Causes of tone
Since the uterus is a muscular organ, it cannot remain in a state of constant relaxation. Tension, even slight, is always present in the uterus. Moreover, if the tone is slightly increased in the area of contact between the wall and the embryo, this indicates that the latter is taking root well.
Minor inflammation may be caused by increased blood flow to that particular area. In this way, the mother’s body supplies the embryo with the substances necessary for its life and development. An ultrasound will characterize this area as edematous, which is understandable and is also considered tone during pregnancy.
The tone can be general, that is, it extends to the entire organ, or local. The latter is divided into hypertonicity along the posterior wall of the uterus and the same condition along the anterior wall.
The muscles of the reproductive organ can be tense for the following reasons:
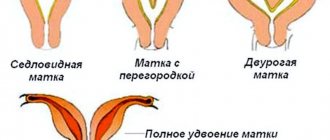
- Uterine pathologies. These include endometriosis and fibroids. Hypertonicity of the posterior wall of the uterus and problems with bearing a child are closely related to the anatomical features of the uterus. It can be saddle-shaped, bicornuate, or have other structural features. Such anomalies can create difficulties in the process of bearing a child;
- Lack of progesterone. Usually triggered by underdevelopment of the genital organs or an abundance of male hormones (androgens);
- Viral infections. They significantly weaken the immune system, which does not have the best effect on the uterus. Infections are accompanied by symptoms such as itching and burning of the external genitalia, qualitative changes in discharge.
- Oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios. The abundance or lack of amniotic fluid equally negatively affects the muscle layer specifically of the posterior uterine wall;
- Stress. They have a detrimental effect on the body as a whole. They weaken the reserves of a pregnant woman’s body, causing the maca to strain unnecessarily;
- Stretching of the uterine muscles. Often occurs in the presence of multiple pregnancies or carrying a large fetus;
- Inflammation in the ovaries or uterus. Such processes can cause alternating tension and relaxation of the reproductive organ;
- Excessive physical activity. They make internal organs tense, the uterus is no exception. Lifting weights or excessive exercise does not have the best effect on the condition of the uterus.
- Different Rh factors in the blood of mother and fetus. In case of Rh conflict, the process of rejection of the fetus by the mother's body may begin. At this time, the tone of the reproductive organ increases significantly.
- Abortions performed by a woman before her current pregnancy can also cause hypertension. This also includes miscarriages and premature delivery.
- Changes in intestinal motility. The latter changes in size due to the accumulation of gases and puts pressure on the body of the uterus, causing tension in its muscles.
What thickness of the myometrium is normal, what deviations are acceptable?
The muscular layer of the uterine wall is called the myometrium. At different stages of the menstrual cycle and during pregnancy, its thickness may change. At the same time, it is important to determine the true cause of the thickening, so as not to miss the beginning of the development of a dangerous pathological process in the body. A common symptom in women is local thickening of the myometrium along the anterior wall of the uterus. Possible changes in the thickness of the uterine wall may be associated with the hormonal status of the woman at the time of the study and other factors that do not always indicate the presence of the disease.
At its core, thickening can be both a gynecological and obstetric indicator. And even endocrinology sometimes plays a role in the development and symptoms of local myometrial thickening.
Thus, thickening is observed during menstruation, and in the subsequent stage of endometrial proliferation it disappears. Such fluctuations are normal, because they are directly related to changes in the level of progesterone and estrogen in the female body. For example, upon the onset of the second phase of the menstrual cycle, the thickness of the myometrium can be 10-14 mm, whereas after the end of menstruation it is already 1-2 mm.
It is clear that during pregnancy, myometrial thickening increases in proportion to the duration of pregnancy itself. This is due to a general increase in the volume of the organ where the unborn baby develops, with physiological changes in accordance with hormonal levels and fetal growth.
Thickening of the uterine wall is an ultrasound indicator and, in addition to physiologically normal thickening during pregnancy, can be detected in the following pathological conditions:
- Threat of miscarriage
- Uterine fibroids at any stage
- Adenomyosis
- Endometritis of the uterus.
Let's take a closer look at these pathologies.
According to objective data, ultrasound in the early stages of pregnancy (in the first trimester) reveals local thickening along the anterior wall of the uterus. If this sign is detected before five weeks of pregnancy, then this is not a pathology and only indicates that implantation of the fertilized egg has occurred and its immersion into the wall.
If, in addition to thickening, hypertonicity of the uterus and a scaphoid or drop-shaped shape of the embryo are detected (which in itself is a pathology), as well as a visible change in the outer contour of the uterus - its raised section of the uterine wall above a flat surface, then they speak of a threat of miscarriage.
The same can be said if the same local thickening of the myometrium is found along the posterior wall of the uterine vault. However, ultrasound data must also be confirmed by an objective study of the woman’s condition and reliable clinical indicators - nagging pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, spotting, as well as additional detection of an area of subarachnoid hematoma during the study. Such a hematoma is formed due to detachment of the ovum.
The video describes uterine fibroids:
Every third woman over 30 years old has myomatous nodules in the uterus. Having different sizes and shapes, they are located in the walls, bottom and dome of the organ. In the body, these nodules are located along the anterior and posterior walls of the uterus. At the onset of atypical growth of myomatous nodes, ultrasound clearly reveals local thickening of the uterine wall.
When fibroids are examined, a lumpy and tense surface is determined, and local compactions are sometimes found. By palpation it is also possible to detect that the thickened posterior wall of the uterus (or anterior) creates an asymmetry of the organ.
Adenomyosis is a common case of inflammation of the uterus, in which the endometrium grows into other layers of the uterine wall. Along with such symptoms of adenomatosis as spotting, irregular menstruation, pain, examination also reveals thickening of the uterine walls, including the posterior wall of the uterus. And, although the term “adenomatosis” is registered in the international histological classification, it can still be regarded as one of the forms of endomeriosis, when serious changes appear in the muscle layer of the uterus.
There is no clear answer to the question of what endometriosis is. The endometrium is the inner layer, lining the wall of the organ. Inflammation and morphological changes in the structure of endometrial tissue are called endometriosis. Until recently, endometriosis was considered a manifestation of various diseases of the genital organs in women, and only very recently it was identified as an independent nosological entity. Despite its wide distribution among women, there are still many blind spots in this disease for gynecologists.
This disease is discussed in more detail in the video:
One of the forms of this disease - internal endometriosis - indicates that the foci of endometriosis are located in the thickness of the endometrium. A common symptom of this condition is local thickening in the area where endometriosis nodes are located along the posterior wall. Malignant neoplasms in the uterine cavity also lead to local thickening. Moreover, in addition to the area of thickening, the asymmetry of the organ becomes apparent due to the development of a tumor in one of the walls of the organ.
