Thickening of the uterine wall does not always indicate a serious pathology. In some cases, this is due to hormonal changes. To determine the real cause of the thickening, a detailed examination should be performed. Often, wall thickness is detected during ultrasound, hysteroscopy, and MRI. An ordinary examination by a gynecologist is not a diagnostic method for thickening, since the doctor cannot visually determine the exact size of the deviation from the norm.
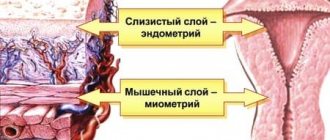
The walls of the uterus are divided into three layers in their structure. The inside of the organ cavity is covered with a mucous membrane; the outside of the uterus is covered with a serous layer. Between them is the myometrium, a muscle layer that is of great importance for many functions of the female body. It is responsible for the contraction of the uterus during and after childbirth, as well as during menstruation. The endometrium, that is, the inner layer, has certain functions during ovulation, menstruation, and in the first days of pregnancy.
When the wall thickens, we are usually talking about an increase in the muscle layer; such changes (often in the anterior wall) can accompany menstruation or pregnancy, but if the increase in thickness is significant, then you should think about a more thorough examination to prevent dangerous pathologies.
Causes of the disease
According to medical data, thickening of the walls of the uterus occurs during the following processes in the female body:
- adenomyosis;
- myoma;
- threat of miscarriage;
- endometritis.
Adenomyosis is an inflammatory disease characterized by the growth of the inner layer of the uterus into its other membranes. In this case, the woman suffers from pain, discharge, and irregular cycles. Thickening will be observed not only in the front, but also in the back wall. Complications of adenomyosis include tumors and infertility.
Myoma is a benign neoplasm that occurs in the myometrium.
Accounts for 12-25% of all diseases in the field of gynecology. Most often, fibroids appear during menopause. The woman experiences cramping pain, pressing sensations, and bleeding occurs, sometimes leading to anemia. The functions of the rectum and bladder may be impaired. Myoma often leads to infertility.
The reasons for the threat of miscarriage vary. These include bad habits of the expectant mother (especially smoking), physiological problems, excessive exercise, and the use of drugs, creams, and medicines prohibited during pregnancy. It happens that the threat does not affect the further bearing of the child, and everything ends well. But this is too serious a disease that threatens the life of the unborn baby, so it is necessary to take all measures prescribed by the doctor in a timely manner to preserve the pregnancy.
Endometritis is inflammation in the inner, mucous layer of the organ. It causes fever, purulent discharge, nausea, weakness, pain, and vomiting. The endometrium thickens, calcification and fibrosis appear in it. The menstrual cycle is disrupted.
Return to contents
Reasons for the development of pathology
Today, increased myometrial tone can develop for various reasons.
Reasons for the increase
Most often, the development of hypertension is observed as a result of changes in a woman’s hormonal levels, that is, a decrease in progesterone levels.
This disorder is especially dangerous at the very beginning of pregnancy, when the final formation of the placenta has not yet occurred. In addition, the following causes of pathology can be identified:
- Myometrial tone can increase when a woman’s production of the male sex hormone, androgen, increases;
- often experts diagnose hypertonicity with underdevelopment of the reproductive organ and its small size;
- increased uterine tone can be diagnosed when the expectant mother’s history includes various inflammatory diseases of the uterus or malignant neoplasms.
- tone can increase under the influence of various stressful situations, constant anxiety, smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
- uterine fibroids cause hormonal imbalance in the female body and tone is often diagnosed precisely with this pathology;
Local hypertonicity occurs predominantly in endometriosis, when pathological cells cause structural changes in muscle fibers.
Often doctors are faced with such a pathological condition of the female body as uterine hypotonicity. During pregnancy, such a pathology does not pose any significant threat to the woman and the baby, however, if this condition develops during labor, various kinds of complications may arise.
Risk factors
In addition to the reasons that lead to increased myometrial tone, risk factors can be identified. Most often, experts diagnose pregnancy failure in the presence of certain medical factors:
- identifying various pathologies during pregnancy;
- genetic predisposition;
- diseases of various types in the genital and internal organs;
- progression of inflammatory processes in the reproductive system;
- thyroid diseases;
- harmful production, that is, an increase in the tone of the uterus can occur with constant interaction of a woman with harmful substances, with heavy physical labor and daily work;
- The age of the pregnant woman plays an important role, since doctors note that after 35 years, women become susceptible to uterine hypertonicity;
- irrational organization of her daily routine, that is, the woman does not get enough rest.
Treatment of pathology
You cannot choose therapy on your own. Diseases of the female reproductive system should be treated exclusively by an experienced gynecologist.
For adenomyosis, painkillers and contraceptives are prescribed (to reduce pain and bleeding). A special intrauterine device alleviates the unpleasant symptoms, but after its removal everything repeats.
In severe cases, surgery is necessary. If the bleeding is too severe, uterine fibroids are also observed, and if the woman does not plan to have any more children and is over the age of 45, then the uterus can be removed.
Hormonal drugs are used to treat fibroids. But they have only a temporary effect, and after the completed course of therapy, the growth of pathological nodes resumes. Doctors perform uterine artery embolization as an alternative to surgical treatment. But still, most women agree to the operation.
For endometritis, vitamin therapy, immunomodulators, and antibiotics are used. Curettage is prescribed when the uterus is not cleared after childbirth or abortion. In addition, physiotherapy is a method of treating endometritis.
