During pregnancy, a woman should visit an obstetrician-gynecologist at least 7 times. At each examination, the specialist conducts routine examinations that help determine how the pregnancy is progressing. These include measuring blood pressure and pelvic dimensions, listening to heart sounds and palpation of the fetus, and diagnosing concomitant somatic diseases.
One of the most important methods of examining a pregnant woman is measuring the abdominal circumference and the height of the uterine fundus. The obtained figures are compared with the norms for a given gestational age, which makes it possible to judge deviations in the size of the fetus or other pathologies.
Increase in abdominal volume during pregnancy
Typically, a sharp increase in abdominal volume occurs at the 16th obstetric week; it is from this period that abdominal girth is measured during pregnancy. An earlier examination does not make sense, since until this time the enlarged uterus does not push the anterior abdominal wall forward.
On average, abdominal circumference during pregnancy increases by 2-3 centimeters every 2 weeks of gestation.
, respectively, by 1-1.5 centimeters in 7 days. Normally, in the absence of excessively developed subcutaneous fat, when examined at 16 weeks, the abdominal girth is 70-75 centimeters. It follows from this that the abdominal circumference at 27 weeks of pregnancy should be 81-86 centimeters.
In normosthenic women, the abdominal circumference at 32 weeks of pregnancy should approach 90 centimeters, and by the time of birth it should reach 95-100 centimeters. However, the results of this measurement are quite subjective and depend on the figure and physique before the child is conceived. Therefore, it is considered more correct to track the dynamics of the increase in abdominal volume, which should grow evenly throughout the pregnancy.
Abdominal girth measurement functions
Abdominal circumference during pregnancy is an important method of examining the expectant mother. This measurement makes it possible to judge the intrauterine growth of the unborn child and to suspect a multiple pregnancy or pathology. Usually, a study of the size of the abdominal circumference is carried out simultaneously with determining the height of the uterine fundus, which gradually and naturally increases in accordance with the gestational age.
In addition, the measurements listed above help indirectly determine the weight of the fetus using the formula:
FW * FWDM = fetal weight.
where OZ is the circumference of the abdomen, and VSDM is the height of the uterine fundus.
Comments (3)
Sometimes it seems to me that it would be nice for our gynecologists to read at least articles like this. My uterine fundus height during pregnancy was higher than normal, but the doctor didn’t care. She said everything was fine. Already at the maternity hospital they said that there was a lot of water and this caused the child to have problems. Now I understand that every centimeter is important to ensure that everything goes well with the child.
And I was lucky in this, I was observed by a qualified doctor. Throughout my entire pregnancy, the height of the uterine fundus coincided with the gestational age, that is, at 24 weeks the UMR was equal to 24 cm, at 28 weeks - 28 cm, although at one time, according to the results of an ultrasound at 28 weeks, I was even diagnosed with oligohydramnios, although this is not measured by centimeters had no effect. It’s good that I completed the course of treatment on time and everything returned to normal.
Unfortunately, I was very unlucky with the doctor. It turned out that during the examination they said that everything was fine with me, but in reality it turned out to be wrong, the number of weeks did not coincide with the centimeters. Although the doctor confidently asserted that everything was fine. It turned out that I I’m not the only one, the girls in the ward said the same thing, in general, a negligent attitude towards young mothers. Thank God, everything worked out and I gave birth to a healthy baby normally.
Normal abdominal circumference
| Gestational age | Abdominal circumference, cm |
| 20 weeks | 70-75 |
| 22 weeks | 72-78 |
| 24 weeks | 75-80 |
| 26 weeks | 77-82 |
| 28 weeks | 80-85 |
| 30 weeks | 82-87 |
| 32 weeks | 85-90 |
| 34 weeks | 87-92 |
| 36 weeks | 90-95 |
| 38 weeks | 92-98 |
| 40 weeks | 95-100 |
Reasons for deviation from the norm
If the abdominal circumference does not correspond to the gestational age, the likelihood of fetal pathology or pregnancy complications increases. Decreased abdominal girth occurs
:
- When the amount of amniotic fluid decreases. This pathology occurs in post-term pregnancy, early rupture of amniotic fluid and concomitant diseases of the fetus.
- With fetal malnutrition. Retarded growth and development of the unborn child.
- With an excessively wide pelvis, when the fetus “falls” into its cavity. Due to insufficient nutrition of the mother.
An increase in abdominal circumference may cause
:
- Increased amount of amniotic fluid. This occurs due to the presence of diabetes mellitus in the mother, or due to infection or defects of the fetus.
- Large child sizes. Can be observed normally. A large fetus almost always accompanies a post-term pregnancy; very rarely, an increase in the weight of the unborn child is caused by pathological reasons.
- Multiple pregnancy. It is quite natural that 2 or more children in the womb will cause her belly to become excessively enlarged.
- Fetal position. When the baby is positioned perpendicular to the axis of the uterus, the abdominal girth may be increased.
- Narrow pelvis. With this anatomical feature, the child takes a higher and more forward position.
- Hydatidiform mole and chorinepithelioma. Rare diseases in which tumor tissue grows in the uterine cavity.
- Errors in diet. Sometimes the reason for an expectant mother's belly enlargement is not her unborn child, but excessive consumption of high-calorie foods.
Do not forget that abdominal circumference during pregnancy may not meet the norm due to incorrect measurements, so it is better to undergo routine examinations with one qualified doctor.
Measuring abdominal circumference at home
The study will be more reliable if the abdominal circumference is measured by another person. Self-measurement has a large error; you should not trust it 100%.
