Follicles are special round-shaped formations within which eggs mature. Their number is established in a girl during intrauterine development. If initially there are about half a million of them, then an adult woman has on average only 500 of them. Maturation of the follicle is a prerequisite for the formation of a full-fledged egg
. Without this process, a woman is unable to become pregnant.
It is quite complex and multi-stage. The process of maturation in the ovary begins in the first phase of the menstrual cycle. This is facilitated by the hormones lutein and progesterone. Their insufficient quantity can upset the balance of the functionality of the reproductive system.
Every month, several (up to 10) follicles develop in the female body. However, only one of them reaches the required size. He is considered dominant. The remaining bubbles begin to regress. If there is a failure in the hormonal system, then these small formations do not die off and prevent the dominant follicle from growing to the required size.
If you have a normal and regular menstrual cycle, you can determine the period of maturation yourself: according to your own feelings, by measuring basal temperature. In patients who have undergone ovarian stimulation, this process is monitored using an ultrasound procedure performed on different days.
The following symptoms indicate that the follicle has matured and the woman will soon begin ovulation:
- nagging pain localized in the lower abdomen;
- an increase in the amount of white mucous discharge from the vagina (some patients confuse it with thrush);
- a decrease in rectal temperature, which occurs 12-24 hours before the day of ovulation, and then an increase by 0.2-0.5 degrees;
- increased levels of progesterone in the blood (this can be determined using special tests);
- mood change: the woman becomes more sensitive and irritable.
During one menstrual cycle, one follicle usually matures in a woman’s body. However, in some cases there may be several of them. There is no pathology in this; the patient simply has an increased chance of fertilizing the egg or having a multiple pregnancy.
Why doesn't ripening happen?
The diagnosis of infertility has not been uncommon for a long time. Moreover, the main reason here is often that the follicles simply do not mature. In this case, you need to do a thorough examination, determine the cause of the pathology and begin treatment. A disruption in the maturation process can be caused by:
If the functionality of the reproductive system is impaired, a mature follicle does not appear at all, so it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor and undergo treatment.
The previously mentioned factors can disrupt the formation process of the presented formation or cause its regression. The follicle fails to grow to the desired size or does not rupture. Ovulation, and therefore pregnancy, does not occur. But even if the egg is ready for fertilization, and the endometrium (endometrium) does not have the required thickness, it simply will not settle in the uterus.
If the follicle matures too early or too late, then this can also be considered a deviation.
You also need to pay special attention when a woman’s ultrasound reveals numerous bubbles in the ovarian area. Here the patient is diagnosed with ovaries. On the monitor, the specialist can see a large number of bubbles. They are located along the periphery of the ovary. These bubbles interfere with the development of the dominant formation, since it cannot mature normally. If the endik is thin, then pregnancy may not occur, despite successful fertilization of the egg.
What does the absence of DF indicate?
Sometimes, when the doctor does an ultrasound, it is determined that there is no dominant follicle. This may be due to the following reasons:
- Cell development occurs very slowly. In such cases, ovulation does not occur, but hormone tests show normal levels.
- The cell develops to the required size, but it does not rupture and, accordingly, ovulation also does not occur.
- Stopping the DF at one of the phases.
- If there is no DF, then this may indicate a dormant mode of the appendages.
- Also, an ultrasound may not show the presence of DF if there is early menopause. Throughout life, a certain number of follicles are produced in the appendages, and the absence of viable cells on ultrasound suggests that they simply may no longer exist in the ovaries.
Important! For a woman planning a pregnancy, any deviation from the norm requires consultation with a specialist and possible treatment.
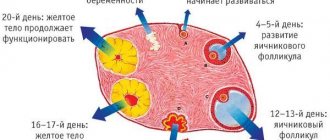
Follicle maturation by cycle day
Follicles in the ovary. Maturation of the dominant
The follicle matures gradually. On an ultrasound it can be seen like this:
- on the 7th day, small 5-6 mm bubbles are visible in the ovarian area, containing fluid;
- from day 8, intensive growth of education begins;
- on the 11th day, the size of the dominant follicle is 1-1.2 cm in diameter, while the rest begin to regress and decrease;
- from the 11th to the 14th day of the menstrual cycle, the size of the formation is already approaching 1.8 cm;
- on the 15th day, the follicle becomes very large (2 cm) and bursts - an egg ready for fertilization comes out of it, that is, ovulation occurs;
If the follicular formation is larger than 2.5 cm, then we can already talk about the presence of a cyst.
In this case, it is necessary to carry out treatment.
Many women worry whether their menstrual cycle will be disrupted after hysteroscopy. This procedure is performed to examine the inner surface of the uterus. Most often, it is necessary to make a diagnosis of endometriosis. It should be done on days 6-10 of the menstrual cycle, while follicle maturation is on the 7th day. That is, hysteroscopy does not have a significant negative effect on a woman’s reproductive function.
Stages of follicle maturation
The presented process begins in adolescence. As soon as a girl’s body matures and her reproductive system becomes ready to produce full-fledged eggs, she has the opportunity to become pregnant.
In its development, the follicle goes through several stages:
- Primordial. At this stage, the female reproductive cell is immature and is covered with follicular cells. Before puberty, there are a lot of noocytes in a girl’s body. Further, there are much fewer of them.