As a result, we can say that even in the presence of established local thickening of the myometrium, there is no need to think about bad prognosis. The culprit may be a normal hormonal surge that does not go beyond physiology. By visiting a gynecologist or endocrinologist, it is most often possible to correct a woman’s hormonal levels and, thereby, relieve her of unreasonable fears.
Based on materials from netmiome.ru
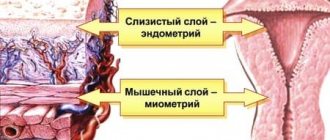
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ, the wall of which consists of several membranes:
- The inner lining is called the endometrium.
- The muscular layer consists of smooth muscle and is called the myometrium.
All layers of a woman’s reproductive organ, which make up her wall, are responsible for a certain role in the process of growth and development, life and disease in women. The endometrium is the internal proliferative layer lining the uterine cavity. The hormonal cycle and its phase determine the degree of endometrial thickening. It is also important to recall why this layer of the uterine wall thickens.
The most important point is pregnancy. The fertilized egg moves through the fallopian tubes into the organ cavity, where the thickened inner layer is ready to receive it for the further development of pregnancy. The fertilized egg is attached to the front wall; localization of the place where the egg is attached to the rear wall is considered more favorable.
Myometrial thickening during pregnancy is normal. Because in order to carry a pregnancy to term and then give birth to a child, you need sufficiently powerful muscle mass for the uterus. Therefore, during pregnancy, thickening of the myometrium of the entire uterus or local thickening of the muscle wall occurs. It should be noted that local thickening is normal only until a short period of pregnancy, up to about 5 weeks. Next, the process of increasing the muscle mass of the uterus should occur evenly throughout the entire organ. You should be very careful about this factor, since the expression: “a disease is easier to prevent than to treat” must always be remembered.
Local thickening of the myometrium can be caused by several factors:
- Pregnancy up to 2 months can be considered a variant of the normal development of pregnancy;
- Hormonal status of a woman. The examination can be repeated or performed on another day of the cycle to exclude the disease;
- Pregnancy after 6 weeks, occurring with pathological abnormalities: pregnancy threatening to be terminated in the early stages, for example.
- Various diseases of the uterus. This includes pathological conditions such as endometriosis, adenomyosis, endometritis, and fibroids.
In the first few weeks of pregnancy, local thickening of the myometrium of the anterior wall of the uterus can often be observed. This condition does not indicate a disease; it only indicates that pregnancy has taken place and the fertilized egg has begun to implant in the thickened inner layer of the uterus. Further, this local thickening of the myometrium of the anterior wall or posterior wall of the uterus in the normal course of events should disappear, and the myometrium will proliferate evenly.
If there is a threat of miscarriage (miscarriage) at a later stage, thickening of the myometrium both on the anterior wall and on the posterior wall of the uterus, as a rule, is combined with uterine hypertonicity. The ultrasound picture of myometrial hypertonicity is characterized by the following factors:
- Local thickening of the myometrium is clearly visible against the background of the pathological shape of the embryo;
- A violation of the contour of the uterus along the outer line is often visible - part of the wall is raised;
- A local thickening of the myometrium is clearly visible on the posterior wall of the uterus.
The woman’s subjective complaints also indicate the presence of a threat to pregnancy and hypertonicity (pathological tension of the muscular frame of the uterine wall) as additional factors to the ultrasound data, which indicate the presence of a threat to pregnancy and hypertonicity (pathological tension of the muscular frame of the uterine wall):
- Frequent aching pain in the lower abdomen.
- Often pain in the lower abdomen is accompanied by pain in the sacrum and lumbar back.
- Vaginal discharge that appears against the background of these pains: bloody or streaked with blood.
Local thickening of the uterine wall (myometrium) is often observed in women in middle age.
This is approximately from 30 to 45 years. The hormonal landscape changes over the course of life, additional diseases, previous operations or pregnancies. All these factors leave traces in the muscle layer in the form of small local thickenings. They have a nodular structure, the location can vary and are found throughout the body of the uterus: on the back wall, the front wall or in the upper part of the uterus. The factor of changes in the intensity of hormone secretion and changes in their ratio depending on the woman’s age must be taken into account and regularly monitored by a specialist. This is necessary in order to promptly notice the development of fibroids in case of possible growth of nodes in the anterior or posterior wall of the uterus. The degeneration of nodular local thickenings into a muscular tumor of the uterus is quite easy to notice with an objective examination. The surface of the uterus becomes noticeably bumpy and uneven. These formations are quite recognizable upon palpation. The woman’s organ loses its symmetrical structure, as either the posterior wall or the anterior wall thickens unevenly, often these changes are local.
Internal endometriosis (adenomyosis) is the most common localization of endometriosis. Clinical manifestations of endometriosis of the uterine body vary depending on the degree of spread of the process into the myometrium. It is usually customary to distinguish the main forms of the disease:
- Diffuse form;
- Focal or nodular form.
In the diffuse form of the disease, a woman complains of bleeding outside of menstruation. The menstruation itself is so profuse that it can take on the character of hemorrhage and is accompanied by painful sensations.
The nodular form of the disease is characterized by almost the same subjective complaints, but an objective examination reveals numerous local thickenings of the myometrium, the uterus is sharply painful on palpation.
Other diseases of women characterized by local thickening of the myometrium may be:
- Endometritis is an inflammation of the inner lining caused by infectious agents;
- Tumor formations of various etiologies. These can be benign as well as malignant.
The detection of local thickening of the uterine wall (myometrium) in itself is not necessarily a sign of pathology, but in combination with the above factors, it can pose a serious threat to a woman’s health.
In order for a woman to feel healthy, it is necessary to regularly see a gynecologist for preventive purposes. This should be done at least once every 6 months, even without any complaints. If there are any signs of the disease: pain, discomfort, itching, discharge, bleeding outside of menstruation, then this is definitely a reason to consult a doctor immediately!
Based on materials from vseomatke.ru
Main features
One of the signs of hypertonicity is pain in the lumbar region
The phenomenon of uterine tone along the posterior wall can be asymptomatic. This pathology can often be diagnosed only after an ultrasound procedure. But sometimes the tone of the posterior wall of the uterus during pregnancy is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- pain in the lower abdomen (similar to menstrual pain);
- lower back pain;
- increased pain due to fatigue or physical overload;
- the reproductive organ is tense and seems to “turn to stone” (this condition most often accompanies the last trimester of pregnancy).
The presence of one or more of these symptoms may indicate the tone of the uterus along the posterior wall, in which case you should immediately consult a doctor. A particularly alarming sign is spotting or heavy vaginal bleeding. When they appear, the woman should immediately call an ambulance and try to calm down as much as possible. At this stage of medical development, doctors often manage to save a child in the womb.