A pregnant woman should take a lying position on a fairly hard surface with her stomach up, her arms should be extended along her body. The measuring tape should pass through the strongest curve of the spine at the back, and through the navel at the front. The expectant mother should first empty her bladder and not strain her abdominal muscles.
Source: mymammy.info
Independent measurements
Self-measurement of the height of the dome-shaped part of the uterus above the womb is much simpler than deciphering the measurements. A woman can easily do this at home without outside help. Knowing how doctors do this (described above), you can similarly use a measuring tape, and if you don’t have it at hand, then use the method of two folded fingers. It is important to go to the toilet, empty your bladder and take a comfortable horizontal position with your knees slightly bent.
A bed with a soft mattress is not suitable for measurements - the surface on which the expectant mother will sit must be hard. The self-determination algorithm is quite simple:
- determine the location of the pubic bone and its upper border;
- carefully feel the bottom part of the reproductive organ, smoothly rising from the edge of the pubic bone to the navel and above (the bottom feels like a comb with uneven contours);
- Using any of the methods described above, measure the distance from the edge of the pubis to the high bottom point.
Do not make mistakes, try to apply the zero mark of the centimeter tape to the edge of the pubic bone. Remember that VDM is measured not in mm, but in cm.
Be sure to take into account the characteristics of your pregnancy, in particular the position of the fetus (the doctor will inform you about this at the appointment), the number of children; in case of twins, the weight of the fetuses will be less, and the size of the uterus will be larger due to stretching of the walls.
Examination of a pregnant woman
After collecting a medical history from a pregnant woman, any obstetric examination at any stage of gestation involves performing an external obstetric examination. This diagnostic method allows you to detect signs of abnormalities in the body of a pregnant woman with minimal cost.
One of the key points is measuring height, weight, fundus height and abdominal circumference (AC). These numbers are determined to compare with the norm during a specific period of pregnancy.
Normal values are arithmetic averages for the entire population of women at a specific period of gestation. This means that normal numbers can vary greatly depending on the build and genetic makeup of each person.
Measurement Rules
The girth or circumference of the abdomen must be measured according to certain rules, otherwise its comparison with normal sizes will not be indicative enough.
Abdominal circumference during pregnancy is determined as follows:
- A flexible measuring tape is used for measurement.
- The most correct measurement will be with the woman standing.
- Circumference is measured at the level of the navel, this level usually coincides with the first lumbar vertebrae on the back.
- You should not measure coolant at the level of the most protruding part of the abdomen; this measurement will be incorrect.
The volume of the abdomen changes regularly during pregnancy. This is influenced by several factors at once. Moreover, a single deviation of the indicator from the norm does not play a significant role, since then the size and weight of the fetus and amniotic organs can change and return to normal. Therefore, in order to judge the presence of deviations in the coolant indicator, it is necessary to measure it several times at different periods of gestation.
Coolant measurement can be carried out at home. To do this, you only need to have a measuring tape. The data obtained at different times should be recorded and then reported to your doctor.
Size by week of pregnancy
The size of the coolant is an extremely variable indicator. It is for this purpose that tables with average volume values have been developed. The data in the tables may differ slightly from each other, since the studies were carried out by different specialists, each of whom has his own idea of the boundaries of normality and pathology.
Abdominal circumference by week of pregnancy is determined according to the following table:
Table of abdominal volumes during pregnancy
| Gestational age in weeks | Coolant in mm |
| 14 | 85 |
| 15 | 93 |
| 16 | 102 |
| 17 | 112 |
| 18 | 124 |
| 19 | 134 |
| 20 | 144 |
| 21 | 157 |
| 22 | 169 |
| 23 | 181 |
| 24 | 193 |
| 25 | 206 |
| 26 | 217 |
| 27 | 229 |
| 28 | 241 |
| 29 | 253 |
| 30 | 264 |
| 31 | 274 |
| 32 | 286 |
| 33 | 296 |
| 34 | 306 |
| 35 | 315 |
| 36 | 323 |
| 37 | 330 |
| 38 | 336 |
| 39 | 342 |
| 40 | 347 |
| 41 | 350 |
Of course, all bellies cannot be measured using the same standard, that is, all women cannot have the same “waist” circumference at the same time.
It is worth considering that the size of the coolant before the 30th week of pregnancy is not a sufficiently indicative value, since quite significant changes in the volume of the fetus and amniotic structures can occur in the first two trimesters.
After 30 weeks, doctors not only monitor the progress of pregnancy, but also begin to plan preparations for childbirth, so any anthropometric indicators become highly important.
Reasons for rejection
Before you understand why the volume of the abdomen may increase or decrease at specific periods of gestation, you should understand what indicators affect the coolant.
So, the circumference of the abdomen, and therefore its volume, is made up of the following values:
- The appropriate size before pregnancy is influenced by the woman’s constitution, the volume of subcutaneous tissue, height and body weight.
- The size of the fetus, which steadily increases with gestation.
- The volume of amniotic fluid is one of the most variable and important indicators.
- The size of the placenta and amniotic membranes affect the coolant to a lesser extent.
- The condition of the wall and cavity of the uterus - with anomalies or neoplasms, the volume changes seriously.
Knowing the main factors that can change the coolant, we can identify pathological conditions that lead to an increase or decrease in the circumference.
Since abdominal circumference is an approximate and variable size, changes should be taken seriously. Additional research methods are always used to confirm or refute a preliminary diagnosis.