- Primary. Here the presented cells begin to quickly divide and form follicular epithelium. Next, a shell of connective tissue appears. The egg is located closer to it. At this stage, the granular cells of the follicle begin to produce a clear protein liquid. It is she who nourishes the growing egg.
- Secondary follicle. The epithelium of the formation differentiates and becomes thicker. The follicular cavity begins to form. The amount of the nutrient increases as the need for it increases. The membrane is formed separately near the egg. She subsequently takes over nutritional functions.
- Tertiary follicle. At this stage, the presented formation is fully mature and ready for ovulation. Its size is about 1.5 cm. Having reached its maximum size (2.1 cm), it ruptures, releasing a full-fledged egg.
After ovulation is completed, the follicle transforms into the corpus luteum. It is of great importance for the normal development of pregnancy in a woman in the early stages. If the maturation process is disrupted, a woman cannot become pregnant.
Sometimes it may be necessary to mature the follicles. In general, maturation is a complex biological process that can be disrupted by various internal or external factors. Therefore, a woman is obliged to take care of her health. If you still had to do stimulation, then you must strictly follow all the doctors’ recommendations.
The size and number of follicles play an important role in conception, as they are a reflection of a woman’s ability to give birth, become pregnant and carry a child. The article talks about what causes premature ovarian failure and what it means, what treatment is necessary and how to give birth to children if there are no follicles on ultrasound.
By the time of the first menstruation, more than 300 thousand follicles are found in the ovaries of girls. During life before the onset of menopause, each monthly cycle is accompanied by death after ovulation. If a woman detects, usually in the middle of the cycle, discharge from the genital tract like egg white or clear mucus, this means that the dominant follicle has burst and ovulation has occurred.
Of the total number, only 0.1% of follicles ovulate, the remaining 99.9% decrease. If the dominant follicle, which has stopped developing, begins to decrease without reaching mature size, then the cycle is called anovulatory, i.e. ovulation has not occurred and conception is impossible this month.
Estrogen, progesterone and male sex hormones in minimal quantities are responsible for the functioning of the ovaries. Hormonal disorders worsen reproductive function: the follicular apparatus is depleted, menstruation ends, and conception becomes impossible.
Typically, the dominant follicle develops in one ovary. If two follicles develop simultaneously in two ovaries, then the chances of conceiving twins increase by 2 times, but this requires that they reach their peak development and burst at the same time.
Developmental pathologies
Egg release in women is impossible in the absence of a dominant follicle. This happens due to hormonal imbalance and various diseases:
- it is not formed when follicle-stimulating hormone decreases or luteinizing hormone increases in the blood;
- regression or atresia occurs due to hormonal disorders, including an increase in insulin in the blood;
- observed on ultrasound if ovulation does not occur. It does not undergo regression, is of normal size or slightly enlarged (overripe). Sometimes women have dominant and persistent follicles in different ovaries;
- A follicular cyst is formed from a dominant follicle that continues to grow. Fluid accumulates inside, the size of the cyst on ultrasound is more than 25 mm, if there are many of them, then this condition is called polycystic;
- luteinization. In place of the dominant follicle without ovulation, the corpus luteum is formed.
Important!
If the follicle persists, its membrane may rupture and the egg will be released into the abdominal cavity. In this case, pregnancy cannot occur due to the inferiority of the egg.
All these pathologies require study and additional examination. It is necessary to check the hormonal level in a woman’s blood and find the reason for its change. These may be endocrine diseases, pathology of the pituitary gland, anomalies of ovarian development.
The number of follicles is normal
The menstrual cycle is accompanied by hormonal changes, so the number of follicles in the ovary depends on the specific day:
- on the 5th day of the cycle – up to 10 follicles ranging in size from 2 to 6 mm;
- from 7 to 9 days of the cycle - from 10 to 20 follicles, one of which (dominant) is up to 15 mm in size, the rest are half as large;
- from 11 to 14 days of the cycle - the dominant follicle can reach 25 mm.
Giving a child life becomes possible if there are more than 7-16 follicles. If there are 4-6 of them, then there is little chance. If there are less than 4 or none at all, then natural conception is almost impossible. In the latter case, it is recommended to do IVF, look for a surrogate mother or donor eggs if treatment with hormonal drugs does not produce results. If a woman has undergone IVF, pregnancy usually occurs successfully and is closely monitored by a doctor.
Not all females ovulate on days 14-16. Depending on the characteristics of the body and the number of days in the cycle, the growth of the dominant follicle can vary greatly from day to day. For example, if the cycle is 40 days, then ovulation is likely to occur on the 20th. Accordingly, on the 14th day of the cycle, the follicles in the ovaries will be smaller.
To track ovulation, the doctor prescribes folliculometry - counting the number and size of follicles.
DF sizes during ovulation
In medicine, there is no clear answer to what size the DF is during ovulation. Many gynecologists claim that its size is 18-24 mm. The dimensions of this cell largely depend on the individual characteristics of each woman’s body and on the regulation of folliculogenesis hormones.
At each stage of its development, the DF has different sizes:
- Primordial - diametrical size does not exceed 0.05 mm.