Exercise “Cat” will help cope with tension in the reproductive organ
Attention! Even if the symptoms of hypertonicity were relieved at home, the expectant mother should immediately visit a medical facility. There a full examination will be carried out with further selection of therapeutic methods.
- therapy with hormonal drugs (recommended if the pregnant woman’s body lacks the substances necessary for the child);
- sedatives (calming) drugs;
- treatment with antispasmodics;
- taking medications that contain magnesium;
- bed rest (strict adherence);
Hypertonicity of the uterus along the posterior wall is not always considered dangerous for the mother and baby in her womb. However, a woman should pay close attention to such a diagnosis. Taking care of your health, proper sleep and nutrition, and the absence of stress and bad habits will help your pregnancy proceed easily and calmly. The joy of meeting the baby soon and the unconditional love of a mother for her unborn baby can eliminate all unpleasant symptoms. However, we should also not forget about systematically visiting a doctor to monitor the condition of the expectant mother.
←Previous article Next article →
Local thickening of the myometrium can be either on the anterior or posterior wall. Why is this factor dangerous for pregnancy, and what are the acceptable deviations?
Why does the myometrium thicken?
In some pregnant women, diagnostic studies reveal thickening of the myometrium. In gynecology, the muscular layer of the uterus is called the myometrium. Its thickness varies depending on what stage of the menstrual cycle a woman is at or during pregnancy. To prevent the development of pathological processes, you need to know what caused the thickening of the myometrium.
Quite often, local thickening occurs on the anterior wall of the uterus. This is due to hormonal disorders or gynecological, obstetric and even endocrinological diseases of the woman.
Changes can be detected during menstruation, which gradually disappears. The levels of progesterone and estrogen change, which contributes to normal fluctuations in myometrial thickness.
Thus, phase 2 of the menstrual cycle can affect local thickening of the myometrium up to one and a half centimeters, and after the end of the menstrual cycle the thickness can be only a couple of millimeters.
The myometrium may also become tense due to the duration of pregnancy. This is due to the fact that the fetus is enlarged and hormonal and physiological changes occur. Using ultrasound, you can detect not only normal thickening, but also identify pathologies such as:
- uterine fibroids;
- threat of miscarriage;
- adenomyosis;
- endometriosis.
Why is there a threat of miscarriage?
After an ultrasound examination, which is performed in the first trimester of pregnancy, the specialist records local thickening of the myometrium along the anterior wall of the uterus. The thickening indicates pathological disorders after 5 weeks; before this period, the thickening indicates implantation of the fertilized egg, which is not a pathological process.
The threat of miscarriage may arise due to the following reasons:
- if the embryo has a drop-shaped or scaphoid shape;
- if the uterus is in a state of hypertonicity;
- if the external contours of the uterus are greatly changed.
Adenomyosis and endometriosis
Quite often, adenomyosis develops during inflammatory processes in the uterus. With this disease, the endometrium is able to grow into the layers of the uterine walls. This disease can be identified in the presence of such signs as: discharge, spotting, menstrual irregularities, pain - the study can reveal both local thickening of the anterior wall of the uterus and the posterior one. Adenomyosis is a form of endometriosis in which there is significant impairment of the muscular layer of the uterus.
The endometrium is the lining layer of the uterus. During inflammatory processes, endometrial cells are damaged and endometriosis develops. Previously, medical experts believed that this disease was a sign of certain gynecological diseases. Modern medicine has identified it as an independent nosological unit. One of the forms of this disease is the internal form of endometriosis, which indicates the location of inflammatory foci in the thickness of the endometrium. With endometriosis, there is often local thickening of the myometrium along the posterior wall. This form of thickening can lead to the development of malignant neoplasms of the uterus. In this case, not only thickening is observed, but also a pronounced asymmetry of the uterus due to the development of a lesion in its wall.
What are the dangers of uterine hypertonicity?
Hypertonicity of the uterus during pregnancy requires maximum attention. This is due to the fact that the fetus needs a normal supply of nutrients and oxygen. This significantly affects the further course of pregnancy. Most often, hypertonicity is accompanied by vascular compression, and the importance of these vessels lies in the fact that they contribute to the nutritional and oxygen supply of the fetus. This factor adversely affects the fetus. However, premature birth or miscarriage are not always provoked due to myometrial hypertonicity.
What are the reasons for the development of myometrial hypertonicity? Often these factors include the following:
- When hormonal levels decrease. This condition is especially dangerous for pregnancy up to 10 weeks. This is due to the fact that the placenta is just being formed during this period.
- When androgen levels increase, the myometrium undergoes hypertonicity.
- Diseases suffered during pregnancy. Tumors, inflammations, abortions and infectious diseases also cause increased uterine tone.
- Multiple external factors also affect myometrial tone. These may include malnutrition, lack of sleep, alcoholism, smoking or constant anxiety.
- Another factor in myometrial hypertonicity is underdevelopment of the uterus or its small size.
How to properly prevent myometrial hypertonicity is a question that interests many pregnant women.
To prevent such a condition, even when planning a pregnancy, a woman must be fully examined for all infectious diseases and eliminate existing ones.
Infections during pregnancy are dangerous not only due to hypertension, but also due to much more dangerous actions (during childbirth, a child can acquire many quite unpleasant diseases that cause blindness or even death). In addition to hypertonicity, there is also a condition of uterine hypotonicity, which during pregnancy may not cause any inconvenience, but problems may arise during childbirth.
During pregnancy, a woman should be as nervous and physically overexerted as possible. She better learn not to worry. If the first signs of increased myometrial tone occur, you should not panic, but consult with an endocrinologist and gynecologist.
You should not think that thickening is a consequence of factors only due to the threat of pregnancy; often the cause may be a hormonal surge, which remains within the normal range. Hormonal levels are corrected when visiting a gynecologist or endocrinologist. These doctors prescribe the correct treatment, thanks to which the woman does not have to worry about pregnancy.
Pregnancy is an important period in the life of every woman, however, it is often overshadowed by various troubles and complications. One of these pathological conditions of the expectant mother is thickening of the myometrium, the progression of which can lead to fetal death. That is why it is important to know the reasons for the development of this condition and the symptoms of its manifestation.
Endometrial problems
With the correct hormonal background, the development of the uterine mucosa should proceed according to the following scheme:
For days 1 and 2 - not less than 0.5, but not more than 0.9 cm - the beginning of the bleeding phase, the desquamation stage;
For days 3 and 4 - at least 0.3, but not more than 0.5 cm - regeneration stage;
For days 5, 6 and 7 - not less than 0.6, but not more than 0.9 cm - the beginning of the proliferation phase;
For days 8, 9 and 10 - no less than 0.8 and no more than 1.0 cm;
From 11 to 14 days - no less than 0.9 and no more than 1.3 cm;
From 15 to 18 days - no less than 1.0 and no more than 1.6 cm - the beginning of the secretion phase;
From 19 to 24 days - no less than 1.0 and no more than 2.1 cm;
From 25 to 27 days - no less than 1.0, but no more than 1.8 cm.