Increase in abdominal circumference
If the abdominal circumference deviates from the normal value by 2-3 centimeters, there is no need to worry. Only significant changes can indicate pathological changes.
The size of the coolant exceeds normal in the following pathological processes:
- Large fetus - this condition is an obstetric complication, since it requires special tactics during delivery. Vaginal birth with a large fetus can cause severe injuries to the perineum and reproductive organs.
- Multiple pregnancy - usually this feature is detected quite early - during the first screening ultrasound. If there are two fetuses in the uterine cavity, the OB increases significantly; the norms for this indicator are not applicable for multiple pregnancies.
- Oblique and transverse position of the fetus - these features of the position of the baby in the uterine cavity can significantly affect the circumference. Until the third trimester, the location changes several times, so there is no need to worry ahead of time.
- A narrow pelvis is a constitutional feature of a woman’s anatomy. The pelvis can be narrow anatomically - this is due to the structure of the bones, or functionally - when the size of the fetus and the woman’s pelvis do not match. Towards the end of pregnancy, the fetus does not descend into the plane of the entrance to the pelvis, this leads to an increase in coolant.
- Polyhydramnios is a fairly common pathological process. Diseases of the kidneys, endocrine glands, intoxication and other diseases increase the volume of amniotic fluid. An ultrasound is performed to confirm the diagnosis.
- Anomalies of the uterus and tumors - the size of the uterus can be affected by bridges in the uterine cavity, its congenital anomalies, as well as benign and malignant tumors.
Reducing abdominal circumference
Not only an increase, but also a decrease in coolant relative to the gestational age can indicate a pathological process in the body of the fetus and a pregnant woman.
The following diseases and conditions can reduce the circumference:
- Error in gestational age - regular deviations from the norm in size in the absence of pathological processes may be due to the fact that the woman or obstetrician incorrectly determined the gestational age.
- Fetal hypotrophy is a condition that combines deviations in the development of the baby that differ in origin and severity. They can affect its size and weight. Intrauterine growth retardation syndrome in modern conditions responds well to treatment if detected in a timely manner.
- Wide pelvis - in this condition, the fetus may descend prematurely into the pelvic cavity, which reduces coolant. In this case, you should pay attention to the condition of the cervical canal. Isthmicocervical insufficiency with a wide pelvis can lead to premature termination of pregnancy.
- Oligohydramnios - amniotic fluid during various pathological processes can not only increase in volume, but also decrease. This affects the size of the abdomen and its circumference.
- Endocrine diseases in the body of the expectant mother. Very often, the coolant lags behind normal values in hypothyroidism. A decrease in the level of thyroid hormones slows down the growth of the baby and amniotic organs, and reduces the volume of amniotic fluid.
The listed pathological processes always require additional diagnostics. A final diagnosis cannot be made solely on the basis of measuring the abdominal circumference of a pregnant woman.
Source: krasgmu.net
If the values do not meet the standards
The dome-shaped part of the female reproductive organ grows simultaneously with the baby, increasing over the weeks of pregnancy, in fact, this is why the AMR is measured so diligently. Until the 27th week of pregnancy, height increases by about a centimeter or two per week, after 28 weeks the rate decreases slightly, and the bottom rises by about 1.5 cm per week, and after 36 weeks the growth rate decreases to a minimum of 0.2–0. 5 cm per week. If, over the course of several measurements of growth, VDM is not observed or, conversely, growth is too fast, they speak of a discrepancy with the deadlines.
A lag of 2 centimeters or more from the standard values may be due to one of the following reasons:
- incorrectly set pregnancy dates, delayed ovulation;
- healthy baby, but with low body weight (genetic inherited constitution);
- IUGR—intrauterine growth retardation;
- small amount of water;
- transverse or oblique position of the fetus in the uterine cavity;
- wide pelvis of the expectant mother.
Exceeding the VSDM by 2 centimeters or more from the standard values may indicate:
- incorrectly determined gestational age;
- incorrect measurement (for example, with a full bladder);
- narrowness of the woman's pelvis;
- multiple pregnancy;
- a healthy baby, but with a large body weight (hereditary factor);
- the woman has diabetes mellitus, including its gestational type;
- polyhydramnios;
- breech presentation of the fetus, in which the baby’s legs or buttocks are directed forward.
You shouldn’t immediately start worrying and getting nervous - this is generally unnecessary in such a situation. In addition, according to medical statistics, the most common reason for deviations of VSDM from real indicators is a banal error in determining the gestational age or incorrect calculation. This is possible with an irregular female cycle, when a woman does not remember the date of her last menstruation after IVF.
The second most popular reason is the weight of the fetus. You need to understand that the baby does not always have to weigh exactly as much as indicated in the tables with standards. There is a genetic predisposition, and after 10 weeks of pregnancy, all children grow up according to their own genetic program, which was laid in them by their parents.
One is destined to be large, and the other - miniature. In this case, both of them will be completely healthy children. Look carefully at yourself, at your partner, at your parents and his parents. Assess your height, weight, build. Perhaps this is exactly your case.
If developmental delay is suspected, an ultrasound with Doppler is prescribed, and from 30-31-32 weeks - CTG, this allows you to find out how well the baby’s heart is beating, whether he is receiving enough nutrition from the bloodstream. Conduct an examination for intrauterine infections. With IUGR, there are a lot of methods of providing assistance, and in most cases, doctors manage to normalize its growth rate in the shortest possible time, by eliminating the cause that negatively affects the child.