- Preantral - the cell dimensions are already 0-15-0.2 mm.
- Antral - the diametric size of the follicle reaches 0.5 mm.
- Dominant - the cell size at this stage can be 17-18 mm.
- Preovulatory – the DF value is 20-24 mm.
Reasons for the absence of follicles in the ovaries
After age 45, the disappearance of follicles is a natural process called menopause. Reproductive abilities for pregnancy gradually decrease until they disappear completely, hormonal function fades, then menstruation stops against the background of progressive depletion of follicular function.
The term “premature menopause (menopause)” is being replaced by “premature ovarian failure,” although the essence of the disease remains common.
The causes of premature ovarian failure (the complete absence of follicles or eggs that do not respond to hormonal stimuli) during reproductive age are as follows:
- genetics;
- autoimmune disorders;
- viral infections;
- toxins;
- starvation, unhealthy diet;
- excessive smoking;
- alcohol consumption;
- chemotherapy;
- radiotherapy;
- on the pelvic organs;
- incorrectly administered hormonal therapy.
Due to the close connection of female sex hormones with the nervous system, the absence of follicles on ultrasound can be a temporary phenomenon caused by stressful situations, depression, and excessive stress. Usually the next cycle is restored and continues to operate as usual. In other cases, treatment with hormonal drugs is a prerequisite for maintaining health and the ability to conceive a child.
Treatment is necessary for those women whose failure is caused by endocrine diseases, severe changes in weight, or unsuccessful use of contraceptive drugs.
What to do if there are no follicles
First, you need to make sure that the doctor who made the diagnosis is competent. It is advisable to contact another specialist and do a repeat ultrasound on a different device in the next cycle.
Before you panic, you should start treating the disease from specialists and at the same time take advantage of the opportunities to solve the problem:
- Normalize your lifestyle: quit smoking, give up alcohol, exercise in a reasonable amount, maintain a routine.
- Adjust your diet: give up salty, fatty, spicy foods. Reduce consumption of citrus fruits, pineapples, pears, cabbage, rice. Legumes, vegetables, pomegranates and apples have a positive effect on ovulation.
- Use traditional methods: sage, plantain, aloe stimulate ovulation.
- Inhale the vapors of essential oils: sage, basil, cypress, anise.
- Consult a specialist about vitamin therapy. Folic acid and vitamin E effectively combat insufficient ovarian activity.
- Treat viral infections, including STIs.
- Eliminate psycho-emotional stress, stress, and, if necessary, use medications that calm the nervous system (valerian, glycine, etc.)
It happens that the above methods are sufficient to normalize the functioning of the ovaries and improve well-being, but the main way to solve the problem is to see a doctor and undergo hormonal therapy under strict control.
Depending on the cause of the dysfunction, eliminating it will help normalize the functioning of the female organs. For example, if the disappearance of follicles occurred due to a sudden weight gain, then its normalization is sufficient for recovery.
Before using additional methods to solve the problem, consultation with a specialist is required.
Treatment in the absence of a dominant follicle
A non-growing dominant follicle is observed in patients with inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system. Constant stress, depression, abortions - all this can also cause improper development or the absence of a “dominant” at all. The doctor prescribes medications to restore normal ovarian function only after a comprehensive diagnosis. Often the problem is solved with the help of hormonal therapy.
Clostilbegit is a drug often prescribed by gynecologists to women who are planning to have a baby. The product is very popular in Russia, but it should be taken strictly as directed by your doctor. Clostilbegit has many contraindications and is not suitable for all girls. However, any hormonal drug taken uncontrollably can harm the female body rather than strengthen it.
To improve the functioning of the reproductive system, they also take folic acid and multivitamins. The drugs are selected individually, as is their dosage. The doctor takes into account the patient’s age and general health.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a number of studies:
- Examination by a gynecologist. It is important to describe in detail your health, symptoms, first signs, past illnesses, surgeries, etc.
- Data about the menstrual cycle. It is necessary to indicate the duration of the cycle, regularity, features of discharge, etc.
- Blood test for the hormones FSH, TSH, LH, AMH, estradiol, prolactin.
- Smear for flora and STDs.
- Ultrasound of the pelvis with detailed characteristics of the condition.
- Mammography.
- Analysis for oncocytology, tumor markers.
Symptoms and methods for diagnosing atresia
If a woman does not have any gynecological diseases or pathologies, sexual intercourse is carried out regularly, but conception does not occur, it is quite possible that the cause is atresia.
You can also suspect the presence of pathology based on disruptions in the menstrual cycle. Menstrual flow may be absent for a long time (amenorrhea - no menstruation for several cycles), and then will be replaced by bleeding. Such bleeding occurs 1 to 3 times a year. Their duration varies from two days to three weeks, which depends on the individuality of the organism. The blood itself is released in small volumes, but may contain clots. A woman’s general health may deteriorate, irritability and insomnia may appear. A nagging pain is often felt in the lower abdomen.
Important: The pathology is provoked by serious hormonal disorders and can provoke the development of polycystic ovary syndrome and cause infertility.