Return to contents
Local thickening of the uterus during pregnancy. Causes and treatment of thickening of the uterine wall
Thickening of the wall of the main reproductive organ - the uterus - occurs in women of various age groups. The cause of myometrial compaction of varying localization and extent is hormonal imbalance, the etiology of which is considered to be several factors.
Thickening of the uterine layers is associated with certain clinical symptoms that significantly change the general condition of the fair half of the population. Various medical fields are busy searching for the most effective method of eliminating this gynecological problem.
The cervix is normal
To understand whether the cervix has become lumpy or not, it is necessary to regularly conduct self-examination on different days of the cycle. During pregnancy, the surface and condition of the organ may change.
In the absence of serious diseases, the cervix should feel smooth to the touch.
Normal state of the organ surface:
- During ovulation, organ tissues soften, become loose and moist to the touch,
- immediately before menstruation, the cervix is hard and dry, drops low, in women who have given birth, the pharynx may be slightly open,
- during pregnancy, the cervix should be firm to the touch, located high from the vaginal opening by the end of the first trimester,
- softening of the cervix and its dilatation in pregnant women indicates the development of cervical insufficiency or the onset of labor.
The cervix of nulliparous women always feels smoother and harder to the touch; surface changes occur after childbirth or abortion and consist of scarring. It is scars that most often make the cervix lumpy to the touch.
Ultrasound of the uterus and ovaries against the background of various diseases
Uterine fibroids are manifested on ultrasound by an increase in the overall size of the uterine body, a change in its contours, as well as the presence of a node in the myometrium (hyperechoic zone). https://www.sitemedical.
ru/content/%D0%BE%D0%B1%D1%8A%D1%8F%D1%81%D0%BD%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%B5-%D0%BC% D0%B8%D0%BE%D0%BC%D1%8B-%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%B8%D1%87%D0%B8%D0%BD%D1%8B-%D1%81% D0%B8%D0%BC%D0%BF%D1%82%D0%BE%D0%BC%D1%8B-%D1%87%D0%B5%D0%BC-%D0%BE%D0%BF% D0%B0%D1%81%D0%BD%D0%B0-%D0%BC%D0%B8%D0%BE%D0%BC%D0%B0-%D0%BB%D0%B5%D1%87% D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%B5.
Complications and prognosis
A disease such as adenomyosis has its consequences. It leads to iron deficiency anemia, manifested by fainting, headache, memory loss, and decreased performance. In addition, nearby organs may be involved in the pathological process. The saddest complications of adenomyosis are the development of malignant neoplasms and/or infertility.
Uterine fibroids have a favorable prognosis with timely treatment. But in its advanced form it is the cause:
- necrosis of myomatous node;
- anemia;
- infertility;
- pregnancy failures;
- bleeding after childbirth;
- hyperplasia;
- cancer.
Today, young women are increasingly affected by fibroids, although 20 years ago this disease was considered typical for patients over 40 years of age.
Endometritis is a serious pathology, but after proper treatment, 90% of patients can become pregnant. Complications of endometritis include:
- parametritis;
- adnexitis (inflammation of the appendages);
- sepsis;
- pelvic pain (pelvic pain syndrome);
- pregnancy failures;
- infertility;
- cycle disorders;
- thrombophlebitis (a dangerous disease that sometimes leads to death).
Thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities and pelvic veins threatens pulmonary embolism, which, in turn, often causes death in patients. This usually occurs after operations under general anesthesia.
Infertility is not curable in all cases, even at a young age.
Often its cause lies in visiting a doctor too late, or insufficient attention to one’s health. Women think about the reproductive function of their own body only when they have already decided to have a child, but sometimes it turns out that treatment should have been carried out 5 or more years ago. Expensive surgeries or artificial insemination do not always help. Surrogacy is not practiced in the CIS countries.
Content
The uterus consists of three layers: serous, muscular and mucous membranes. As a rule, when we talk about thickening, we mean changes in the endometrium, or mucous membrane. This pathology can occur in women of all ages for completely different reasons.
Treatment for thickening of the uterine wall
Treatment of uterine hyperplasia directly depends on the cause of the disease. For example, for adenomyosis, painkillers and birth control medications are prescribed to reduce pain and bleeding. The symptoms of the disease can be partially eliminated with the help of a spiral, which is placed for a short time. But after its removal, the signs of the disease return again.
Doctor's prescriptions for hyperplasia
When diagnosing a benign neoplasm, hormonal drugs are prescribed, which only temporarily stop the growth of pathological nodes. Combined oral contraceptives are most often prescribed to young and nulliparous girls in whom hyperplasia is accompanied by heavy bleeding.
Thickening of the uterine wall often occurs due to hormonal imbalance, so synthetic analogues are used to restore balance. The duration of treatment is no more than three months. The patient may complain of occasional bleeding, which is considered normal.
Very often, drug therapy does not help, so the attending physician prescribes surgery:
- Curettage of the uterine cavity is carried out to remove the problem area of the mucous membrane and stop bleeding. Removed biological materials must be sent to a laboratory for testing.
- Cryodestruction is carried out to expose the affected area to low temperatures. As a result, the thickened part of the uterus is rejected.
- Thickening of the mucous membrane can be removed using a laser or high temperatures. The endometrium recovers in a short time after surgery.
Prognosis and complications
The consequences of thickening the uterine wall can be different and depend on the disease that caused this pathology. For example, advanced cases of adenomyosis can lead to iron deficiency, frequent headaches and fainting, decreased performance and memory impairment. Advanced cases of the disease most often become the cause of malignant tumors.