The width of the pelvis plays an important role. In women with a narrow pelvis, the belly becomes noticeable much faster, because the uterus quickly leaves the tight pelvis and rises higher, ahead of the average values. A wide pelvis is more spacious, and slight deviations of the VDM in a smaller direction are possible.
An examination in case of deviations of the VDM from the norms is prescribed in any case, because it is better, as they say, to be safe. It includes a woman donating blood for sugar and infections, ultrasound and Doppler ultrasound.
But even if the reasons are not found and the genetic characteristics of the child are assumed, the woman will be monitored more closely, and she may have to visit the doctor more often, as well as undergo tests.
General characteristics of the concept
As pregnancy progresses, a lot changes in a woman’s body. Internal changes are often associated with the fact that as the fetus develops, the uterus acquires the appropriate size and other organs move to give it enough space.
The distance from the pubic bone to the highest point where the uterus can be felt is called its height. It turns out that the height of the uterine fundus is the size to which the uterus grows during pregnancy.
This is one of the possible indirect indicators by which the level of fetal development can be determined.
Measuring the height of the uterine fundus: with a doctor and independently
In the first trimester, the enlarged uterus can be felt by a gynecologist through the vagina. You should not do this on your own for a short period of time. But as the fetus grows, this is easier to do - at the beginning of the second trimester, the uterus extends beyond the boundaries of the pelvic bones, and it is easy to feel it through the abdomen.
During the appointment, the doctor feels the abdomen and measures it with a centimeter tape, then writes down the results. At home, you can try to repeat its actions.
Before taking measurements, you need to empty your bladder - otherwise the readings may be inaccurate.
To measure the height of the uterine fundus, you will need a centimeter tape - the most common one used by seamstresses to take measurements. You will need to lie on your back and straighten your legs. Then gently palpate the abdomen with your fingers, starting from the pubic joint upward. The abdomen will be quite hard to a certain point. This point is the fundus of the uterus. Then you need to measure the distance from the beginning of the path to this point. This indicator is the height of the uterine fundus.
Watch the video that shows how to measure correctly:
Measuring technique
Doctors establish the actual period of an “interesting position” based on the condition of the uterus earlier, before the reproductive organ rises from the pelvis. In the first trimester of pregnancy, palpation is used for this purpose - a bimanual method of gynecological examination (one hand is inserted into the genital tract, and the other is pressed on the lower abdomen to determine the boundaries of the organ). You can't feel anything from the outside. This method does not provide very accurate information, but an experienced obstetrician can establish pregnancy using the two-handed method with an accuracy of up to a week.
You can measure how much the fundus of the uterus has risen using a centimeter tape, a pelvis gauge, and also the width of your fingers located transversely. It is permissible to determine VSDM based on anatomical landmarks.
To measure correctly, the pregnant woman needs to take a lying position. She is asked to sit on the couch on her back, with her legs slightly bent at the knees. It is important that before the measurement the woman visits the toilet and be sure to empty the bladder of its natural contents.
Next, the obstetrician-gynecologist needs to determine in what position the baby is located, where the fundus of the uterus is, and also what part of the baby’s body is adjacent to it. The doctor places both palms on the stomach, and points the fingertips towards each other (Leopold's first obstetric maneuver). This establishes the most distant point of the bottom part of the reproductive organ relative to the line of the pubic bone. Then they apply a measuring tape to this point and simply determine the numerical value, which expresses the height of the uterine fundus.
If the doctor is a big fan of the old school of obstetrics, then he can use the finger method. He presses his fingers together (middle and index), they should be located transversely on the stomach. The height is determined in fingers, and then converted to centimeters (2 transverse fingers = 3–4 centimeters)
Norms for the height of the uterine fundus at different stages
What can be considered normal in a particular case depends on several factors:
- number of pods;
- child's size;
- intrauterine position of the child;
- individual characteristics of a woman’s body;
- presence of pathological conditions.
If there is only one child, the size is within the normal range, the position in the womb is correct and the woman does not have any features affecting the size of the uterus (for example, there is no polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios, and her height is average and her build is normal), then the indicator will be equal to:
- 6 cm at 16 weeks;
- 12-14 cm at 20 weeks;
- 20 cm at 24 weeks;
- 24-26 cm at 28 weeks;
- 28-30 cm at 32 weeks;
- 32-34 cm at 36 weeks;
- 28-30 cm at 40 weeks.
It is also considered normal if the indicator is approximately equal to the gestational age in terms of weeks: how many weeks is the indicator in centimeters.
The height of the uterine fundus is constantly increasing. It decreases by a couple of centimeters only a few days before giving birth.
With multiple pregnancies, the picture changes somewhat. At week 16, the normal range is from 15 to 28 centimeters. Indicators may exceed the norm by 2 to 12 cm compared to a singleton pregnancy.
It is not uncommon that up to 28 and even up to 30 weeks of pregnancy with twins, indicators barely exceed the norm for pregnant women with one child. There is no need to panic: babies may lie and develop differently, but it is better not to refuse additional examination.
If deviations exceed 3 cm, our doctors may be puzzled by finding the reasons and send the expectant mother for additional examinations and even prescribe treatment. Often examinations show that everything is fine with the children, but still gynecologists stubbornly prescribe Actovegin, Curantil and other unnecessary therapy in this situation. Therefore, in civilized countries they do not rely on this indicator and do not measure it at all.
Many accredited obstetricians and gynecologists consider the measurement of fundal height to be an ancient teaching of the Soviet medical school, and therefore they rely only on the results of fetal ultrasound.