These are the main symptoms by which a woman can suspect a problem and consult a specialist. As a rule, this symptomatology is a reason for additional diagnostics, consisting of the following procedures:
- Compulsory ultrasound examination. The procedure makes it possible to detect the absence of ovulation, the presence of the corpus luteum, and also determine the free fluid behind the uterus.
- Using the histological method, a scraping of the endometrium is examined. This allows us to determine the presence of proliferation (cell growth), as well as diffuse or focal hyperplasia.
- The pupil symptom at the external opening of the cervical canal is functionally diagnosed. If its dimensions reach 3 mm, a specialist may prescribe an additional examination in the form of a colpocytogram - a smear to determine the numerical ratio of cells from different layers of the vaginal epithelium.
- One of the mandatory diagnostic methods is blood testing for hormones.
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, treatment must begin immediately. This is especially important for women planning a future pregnancy. After all, the most common complication that occurs with this pathology is infertility.
Important: A woman can independently determine the onset of ovulation by measuring basal temperature and drawing up a schedule. Lack of ovulation may indicate atresia.
Treatment
Therapy is selected based on the cause of the dysfunction. The most commonly used treatment methods are:
- HRT (artificial normalization of sex hormones using drugs).
- Physiotherapy (ultrasound, electrophoresis, etc.)
Before prescribing HRT, the specialist is obliged to inform the patient about side effects, contraindications, and positive changes. It is appropriate to prescribe HRT only after hormonal tests have been carried out, otherwise the doctor’s competence should cause mistrust.
If there are contraindications, the patient is prescribed homeopathic remedies and phytoestrogens.
Traditional treatment methods
Traditional medicine can only be used after consultation with a doctor, otherwise the body’s condition may deteriorate irreversibly due to serious complications.
Having received permission from your attending physician, you can use the following useful traditional medicine recipes:
- Cabbage juice. Drink 0.5 cups per day on an empty stomach.
- Beet juice. Dilute with cold water, take 1 tbsp. l. 1 ruble/day.
- Decoction of boron uterus. Add 1 tbsp to 300 ml of water. l. herbs, cook for 10 minutes. Infuse and take 1 tbsp. l. up to 5 rubles/day for 3 weeks, then take a break for a week.
- A decoction of lungwort, licorice root, calamus, horsetail or aralia (any mixture of your choice). Add 2 tbsp to 2.5 cups of boiling water. l. plants, drink 100 ml. 3 rubles/day before meals.
Properly selected hormonal therapy, together with other methods, gives positive results: hormonal levels are normalized, and the patient develops follicles. There is a chance to get pregnant naturally, without resorting to artificial insemination, donors and surrogates.
Normalization of lifestyle, stable psycho-emotional state and good mood have a powerful effect in the fight against the disease. Having achieved the appearance of at least 4 follicles in the ovary with the help of treatment, a woman has a chance to become a happy mother of a child born naturally.
Every year, doctors record more and more cases of women’s inability to have children. The development of medicine and technology, unfortunately, does not yet make it possible to completely cure all disorders of the human genitourinary system. More and more couples are faced with the need for artificial insemination or surrogacy, and more and more often doctors are talking about the importance and necessity of family planning.
In this article we will talk about ovulation and the dominant follicle: what does a “dominant follicle” mean, are there two dominant follicles (in both ovaries), what is indicated by the size or absence of a dominant follicle.
Ovulation and dominant follicle
The follicle is the container for the egg. In the middle of the developmental phase, the dominant follicle is quite noticeable - it is the largest and most well developed of all. Every month, the egg matures and prepares for fertilization - the follicle enlarges 15-20 times, fills with liquid and bursts (approximately on the 14th day of the menstrual cycle). In this case, only one of the many (10-15) follicles fully matures and bursts - the rest stop developing at different stages and die. This is what is called ovulation. When dominant follicles develop in both ovaries, the likelihood of conceiving twins increases many times over. Very often, as a result of hormonal stimulation, several dominant follicles grow, which ovulate and are fertilized simultaneously. This explains the large number of twins and triplets born as a result of artificial insemination or after stimulation of ovulation.
Ultrasound to determine the dominant follicle and monitor it allows doctors to assess the health status of women (their ability to conceive a child) and predict the likelihood of pregnancy, indicating the days of maximum likelihood of conception.
How to grow a dominant follicle?
The most common modern method of stimulating ovulation is hormonal therapy, in particular the administration of clostilbegit. But, despite its widespread popularity, its use is not always justified. Moreover, some women should absolutely not use it. That is why it is so important to be confident in the qualifications of the attending physician and that he has sufficient arguments for prescribing potent drugs. After all, it is known that the higher the effectiveness of the drug, the higher the likelihood of unwanted side effects and the more varied and serious they are.
Remember that the selection of means for stimulating ovulation and the dosage of the selected drugs are purely individual; in no case should hormone stimulation be used without the supervision of a doctor.
Many women report positive dynamics after prescribing a course of vitamin therapy and taking folic acid.
Why is there no dominant follicle?
There may be several reasons why the dominant follicle does not mature and there is no ovulation:
The main condition for the successful restoration of ovulation is an adequate determination of the cause of its disturbance. If this cause has not been identified and eliminated, even repeated stimulation does not always bring results.