The uterus has a more favorable prognosis. Untimely treatment can lead to anemia, miscarriage, infertility, and heavy bleeding after childbirth. Complications of endometritis are characterized by pain in the pelvic region, inflammation of the appendages, infertility or menstrual irregularities.
Thickening of the uterine wall is considered benign, but women with this diagnosis are more susceptible to cancer. Therefore, timely diagnosis and proper therapy will help get rid of the disease and restore the woman’s health.
Useful video about endometriosis:
Contraction of the uterus is a normal condition, just like any other muscle. When muscle fibers contract, the uterus is in good shape, that is, in tension, and the pressure on its internal cavity increases. observed in most women and does not cause harm to health, but in some cases this condition is dangerous when carrying a child and requires special examination and treatment.
Myometrial hypertonicity during pregnancy requires increased attention, because the supply of oxygen and beneficial nutrients to the fetus depends on the condition of the uterus. Along the anterior and posterior walls, hypertonicity of the myometrium causes compressed vessels through which oxygen flows to the child.
Features of physiology
What is thickening of the uterine wall? This is an increase in the mucous layer or endometrial hyperplasia, which is accompanied by an imbalance of estrogen and progesterone in a woman’s body.
Normally, the endometrium undergoes a number of changes throughout the menstrual cycle. First, it increases in volume and grows, preparing for the upcoming attachment of the fertilized egg and pregnancy. However, if conception does not occur, the endometrium is rejected and excreted from the body. This process is regulated by two important female sex hormones: progesterone and estrogen.
Estrogen thickens the uterine wall, while progesterone controls the growth of endometrial cells. If there is a disturbance in hormonal production in the body, a disruption of the menstrual cycle, then cells begin to accumulate in the mucous membrane, which leads to subsequent thickening or hyperplasia of the walls of the uterus.
Thinning of the mucosa
Along with thickening of the walls, depletion of the walls of the uterus is also observed in medical practice. What does thin uterine lining mean? This is a pathological process characterized by underdevelopment of the endometrium. The main causes of thin uterine walls are:
- disruption of the endocrine glands;
- changes in hormonal levels;
- poor circulation in the walls of the uterus;
- consequences of mechanical damage, trauma, and scraping;
- infectious processes.
The mucous layer of the uterine cavity plays an important role in pregnancy. It is the endometrium that is responsible for the implantation of the embryo, the formation of the placenta, as well as the development of blood vessels, which subsequently ensure the supply of nutrients and oxygen to the child.
Depletion or hypoplasia of the uterine walls very often causes infertility or the inability to bear a pregnancy. To eliminate this problem, women are usually prescribed drugs that are analogues of natural progesterone.
Possible reasons
There are several main causes of thickening of the uterine walls.
- Adenomyosis. It is internal endometriosis. Thickening can be either in the anterior layer or in the posterior wall. Adenomyosis in an advanced stage can lead to the development of tumors and infertility.
- Endometritis. Inflammation of the inner mucous membrane of the uterus. In this case, thickening of the endometrium occurs, proliferation of connective tissue and accumulation of calcium in the form of salts.
- Myoma. These are tubercles or nodules formed in the muscle layer of the uterus. They can grow into both the serous and mucous membranes. Myoma in advanced stages can cause disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, genitourinary system, and also lead to the development of infertility and bleeding.
In addition to the above factors, the cause of thickening of the walls may be an irregular menstrual cycle and an imbalance of female sex hormones, diabetes mellitus, severe obesity and a number of chronic diseases of the reproductive system.
Any disruption in hormone production can lead to excessive and uncontrolled cell growth, and subsequently the development of cancerous tumors. That is why it is important to constantly undergo examination by a gynecologist and endocrinologist.
Etiology of the condition
A dense uterus, when detected during a gynecological examination, is an indication for an ultrasound examination. Thickening of the walls of the uterus is called endometrial hyperplasia in clinical practice and is exclusively instrumental indicators. Hyperplasia can be detected on the posterior wall of the uterus or in any other part of it with the following diseases:
- Uterine fibroids. Tubercles in the muscular layer of the uterus occur in almost every woman who has crossed the threshold of 30 years. They vary significantly in size and location and can be located both in the body and in the cervix. Seals in the uterus in the form of nodes are of myomatous origin, but can grow into both the serous and mucous layers of the uterus. Any subserous node is dangerous because it grows into the abdominal cavity.
Myomatous compaction in the uterus, when it reaches a certain size, is clinically manifested by menstrual disorder, dysfunctional uterine bleeding, and severe pain. If these symptoms are ignored and there is no treatment, there is a risk of urination and defecation problems, and there is a high probability of infertility.
With small nodules, gynecologists usually do nothing, but only observe for some time. Small tubercles in the myometrium or on the surface of the uterus are prone to self-resorption.
- Endometritis is an inflammatory process. The pathology begins with minor tingling in the abdomen, which is then accompanied by discharge from the genitals with an unpleasant putrefactive odor. Further, symptoms of general intoxication increase: fibrile temperature, severe weakness, dyspeptic disorders. Gynecological bimanual examination reveals fibrous dense areas on the anterior wall of the uterus or in other areas, a painful organ on palpation, and its significant enlargement.
- Adenomyosis of the uterus is also called internal endometriosis. Signs of the disease are detected during examination using an ultrasound wave, and some symptoms indicate it. Upon palpation examination, the uterus is uneven; it may be lumpy or unevenly enlarged. Menstruation in women is scanty and spotting. Patients complain of poor health, a constant desire to drink, and significant weight loss. Sexual relations do not bring pleasure to women; sexual contacts are accompanied by pain.