VDM does not correspond to the gestational age ((((
Posted by kykolka0612 ,
October 28, 2013 · 7
This is actually what I found out today at the appearance ((((I’m 27 weeks (28 will be on Wednesday), and WMD is 24 (OL 88). But the doctor said that it’s not scary, it will still rise. She’s an older woman , experienced, I go with the 2nd B and am very pleased!!! In general, there is no reason not to trust, but I read it on the Internet (be it not good))), and there they consider a deviation of 3 cm. I’ll say right away, on ultrasound when we were at 22 weeks, my daughter was lying correctly, and in general everything was fine. True, my daughter is small and thin)))) Maybe because of this? Back in the day, B didn’t encounter this, and even today, if I hadn’t noticed what the doctor was writing, I wouldn’t have worried either. Briefly speaking! Girls! Should I worry and go for an ultrasound? Or will the truth rise?
Possible reasons for indicators below normal
There are cases when, when measured, the height of the uterine fundus is less than normal.
Incorrect determination of the deadline is one of the most common reasons. If a woman comes to the LCD for the first time to register in the second trimester, and not before 12 weeks, as expected, then the doctor is not always able to accurately calculate how many weeks the pregnancy has already lasted. Basically, in the situation under consideration, this happens due to the woman having an unstable or long menstrual cycle, as well as in its absence, for example, if the next pregnancy occurred while breastfeeding the previous baby and menstruation has not yet occurred after childbirth. Because of this, actual performance may differ from what was incorrectly assumed to be the case.
Oligohydramnios (insufficient amount of amniotic fluid) can also cause a downward deviation in the indicator: there is little water, therefore, the uterus does not increase in size. May occur due to dehydration, nicotine use and certain medications (for example, ACE inhibitors). An additional symptom of severe oligohydramnios is pain when the fetus moves. To detect oligohydramnios, a routine ultrasound is sufficient.
A wide pelvis with low fundal heights has a simple explanation: the uterus has enough space between the pelvic bones, so it does not need to rise. It is not a pathology.
In addition to a wide pelvis, there may be other physiological features: a miniature figure, the influence of a genetic factor, etc.
Incorrect (transverse or oblique) position of the fetus can also cause a low rate. The explanation is simple - due to this position of the child, the uterus grows not upward, but to the sides.
Fetal growth retardation is the most unpleasant possible reason when a child does not gain enough weight while in the womb. In addition to physiological reasons (short stature of the mother or father), there may be disturbances in the development of the placenta or umbilical cord, the presence of infection, bad habits, as well as blood thickening and, as a consequence, insufficient nutrition of the fetus with nutrients and oxygen. There may not be any obvious symptoms, but during the examination the doctor will notice that the fetus may be delayed in development and will prescribe an ultrasound.
It is believed that the low weight of the expectant mother is the main sign that the baby will be born with low birth weight. Although sometimes this is true, you should not consider this a determining factor. On the contrary, many large women give birth to small, low-weight babies.
Source: zaletela.net
How to calculate a child's weight according to VDM?
To determine the estimated weight of the baby, today they are increasingly resorting to ultrasound diagnostics, since its results are much more accurate. But women can easily apply obstetric formulas, which have already become history, on their own, at least to satisfy their own curiosity. There are several ways.
According to Lankowitz
You need to take the last two sizes indicated on the date of the last visit to the antenatal clinic: the woman’s abdominal circumference and the UMR. You also need to know your height and weight.
The algorithm is as follows: (VSDM + Coolant + height + weight) x10.
Example: gestational age 30 weeks, OB = 115, VSDM = 30, height - 170 cm, weight - 75 kg. (115+30+170+75) X10= 3900. The error of the formula is about half a kilogram, both plus and minus.
According to Bublichenko
For such a calculation, you need to know the exact weight of the expectant mother. It is divided by 200 and multiplied by 10. For example, a pregnant woman who weighs 80 kilograms will have a baby weighing about 4 kilograms. The error is about a kilogram in either direction.
What is abdominal circumference during pregnancy
In the fifth month of pregnancy, a woman’s belly begins to rapidly increase. If at 16-18 weeks the belly was tiny and visually invisible under a layer of clothing, then with the beginning of the 20th week it grows, acquiring a unique shape.
It is from the 20th week that at each scheduled examination the gynecologist takes measurements of the abdomen during pregnancy, and subsequently observes the dynamics in the direction of increase/decrease. Along with the measurements of the belly, the measurement of the height of the uterine fundus (FHH) is reproduced. Based on the abdominal circumference and the size of the uterus, the doctor will determine the period of fertilization, body weight and the development of the baby as a whole, whether it suggests the occurrence of high or low water. If the slightest deviation is detected, he is referred for an ultrasound.
Why do you need to define this parameter?
Every obstetrician considers it his duty to measure the UMR, not only because the instructions provide for this, but also because this method is one of the most accessible in order to understand whether the course of pregnancy is normal. VSDM, despite the fact that the size is associated with errors, is included in the indicators of the gravidogram (general table of indicators for a pregnant woman). This is a special table that displays the entire course of the gestation period in the form of graphs: there is a weight gain graph, a pressure graph, a graph of abdominal circumference and a graph of VSDM.
During almost all weeks of gestation, the height of the uterine fundus is in accordance with the period in numerical equivalent, and only before childbirth, when the abdomen drops, the fetus moves lower and begins to press its head against the internal os of the cervix, helping it to mature and prepare for dilation during childbirth, VSDM decreases. The belly also visually becomes lower, and it becomes somewhat easier for the expectant mother to breathe and move.