Diagnosis of the causes of ovulation disorders cannot be based only on an analysis of basal temperature charts (even if charts of several cycles are available). Diagnostics should be comprehensive - medical examination, hormonal analysis, ultrasound diagnosis of follicle development over a number of cycles (and not as a result of a one-time visit to the doctor).
The follicles in a woman’s ovaries allow her to become pregnant, but only if they are of normal maturity and of good quality. Deviations from the norm can lead to the development of cysts and sometimes infertility. There are several reasons why this happens, so you need to seek medical help immediately if the slightest discomfort occurs, as women’s health can be greatly affected. The size of the follicles, as well as their number, play an important role.
What does DF in the left or right ovary indicate?
The physiology of the female body dictates that both appendages should ovulate alternately, but based on medical research data, DF most often forms in the right ovary.
Most likely this is due to different physiological loads: the right side of the human body always takes a much more active part in vital processes, which contributes to a more intense blood supply to this particular appendage.
Dominant follicles can develop in both ovaries simultaneously or with a slight delay, which is not considered a deviation. As a result of this, two or more developed oocytes are formed, since the likelihood of a multiple pregnancy is very high.
The development of two dominant vesicles can provoke superfecucation - fertilization of eggs by sperm from different partners, provided that all oocytes burst at the same time. Why this happens, no one can say for sure.
Read on to find out what the size of your DF is during ovulation.
Follicle and its function
The main job of the follicles of the left and right ovaries is to protect the eggs from the harmful effects of various factors.
The eggs that are inside the follicles have not yet matured, so their protection, the normal course of maturation and fertilization, and the course of pregnancy largely depend on the abilities of the follicles.
In females, the development of the reproductive system occurs already in the perinatal period - the number of egg follicles is formed and changes in this number never occur.
One follicle matures in a month. In addition to their protective function, they produce female hormones called estrogens.
The normal number of follicles maturing in the ovaries
Their number is calculated taking into account the day of the menstrual cycle.
For example, multiple, 2-3 days after menstruation, are not a pathology. Then they develop differently.
In the middle of the cycle, one or two of them are larger than the rest. By the end of the cycle, there is one big one left. It is from this that the egg comes out, mature and ready for fertilization. This follicle is called dominant, prevailing.
The onset of menstrual flow indicates that a rupture has occurred.
When a norm is violated: causes and consequences
A violation is said to occur when there are more than 10 follicles in one ovary. Pathology can only be detected through ultrasound of the pelvic organs. Moreover, their number does not change during the cycle. When there are a lot of them, this does not at all indicate any disease. This phenomenon can be explained by overwork, frequent stress, and emotional stress. Their number usually returns to normal after the first ovulation.
Underdevelopment can be caused by other reasons:
- Incorrectly selected oral contraceptives;
- Thyroid dysfunction;
- Excessive production of prolactin;
- Problems in the functioning of the endocrine system.
This disorder and its cause can be identified through a number of diagnostic procedures and gynecological examination.
In any case, there are two options for the development of the disorder: the first is a normal menstrual cycle with one dominant follicle; the second – there is no dominant, the egg does not mature, the cycle is disrupted, there is no possibility of fertilization.
In the latter case, an accumulation of male sex hormone occurs in the woman’s body, which entails the absence of pregnancy.
The role of dominant follicles
As a rule, they develop differently in the two ovaries. When both are diagnosed as dominant, there is a chance of conceiving twins. But this will only happen if they both ovulated, which is quite rare.
Two dominant follicles matured in one ovary increase the chances of a multiple pregnancy.
Persistence of the follicle of the left or right ovary
Confirmation of such a diagnosis is very bad news. This means that the dominant follicle develops as it wants until the moment of rupture. As a result, it does not allow the egg to be released and over time it can transform into a cyst.
Persistence prevents ovulation. Pathology can be triggered by hormonal imbalance, excessive amounts of male sex hormone. Delayed treatment leads to infertility.
Treatment consists of taking hormonal drugs. In addition, it is necessary to have a comprehensive effect on the body. First you need to suppress male hormones. Therapy lasts from 5 to 9 days of the cycle. Then the hormones are administered intramuscularly from day 9 of the cycle. Therapy lasts 5-7 days. In addition, stimulation of the pelvic organs is carried out. For this purpose, laser therapy, massage, and ultrasound are used.
Absence of follicles in both ovaries
This condition is caused by dysfunction of these organs or early menopause. The disorder is eliminated through hormonal therapy.
What is it if antral follicles are found in the ovaries?
With the development of artificial insemination technologies, scientists began to pay attention to the qualitative and quantitative composition of eggs. These parameters allow you to assess how high a particular woman’s chance of becoming pregnant is. Antral follicle counting was developed for this purpose.
What are antral follicles?
These are follicles whose size does not exceed 8 mm. They are counted using transvaginal ultrasound. The results of their calculation make it possible to establish the ovarian reserve - the number of eggs ready for immediate fertilization.
If there are less than 4 antrals, then ovarian stimulation will be low, the probability of pregnancy is the same, so IVF is recommended. If there are about 7 of them, you can try to conceive a baby on your own.
When their number ranges from 18 to 26, then the possibility of successful conception is the highest.
If there are more than 26 of them, then there is a possibility of developing polycystic ovary syndrome.