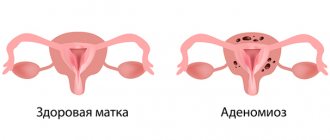
Adenomyosis affects the inner lining of the uterus, it takes on a cellular appearance and becomes abnormally thick. Thickening of the posterior wall of the uterus compresses the genital appendages and disrupts their function.
There are some other reasons why the wall of the uterus thickens, but they are directly related to the physiological state of pregnancy.
Main symptoms
Thickening of the uterine wall is not one of those diseases that are completely asymptomatic and unnoticed by a woman. The main signs accompanying endometrial hyperplasia are:
- sharp pain in the lower abdomen;
- mood swings;
- bleeding not associated with menstruation;
- unusual vaginal discharge with a pungent odor or unusual consistency;
- long menstrual cycle.
At least one of the above symptoms should definitely alert a woman. If you experience pain or menstrual irregularities, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. Untreated hyperplasia in a timely manner can cause the development of serious diseases.
Diagnosis and treatment
Before prescribing treatment, it is necessary to undergo a number of diagnostic tests and examinations. First, a smear is taken from the cervix. This allows you to examine cells in detail and check for the presence or absence of malignant neoplasms. For the same purpose, a biopsy or curettage is performed.
Using ultrasound, it is possible to obtain information about the structure and structure of the uterus, the thickness of the layers and changes in the walls of the organ. For a more detailed study, the doctor may prescribe a hysteroscopy. This procedure is performed using a device that is inserted into the uterine cavity and allows visualization of any abnormal areas of the walls.
Since hormonal imbalances and infectious diseases are common causes of thickening, it is recommended to conduct a blood test to determine the level of progesterone and estrogen, as well as the presence of antibodies to various bacteria and viruses.
After all diagnostic measures have been carried out, the doctor prescribes the most effective and safe treatment. It completely depends on the degree of endometrial hyperplasia, concomitant disorders in the body, as well as on the main symptoms of the disease.
For adenomyosis, drug treatment is most often prescribed. The main medications are painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs and contraceptives.
If thickening of the uterine walls is caused by changes in the hormonal system, synthetic analogs of the hormone progesterone are prescribed, which stimulate the rejection and removal of the old layer of cells.
In extreme cases, in the presence of numerous uterine fibroids, as well as severe bleeding, surgical intervention is performed. In this case, the abnormal layer of the endometrium is removed. This method of treatment is used only in cases where the patient is over 45-50 years old and is no longer planning a pregnancy. But in case of emergency bleeding, cleaning is carried out regardless of age. In addition, if ambiguous results are obtained after an aspiration biopsy, gynecologists also perform curettage. This is most often done using traditional curettage.
Thickening of the walls of the uterus has many causes. Correct and detailed diagnosis will allow you to choose the most effective and safe treatment.
The muscular layer of the uterine wall is called the myometrium. At different stages of the menstrual cycle and during pregnancy, its thickness may change. At the same time, it is important to determine the true cause of the thickening, so as not to miss the beginning of the development of a dangerous pathological process in the body. A common symptom in women is local thickening of the myometrium along the anterior wall of the uterus. Possible changes in the thickness of the uterine wall may be associated with the hormonal status of the woman at the time of the study and other factors that do not always indicate the presence of the disease.
Myometrial thickening during pregnancy: normal or pathological?
One of the components of the uterine layer is the myometrium, the thickness of which can vary depending on the day of the menstrual cycle, as well as in the event of pregnancy. Particular importance is attached to identifying the cause of thickening of the muscle layer, which allows timely detection of pathological changes in a woman’s body.
One of the common symptoms that is detected in females is considered to be a local thickening of the muscle layer along the anterior wall of the uterus. However, often the thickness of the uterine wall is prone to changes under the influence of a decrease or increase in the level of hormones in the female body, or under the influence of other factors. It is for this reason that the detection of thickening of the muscular layer of the reproductive organ does not always signal any pathology.
Possible reasons for changes in myometrial thickness
At its core, thickening can be both a gynecological and obstetric indicator. And even endocrinology sometimes plays a role in the development and symptoms of local myometrial thickening.
Thus, thickening is observed during menstruation, and in the subsequent stage of endometrial proliferation it disappears. Such fluctuations are normal, because they are directly related to changes in the level of progesterone and estrogen in the female body. For example, upon the onset of the second phase of the menstrual cycle, the thickness of the myometrium can be 10-14 mm, whereas after the end of menstruation it is already 1-2 mm.
It is clear that during pregnancy, myometrial thickening increases in proportion to the duration of pregnancy itself. This is due to a general increase in the volume of the organ where the unborn baby develops, with physiological changes in accordance with hormonal levels and fetal growth.
Thickening of the uterine wall is an ultrasound indicator and, in addition to physiologically normal thickening during pregnancy, can be detected in the following pathological conditions:
- Threat of miscarriage
- Uterine fibroids at any stage
- Adenomyosis
- Endometritis of the uterus.
Let's take a closer look at these pathologies.
Threat of miscarriage
According to objective data, ultrasound in the early stages of pregnancy (in the first trimester) reveals local thickening along the anterior wall of the uterus. If this sign is detected before five weeks of pregnancy, then this is not a pathology and only indicates that implantation of the fertilized egg has occurred and its immersion into the wall.
If, in addition to thickening, hypertonicity of the uterus and a scaphoid or drop-shaped shape of the embryo are detected (which in itself is a pathology), as well as a visible change in the outer contour of the uterus - its raised section of the uterine wall above a flat surface, then they speak of a threat of miscarriage.