What determines the size of the belly during pregnancy?
We often notice that pregnant women have bellies of different sizes and configurations, even if the girls have an identical pregnancy period. What determines the size of the belly during pregnancy and why do the volumes and shapes of bellies vary so much?
The size of the abdomen, its shape, the intensity of growth - this is all individual. Still, there are factors that influence its dimensions. Namely:
- woman's body constitution;
- general weight gain during pregnancy;
- baby's weight;
- number of fruits;
- child's location;
- amount of amniotic fluid;
- abdominal condition;
- number of pregnancies.
The initial guideline that determines the size of the abdomen during pregnancy is the constitution of the girl’s body, her anatomical structure. Thus, girls with a slender build and narrow hips will have a larger belly in size and volume than overweight women with wide pelvic bones. Skinny girls will show off their protruding belly a little earlier than plump girls. But for owners of a wide pelvis, labor and the process itself, as experts explain, are easier and faster.
The size of a pregnant woman's belly depends on her overall weight gain. Girls who adhere to the opinion “if you’re pregnant, you need to eat for two,” gain weight faster and sometimes break records for belly size. Pregnant women who eat a healthy, balanced diet have a neat little tummy. Experts explain that in the first trimester a woman needs to gain about 2 kg, then until the ninth month, 0.5 kg per week. At the finish line, the 9th month, the weight should no longer increase.
The size of the belly of pregnant women directly depends on the height and weight of the little one. As mentioned above, mothers with a good appetite set out to fatten their baby, especially in the last months of pregnancy. Due to the large size of the belly, the stomach of such women is larger. In fact, as doctors will assure, by “feeding” a child, especially in the last stages, a woman is doing a “disservice” to both herself and the baby. So, as with a large fetus, it is more difficult to give birth on your own. Often in such cases they resort to surgical intervention.
The number of fetuses in the womb also affects the size of the abdomen. With multiple pregnancies, the belly grows faster than a single pregnancy, and at 28 weeks it can reach the prenatal size of a normal pregnancy, and by 30-32 weeks - its maximum size.
The position of the baby in the womb (how it attaches to the wall of the uterus) affects the size of the belly. The belly will look more voluminous if the baby is attached to the front wall of the uterus; if it is attached to the back wall, it will be more accurate.
The amount of amniotic fluid in the uterus is a factor that determines the size of the abdomen. In gynecology, there are the concepts of “polyhydramnios” and “oligohydramnios” - excess/lack of fluid for the existence of the fetus. Based on the amount of amniotic water, the size of the tummy of expectant mothers is formed.
A woman's physical characteristics also affect the size of her belly. Girls with strong abdominals have a smaller belly than pregnant women with weak muscles. In addition, physically prepared women in labor “push” the baby out of themselves much faster during the birth process.
Abdominal coverage depends on the number of pregnancies. The uterus of first-time mothers is smaller and more elastic, so the tummy in this version will be neater and smaller in size. In “experienced” mothers, due to the enlargement of the uterus and its weak tone, the belly will become larger with each new pregnancy.
How to measure abdominal circumference during pregnancy
It is more advisable to carry out the procedure for measuring abdominal volume from the 20th week. At this stage, the belly is getting rounder, and at each appointment with the gynecologist, measurements will be taken from it, the data will be entered into the exchange card. Measuring the abdominal circumference is a very important point in pregnancy management. Based on this information, as well as based on data on the height of the uterine fundus, the gynecologist calculates the estimated size of the fetus and monitors the dynamics of its growth.
To correctly measure abdominal circumference during pregnancy, you need to carry out the following manipulations:
- empty the bladder (for the most accurate indicators, measurements are taken with an empty bladder);
- take a horizontal position with straightened legs;
- expose the abdominal area;
- Measure using a measuring tape.
Cover the abdomen with a ribbon: at the bottom of the back along the curve of the lower back, and in front at the level of the umbilical cavity.
As already mentioned, belly volume data alone is not enough to fully assess the baby’s growth. Measurements of the size of the uterine fundus are necessary. You need to do the following steps:
- empty your bladder;
- fall onto a horizontal surface;
- Take measurements using a measuring tape.
The measuring device should extend from the beginning of the pubis to the protruding point of the uterine fundus.
Based on the abdominal circumference and the height of the uterine fundus, the gynecologist calculates the estimated weight of the child: multiplies the indicators (OB x VSDM).
How to independently determine VDM?
If you wish, you can find out the WYD on your own. To do this, you need to follow the steps below step by step.
First step. Empty your bladder.
Second step. We return from the toilet, lie down on the bed and straighten our legs.
Third step. We find the point where our uterus ends. To do this, we place our hands on the midline of our abdomen. This should be done in the area of the pubic bone. Slowly move your fingers upward and try to find a place where the density of the abdomen becomes softer. This is where the bottom is located.
Fourth step. Using a simple measuring tape, we determine the distance between the found bottom and the starting point of our research. You are already familiar with the normal indicators for each period.
If the found value deviates too much from the statistical average for your period, this may indicate either the presence of various disorders and deviations (listed earlier) or the initially incorrectly determined gestational age.
Thus, regular monitoring of the dynamics of uterine enlargement allows you to monitor the development of pregnancy and promptly detect various types of abnormalities. Do not ignore this event, go to a consultation with a doctor and follow his recommendations.
Health to you and your child!
Abdominal circumference norms during pregnancy by week: deviations from the norm
During pregnancy, abdominal circumference changes, one might say, from week to week. From the 16th week, with the increase in the size of the uterus, the tummy gradually grows and at the beginning of the 20th week, the gynecologist carries out the first planned measurement of its circumference.