What does it mean if many follicles are detected in the ovary?
This pathology can be triggered by taking hormonal contraceptives, increased prolactin, stress, sudden weight loss, obesity, and endocrine disorders. This means that pregnancy due to the disease is unlikely, as it is accompanied by many sexual dysfunctions.
This pathology is called polycystic disease, but it has nothing to do with the growth of cysts. It is mandatory for a woman to undergo a comprehensive diagnosis. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, treatment begins.
Therapy is aimed at achieving the following results:
- decreased levels of male hormones;
- normalization of the cycle if it is disrupted;
- pregnancy (if necessary);
- prevention of metabolism.
Therapy may include a low-calorie diet, hormonal drugs, metaphormin, antiandrogens, and ovulation-stimulating agents.
INTERESTING!
A dominant occurs most often, but with artificially stimulated ovulation it grows on both. And in this case, the chance of conceiving twins increases.
When there is no dominant follicle: why and what to do
If there is no dominant follicle, then there will be no conception.
If conception does not occur for more than a year of regular attempts, it is time to talk about infertility. Infertility is the absence, over several cycles, of a leading follicle within which the egg should mature.
Why is the “dominant” not developing, how should the female body work correctly, and how to get rid of this problem? There are many questions. But first things first.
The photo shows the dominant follicle. It happens that it simply does not exist, and it is not produced from cycle to cycle.
Stages of follicle development
A girl who is still in the womb has a certain number of eggs. They are inactive until menstruation begins. The follicles then begin to grow and die each month. Their development occurs in stages.
Stages of follicle maturation:
- First phase (beginning of the cycle). At this point, several equally sized follicles develop.
- The second phase is the emergence of a “leader”. This happens around day 8-10 of the cycle. One of the structural components of the ovary becomes larger than the others. He is the leader. The remaining follicles become smaller and begin to die.
- The onset of ovulation (12-14 days). The “dominant” becomes the maximum size. A rupture occurs and a mature egg emerges. Instead of the leading follicle, a corpus luteum is formed, which supplies the female body with the hormone progesterone, which is important for maintaining pregnancy.
The appearance of a leading follicle is possible on any or even both ovaries at the same time. However, it usually ripens on the right.
The appearance of a “dominant” on both ovaries is a common occurrence when ovulation is additionally stimulated, as well as during IVF or artificial insemination.
By the way, if a dominant follicle has formed in both ovaries, the girl has a chance to get pregnant and give birth to twins or even triplets. But if a woman does not develop a “dominant”, then ovulation and conception do not occur.
The problem with the appearance of a dominant follicle can be identified using ultrasound diagnostics.
What examination is prescribed?
The absence of a “dominant” is not always a sign of illness. Any healthy representative of the fairer sex experiences periods when the follicle does not form. Anovulatory cycles 3-4 times annually are considered the norm. The ovaries seem to “go on vacation.”
In women after 30 years of age, such periods become more frequent every year. With early menopause, which occurs before the age of 45, the eggs “fall asleep” more often. Although most women of this age do not plan to conceive, experts recommend not ignoring changes in the body. Gynecologists often suggest that patients get rid of the problem with the help of hormonal therapy.
If a woman of childbearing age has these abnormalities, this indicates pathology. In this case, treatment is mandatory. The attending physician will be able to tell about the reasons for the non-developing dominant follicle only after conducting research.
The examination consists of:
- examination by a gynecologist;
- hormonal blood tests. It will help you find out the level of hormones necessary for the proper functioning of the female body at different stages of the cycle;
- Ultrasound diagnostics. The procedure for tracking the functioning of follicles is called folliculometry. The diagnostician monitors the functioning of the ovaries throughout the menstrual cycle. The procedure is repeated for a number of cycles.
It is important for a gynecologist to know the length of the cycle. If it is too long or, conversely, too short, this may indicate a malfunction of the ovaries. The absence of a “dominant” is often associated with changes in the level of hormones in a woman’s body. For proper development of follicles, certain levels of several hormones are required.
Namely:
- Luteotropic.
- Follicle-stimulating.
- Estrogen.
- Progesterone.
All of them are important at certain stages of egg maturation. When these hormones are not enough in the body, or they are distributed incorrectly, the “dominant” does not develop.
To identify the reasons for the absence of a dominant follicle, it is necessary to donate blood to determine the amount of hormones.
Behavior of the follicle during disturbances in the body
There are several reasons for the absence or improper development of the “dominant”. However, there is only one outcome - ovulation does not occur. A pathological change in the body can cause the follicle to behave “wrongly”. Read more about what can happen if his behavior is abnormal.
The appearance of a persistent follicle
A lack of luteinizing hormone or progesterone can lead to the development of a persistent follicle rather than a dominant one. Its growth is observed.
However, having reached its maximum size, the “dominant” does not break at the right moment. The egg remains inside the follicle.
One of the signs of persistence - “dominant” is visible on diagnosis throughout the entire period of menstruation, and sometimes even after it.
Other characteristic features of persistence:
- no corpus luteum;
- increased levels of estrogen in the body;
- Progesterone levels, on the contrary, are reduced;
- absence of fluid behind the uterine cavity.