If there are violations, then additional research is needed to refute or confirm the deviations. Increased m-echo, what could this mean? If, with an enlarged m-echo, glandular-cystic formations are observed, then this is a sign of benign tumors, if there are oval neoplasms with a distinguishable body and stalk - After menopause, such changes can be attributed to precancerous conditions of the endometrium.
A woman's uterus is pear-shaped. Anatomically, it distinguishes between the neck, body and bottom. When conducting an echographic examination, its size and position relative to the median plane can be determined. The size of the uterus in a nulliparous woman and a woman who has children is different and ranges in width from 34 to 54 mm.
What is M-echo?
Ultrasound of the endometrium of the uterus evaluates its thickness, structure and checks whether the condition of the endometrium corresponds to the phase of the menstrual cycle. This value is usually referred to as M-echo of the uterus. The thickness of the endometrial layer is usually taken to be the maximum size of the anteroposterior M-echo value.
How do the M-echo values of the uterus change?
- During the first two days of the menstrual cycle, the M-echo is visualized into heterogeneous structures with reduced echogenicity. The thickness is 5-9 mm.
- Already on days 3-4, the M-echo has a thickness of 3-5 mm.
- On days 5-7, there is some thickening of the M-echo up to 6-9 mm, which is associated with the course of the proliferation phase.
- The maximum value of M-echo is observed on days 18-23 of the menstrual cycle.
From all of the above, we can conclude that the M-echo of the uterus does not have a constant value, but normally it is in the range of 0.3-2.1 cm.
In total, there are 4 degrees of M-echo of the uterus, each of which corresponds to the state of the endometrium at the moment:
- Degree 0. Observed in the proliferative phase, when the estrogen content in the body is low.
- Degree 1. Observed in the late follicular phase, when the glands become enlarged and the endometrium thickens.
- Degree 2. Reflects completion.
- Degree 3. Observed in the secretory phase, which is accompanied by an increase in the concentration of glycogen in the endometrial glands.
Median M-echo
The median M-echo of the uterus is an important indicator, which is the reflection of ultrasound waves from the walls of the uterine cavity and endometrium.
The median M-echo is determined in the form of a homogeneous hyperogenic structure, which corresponds to the secretory phase of the cycle. This is due to the increased glycogen content in the glands, which occurs as a result of the effects of progesterone.
In order for the fertilized egg to implant normally and pregnancy to occur, it is necessary that the M-echo of the uterus be 12-14 mm. In the case where the M-echo has a lower value, the probability of pregnancy is low, but its occurrence is still possible, which is explained by the individuality of each organism.
Any woman who is concerned about her health should regularly visit a gynecologist and undergo examination. The most accessible and common way to diagnose pathologies of the female reproductive system is ultrasound. The list of mandatory annual ultrasound examinations includes the uterine echo procedure. It will be useful for every woman to know what it is, why such an examination is necessary and how to decipher the norms of a uterine echo.
Ultrasound of the pelvis - 1000 rubles, including ECHO of the uterus - 1000 rubles. Consultation on diagnostic results (optional) - 500 rubles.
Myometrial thickening during pregnancy: normal or pathological?
When talking about local thickening of the myometrium, experts mean increased uterine tone.
One of the components of the uterine layer is the myometrium, the thickness of which can vary depending on the day of the menstrual cycle, as well as in the event of pregnancy. Particular importance is attached to identifying the cause of thickening of the muscle layer, which allows timely detection of pathological changes in a woman’s body.
One of the common symptoms that is detected in females is considered to be a local thickening of the muscle layer along the anterior wall of the uterus. However, often the thickness of the uterine wall is prone to changes under the influence of a decrease or increase in the level of hormones in the female body, or under the influence of other factors. It is for this reason that the detection of thickening of the muscular layer of the reproductive organ does not always signal any pathology.
What is M-echo of the uterus?
Basically, women undergo a thorough diagnosis only if they want to become pregnant or already upon the occurrence of this event, as well as if they suspect the development of a pathological process in the reproductive system. This is very careless about your health. Full control of the reproductive organs must necessarily include M-echo of the uterus.
M-echo of the uterus, or midline echo, is part of an ultrasound examination of the uterus, which evaluates the thickness and structure of the endometrium, the outer layer lining the surface of the uterus. The quality of the endometrium depends on the level of sex hormones in a woman’s body.
Special attention should be paid to the midline echo during reproductive age, but even more careful during menopause, since with the decline of reproductive function the risk of developing cancer increases.
Changes in the myometrium during pregnancy
Doctors diagnosing local thickening of the myometrium when expecting a child indicates that the woman has increased uterine tone. Of course, during the process of childbirth this is considered very important, but in other cases such increased contraction of the reproductive organ is accompanied by unpleasant painful sensations.
Local thickening of the muscle layer during pregnancy is a dangerous pathology that requires increased attention and control.
Hypertonicity of the uterus can result in disruption of the supply of nutrients and oxygen to the baby, as well as an increase in the risk of an unfavorable outcome for the child.
Thickening of the myometrium does not necessarily mean that such a dangerous process will necessarily end in a miscarriage or the onset of labor ahead of schedule. However, medical practice shows that increased uterine tone both along the anterior and posterior walls causes compression of the blood vessels and the result of this is a disruption in the supply of oxygen and necessary elements to the fetus. This means that with this condition of the reproductive organ, the risk of developing disorders in the fetus increases and even its death is possible.
What pathologies does the examination reveal?
Echography is a valuable procedure that can detect serious pathologies of the endometrium at an early stage of development. The main ones:
- Hyperplasia is a benign disease in which the endometrium grows and, as a result, thickens and increases its volume.
- Hypoplasia is underdevelopment of the endometrium, its insufficient growth.
- Endometrial cancer is an extremely dangerous pathology, in most cases affecting postmenopausal women. With timely diagnosis, there is a good prognosis for recovery - 95%.
Causes of myometrial thickening during pregnancy
Local thickening of the muscle layer during pregnancy signals increased uterine tone, and this can occur for the following reasons:
- During pregnancy, there is a change in the level of hormones in the body and this is usually expressed in a decrease in the production of progesterone. This pathological condition is considered especially dangerous in the first weeks of pregnancy, when the process of placenta formation has not yet completed;
- The uterine myometrium may thicken as a result of increased levels of male hormones such as androgens.
Often the cause of increased uterine tone is;
Improper formation of the reproductive organ and its small size can cause local thickening of the muscle layer.
