let us immediately make a reservation that from a medical point of view, these tips are unproven. But since folk remedies are much safer than synthetic drugs, you can try. So, the top natural remedies:
- Nettle. A hemostatic plant known since ancient times. You can brew it and take a glass three times a day. This plant should not be taken by people who are at risk of blood clots, as nettle thickens the blood;
- Water pepper. The active ingredient is vitamin K. You should start taking the decoction a few days before your expected period. Drink half a glass half an hour before meals;
- Plants containing ascorbic acid: lemon and parsley. Large amounts of lemon can cause stomach ulcers.
As we can see, there are ways to delay your periods, but you can resort to them only in extreme cases. Frequent use of medications can cause disruption in a woman’s endocrine system and lead to illness.
Not everyone can use them, even in rare cases. Women with irregular cycles, over 40 years of age, and smokers are prohibited from using these methods without first talking with a gynecologist. Is it necessary to risk your health for the sake of dubious convenience?
Recommended Articles
“Harmless” cyst of the corpus luteum of the ovary
Symptoms and treatment of endometrial hyperplasia
Ovarian dysfunction: symptoms, causes, diagnosis
Side effects
- Mental reactions: nervousness, depressed mood, irritability, weakened libido.
- Immune reactions: hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
- Metabolic reactions: changes in blood fat composition, increased appetite.
- Reactions from the nervous system: migraine pain, dizziness.
- Reactions from the senses: intolerance to contact lenses, conjunctivitis, visual disturbances, hearing loss, tinnitus.
- Reactions from the circulatory system: increased pressure, arterial hypotension, arterial hypertension, varicose veins, collapse, vein thrombosis.
- Reactions from the digestive system: flatulence, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea.
- Skin reactions: acne, chloasma, pigmentation disorders, hair loss, hyperhidrosis, dry skin, urticaria, erythema, eczema, itching, hypertrichosis, erythema nodosum.
- Reactions from the musculoskeletal system: feeling of heaviness, lumbodynia, muscle disorders.
- Reactions from the genitourinary system: dysmenorrhea, increased vaginal discharge, amenorrhea, lower abdominal pain, breast fibroadenoma, galactorrhea, vaginal candidiasis, menorrhagia, vulvovaginitis, premenstrual syndrome.
- General reactions: swelling, fatigue, weight gain.
The following side effects were also identified when using Belara:
- increased risk of biliary tract diseases;
- increased risk of arterial and venous thromboembolism;
- increased risk of benign tumors in the liver; in isolated cases, intra-abdominal bleeding may develop;
- exacerbation of chronic inflammatory bowel diseases.
Belara, like the vast majority of contraceptives, can cause headache, weakness, and spotting. In addition, the following symptoms are known:
- disorders of the organs of perception (hearing, vision);
- pain in the back, muscles; allergic skin reactions;
- swelling of the lower extremities;
- increased appetite, weight gain;
- hyperfunction of the sweat glands;
- bowel dysfunction, nausea;
- emotional depression, irritability.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytpolicyandsafetyru
In rare cases, signs of diseases caused by the prescription of tablets have been noted:
- varicose veins;
- neoplasms in the mammary glands and liver;
- candidiasis;
- diseases of the gallbladder and excretory tract;
- thromboembolism.
If the above symptoms occur, discontinuation of the drug, consultation with a doctor, and, if necessary, treatment are necessary.
Interaction
All drugs that stimulate intestinal motility clearly influence the decrease in contraceptive activity. Rifabutin, barbiturates, anticonvulsants, Modafinil, drugs based on St. John's wort reduce the concentration of ethinyl estradiol, as well as the antibiotics Tetracycline, Ampicillin and derivatives.
An increase in the level of ethinyl estradiol occurs as a result of simultaneous intake of Ascorbic acid, Paracetamol, blockers of the activity of microsomal liver enzymes, Atorvastatin.
The following substances may lower the concentration of ethinyl estradiol in the blood and reduce contraceptive activity:
- all medications that increase intestinal motility or inhibit absorption;
- substances that activate microsomal liver enzymes, such as Rifabutin, Rifampicin, barbiturates, Griseofulvin, anticonvulsants, Barbexaclone, Modafinil, protease inhibitors, Primidone, St. John's wort preparations;
- a number of antibiotics (for example, Tetracycline, Ampicillin).
When using such drugs simultaneously, it is necessary to use additional barrier methods of contraception during therapy and for a week after it. When taking substances that lower the concentration of ethinyl estradiol in the blood due to the activation of microsomal liver enzymes, additional barrier methods should be used within four weeks after the end of therapy.
The following substances may increase the concentration of ethinyl estradiol in the blood:
- substances that inhibit the sulfation of ethinyl estradiols in the intestine (Ascorbic acid, Paracetamol);
- substances that block the activity of microsomal liver enzymes (antifungal imidazoles, indinavir, troleandomycin);
- Atorvastatin.