There is also another option for the behavior of follicles - the absence of their growth at all. This period for the ovaries is called “sleeping”.
Follicular growth regression
Another type of deviation from the norm is slow maturation and stopping of follicle growth at a certain point in development. Then they begin to “deteriorate”. Another type of abnormal behavior is when the dominant follicle develops, but does not grow to the required size for ovulation. In this case, a hormonal blood test will not show any deviations from the norm.
Follicular cyst formation
The picture shows a follicular cyst of the left ovary.
A follicular cyst occurs if the “dominant” continues to grow, does not release an egg, and accordingly, ovulation does not occur. The cause of the appearance of a benign formation is most often a change in the amount of hormones in the female body.
But there are other factors that influence the appearance of a cyst.
Here are some of them:
- Presence of chronic diseases;
- Lack of regular sex life;
- Frequent abortions or miscarriages;
- Mental disorders in women.
Surgery performed on the organs of the genitourinary system could also influence the appearance of pathological changes. The presence of a follicular cyst affects the regularity and duration of the menstrual cycle.
A cyst can form on the corpus luteum. This happens if, after the rupture of the follicle, too much fluid has formed (it is always formed, but not in large quantities) or it contains blood.
If you detect a follicular cyst, do not worry - no special treatment is required. The formation disappears on its own after several cycles, and if pregnancy occurs, after the first trimester.
Treatment in the absence of a dominant follicle
A non-growing dominant follicle is observed in patients with inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system.
Constant stress, depression, abortions - all this can also cause improper development or the absence of a “dominant” at all.
The doctor prescribes medications to restore normal ovarian function only after a comprehensive diagnosis. Often the problem is solved with the help of hormonal therapy.
Clostilbegit is a drug often prescribed by gynecologists to women who are planning to have a baby. The product is very popular in Russia, but it should be taken strictly as directed by your doctor.
Clostilbegit has many contraindications and is not suitable for all girls. However, any hormonal drug taken uncontrollably can harm the female body rather than strengthen it.
Under no circumstances should you take any hormonal medications without a prescription!
To improve the functioning of the reproductive system, they also take folic acid and multivitamins. The drugs are selected individually, as is their dosage. The doctor takes into account the patient’s age and general health.
Questions for a specialist
Practicing obstetrician-gynecologist Natalya Yuryevna answers the questions.
- I took a course of Cyclodinone to regulate my too short menstrual cycle. It has become longer, but now after menstruation I feel very unwell. Diagnostics did not show the growth of a dominant follicle. What should be done? Answer : An in-depth examination is necessary, including hormonal blood tests on certain days of the cycle. Consultation with an endocrinologist is also necessary.
- After four years of taking Regulon, I cannot get pregnant, although I stopped taking the drug more than 6 months ago. The dominant follicle does not develop, the cycle is too long. What should I do? Answer : You need to contact a gynecologist-endocrinologist and get tested for hormones. After the examination, the doctor will prescribe treatment to restore ovarian function.
- Is pregnancy possible if the follicle grows and decreases in size closer to ovulation? Answer : This is a sign of ovarian dysfunction. You and your partner need to be tested. For you - the amount of hormones in the blood (prolactin, insulin, reproductive and thyroid glands), for your partner - a spermogram. Based on the results, the doctor will prescribe treatment.
- Can taking Utrozhestan during the period from 16 to 25 days of the cycle cause the formation of a follicular cyst? A similar problem has arisen before, and without treatment the formation did not disappear. Answer : While taking the drug in phase 2 of the cycle, an ovarian cyst should not form. If cysts are present, any ovarian stimulation is prohibited. Contact your doctor to prescribe treatment. Monitoring for pathological changes is necessary.
Prescribing potent drugs in the absence of a dominant follicle is not always justified. It should be remembered that the more effective the product, the higher the risk of side effects.
Therefore, first of all, a woman with such a problem needs to find a qualified doctor who can justify the prescription of certain medications. The key to success will be an adequate determination of the cause of ovulation disorders.
Most patients noted positive dynamics after taking vitamins and folic acid.
Brief summary
Source: https://ekobesplodie.ru/besplodie/kogda-dominantnogo-follikula-net-pochemu-i-chto-delat
Why is it missing?
When the dominant does not appear, a woman becomes pregnant. The causes of this pathology are as follows:
- ovarian cyst;
- "sleeping" ovaries;
- disturbances in the development of the dominant.
Persistence
When there is not enough progesterone and luteotropin in the body
, the follicle, having assumed the desired size, cannot rupture and release the egg.
In this case, it is called persistent, and the pathology is called persistence. Her signs are:
- there is no fluid behind the uterine cavity;
- the amount of estrogen is very high;
- and the amount of progesterone is too low;
- the corpus luteum does not develop.
ATTENTION!
With persistence, the dominant remains on the ovary throughout the entire menstrual cycle, and sometimes it can be fixed even after the end of the cycle. Thus, the body seems to be ready for ovulation, but it does not occur.
Cyst
When the follicle fails to rupture and release an egg, but instead continues to grow, it turns into an ovarian cyst.
. This cyst is a benign formation that occurs due to hormonal imbalance.
The risk of its occurrence is increased by factors such as:
- chronic diseases of the pelvic organs;
- frequent abortions;
- genitourinary operations;
- wrong diet.
