The second trimester of pregnancy lasts from 14 to 26 weeks. According to the majority of expectant mothers, this is the most comfortable and pleasant period of all nine months of waiting. The woman finally fully realizes her condition, subconsciously becomes a mother: psychologically balanced, intuitive, wise and sentimental.
Such a psychological picture always accompanies physical changes in the female body. And there is no dilemma about what is more important: psychology or physiology; in any pregnant case, they equally present to the environment the unusual state of the expectant mother.
During this period, a pregnant woman pays special attention to changes in her stomach and who is in the stomach. It is these twelve weeks that can become almost a revelation for first-time mothers - after all, the intensive growth and development of the baby greatly affects the mother’s body. And for those who are experiencing this for the first time, they study and analyze new things in their condition with genuine interest and caution, and with special trepidation, mothers for the first time monitor the changes in their belly. Until week 26, it will become rounded, rise and protrude forward.
When does the belly begin to grow during pregnancy? At what month does the belly become visible?
As soon as a woman finds out that she is pregnant, she cannot wait to share her joy with the whole world. The expectant mother is waiting for external signs of her new condition to appear. The main one is a growing belly.
During the first pregnancy
If this is your first pregnancy, this can only be determined visually at 16-18 weeks. When a woman is plump, pregnancy will not be visible for some time.
External changes depend on:
- width of the pelvic organs;
- the place of attachment of the embryo to the walls of the uterus;
- the pace of its development;
- volumes of fetal fluid.
If we talk about average numbers, active growth of the abdomen is observed from the middle of the second trimester.
During the second and subsequent pregnancies
With subsequent pregnancies, the dates shift. Especially if the first baby was born with an interval of 1.5-2 years. Based on the mother's figure, a new pregnancy can be seen already at 12-13 weeks. If the mother was engaged in physical education, did exercises to strengthen the abdominal muscles, the tummy will become visible at 14-15 weeks.
For fat girls
When a woman is overweight, the growing belly will not be noticeable for a long time. But this does not mean that it is growing slower. Both the fetus and the uterus increase in size, and the volume of amniotic fluid increases.
Since obese women already have round shapes, pregnancy can sometimes be hidden until the birth itself.
For skinny girls
In women who naturally have narrow hips and low weight, the uterus quickly extends beyond the boundaries of the small pelvis. If, in addition to this, the abdominal muscles are poorly developed, the belly will appear even faster - by 14-15 weeks.
Pregnancy with twins
If an expectant mother is expecting two babies at once, she will notice external changes by the 10th week. Her belly looks 15-16 weeks at the end of the third month. By week 20, it makes walking difficult and prevents bending.
Fundal height of the uterus by week
Throughout pregnancy, gynecologists measure standing height and uterine size week by week. This helps them not only determine the duration of pregnancy, but also make a conclusion about its course - whether there are developmental abnormalities in the fetus or whether the development is normal. Therefore, you should not be surprised that your leading doctor pays special attention to this organ during each examination. Remember, he is not worried about himself, but about you and your baby. Are you wondering how your pregnancy is going, but you can’t decipher the numbers? In today’s article we will tell you in detail what the height of the uterine fundus depends on by week, and also introduce you to the table in which the norms are set.
Factors that affect abdominal growth during pregnancy
Every expectant mother is unique. And everyone’s belly grows differently. Let's look at the general factors that influence this process.
Heredity
The biological nature of fetal development depends on a set of genes. You can guess at what rate the baby will grow and develop if you find out how this happened with close relatives of both parents - mothers, grandmothers.
Physiological features
The size and shape of the tummy is influenced by a woman’s body type - her weight, height, and the structure of the pelvic organs. It is generally accepted that a slender girl will develop a belly faster than a girl who is prone to obesity. In reality this is not the case - in the first case it is simply more noticeable.
Fetal growth rate
The speed at which the baby gains weight is directly dependent on the physique of the parents - mainly the expectant mother. If, due to genetics, a child should be born large, the belly will accordingly increase in size faster.
Type of presentation
How noticeable the belly will be depends on where exactly the fertilized egg is attached. If the baby is located in the anterior wall of the uterus, the belly will appear larger. If it is near the spine, in the first months it may not be noticeable at all that the woman is pregnant.
Number of births
During the first pregnancy, the abdominal muscles are not accustomed to such loads and stretch slowly. With subsequent ones, these processes occur faster and are not accompanied by discomfort.