Some risk factors can be identified, the presence of which can provoke an increase in tone in the expectant mother and, accordingly, thickening of the myometrium:
- work in unfavorable production conditions, which manifest themselves in women’s contact with chemicals, long business trips and night shifts;
- the age of the expectant mother has a significant impact on the course of pregnancy and it has been proven that after 30 years, increased uterine tone is diagnosed much more often than at a younger age;
- a woman is constantly in a stressful state;
- alcohol and smoking abuse during pregnancy;
- improper organization of the daily routine, that is, not enough time is allocated for rest and sleep.
- Thickening of the muscular layer of the uterus during menstruation and during the transition to the next stage, when the endometrium is restored, is considered normal. This process is due to the fact that there is an active change in the content of hormones such as progesterone and estrogen.
During pregnancy, a characteristic phenomenon is the thickening of the myometrium in accordance with the gestational age.
This is due to the fact that with the development of the child, intensive growth of the reproductive organ occurs, and there is also a change in hormones in the body of the expectant mother. During pregnancy, thickening of the uterine wall is an ultrasound indicator that can signal that a woman’s body is affected by various diseases:
- increased risk of spontaneous miscarriage;
- progression of uterine fibroids at any stage of its development;
- adenomyosis;
- uterine endometritis.
What does an ultrasound echo of the uterus show, why is it prescribed?
M-echo of the uterus is an indispensable screening for:
- evaluate the structure of the layer lining the uterus;
- measure its thickness;
- check whether the condition of the layer corresponds to the phase of the menstrual cycle;
- assess the readiness of the endometrium for embryo attachment;
- diagnose inflammation and assess its degree of development;
- identify compactions and other neoplasms with abnormal echogenicity;
- eliminate the adhesive process in the premenopausal period.
The state of the endometrium is affected by the phase of menstruation. In the first phase, called the follicular phase, the uterine lining grows under the influence of estrogens. With the release of the egg - the onset of ovulation - comes the second phase of the cycle - the luteal phase. During this period, the endometrium noticeably thickens and develops under the influence of progesterone, which prepares the surface of the uterus for the possible implantation of a fertilized egg. If fertilization does not occur, progesterone and estrogen begin to be produced in smaller quantities, the endometrium is rejected and menstruation occurs. During menopause, such changes do not occur. Knowing these features, you can very accurately identify any abnormalities in the endometriotic layer of the uterus.
Threat of miscarriage
The main method for diagnosing pregnancy is ultrasound, which allows us to identify fetal development and various deviations from standard indicators. Visualization of the fertilized egg with or without an embryo in the uterine cavity is an indicator that the woman has an intrauterine pregnancy. An ultrasound scan in the early stages usually shows local thickening of the muscle layer along the anterior wall of the uterus.
Identification of this sign in the early stages of pregnancy is an indicator of successful implantation of the fertilized egg and its immersion into the uterine wall.
In the event that the fertilized egg is attached outside the uterine cavity, its visualization in this case is difficult and is an indicator of the development of an ectopic pregnancy.
One of the signs of possible danger of termination of pregnancy may be:
- hypertonicity of the reproductive organ;
- the embryo has a lid-shaped or teardrop-shaped shape;
- changes in the external contour of the uterus are clearly expressed, that is, there is a raised portion of the wall above the surface;
- adenomyosis.
One of the dangerous and unpleasant pathological conditions of the uterus is adenomyosis, which is accompanied by the development of an inflammatory process and the germination of the endometrium into other uterine layers. The main signs of this pathology are:
- the appearance of bleeding during the intermenstrual period;
- pain in the abdominal area;
- thickening of the posterior wall of the uterus.
Experts classify adenomyosis as a form of endometriosis, the progression of which causes significant changes in the myometrium.
One of the most dangerous forms of this pathology is internal endometriosis, in which the affected areas are localized in the thickness of the endometrium. Most often, the main symptom of such a pathological condition is local thickening at the site of localization of endometriotic nodes along the posterior wall. In addition, local thickening of the muscle layer develops when the uterine cavity is damaged by malignant neoplasms. This pathological process leads to the development of asymmetry of the reproductive organ as a result of the appearance of a tumor on one of the walls of the uterus.
Increased uterine tone, which is accompanied by thickening of the myometrium, is a dangerous pathological condition of a woman.
Its development in the female body can lead to unpleasant consequences, and even the loss of a child. Experts have their own point of view on this matter, and they believe that an important place in pregnancy planning should be given to preventive measures to prevent local thickening of the myometrium.
In order to give birth to a healthy baby and not encounter various complications during labor. Even at the stage of pregnancy planning, it is important to be examined for the presence of various infections in the body and consult an endocrinologist about the state of your health. During pregnancy, it is necessary, if possible, to avoid high mental and physical effects on the body and, at the first signs of increased uterine tone, seek help from specialists. Today, this pathology is successfully treated, but the main thing in this case is timely access to doctors.
Pregnancy is an important event in a woman’s life, but often during its course a pathology such as increased myometrial tone is diagnosed. It is important to know the symptoms of this pathology and the possible causes of its development. Timely consultation with a doctor will help avoid various complications.
Myometrial structure
The muscular wall of the uterus has a complex structure. It consists of several layers:
- Circular (vascular). Consists of rings of pipes. There are many vessels included. The strongest layer of the uterus.
- Longitudinal (subserosal). Includes longitudinal and circular muscle fibers.
- Submucosal. Consists of longitudinal homogeneous fibers. The most fragile of all layers.
This structure helps the uterus to contract well during childbirth and push out fluid during menstruation. The frequency of contractions is regulated by female sex hormones - oxytocin and estrogen. The structure of the muscular uterine wall is examined with ultrasound, but if this does not show a clear picture of the state of the uterine cavity, then the method of hysteroscopy can be used.
Causes of development of myometrial hypertonicity and treatment methods
The causes of hypertension during pregnancy may lie in structural changes in the uterine wall
Pregnancy is the most long-awaited and exciting event for a woman, but its course is often overshadowed by various diseases. Often, when visiting a gynecologist, you can hear such an unpleasant diagnosis as “myometrial hypertonicity,” which causes a lot of worry and anxiety in the expectant mother. Most often, the specialist decides to place the pregnant woman in a medical institution to undergo appropriate treatment or assigns strict adherence to bed rest at home.
What is actually dangerous about myometrial hypertonicity during pregnancy that such drastic measures are required? In fact, increased myometrial tone during pregnancy is considered a dangerous pathological condition that requires increased attention. This is explained by the fact that the supply of sufficient nutrients and oxygen to the developing fetus, as well as the favorable end of pregnancy, subsequently depends on this.
Features of the pathology
From a biology course we know that the uterine cavity is lined with three layers:
- endometrium;
- myometrium;
- parimetry.