The same can be said if the same local thickening of the myometrium is found along the posterior wall of the uterine vault. However, ultrasound data must also be confirmed by an objective study of the woman’s condition and reliable clinical indicators - nagging pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, spotting, as well as additional detection of an area of subarachnoid hematoma during the study. Such a hematoma is formed due to detachment of the ovum.
Causes of myometrial thickening during pregnancy
Local thickening of the muscle layer during pregnancy signals increased uterine tone, and this can occur for the following reasons:
- During pregnancy, there is a change in the level of hormones in the body and this is usually expressed in a decrease in the production of progesterone. This pathological condition is considered especially dangerous in the first weeks of pregnancy, when the process of placenta formation has not yet completed;
- The uterine myometrium may thicken as a result of increased levels of male hormones such as androgens.
Often the cause of increased uterine tone is;
- benign neoplasms in the uterine cavity;
- various injuries and abortions;
- progression of acute infectious diseases in the female body;
- infections that are predominantly sexually transmitted.
Improper formation of the reproductive organ and its small size can cause local thickening of the muscle layer.
Some risk factors can be identified, the presence of which can provoke an increase in tone in the expectant mother and, accordingly, thickening of the myometrium:
- work in unfavorable production conditions, which manifest themselves in women’s contact with chemicals, long business trips and night shifts;
- the age of the expectant mother has a significant impact on the course of pregnancy and it has been proven that after 30 years, increased uterine tone is diagnosed much more often than at a younger age;
- a woman is constantly in a stressful state;
- alcohol and smoking abuse during pregnancy;
- improper organization of the daily routine, that is, not enough time is allocated for rest and sleep.
- Thickening of the muscular layer of the uterus during menstruation and during the transition to the next stage, when the endometrium is restored, is considered normal. This process is due to the fact that there is an active change in the content of hormones such as progesterone and estrogen.
During pregnancy, a characteristic phenomenon is the thickening of the myometrium in accordance with the gestational age.
This is due to the fact that with the development of the child, intensive growth of the reproductive organ occurs, and there is also a change in hormones in the body of the expectant mother. During pregnancy, thickening of the uterine wall is an ultrasound indicator that can signal that a woman’s body is affected by various diseases:
- increased risk of spontaneous miscarriage;
- progression of uterine fibroids at any stage of its development;
- adenomyosis;
- uterine endometritis.
Uterine fibroids
The video describes uterine fibroids:
Every third woman over 30 years old has myomatous nodules in the uterus. Having different sizes and shapes, they are located in the walls, bottom and dome of the organ. In the body, these nodules are located along the anterior and posterior walls of the uterus. At the onset of atypical growth of myomatous nodes, ultrasound clearly reveals local thickening of the uterine wall.
When fibroids are examined, a lumpy and tense surface is determined, and local compactions are sometimes found. By palpation it is also possible to detect that the thickened posterior wall of the uterus (or anterior) creates an asymmetry of the organ.
Adenomyosis of the uterus
Adenomyosis is a common case of inflammation of the uterus, in which the endometrium grows into other layers of the uterine wall. Along with such symptoms of adenomatosis as spotting, irregular menstruation, pain, examination also reveals thickening of the uterine walls, including the posterior wall of the uterus. And, although the term “adenomatosis” is registered in the international histological classification, it can still be regarded as one of the forms of endomeriosis, when serious changes appear in the muscle layer of the uterus.
Endometriosis
There is no clear answer to the question of what endometriosis is. The endometrium is the inner layer, lining the wall of the organ. Inflammation and morphological changes in the structure of endometrial tissue are called endometriosis. Until recently, endometriosis was considered a manifestation of various diseases of the genital organs in women, and only very recently it was identified as an independent nosological entity. Despite its wide distribution among women, there are still many blind spots in this disease for gynecologists.
This disease is discussed in more detail in the video:
One of the forms of this disease - internal endometriosis - indicates that the foci of endometriosis are located in the thickness of the endometrium. A common symptom of this condition is local thickening in the area where endometriosis nodes are located along the posterior wall. Malignant neoplasms in the uterine cavity also lead to local thickening. Moreover, in addition to the area of thickening, the asymmetry of the organ becomes apparent due to the development of a tumor in one of the walls of the organ.
As a result, we can say that even in the presence of established local thickening of the myometrium, there is no need to think about bad prognosis. The culprit may be a normal hormonal surge that does not go beyond physiology. By visiting a gynecologist or endocrinologist, it is most often possible to correct a woman’s hormonal levels and, thereby, relieve her of unreasonable fears.
All layers of a woman’s reproductive organ, which make up her wall, are responsible for a certain role in the process of growth and development, life and disease in women. The endometrium is the internal proliferative layer lining the uterine cavity. The hormonal cycle and its phase determine the degree of endometrial thickening. It is also important to recall why this layer of the uterine wall thickens.
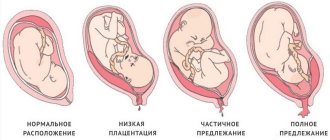
The most important point is pregnancy. The fertilized egg moves through the fallopian tubes into the organ cavity, where the thickened inner layer is ready to receive it for the further development of pregnancy. The fertilized egg is attached to the front wall; localization of the place where the egg is attached to the rear wall is considered more favorable.
Myometrial thickening during pregnancy is normal. Because in order to carry a pregnancy to term and then give birth to a child, you need sufficiently powerful muscle mass for the uterus. Therefore, during pregnancy, thickening of the myometrium of the entire uterus or local thickening of the muscle wall occurs. It should be noted that local thickening is normal only until a short period of pregnancy, up to about 5 weeks. Next, the process of increasing the muscle mass of the uterus should occur evenly throughout the entire organ. You should be very careful about this factor, since the expression: “a disease is easier to prevent than to treat” must always be remembered.