Weight gain
Many women believe that during pregnancy, especially in the 3rd trimester, it is necessary to eat for two, otherwise the baby will not receive enough nutrients necessary for normal development. As a result, they get better, and not only in the stomach.
What should be the height of the uterine fundus by week?
The height of the uterine fundus should increase over the weeks of pregnancy. This is very important, since in this way the doctor, without performing an ultrasound, can say with a high degree of probability whether the fetus is developing, whether the pregnancy has frozen, whether the child is lagging behind in development, whether the amount of amniotic fluid is normal, etc.
The height of the uterine fundus by week of pregnancy is reflected in the graph, which is printed in the dispensary card of each expectant mother. This chart is created by a doctor or nurse who fills out the chart.
Many women have a rough understanding of the issue of fundal height by week of pregnancy: we also have a table of average values on our website. You should know that the average values approximately coincide with the duration of pregnancy. For example, at 30 weeks the height of the uterus will also be 30. Errors of 2-3 cm are allowed in one direction or the other. But because of them, especially if the abdominal circumference also does not increase enough over the weeks, many doctors prefer to play it safe and admit women to the hospital for treatment in order to improve blood flow in the placenta and umbilical cord. Although in reality these measures are ineffective.
Table of uterine fundus height (UFH) and abdominal circumference by week of pregnancy (WG)
:
Why is it necessary to measure abdominal circumference in pregnant women?
Based on the speed at which the belly grows, the doctor at the antenatal clinic draws conclusions about the development of the fetus and the condition of the uterus. Normally, the belly grows unevenly and if this process slows down, there is no need to worry. On the contrary, if it quickly increases in size, there is a possibility of a large newborn being born. To exclude possible pathologies, the specialist prescribes an additional examination for the woman:
- blood test for amniotic fluid;
- Ultrasound.
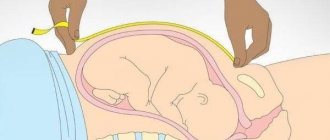
Abdominal circumference is measured at each week of pregnancy. This will require a centimeter.
Algorithm of actions:
- stand up and straighten up;
- place the centimeter at the level of the umbilical zone;
- wrap the belly and determine the result.
Important! Measurements are taken every day at the same time of day. If the deviations are insignificant, the reasons for this are fetal fluid. Their number may vary during the day. But if the fluctuations are significant, especially at 38-39 weeks, this is a reason to consult a doctor.
What to do when your belly size is not normal
If during routine examinations the abdominal circumference increases evenly, but at the next visit the measurement data remains unchanged, this is a reason to immediately contact a gynecologist. If necessary, the doctor will direct you to undergo additional examinations and tests.
Each person's body is individual, exceptions to the rules are always possible. Do not panic immediately if the indicators differ from the average statistical norms. Any measurement may be wrong. The data obtained largely depend on the skills and experience of the doctor, the position of the fetus at the time of measurement, and the settings of the ultrasound machine.
Deviations from the norm
The rate of abdominal growth can say a lot about the development of the child and the course of pregnancy in general. Let’s consider in detail what is normal and what is considered pathology.
Big belly during pregnancy
Most often, the voluminous tummy of the expectant mother has nothing to do with pathology. The reasons for this phenomenon:
- a pregnant woman moves and moves little, ignores walks and health-improving exercises - the most common situation;
- large fruit is hereditary;
- the woman is obese to one degree or another;
- polyhydramnios;
- multiple pregnancy.
Advice! To exclude abnormal processes in the later stages of pregnancy, discuss the issue of a large belly with a gynecologist.
Small belly during pregnancy
A miniature belly is not always an anomaly. Most often this happens for the following reasons:
- weight loss in the woman herself;
- small fetus - this deviation from the norm is genetic in nature and should not cause concern to the expectant mother;
- atypical position of the baby - the stomach seems smaller in transverse or oblique presentation.
Note! A small belly in late pregnancy may indicate physiological abnormalities in the development of the child.
Insufficient amniotic fluid - oligohydramnios - is a medical cause of a small belly. This complication occurs against the background of concomitant diagnoses:
- infections and inflammatory processes in the genital organs;
- lack of placenta;
- hypertension;
- gestosis - its presence is detected by the presence of protein in the urine and excessive swelling.
Belly doesn't grow
What to do if your stomach has stopped growing? The main thing is not to panic. Most likely, you simply do not notice the slow change in size. Especially if we are talking about 37-39 weeks. The baby’s body is fully formed by this time - it’s time to prepare for childbirth.