Such a disorder affects a woman’s menstrual cycle, affecting its duration and regularity. Thus, the cyst interferes with the creation of a new dominant follicle
. However, it rarely needs treatment, and usually goes away on its own within two, sometimes three, cycles.
"Sleeping" ovaries
In this case, we are talking about ovarian dysfunction, in which there are simply no follicles, none at all. They don't grow at all. And ovulation never occurs.
Does not ripen for other reasons
Developmental disorders are a pathology in which the follicles stop at some stage of development and suddenly begin to regress
. In this case, a dominant can be formed, but it will not reach the required size by the time of the ovulation phase.
IMPORTANT!
In case of developmental disorders, hormonal analysis does not show any pathologies, completely corresponding to the norm.
How does follicular atresia affect conception?
A follicle is a structural component of the ovary. It consists of an egg that is surrounded by several organic layers - 1 layer of epithelial cells and 2 layers of connective tissue. A certain number of such components (about 300 thousand) are introduced into a woman’s body during the period of her embryonic development. This number is distributed over the entire subsequent reproductive age of the woman and the monthly menstrual cycle. But this distribution does not mean that all 300 thousand are able to mature and release an egg for further fertilization. Only 400–450 components of the ovary are capable of this.
Every month in a female body of reproductive age, 16–30 follicles begin to develop (this is considered the norm). Every day their numbers are decreasing. By the time of ovulation, only one dominant and mature follicle remains, which is ready to release an egg for further fertilization. What happens to the remaining follicles? Having stopped at a certain stage of their development, these follicles undergo regressive natural changes - atresia (empty). This is a natural physiological process, but there is also a pathological type of atresia.
Important: Sometimes both ovaries contain dominant follicles ready to release a mature egg. If successful fertilization of both occurs at the time of ovulation, the couple should expect twins.
The pathological process of follicle maturation occurs due to a decrease in the secretion of the pituitary gland - follicle-stimulating hormone. And it is characterized by an insufficient amount of special hormones estrogen and progesterone - they stimulate the maturation process and also regulate the process of ovulation. As a result, the follicle does not develop completely, but begins to succumb to regressive changes, the moment of ovulation is absent and subsequently the entire menstrual cycle is disrupted.
What to do?
If you suspect that the dominant is absent, you need to consult a doctor
and undergo a series of examinations. After this, the cause of the pathology will be determined and the necessary treatment will be prescribed. Self-medication should not be done so as not to aggravate the condition.
At the hospital, the doctor will examine you
on the gynecological chair. And since the most common reason for the absence of a dominant is hormonal imbalance, he will prescribe a blood test for hormones.
Moreover, at different stages of the cycle, because for the formation of a dominant in each phase a different amount of hormones is needed
. And the doctor needs to know at what stage and which hormones are not enough.
Also prescribed
folliculometry - a procedure that includes ultrasound diagnostics throughout the entire cycle. This allows you to track the work of the ovaries in each phase.
In addition, the doctor will pay attention to the duration of the cycle, because if it is longer or shorter than normal, this is a sign of ovulation disorders.
ATTENTION!
A cycle when the dominant is not formed occurs several times a year in absolutely healthy women. This is normal and means that the body is, as it were, resting.
Prevention methods
Preventive measures are aimed at supporting the process of creating follicles and preventing disturbances in the functioning of the ovaries.
These include:
- quitting smoking, alcohol, drugs;
- a full sex life with regular sexual intercourse;
- active lifestyle, nutritious diet;
- if possible, avoid stress and excessive physical activity;
- taking measures to protect against STDs;
- exclusion of abortion;
- control of hormone levels in the blood.
And it is mandatory to undergo regular preventive examinations at the antenatal clinic.
What treatment is prescribed?
Since the most common reason for the absence of a dominant follicle is hormonal imbalance, treatment is prescribed with hormonal drugs
. The schedule for their intake is drawn up by the doctor, depending on how saturated the woman’s body is with estrogen.
A week before menstruation, progesterone may be prescribed in the form of a 1% solution by injection. To stimulate the ovaries to grow and develop follicles, doctors recommend estrogen medications such as Estradiol or Hexestrol. However, you cannot start hormonal treatment on your own.
– this will further increase hormonal imbalance.
In addition, if necessary, the doctor can prescribe treatment for inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary area.
In conclusion, we can add that a healthy lifestyle is the best prevention of ovulation problems
. And if the absence of a dominant follicle has already been diagnosed, do not despair: modern medicine can help in recovery.
Bottom line
So, let's summarize all of the above:
- DF is a cell whose growth and development occurs much faster than its fellows. The development of the egg occurs in it until ovulation, during which the outer membrane ruptures and a cell ready for fertilization emerges.
- Successful formation of DF guarantees stable growth of the egg, its release, ovulation and subsequent fertilization.
- DF develops predominantly in the right ovary, although according to physiology it can also mature in the left appendage. The simultaneous ovulation of two main cells in different ovaries is not considered a deviation.
The absence of a dominant follicle may indicate a malfunction of the appendages or problems in the reproductive system. Therefore, in case of any deviations from the norm, it is not advisable to delay a visit to the doctor.