Local thickening of the myometrium can be caused by several factors:
- Pregnancy up to 2 months can be considered a variant of the normal development of pregnancy;
- Hormonal status of a woman. The examination can be repeated or performed on another day of the cycle to exclude the disease;
- Pregnancy after 6 weeks, occurring with pathological abnormalities: pregnancy threatening to be terminated in the early stages, for example.
- Various diseases of the uterus. This includes pathological conditions such as endometriosis, adenomyosis, endometritis, and fibroids.
In the first few weeks of pregnancy, local thickening of the myometrium of the anterior wall of the uterus can often be observed. This condition does not indicate a disease; it only indicates that pregnancy has taken place and the fertilized egg has begun to implant in the thickened inner layer of the uterus. Further, this local thickening of the myometrium of the anterior wall or posterior wall of the uterus in the normal course of events should disappear, and the myometrium will proliferate evenly.
Hypertonicity of the uterus
“Hypertonicity of the uterus... Increased tone of the uterus...” - these words are heard quite often by a pregnant woman. It’s just that whether this is a pathology or a variant of the norm for the expectant mother is sometimes difficult to figure out.
What is the uterus
First, you need to remember that the main tissue that makes up the uterus is muscle. The structural unit of muscle tissue is muscle fiber. According to the laws of physiology, muscle tissue contracts under the influence of any factor.
Thus, the uterus is a muscular organ that sensitively responds to physical stretching and nerve impulses with muscle contraction, that is, an increase in tone.
It should be noted that increased uterine tone can either accompany a normal pregnancy or lead to various complications.
Norm and pathology
It is completely natural and physiological that during pregnancy a woman feels how her tummy sometimes becomes denser. These sensations are nothing more than contractions of the uterus. At later stages, training contractions, or Braxton-Hicks contractions, occur quite often. Depending on the pain threshold, training contractions can be noticeable or barely noticeable for the expectant mother.
They are usually irregular, may stop after walking or resting, and do not increase in intensity or frequency.
But we must not forget that increased uterine tone occurs not only during physiological pregnancy, but can also lead to the threat of miscarriage.
And only an obstetrician-gynecologist can determine in each specific case whether uterine hypertonicity is normal or pathological.
Hypertonicity in early and late pregnancy
Let's look at situations where increased uterine tone can lead to negative consequences. These episodes can occur in any trimester of pregnancy. In the early stages, hypertonicity occurs more often due to the fact that the production of hormones aimed at prolonging pregnancy does not reach the required level.
The main hormone responsible for maintaining normal tone is progesterone. Lack of it in sufficient quantities can cause miscarriage. Another serious problem is structural changes in the uterine wall, such as fibroids, endometriosis, and inflammatory diseases.
In these situations, the wall of the uterus becomes defective and incapable of stretching.
At later stages, hypertonicity can develop not only in the presence of hormonal pathology, but also in case of overdistension of the uterus (with polyhydramnios, large fetus, multiple pregnancy).
In such cases, the expectant mother feels nagging, aching pain in the lower abdomen, in the lower back, and in the sacral area. Towards the end of pregnancy, cramping pain may occur in the lower abdomen.
Diagnosis of hypertension
Of course, the patient’s complaints alone are not enough to make a correct diagnosis. A full examination by an obstetrician-gynecologist is necessary, which the doctor begins with palpation of the uterus. Palpation is performed with the pregnant woman lying on her back, with her legs bent at the hip and knee joints, which eliminates tension in the anterior abdominal wall.
If there is still increased tone of the uterus, the doctor feels compaction, tension, even the sensation of a stone under the hand.
An additional diagnostic method is ultrasound.
It helps to identify areas of local thickening of the muscular layer of the uterus, identify total thickening, and also evaluate the cervix, the condition of which can be used to judge the degree of threat of miscarriage.
Causes of hypertonicity
Uterine contractions can occur due to many factors. First of all, these are various hormonal disorders, such as dysfunction of the adrenal glands and insufficient ovarian function.
In addition, hypertonicity is caused by underdevelopment of the female genital organs or their anomalies, tumor formations in the uterus, infectious diseases and inflammatory processes in the woman’s pelvic organs and the ovum, isthmic-cervical insufficiency, disruptions in the immune system, somatic diseases not related to sexual intercourse sphere. The presented list is far from complete, and only a specialist can understand the reasons for the appearance of high uterine tone.
Why is hypertension dangerous?
Increased uterine tone can lead to spontaneous abortion in both early and late stages, as well as a sharp decrease in uteroplacental blood flow as a result of narrowing of the lumen of the uterine vessels. With long-term hypertonicity, oxygen starvation and fetal growth retardation may occur. That is why, if the expectant mother feels pain in the lower abdomen, she should immediately visit her doctor.
Threatened miscarriage
If there is a threat of miscarriage (miscarriage) at a later stage, thickening of the myometrium both on the anterior wall and on the posterior wall of the uterus, as a rule, is combined with uterine hypertonicity. The ultrasound picture of myometrial hypertonicity is characterized by the following factors:
- Local thickening of the myometrium is clearly visible against the background of the pathological shape of the embryo;
- A violation of the contour of the uterus along the outer line is often visible - part of the wall is raised;
- A local thickening of the myometrium is clearly visible on the posterior wall of the uterus.