According to generally accepted standards, from the 20th week the volume of the abdomen during pregnancy is 70-75 cm. The average increase in circumference is about 2-3 cm every 14 days. That is, by the 30th week the size of the belly will reach 82-87 cm, and by 36-38 weeks - up to 100 cm.
If the size of the abdomen does not correspond to the duration of pregnancy, anomalies or complications in bearing a child are quite possible.
Increased abdominal circumference rates during pregnancy occur if:
- the amount of amniotic fluid exceeds the permissible norm (occurs due to infection or diabetes mellitus);
- multiple pregnancy;
- large fruit;
- non-compliance with diet and nutrition;
- abnormal position of the fetus;
- narrow hips.
Reduced abdominal volume standards during pregnancy occur when:
- decrease in the amount of amniotic fluid (occurs during post-term pregnancy);
- pelvis too wide;
- malnutrition of the child (lag in growth, weight, development of the baby).
Belly shape
Specialists in the field of gynecology pay attention not only to the size, but also to the shape of the abdomen. The correct shape is very important; it should be ovoid, slightly pointed towards the top for first-time mothers. Multiparous women's characteristics change. The abdomen may be round or even slightly angular, this is due to weak abdominal muscles, a large fetus and polyhydramnios. Carrying a hero by a fragile woman also affects the shape of the uterus. The pear-shaped belly is caused by weak muscles that are unable to withstand the load.
With a narrow pelvis and multiple pregnancies, the abdomen is pointed and the size is correspondingly larger. A small, inconspicuous tummy can signal oligohydramnios.
Lack of symmetry may be a signal of abnormal positioning of the fetus. For example, a transverse position can give an oval shape. All this can be clearly seen in the photo.
From all that has been said, we can conclude that the size and shape of the uterus is a necessary criterion when examining and examining a pregnant woman. With their help, you can identify and prevent the development of defects and stunting in a child.
Abdominal volume during pregnancy by week in the table
It was previously mentioned that an active increase in the size and volume of the abdomen during pregnancy is observed from the 20th week. Every 14 days, the girth of the belly increases on average by 2-3 cm. Thus, the acceptable norm for girth of the abdomen at week 20 is 70-75 cm, before the birth of the child - 95-100 cm. The above figures are not absolute indicators of the volume of the abdomen during pregnancy. In the process of measuring circumference, you should take into account the woman’s build, her shape and tendency to be overweight. Taking into account all factors, it is necessary to monitor the dynamics of abdominal growth and, accordingly, the development of the fetus.
Source: EmpireMam.com
Fundal height of the uterus: what is this indicator?
The height of the uterine fundus is important for assessing the vital activity of the fetus. If any deviations from the norm occur, disturbances during pregnancy can be suspected, which helps to choose the right tactics for further management.
Using data on the abdominal circumference and the height of the uterine fundus, the weight of the fetus can be estimated.
Several formulas are used for calculation:
- Calculation according to Yakubova: (coolant (cm)+VDM (cm))/4*100
- According to Jordania: coolant (cm)×VDM (cm)
- According to Lankowitz: (woman’s height (cm)+body weight (kg)+BW (cm)+WMD (cm))*10
- According to Johnson: (VDM -11)*155
- According to Bublichenko: 1/20*body weight (kg)
At 26-28 weeks the fetal weight is 1,000 grams, at 36 weeks it is about 2,500 grams and by the 40th week of pregnancy it reaches 3,300 grams.
How to measure the height of the uterine fundus?
After registration for pregnancy, weight, blood pressure, and heart rate are checked. From the second trimester, they begin to determine the height of the uterine fundus, abdominal circumference, and listen to the fetal heartbeat.
Measurements are taken while lying on the couch, having previously freed the stomach from clothing. A measuring tape is applied to the upper edge of the pubic joint, and with the edge of the palm of the other hand, the tape is drawn up the abdomen to the highest point of the uterine fundus. Then the measuring tape is moved to the level of the navel and the abdominal circumference is measured.
At the end of the appointment, all the data is indicated in the pregnant woman’s chart, which makes it possible to assess changes and conduct an examination in a timely manner.
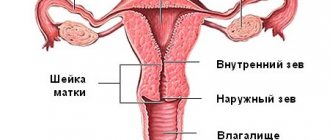
What it is?
The female reproductive organ, which becomes a safe haven for the growing child during pregnancy, resembles a sac. Its lower part is like the knotted part of this bag, it is the narrowest. This is the cervix, which is a round muscle. The widest part of the uterus, the dome-shaped part, is called the fundus. The word “bottom” should not be confusing, because for the growing baby, who will leave the womb during childbirth, this dome-shaped part will really be the bottom. There is only one entrance to the exit hole inside the reproductive organ - this is the cervical canal inside the cervix, and it is located below.
The height of the bottom part of the uterus is a special size that reflects the height to which the bottom part has risen relative to the pubis . Until the end of the first trimester, the parameters of the uterus are small (by the eighth week - no more than a geese egg), and it fits perfectly into the space of the small pelvis.
But the reproductive organ grows quickly, the number of muscle fibers increases, and by the start of the second trimester, the uterus no longer fits in the small pelvis and extends beyond it, into the abdominal cavity, gradually rising upward and supporting the diaphragm. It is for these good reasons that the abdomen grows, its visual enlargement in a woman who is preparing for imminent motherhood.