At the same time, stopping the growth of the fetus at an earlier stage can become a visual sign of a frozen pregnancy. In addition to the fact that the uterus has stopped growing, other symptoms indicate that the fetus has frozen:
- the baby stopped moving;
- bloody discharge appears - it is episodic in nature;
- body temperature increased. The effect of antipyretic drugs is short-term.
Features of changes in the uterus during pregnancy
The size, shape and other characteristics of the organ in question differ according to the stage of pregnancy.
On average, by the 8-9th week the dimensions of the female uterus are similar to the size of a goose egg. At this stage, it is usually impossible to feel it when palpating the abdominal wall, because the organ resides in the pelvic area, and only by 3-4 months does it rise slightly higher than the pubis. There is an increase in the activity of the placental system function. The size of the corpus luteum decreases until it completely disappears. The embryo develops blood vessels and begins to make its first movements.
By the 10-13th weeks of the term, the female uterus grows to an average of 11 cm. The body of the expectant mother is cleansed of various types of toxins and other harmful substances, which leads to a noticeable increase in the severity of toxicosis.
By the 14th-16th weeks, the organ grows to an average of 14 cm. At this stage, the fetus completes the creation of organs.
At the 16th week, the position of the uterine fundus is noted in the space between the woman’s pubis and her navel.
During the 17-18th week, the formation of the placental system is completed. The child's immune system, cerebellum, and limbs are already present. The uterus grows to approximately 18-19 cm.
Starting from the 20th week, the dimensions of the organ in question begin to align with the gestational age. Already from the 21st week, the gap between the fundus and the pubis is approximately 21 cm. Further, with each subsequent week, this figure increases by approximately 1 cm. The fundus of the uterus during this period is located 2 fingers lower than the navel.
During the 22-24th weeks, the dimensions of the organ increase to an average of 23 cm. The embryo, actively developing inside the mother, already has its own bones and muscles and weighs about 0.6 kg. At the 24th week, the bottom is located in the navel area, and its standing height is about 24 cm. The formation of the child’s respiratory system begins.
During the 28th week of the term, the UMR indicator is approximately 28 cm. The bottom itself is located a couple of centimeters higher than the navel.
In the third trimester, at 29-30 weeks, the size of the organ is about 31 cm.
During the 32nd week, the female uterus is located approximately in the center between the pregnant woman’s navel and the xiphoid process of her sternum. The VDM, in this case, is about 32 cm. By the 36th week, the organ in question is located on the line through which the costal arches are connected.
Already from the 38th week of the term, the organ gradually descends. The bottom, at the same time, puts pressure on the female diaphragm and her stomach. Food begins to be digested noticeably slower, and unpleasant heartburn occurs. The average weight of the fetus by this period can reach 2.5 kg.
At the 40th week, as noted, the UMR can be 40 cm, but on average it is less - at the level of 32 cm. The fundus of the uterus during this period lies between the navel and the ribs. The fetus is fully formed, developed and full term. During this period, the body of the expectant mother is actively preparing for an early birth, if it has not yet occurred.
Belly shape during pregnancy
The doctor determines the size of the fetus, its location, the rate of growth and development of organs not only by the size, but also by the shape of the pregnant woman’s abdomen. Moreover, for the same mother, the shape of the abdomen may look different with each new pregnancy.
There are no ideal dimensions here - ideally, the stomach has the correct outline and looks like an elongated egg. During the first pregnancy, it is slightly pointed. The same is observed in fragile girls with a narrow pelvis.
High belly
A high belly is typical for 4-5 months of pregnancy. The size of the fetus is still small, the abdominal muscles cope well with the load. The stomach is tucked up and looks slightly upward. Most often this manifests itself in fragile women with a thin bone structure.
Uneven, crooked belly
If such a situation arose suddenly - for example, two days ago the stomach was regular and rounded, you should tell the obstetrician about the changes. This will exclude pathologies.
When the wrong shape was there to begin with, there is nothing serious about it. This feature is explained by the position of the fetus - often oblique or transverse.
Possible reasons for non-compliance with the VDM
VDM is below normal
If the height of the uterine fundus is lower than normal, this may mean:
- Error in determining the duration of pregnancy;
- Wide, capacious pelvis in tall, large women;
- Intrauterine growth retardation;
- Oligohydramnios – decreased amount of amniotic fluid;
VDM is higher than normal
If AMD is higher than normal, this may indicate:
- Large fruit;
- Multiple pregnancy;
- Narrow pelvis;
- Incorrect fetal positions;
- Polyhydramnios is an increase in the amount of amniotic fluid.