The woman’s subjective complaints also indicate the presence of a threat to pregnancy and hypertonicity (pathological tension of the muscular frame of the uterine wall) as additional factors to the ultrasound data, which indicate the presence of a threat to pregnancy and hypertonicity (pathological tension of the muscular frame of the uterine wall):
- Frequent aching pain in the lower abdomen.
- Often pain in the lower abdomen is accompanied by pain in the sacrum and lumbar back.
- Vaginal discharge that appears against the background of these pains: bloody or streaked with blood.
General recommendations from doctors
Treatment of hypertonicity of the posterior wall of the uterus during pregnancy is selected strictly individually. The woman is recommended to observe strict bed rest for some time, which is not always possible at home, and to refuse any physical activity. You need to try to take a position in which the uterus is as relaxed as possible. This could be on your side or even on all fours. You should eliminate stress, get plenty of rest and sleep at least eight hours a day. Doctors usually also recommend excluding sexual intercourse for a while.
Hormonal changes
Local thickening of the uterine wall (myometrium) is often observed in women in middle age. This is approximately from 30 to 45 years. The hormonal landscape changes over the course of life, additional diseases, previous operations or pregnancies. All these factors leave traces in the muscle layer in the form of small local thickenings. They have a nodular structure, the location can vary and are found throughout the body of the uterus: on the back wall, the front wall or in the upper part of the uterus. The factor of changes in the intensity of hormone secretion and changes in their ratio depending on the woman’s age must be taken into account and regularly monitored by a specialist. This is necessary in order to promptly notice the development of fibroids in case of possible growth of nodes in the anterior or posterior wall of the uterus.
Increased uterine tone
The uterus is the main organ of the female reproductive system. It consists of muscles that form three layers: the outer serous, the inner epithelial and the myometrium located between them. Myometrial fibers branch in three different directions, which allows the uterus to stretch during pregnancy and contract well during childbirth. Too early contraction or excessive tension of the muscles of the organ is called hypertonicity.
Increased uterine tone is most often not a serious complication of pregnancy, but you should not completely ignore this symptom. Muscles can tense locally or throughout the entire internal surface of the organ. Locally, tension can spread along the front or back wall of the muscular organ. The problem can only be accurately diagnosed using ultrasound. Minor nagging pain in the abdomen and discomfort in the lower back do not always indicate the presence of pathology.
Endometriosis of the uterine body
Internal endometriosis (adenomyosis) is the most common localization of endometriosis. Clinical manifestations of endometriosis of the uterine body vary depending on the degree of spread of the process into the myometrium. It is usually customary to distinguish the main forms of the disease:
- Diffuse form;
- Focal or nodular form.
With the disease, a woman complains of spotting outside of menstruation. The menstruation itself is so profuse that it can take on the character of hemorrhage and is accompanied by painful sensations.
The nodular form of the disease is characterized by almost the same subjective complaints, but an objective examination reveals numerous local thickenings of the myometrium, the uterus is sharply painful on palpation.
Other diseases of women characterized by local thickening of the myometrium may be:
- – inflammation of the inner membrane caused by infectious agents;
- Tumor formations of various etiologies. These can be benign as well as malignant.
Forecast
The detection of local thickening of the uterine wall (myometrium) in itself is not necessarily a sign of pathology, but in combination with the above factors, it can pose a serious threat to a woman’s health.
In order for a woman to feel healthy, it is necessary to regularly see a gynecologist for preventive purposes. This should be done at least once every 6 months, even without any complaints. If there are any signs of the disease: pain, discomfort, itching, discharge, bleeding outside of menstruation, then this is definitely a reason to consult a doctor immediately!
Collapse
The time when a woman is pregnant is a wonderful and exciting period. But in addition to positive emotions, pregnancy can bring a lot of anxiety to the expectant mother, because various deviations and complications are not uncommon in this condition. The most alarming symptom of pregnancy is the tone of the uterus along the posterior wall.
Methods for diagnosing pathology
The tone of the uterus during pregnancy along the posterior or anterior wall is diagnosed by ultrasound. If the patient complains of nagging pain and spotting, then an ultrasound scan is performed as indicated at any time. Hypertonicity, characterized by an asymptomatic course, can be diagnosed during a routine examination or ultrasound. The diagnosis is made if the patient complains of cutting pain in the lower abdomen, which becomes stronger during physical activity, discomfort in the lower back, and tension in the uterus.
During ultrasound diagnostics, the doctor assesses the condition of the uterus, how thick the walls of the organ are, how the placenta develops and how well it provides the child with all the necessary nutrients and oxygen. During the procedure, the diagnostician will assess the condition and length of the cervix to detect possible symptoms of dilatation. The gynecologist may prescribe additional tests. This is usually a blood test for progesterone and other hormones.
Causes of tone
Since the uterus is a muscular organ, it cannot remain in a state of constant relaxation. Tension, even slight, is always present in the uterus. Moreover, if the tone is slightly increased in the area of contact between the wall and the embryo, this indicates that the latter is taking root well.
Minor inflammation may be caused by increased blood flow to that particular area. In this way, the mother’s body supplies the embryo with the substances necessary for its life and development. An ultrasound will characterize this area as edematous, which is understandable and is also considered tone during pregnancy.
The tone can be general, that is, it extends to the entire organ, or local. The latter is divided into hypertonicity along the posterior wall of the uterus and the same condition along the anterior wall.