The endometrium is the layer that covers the surface of the uterus from the inside, and the parimetry is a serous film lining the outside of the reproductive organ. However, the most important and complex layer is the myometrium, which is characterized by muscle contraction, which plays a huge role in the successful completion of labor. If during pregnancy such increased muscle tension is diagnosed before the due date, then experts talk about a pathology such as hypertonicity. This pathological condition of the female body causes increased pressure in the reproductive organ and the result of this phenomenon can be the premature onset of labor.
However, diagnosing such a pathology does not necessarily lead to the onset of premature labor or miscarriage, since there are cases of favorable pregnancy outcomes. Most often, increased myometrial tone along the anterior or posterior wall ends with a disruption in the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the fetus, which can negatively affect its further development.
Reasons for the development of pathology
Today, increased myometrial tone can develop for various reasons.
Reasons for the increase
Most often, the development of hypertension is observed as a result of changes in a woman’s hormonal levels, that is, a decrease in progesterone levels.
This disorder is especially dangerous at the very beginning of pregnancy, when the final formation of the placenta has not yet occurred. In addition, the following causes of pathology can be identified:
- Myometrial tone can increase when a woman’s production of the male sex hormone, androgen, increases;
- often experts diagnose hypertonicity with underdevelopment of the reproductive organ and its small size;
- increased uterine tone can be diagnosed when the expectant mother’s history includes various inflammatory diseases of the uterus or malignant neoplasms.
- tone can increase under the influence of various stressful situations, constant anxiety, smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
- uterine fibroids cause hormonal imbalance in the female body and tone is often diagnosed precisely with this pathology;
Local hypertonicity occurs predominantly in endometriosis, when pathological cells cause structural changes in muscle fibers.
Often doctors are faced with such a pathological condition of the female body as uterine hypotonicity. During pregnancy, such a pathology does not pose any significant threat to the woman and the baby, however, if this condition develops during labor, various kinds of complications may arise.
Risk factors
In addition to the reasons that lead to increased myometrial tone, risk factors can be identified. Most often, experts diagnose pregnancy failure in the presence of certain medical factors:
- identifying various pathologies during pregnancy;
- genetic predisposition;
- diseases of various types in the genital and internal organs;
- progression of inflammatory processes in the reproductive system;
- thyroid diseases;
- harmful production, that is, an increase in the tone of the uterus can occur with constant interaction of a woman with harmful substances, with heavy physical labor and daily work;
- The age of the pregnant woman plays an important role, since doctors note that after 35 years, women become susceptible to uterine hypertonicity;
- irrational organization of her daily routine, that is, the woman does not get enough rest.
Myometrium
The myometrium is the muscular (middle) lining of the uterine wall. In a normal state, the myometrial muscles are in a calm, relaxed state, but as a result of the influence of various factors, their tension may increase, i.e. the occurrence of uterine hypertonicity.
In some cases, contraction of the myometrium is necessary (for example, during childbirth or during menstruation), but in other cases, this condition may be a sign of poor women's health.
Hypertonicity of the uterus can lead to uterine bleeding when the hormonal balance changes, including during menopause, and can also cause miscarriage or premature birth of a child.
information The activity of the myometrium is most influenced by the content of hormones in a woman’s body, in particular estrogen and oxytocin.
Myometrium during pregnancy
The appearance of myometrial hypertonicity during pregnancy is one of the important reasons requiring immediate consultation with a doctor.
Despite the fact that increased uterine tone does not always lead to miscarriage or premature birth, this condition is accompanied by compression of the vessels supplying the fetus with nutrients and oxygen, which negatively affects its development.
Myometrial hypertonicity during pregnancy can occur as a result of exposure to the following factors:
- a decrease in progesterone levels during the first 10 weeks of pregnancy (during the period when the placenta is not yet fully mature for independent functioning);
- increased levels of androgens (male sex hormones);
- inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs;
- stress and strong feelings;
- infantility (underdevelopment) of the uterus.
To prevent the occurrence of myometrial hypertonicity during pregnancy, it is recommended:
- determining the level of hormones in the body at the stage of pregnancy planning;
- timely detection and treatment of inflammatory processes in the female genital area;
- refusal of artificial termination of pregnancy;
- reducing stress and anxiety by teaching relaxation techniques and avoiding conflicts.
Conclusion
dangerous If any signs of increased uterine tone appear, the expectant mother should stop doing any work, call an ambulance or a doctor and remain in a horizontal position until the doctors arrive.
In a medical facility, the pregnant woman will receive the necessary assistance, which will help reduce the risk of miscarriage or premature birth.
The main factor contributing to the normal course of pregnancy is maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Thanks to proper nutrition, giving up bad habits and ensuring sufficient physical activity, the hormonal balance in the female body is normalized and the likelihood of having a healthy baby increases.
Source: https://baby-calendar.ru/mama/miometrij/
Symptoms of pathology
In modern medicine, uterine hypertonicity is divided into:
- local increase in myometrial tone, that is, muscle tension in a separate area of the myometrium occurs;
- a general increase in uterine tone is a tension of the entire myometrium.
The following zones of occurrence of hypertonicity in the cavity of the reproductive organ are distinguished:
- An increase in myometrial tone along the posterior wall causes the following symptoms:
- severe nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- pain in the lower back;
- bloody vaginal discharge
- An increase in tone along the anterior wall causes severe pain in the lower abdomen, which is accompanied by severe tension. Increased tone of the uterus along the anterior wall at the end of pregnancy can lead to slower fetal movements. This pathological condition often ends in spontaneous miscarriage.
The back wall is the location of large blood vessels through which nutrients are supplied to the baby. If the myometrium is tense, they are compressed, and the result is fetal hypoxia. Often, increased tone of the uterus along the anterior wall can occur with any external irritation that affects the abdominal cavity.
Features of pathology treatment
Many believe that the spasmodic state of the uterus is the main reason for the development of premature labor and miscarriage, and various abnormalities can be observed during pregnancy.
However, uterine hypertonicity does not always require treatment and is most often resorted to when there are symptoms such as:
- shortened neck and a threat to its opening;
- the appearance of spotting discharge;
- painful sensations in the abdominal area.
If such symptoms are absent, then no special treatment is required. If an increase in the tone of the uterus of a physiological nature occurs, it can be eliminated by simply relaxing the facial muscles and resting on the side. Another relaxing exercise that doctors advise to do if the uterus has high tone is getting on all fours and gently arching your lower back.
When deciding on special treatment for such a pathology, antispasmodic medications are most often prescribed. These remedies do not eliminate the possibility of miscarriage, but they do allow you to get rid of unpleasant symptoms. If there is a history of premature birth, a drug such as Utrozhestan is prescribed.
Complications of pregnancy
Increased tone during pregnancy leads to the progression of such a dangerous condition as fetal hypoxia. With this pathological condition, a narrowing of the lumens of the uterine vessels is observed and an insufficient amount of oxygen reaches the child, and this ends in a violation of the uteroplacental blood flow.