The height of the fundus of the uterus shows how much its growth corresponds to the gestational age , and to a certain extent this size indicates whether everything is in order for the pregnant woman and her child. That is why, at each consultation visit during all months of pregnancy, starting from 12–14 weeks, the doctor measures the VDM (VSDM) and the circumference (girth) of the expectant mother’s abdomen along the navel line. Based on the ratio of these two values using obstetric formulas, it is even possible to calculate the estimated weight of the fetus. Until a certain time, while ultrasound did not exist, this was the only way to find out whether a woman was going to give birth to a large, normal or miniature baby.
Today, specialists pay less attention to VSDM than before, because there are much more diagnostic tools at the obstetrician’s disposal, and their accuracy is much higher. But this parameter for pregnant women was not completely removed from the protocols of the Ministry of Health and obstetric practice.
The determination of AMD can be done either independently or with the help of an obstetrician-gynecologist. It is not difficult.
Fundal height of the uterus by week of pregnancy: table
From the early stages of pregnancy until the end of the first trimester, the doctor conducts an examination in a gynecological chair. The size of the uterus changes depending on the period. By the 6th week it resembles a large chicken egg, by 8 weeks it corresponds to a goose egg, by the 9th week it resembles a woman’s fist, by 10-11 weeks it resembles a man’s fist, and by the 12th week of pregnancy the uterus increases to the size of a newborn’s head and determined at the edge of the pubic arch.
As soon as the fundus of the uterus rises above the womb, the size of the uterine body can be determined through the abdominal wall.
The table shows the norms for the height of the uterine fundus:
| Obstetrics: | Fundal height of the uterus: | ||
| months | weeks | (cm) | distance |
| 4 | 16 | 6-7 | midway between the symphysis and the umbilicus |
| 5 | 20 | 12-13 | two fingers below the navel |
| 6 | 24 | 20-24 | at the level of the navel |
| 7 | 28 | 24-28 | on two transverse finger above the navel |
| 8 | 32 | 28-30 | midway between the umbilicus and the xiphoid process of the sternum |
| 9 | 36 | 32-34 | at the xiphoid process |
| 10 | 40 | 28-32 | midway between the umbilicus and the xiphoid process of the sternum |
As can be seen from the table, in the 9th month the uterine fundus reaches its maximum elevation. Usually 2 weeks before giving birth, women feel that their stomach has dropped and it has become easier to breathe.
In case of multiple pregnancy, the figures exceed the standards by 4 cm or more. For example, at 5 months the height of the uterine fundus can reach 17 cm.
The height of the uterine fundus does not correspond to the gestational age: reasons
The height of the uterine fundus may be affected by the characteristics of the expectant mother’s body or by an erroneous determination of the gestational age.
But changes may also indicate a pathological process:
The height of the uterine fundus is greater than the gestational age:
- polyhydramnios, accompanied by excess production of amniotic fluid, the volume of which can be 1.5 liters or more. Unfortunately, with polyhydramnios, spontaneous abortion often occurs;
- in cases of post-term pregnancy or diabetes mellitus, a large fetus is often diagnosed;
- when the dimensions of the woman’s pelvis and the fetal head do not coincide, they speak of the presence of a narrow pelvis. The head remains mobile above the entrance, which causes premature rupture of amniotic fluid.
The fundus of the uterus may be below the expected gestational age:
- transverse or oblique position of the fetus;
- chronic placental insufficiency, hypoxia, followed by intrauterine growth retardation and fetal development;
- oligohydramnios, when disturbances occur in the secretion, resorption and exchange of amniotic fluid, the amount of which does not reach 500 ml. In most cases, this type of pathology indicates serious problems with the fetus.
To correctly determine the gestational age, other indicators are also assessed:
- the date of the last menstruation, when the countdown begins two weeks from the first day of menstruation;
- from the 18th week, the woman begins to feel fetal movements, if this is not the first birth, and around the 20th week of pregnancy they appear in first-time mothers;
- Ultrasound examination gives the most accurate result.
Find out why a hemoglobin test is important during pregnancy and how to take it!
Vladlena Razmeritsa, obstetrician-gynecologist, especially for Mirmam.pro
Source: mirmam.pro
Basic information about WYD
The condition of the uterus changes significantly throughout pregnancy. So, in the initial stages, this organ can be felt through the vagina. Already by the 12th week, the uterus is in the area of the pubic symphysis, and from the next week it extends beyond the pelvis and can already be felt with your fingers when palpating the abdominal wall.
To determine the indicator in question, with the patient in a supine position, the length of the gap between the highest point of the uterus and the pubic symphysis is recorded with an ordinary measuring tape. The results of each such test are saved in a notebook, which allows you to evaluate the dynamics of changes in the state of the organ.
In general, the size of the uterus in centimeters usually corresponds to the week of pregnancy: at 8-9 weeks - about 8-9 cm, at 40 - about 40 cm.
If during a certain week the AMR indicator does not coincide with the average normal values, deviating upward, the specialist can assume a multiple pregnancy. If there are deviations in the direction of decrease, delayed development of the fetus and various types of pathologies can be diagnosed, for example, oligohydramnios or incorrect position (transverse, oblique), etc.
It is important that the VDM values are recorded regularly and at approximately the same frequency, because one-time measurements are not informative and sufficient for correct diagnosis of pregnancy.
Important! The given indicators for the height of the uterine fundus are the statistical average. This value may vary depending on different circumstances, for example, in large mothers, the uterus is larger than in miniature representatives of the fair sex, therefore, their UGM indicators will also differ.