The muscles of the reproductive organ can be tense for the following reasons:
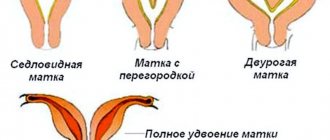
- Uterine pathologies. These include endometriosis and fibroids. Hypertonicity of the posterior wall of the uterus and problems with bearing a child are closely related to the anatomical features of the uterus. It can be saddle-shaped, bicornuate, or have other structural features. Such anomalies can create difficulties in the process of bearing a child;
- Lack of progesterone. Usually triggered by underdevelopment of the genital organs or an abundance of male hormones (androgens);
- Viral infections. They significantly weaken the immune system, which does not have the best effect on the uterus. Infections are accompanied by symptoms such as itching and burning of the external genitalia, qualitative changes in discharge.
- Oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios. The abundance or lack of amniotic fluid equally negatively affects the muscle layer specifically of the posterior uterine wall;
- Stress. They have a detrimental effect on the body as a whole. They weaken the reserves of a pregnant woman’s body, causing the maca to strain unnecessarily;
- Stretching of the uterine muscles. Often occurs in the presence of multiple pregnancies or carrying a large fetus;
- Inflammation in the ovaries or uterus. Such processes can cause alternating tension and relaxation of the reproductive organ;
- Excessive physical activity. They make internal organs tense, the uterus is no exception. Lifting weights or excessive exercise does not have the best effect on the condition of the uterus.
- Different Rh factors in the blood of mother and fetus. In case of Rh conflict, the process of rejection of the fetus by the mother's body may begin. At this time, the tone of the reproductive organ increases significantly.
- Abortions performed by a woman before her current pregnancy can also cause hypertension. This also includes miscarriages and premature delivery.
- Changes in intestinal motility. The latter changes in size due to the accumulation of gases and puts pressure on the body of the uterus, causing tension in its muscles.
Myometrial hypertonicity during pregnancy
If an expectant mother is diagnosed with hypertension, there is no need to perceive it as a terrible disease, because it is not one. Myometrial hypertonicity is the main symptom of the fact that the muscular layer of the uterus is very tense, which should not normally happen during pregnancy, because contractions of the uterus may occur, which will provoke premature birth or miscarriage.
Causes of myometrial hypertonicity during pregnancy
Due to what factors can the myometrium become hypertonic during pregnancy:
- A woman produces insufficient progesterone.
- An inflammatory process occurs in the organs of the genitourinary system (most often the cause is endometriosis).
- Surgical interventions in the uterus that took place before pregnancy.
- There are neoplasms (tumors, cysts) in the uterus or appendages.
- The walls of the uterus are overstretched due to the fact that the woman has multiple pregnancies.
- The expectant mother is constantly exposed to severe physical stress and injury.
- The woman is in a state of severe emotional shock.
- A pregnant woman has diseases of internal organs and systems affecting the uterus.
- Problems with the myometrium occur in older women.
- Problems with intestinal motility can cause myometrial hypertonicity during pregnancy.
Myometrial hypertonicity: localization and symptoms during pregnancy
Hypertonicity is localized in different areas of the myometrium:
- Hypertonicity of the myometrium along the anterior wall during pregnancy is a sign that the process of bearing a child occurs with complications. Very often, the expectant mother feels pain in the lower abdomen, in the perineum, and has a frequent urge to empty her bowels and bladder. With hypertonicity of the myometrium along the anterior wall during pregnancy, uterine bleeding is often observed.
- Hypertonicity of the myometrium along the posterior wall during pregnancy can be asymptomatic for a long time. In the later stages, he may only feel fullness in the perineum and pain in the lower back.
- A pregnant woman will feel 100% hypertonicity of the entire uterus, because with such a pathology the uterus seems to turn to stone, resembling a large ball in appearance. This is a very dangerous symptom that should be reported to your doctor immediately.
Why is myometrial thickening dangerous during pregnancy?
Thickening of the myometrium at different stages of pregnancy, as we mentioned earlier, can be very dangerous for the life of mother and child:
- The worst thing that can happen in the early stages is a miscarriage. Uterine hypertonicity is one of the most common causes of spontaneous abortion.
- Starting from the 2nd trimester, uterine hypertonicity can cause oxygen starvation of the fetus, which in turn will lead to malformations of the child’s internal organs and systems.
- In the 3rd trimester, due to hypertonicity of the myometrium, premature birth occurs. The baby may be born prematurely, and the mother will develop isthmic-cervical insufficiency, and placental abruption will occur, which can ruin the life of the child inside the womb.
- Hypertonicity of the myometrium before childbirth will not result in anything bad for either the mother or the child. On the contrary, contractions of the uterus will prepare it for labor.
What to do with myometrial hypertonicity during pregnancy?
If the thickness of the myometrium exceeds the norm during pregnancy and periodically makes itself felt, then you can perform some exercises to alleviate your condition:
- Get on all fours, arching your back and raising your head. Hold in this state for 1 minute, and then arch your back and lower your head. By doing this exercise, your uterus will be in a state of weightlessness, which will help it relax. After you have done 2-3 sets, sit in a chair and try to completely relax. Drink tea with lemon balm and honey, turn on pleasant music.
- Wear a bandage and eat as many foods as possible that contain magnesium and vitamin B.
- Rub your belly every morning and evening while lying in bed, completely relaxed.
- If your doctor prescribes antispasmodic drugs and the hormone progesterone, you will need to take them on a schedule and maintain strict bed rest so that contractile activity of the uterus is minimal.
Listen to your body every minute, because by some symptoms you can accurately determine for yourself whether everything is okay with you and your baby. At the slightest suspicion of pregnancy complications, immediately go to the doctor to avoid fatal consequences.