Hypoxia can cause the development of various types of abnormalities in the baby and malnutrition.
If no effort is made to eliminate hypertension, this may result in premature onset of labor or spontaneous miscarriage. Today, increased uterine tone can be successfully treated and this helps prevent the development of many complications. The most important thing in such a situation is a timely visit to a specialist for medical help.
Thickening of the uterine wall, what is it? Thickening of the uterus, or in other words, hyperplasia of the myometrial or endometrial layer, is a pathological process of proliferation of uterine structures at the level of the muscular layer (myometrium) or endometrial mucosa.
The pathology is of a polyetiological nature. Many factors play a role in its development, including the hormonal profile. The disease occurs (relatively speaking) in all categories of the female population, regardless of demographic characteristics. However, most often (in 55% of cases) thickening of the walls of the uterus develops in women over 60. What do you need to know about such a problem?
Factors in the development of the disease are multiple. Among them:
- Narrowing of the cervical canal of the cervix. The cervical canal is designed to protect the anatomical structures of the organ, as well as remove menstrual fluid. Otherwise, backflow (reflux) of blood into the uterus occurs. In the long term, this can lead to the development of endometrial hyperplasia due to toxic damage to the body.
- Traumatic lesions of the pelvic organs, including uterine perforation. First of all, the uterus itself. Similar damage is observed during curettage, surgical abortion, hysteroscopy, polypectomy, and other surgical and minimally invasive procedures. Particularly dangerous are operations using abdominal access, which are accompanied by excision of the muscular layer of a hollow organ.
- Insertion of intrauterine devices. During its existence in the cavity of the organ, the spiral can oxidize, poisoning the body.
- Burdened heredity. The condition described is not directly inherited, but the characteristics of the reproductive and other systems are transmitted. According to recent studies, if there was a woman in the ascending line who suffered from thickening of the organ wall, the risk of developing a similar pathology is up to 25-30%, and in the presence of two or more relatives - 35-45%. However, this is not an axiom. It is possible to eliminate unfavorable factors by observing preventive measures.
- Problems with the menstrual cycle. Directly indicate various endocrine pathological processes.
- Physical inactivity. It affects the condition of the hollow organ in a negative way, since circulatory disturbance occurs. This can result in either dystrophy or the development of a secondary vascular network and hypertrophy of the organ.
- Inflammatory diseases of the myometrium and hollow organ in general. Endometriosis and endometritis also have an effect.
- Late labor, excessively active labor in the process of resolution, uterine ruptures and scars.
- Adenomyosis. Germination of the internal structures of the uterus into its other layers. This process is most characterized by thickening of the posterior wall of the uterus and its anterior wall.
- Myoma. It is a benign nodular muscle tumor. It has no tendency to malignancy, but causes compensatory growth of the walls of the organ.
- There is a threat of miscarriage.
- Endocrine pathogenic processes. Like diabetes, thyrotoxicosis, hypogonadism.
These are the main reasons for the formation of the condition.
Normal size of the uterus in women: table based on ultrasound during pregnancy and after childbirth
For women's health, you need to take care of your body. This especially applies to the uterus. This organ is responsible for bearing a child, and if abnormalities, infections or pathologies occur, it is necessary to undergo timely treatment.
A woman needs to know about her body, and what sizes of the uterus are normal, and what sizes indicate problems with the health of the reproductive organ.
Concept of a woman's uterus
The uterus is an important female reproductive organ, which is responsible for bearing a child. It is in this environment that the implantation of the embryo and its development occur. The location of the reproductive organ is in the pelvic area.
Its structure and main functions
The uterus is shaped like a pear. Its peculiarity is compression in the front and back.
Structure of the uterus:
- At the back it is adjacent to the rectum. The front is covered by the bladder. It is held between these organs by strong flexible ligaments. They are penetrated by a network of blood vessels and nerve endings.
- The uterus has three openings or exits. From below, the cervix passes into the vagina. At the location of the bottom of the organ there are exits to the right and left fallopian tubes.
- The bottom of the reproductive organ is located above the line where the fallopian tubes exit. The body itself has the outline of a triangle. They taper as they become the round cervix. It is an extension of the body.
- The cervix has a third of the length of the entire organ . The outer end exits into the upper part of the vagina. This segment is called the supravaginal part. There are edges on the back and front walls. They separate them from each other.
- The visible part of the cervix in the vagina is covered with epithelium . This part contains an important zone in which inflammation processes can occur. The ecclesiastical canal has a mucus plug. A secret comes out of it. It prevents viruses and infections from entering the uterine cavity.
The structure of the walls of the uterus is presented in the form of three layers of tissue:
- The mucous membrane, which is the inner layer.
- Muscle tissue that forms the middle layer.
- The serosa is the outer layer of the reproductive organ.
The uterus in the female body has the following important functions:
- Protection of the genitals and peritoneum from infections that can come from the vagina.
- Cleansing the vagina and uterus of dead tissue or blood cells through menstruation.
- Creates conditions for sexual intercourse and transports sperm to the fallopian tubes.
- Creates conditions for the development of the embryo and implantation of a fertilized egg into the uterus.
- Strengthens the pelvic floor.
What is ultrasound used for?
The use of ultrasound helps to distinguish the 3 layers of the uterine cavity. Doctors usually pay attention to endometrial tissue. It is he who is updated monthly when a woman gets her period. During pregnancy, a fertilized egg is located in this layer.
It is the violations in the structure of the endometrium that will help determine the use of ultrasound. Ultrasound examination reveals muscle tissue and allows you to detect a violation in its layer.
Types of examinations for women
A woman seeks help from a gynecologist when unusual abnormalities appear in the menstrual cycle or when planning pregnancy.
When diagnosing a problem, a specialist may resort to the following examinations:
- Manual examination;
- Examination using a gynecological speculum;
- Smear analysis for vaginal microflora;
- Analysis of material to identify viruses and infections;
- Colposcopy;
- Ultrasound examination;
- Hysteroscopy and laparoscopy;
- Taking blood for hormone analysis.
The size of the uterus is normal according to ultrasound during reproductive age
The normal uterine size indicators for each nulliparous woman look different. It is individual in nature. It all depends on the size of the organ. This is considered a third of the length of the uterus.
Basic indicators
The following factors can influence the indicators:
- Endocrine system disorders;
- Number of times of conception, pregnancy and past births;
- Individual indicators of a woman’s body;
- Phases of the menstrual cycle.
Indicators during menstruation can fluctuate from the beginning of the cycle to the end. The minimum values may be on the first day, and the maximum on the last. Normal condition during ultrasound examination of the uterus, the thickness of the mucous membrane depends on the menstrual cycle. On days 5 or 7 this figure does not exceed 6 mm. After two weeks it increases from 7 to 14 mm.