Also, to monitor the condition of the fetus, its growth rate and the amount of amniotic fluid, the abdominal circumference (AC)
at the level of the navel. This indicator very much depends on the individual characteristics of the woman and the thickness of the subcutaneous fat, so the dynamics of the increase in circumference are taken into account. Using these two indicators at the end of pregnancy, you can calculate the expected weight of the fetus. To do this, you need to multiply the VDM value by the coolant. So, for example, if the VDM is exactly 36 cm, and the coolant is 95 cm, then we get the possible weight of the child - 3420 grams.
Information If the indicators of the height of the uterine fundus do not correspond to the term by more than 3 cm, then the doctor prescribes additional examinations for the pregnant woman. An ultrasound of the fetus, Doppler ultrasound and cardiotocography are performed and, based on the results obtained, treatment is prescribed and the tactics for the upcoming birth are determined.
What should the belly feel like during pregnancy?
During normal pregnancy, the belly is soft to the touch. If you feel hardness when palpating, this indicates increased tone of the uterus. If the situation is not controlled, it can harm the baby. Uterine tone causes premature birth and provokes early miscarriages.
Note! In 3-5 months of pregnancy, the cause of sudden hardening of the abdominal tissue is flatulence. At 36-39 weeks, the belly becomes hard when the baby moves. In this way, the uterus reacts to the movement of the fetus. After the child calms down, the muscles relax, tension subsides and the stomach becomes soft again.
Compliance with deadlines and table
If the girth of a pregnant woman’s abdomen is a rather individual and subjective value (ladies’ bellies have different sizes even before the onset of an “interesting situation”), then VSDM depends little on how thin or curvy the lady is, tall or short. This value is more constant, and therefore we can talk about average norms for the height of the bottom point of the reproductive organ for different stages of pregnancy.
Source
| Duration in weeks | Abdominal circumference in cm |
| 20 | 70-75 |
| 22 | 72-78 |
| 24 | 75-78 |
| 26 | 77-82 |
| 28 | 80-85 |
| 30 | 82-87 |
| 32 | 85-90 |
| 34 | 87-92 |
| 36 | 90-95 |
| 38 | 92-98 |
| 40 | 95-100 |
What sensations does a woman have when her belly appears during pregnancy?
As the belly increases in size, the sensations of the expectant mother change:
- the skin stretches - this causes cracks and peeling of the epidermis. When stretched, soft tissues cause itching. As the abdomen grows, stretch marks develop - it is not easy to eliminate them later;
- the fetus grows and puts pressure on the pelvic organs. Against this background, the pressure increases, internal discomfort appears, and the woman’s gait changes. The number of urinations increases. Constipation occurs;
- The muscles stretch along with the skin; the process is often accompanied by painful sensations.
How the uterus changes
Of course, changes in the volume of the tummy are most directly related to the uterus. Initially, this organ resembles a pear. But after two months it rounds up and increases approximately three times. The shape of the woman’s reproductive organ changes in the second half of the “interesting position” - it becomes ovoid.
It is clear that the uterus behaves differently in different trimesters of pregnancy. And this most directly affects the size of the abdomen. From conception to childbirth, this organ increases 10 times - from 50-100 g. up to one kilogram!
And also amniotic fluid, which may be higher than normal. The muscles lengthen and thicken. The doctor records all changes using obstetric examinations. To obtain more accurate results, ultrasound and necessary tests are prescribed .
Additional questions
How can you tell by the condition and appearance of your belly whether everything is normal with your pregnancy and baby? Let's consider the most popular questions that concern future parents.
What does a red belly mean during pregnancy?
There are several reasons that cause redness in the abdomen:
- an allergic reaction is the most common situation. The immune system is weakened by the double burden on the body and those factors that previously did not cause intolerance can provoke redness. For example, household chemicals, food, drinks. What should I do? Contact a specialist - if no pathologies are identified, the doctor will prescribe a course of antihistamines;
- Miliaria - in addition to redness, it is accompanied by increased sweating and itching. Occurs when wearing a bandage, clothing made of synthetic fabrics, or failure to comply with personal hygiene rules. Eliminate irritating factors, treat problem areas with chamomile, calendula or a solution of salicylic alcohol;
- malfunction of internal organs - most often the liver and gall bladder manifest themselves this way. The organs cannot cope with the high load, the outflow of bile is difficult and causes local redness.