Uterus dimensions
| Group of women | Length, mm | Width, mm | Thickness, mm |
| Women of reproductive age | 47 | 35 | 50 |
| Women who have not given birth but were pregnant | 54 | 38 | 55 |
| Women after childbirth | 61 | 42 | 60 |
The size of the uterus is normal according to ultrasound during menopause
During menopause, women are prescribed an ultrasound of the reproductive organ. This examination is standard for diagnosing pathologies. This method provides fairly accurate information. The ultrasound method is considered safe and women do not dislike the process.
Dimensions
| Period | Length, mm | Width, mm | Thickness, mm |
| First 5 years | 56 – 58 | 30 – 32 | 41 — 42 |
| After 5 years | 51 – 54 | 26 – 28 | 37 – 39 |
Permissible deviations from the norm
The gynecologist usually evaluates the deviation from the normal size of the reproductive organ and prescribes an ultrasound examination on the first day of menstruation.
Deviations in women can be presented in a table
| Length deviation | Width deviation | Thickness deviation | |
| Women of childbearing age, during pregnancy and childbirth | 3 mm | 6 mm | 2 mm |
| During menopause | Length deviation | Width deviation | Deviation of anteroposterior size |
| Before 5 years and after 5 years | Up and down by 30 mm |
Reasons for changes in the size of the uterus When the length, width and thickness of the reproductive organ begins to change, then first of all they talk about reproductive function:
- Girls under 1 year of age have a uterus size of up to 4 cm.
- Afterwards the organ is reduced in size by 2 times.
- The uterus remains in this state for up to 7 years.
- Afterwards, until puberty, it increases and stabilizes.
- Subsequently, serious changes in the uterus occur with pregnancy.
Then it stretches and contracts after childbirth. Small increases before pregnancy may occur for normal reasons. - Menopause or menopause in women also causes changes in the size of the uterus.
During this period, female sex hormones, progesterone and estrogen, are not able to be produced by the body in the required quantities.
What does a reduced uterine size mean?
When specialists, based on ultrasound results, observe small indicators of the size of the uterus, they indicate the presence of a small reproductive organ.
There are several stages when deviation from the norm may appear in a reduced form:
- The hypoplastic stage indicates a normal state of the uterus, which corresponds to adolescence.
- The infantile stage usually manifests itself in a child, but if it occurs in an adult woman, this indicates a deviation.
- The aplasia stage manifests itself in a teenager, the uterus develops like that of a small child.
When the reproductive organ is underdeveloped, the following symptoms may occur:
- Menstruation came at the age of 16 years;
- Late puberty;
- Girls suffer from signs that are not typical for their body;
- There is no menstrual cycle or it is not constant;
- Conception cannot be achieved for a long time.
A small uterus is a problem that is associated with underdevelopment of the reproductive organs. In order to conceive, a woman will have to take a lot of effort.
What does an increased size of the uterus indicate?
When experts discover deviations from the normal size of the uterus in women, this negatively affects their health.
An enlarged condition may be normal in the following cases:
- When does puberty occur?
- The moment of the beginning of pregnancy.
- After childbirth, for some time.
When a woman has an enlarged uterus, this may indicate the occurrence of pathological processes.
This condition can be caused by:
- Uterine fibroids cause benign formations.
- A uterine cyst is a pathological formation in its tissues.
- Formations in the form of cancerous tumors.
- Proliferation of the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity.
- Disturbances in the endocrine system.
During this time, women experience the following symptoms:
- Feeling of pain in the lower abdomen.
- Frequent urination or urinary incontinence.
- Disruption of the menstrual cycle, and they become abundant.
- The total weight increases.
- Headaches occur.
Size of the uterus during pregnancy and after childbirth
During an ultrasound examination and detection of pregnancy, the size of the reproductive organ will increase. The main indicator at this moment is the length of the uterus.
The gynecologist monitors her indicators starting from the 3rd trimester. Before this period, the size of the uterus is checked by manual examination or ultrasound examination using a vaginal probe.
A specialist is able to determine the gestational age by the size of the reproductive organ. He is able to detect abnormalities using the size of the uterus. The gynecologist is able to use palpation to determine how the organ will increase further.
This happens when a woman begins her 3rd month of pregnancy. With each week, 1 cm is added to the previous size. At the time of birth, this figure can reach up to 40 cm.
If a slight deviation from the norm occurs, this is not a pathology in all cases. The indicators for each woman are individual and if they are good enough, the specialist recommends undergoing a preventive examination once a year.
Symptoms
Symptoms of hyperplasia are numerous. It all depends on the intensity of the process, its nature, as well as the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. Thickening may occur without visible manifestations. Among the characteristic features are:
- Pain syndrome . Localized in the lower abdomen. The intensity of pain varies: from minor discomfort to unbearable pain. Patients characterize the discomfort as “aching”, “pulling”, “shooting”. The syndrome radiates to the legs, groin area, navel, lower back.
- Menstrual cycle disorders, while periods themselves can become either too frequent or too rare. The duration of the menstrual cycle also increases dramatically.
- Bleeding of unknown origin. Typically, the amount of blood is minimal, but this is a warning sign.
- Intense premenstrual syndrome with irritability, headaches, and abdominal and chest pain.
- Intermenstrual discharge of unusual consistency or character. Usually with an unpleasant odor.
Symptoms develop simultaneously, which is typical for problems with the reproductive system.
Diagnostics
A consultation with a gynecologist is mandatory. During the initial examination, anamnesis is collected (the doctor finds out what diseases the patient and her relatives have suffered or are suffering from), and an oral questioning of the patient about complaints, duration, type and nature.
It is necessary to conduct a bimanual examination and examination using mirrors. In the following, the following specialized manipulations are shown:
- Ultrasound examination of the uterus and
- Anti-inflammatory drugs of non-steroidal origin, if adenomyosis occurs.
- Birth control pills.
- If hormonal disorders occur, the use of synthetic progesterone substitutes is indicated.
- In case of intense bleeding, surgical intervention is performed to achieve hemostasis and remove the abnormal layer of the endometrium or myometrium.
Painkillers based on metamizole sodium.
What affects the results of M-echo
Various factors, in addition to age and phase of the menstrual cycle, influence changes in the thickness and structure of the endometrium:
- hormone therapy;
- the onset of pregnancy (in the last week of the cycle the endometrium can thicken up to 22 mm, while the fertilized egg has not yet had time to descend into the uterus from the fallopian tube);
- recent birth;
- recent ;
- pathologies of the uterus (hyperplasia, etc.).
For this reason, only a specialist can accurately and reliably evaluate the results of an M-echo of the uterus, taking into account the patient’s medical history and make a correct diagnosis.