Why is my stomach cold?
In 90% of cases, this phenomenon is a consequence of a physiological nature and is considered the norm. Main reasons:
- a woman’s psychological reaction to a new condition for her;
- low body temperature;
- excess weight.
Why does your stomach throb during pregnancy?
Pulsating movements are provoked by the following factors:
- the baby moves, hiccups;
- the inferior vena cava is compressed;
- uterine tone;
- risk of miscarriage;
- training contractions;
- ectopic pregnancy in the first weeks of its course.
If the pulsation occurs rarely and briefly, there is no need to worry. When the situation repeats, there is a risk of fetal hypoxia.
Why is the belly smaller during pregnancy in the morning than in the evening?
This is absolutely normal. Fluctuations in weight do not exceed 400 grams. By evening, all body systems are not working at full capacity - food is digested slowly. Gas formation and bloating are activated. In the morning everything goes away and the stomach seems smaller.
Causes of veins appearing on the abdomen
The presence of varicose veins provokes the appearance of veins on the abdomen. This is facilitated by:
- The uterus grows, pressing on the vena cava. The outflow of blood is disrupted;
- the vessel and veins are stretched - weak ones burst. As a result, spider veins appear;
- to saturate the fetus with blood, its volume increases by 40%. The veins have a double burden;
- internal organs shift, intra-abdominal pressure increases;
- The hormonal balance changes - progesterone and estrogen make the blood vessels thinner.
Why is the stomach low?
The main factors that provoke prolapse of the abdomen, doctors include:
- the structure of a woman’s body;
- low placenta previa;
- undeveloped abdominal muscles;
- second and subsequent pregnancies;
- the beginning of labor.
What should the belly look like before giving birth?
You can understand that the body is preparing for childbirth by the following signs:
- the stomach protrudes forward, its shape resembles a pear;
- its position falls below the level of the hip bone;
- the number of stretch marks is increasing;
- to the touch - elastic.
Objective examination of a pregnant woman
The examination of the expectant mother is carried out at the first appearance at the antenatal clinic and registration for pregnancy. An objective examination is carried out not only by an obstetrician-gynecologist, but also by a therapist with a dentist, an ENT doctor with an ophthalmologist, and, if indicated, an endocrinologist and surgeon, a cardiologist and a urologist. If necessary (presence of children with congenital malformations, hereditary diseases, etc.), medical genetic counseling is prescribed.
During an objective examination, the following is studied and measured:
- woman's body temperature;
- height and weight of the expectant mother (necessary for predicting future weight gain and identifying edema);
- blood pressure (measured at each visit to the antenatal clinic);
- body type (normosthenic, asthenic or hypersthenic);
- pelvic dimensions;
- color and condition of the skin and mucous membranes;
- shape of the mammary glands, their palpation;
- examination of the abdomen and palpation;
- condition of the symphysis pubis by palpation (are there any discrepancies);
- the state of the organs of the cardiovascular system and gastrointestinal tract, lungs, nervous and endocrine systems, as well as excretion;
- condition of teeth, etc.
Tips and tricks - how to avoid stretch marks
Take note of effective ways to combat stretch marks:
- prevention - after taking a bath, use a nourishing cream. If you do this regularly, stretch marks will not appear;
- olive oil - warm a few drops in your palms and rub into problem areas with gentle movements;
- breathing exercises - learn to breathe correctly. This way you will saturate your body with oxygen and strengthen your abdominal muscles;
- cosmetology procedures - you can take the course 4-5 months after giving birth;
- restorative creams, lotions, body milk - they are well absorbed into the skin, relieve physical discomfort, help the skin stretch and maintain tone.
Ultrasonography
Measuring the expectant mother’s abdomen with a “centimeter” is a mandatory measure at every visit to the obstetrician and allows one to suspect a possible pathology during pregnancy. A reliable method to resolve the doctor’s doubts and determine any abnormalities during the gestation period is ultrasound. Using ultrasound you can find out:
- the most accurate gestational age;
- fetal height and weight;
- determine whether the embryo/fetus is alive or dead;
- localization of the placenta;
- size and thickness of the placenta;
- whether the pregnancy develops in a short period of time (exclude frozen one);
- identify trophoblastic disease;
- exclude ectopic pregnancy;
- determine the position/presentation of the unborn baby;
- diagnose fetoplacental insufficiency.